Chapter 14: Overview of Antimicrobials and Their Mechanisms
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Selective Toxicity
Harms microbes without damaging the host.
Chemotherapeutic Agent
Chemical used in medical practice for treatment.
Antibiotic
Substance made by microorganisms to inhibit growth.
Antimicrobial Agent
Chemical similar to antibiotics, often synthetic.
Spectrum of Activity
Range of organisms affected by an antimicrobial.

Narrow Spectrum
Targets specific subsets of bacterial pathogens.
Broad Spectrum
Targets a wide variety of bacterial pathogens.
Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Lowest concentration preventing organism growth.
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
Lowest concentration killing the organism.
Kirby-Bauer Test
Measures antibiotic susceptibility using agar diffusion.
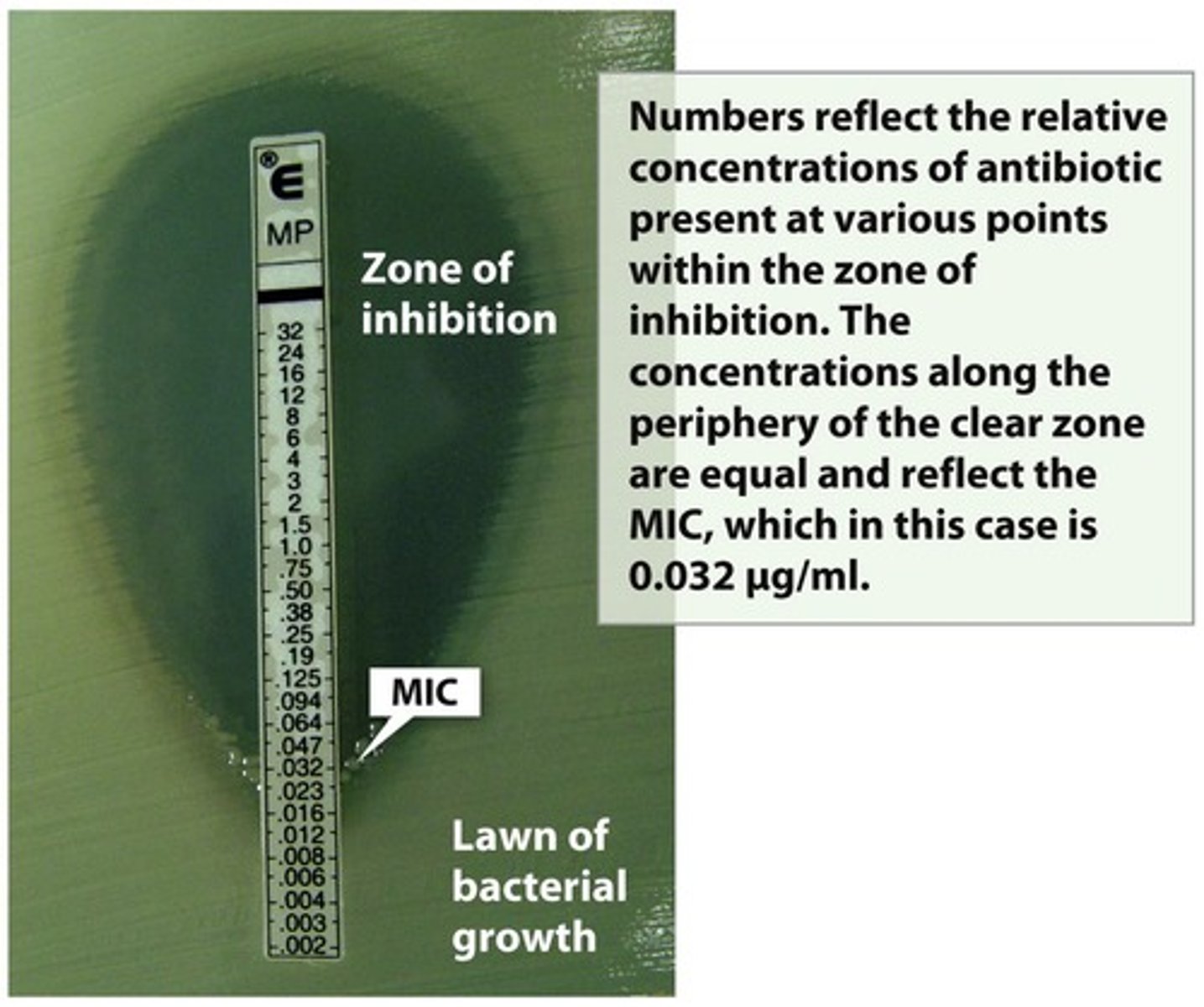
E-test
Determines MIC using a gradient strip method.
Dosage
Amount of medication given over time.
Half-life
Time for 50% of drug to be eliminated.
Empirical Therapy
Initial treatment before specific diagnosis is known.
Targeted Drug Therapy
Treatment based on specific pathogen identification.
Synergism
Combined effect of drugs greater than individual effects.
Antimicrobial Resistance
Microorganisms' ability to withstand drug effects.
Prontosil
First synthetic antimicrobial discovered in the 1930s.
Sulfanilamide
Active breakdown product of prontosil, first synthetic.
Penicillin
First natural antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming.
Chemotherapeutic Index
Maximum tolerable dose divided by minimum effective dose.
Ideal Antimicrobial Attributes
Soluble, selective, stable, non-allergenic, cost-effective.
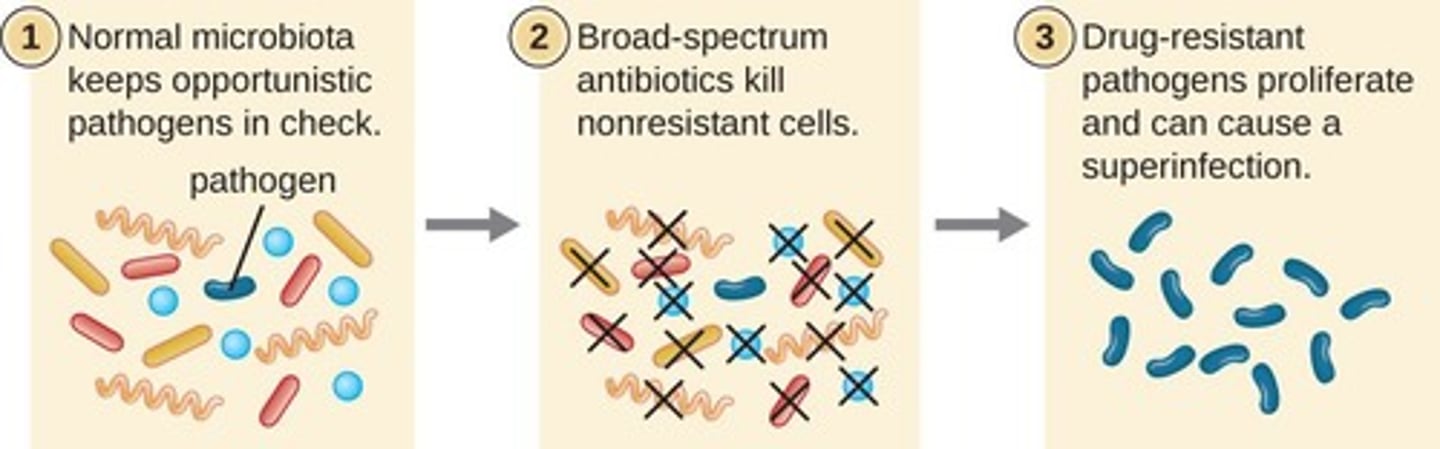
Superinfections
Infections resulting from antibiotic treatment disrupting normal flora.
Chemotherapeutic Index
Ratio of toxic dose to therapeutic dose.
Synergism
Combined effect greater than additive effect.
Antagonism
Drugs interfere with each other's effectiveness.
Selective Toxicity
Targets unique structures in bacterial cells.
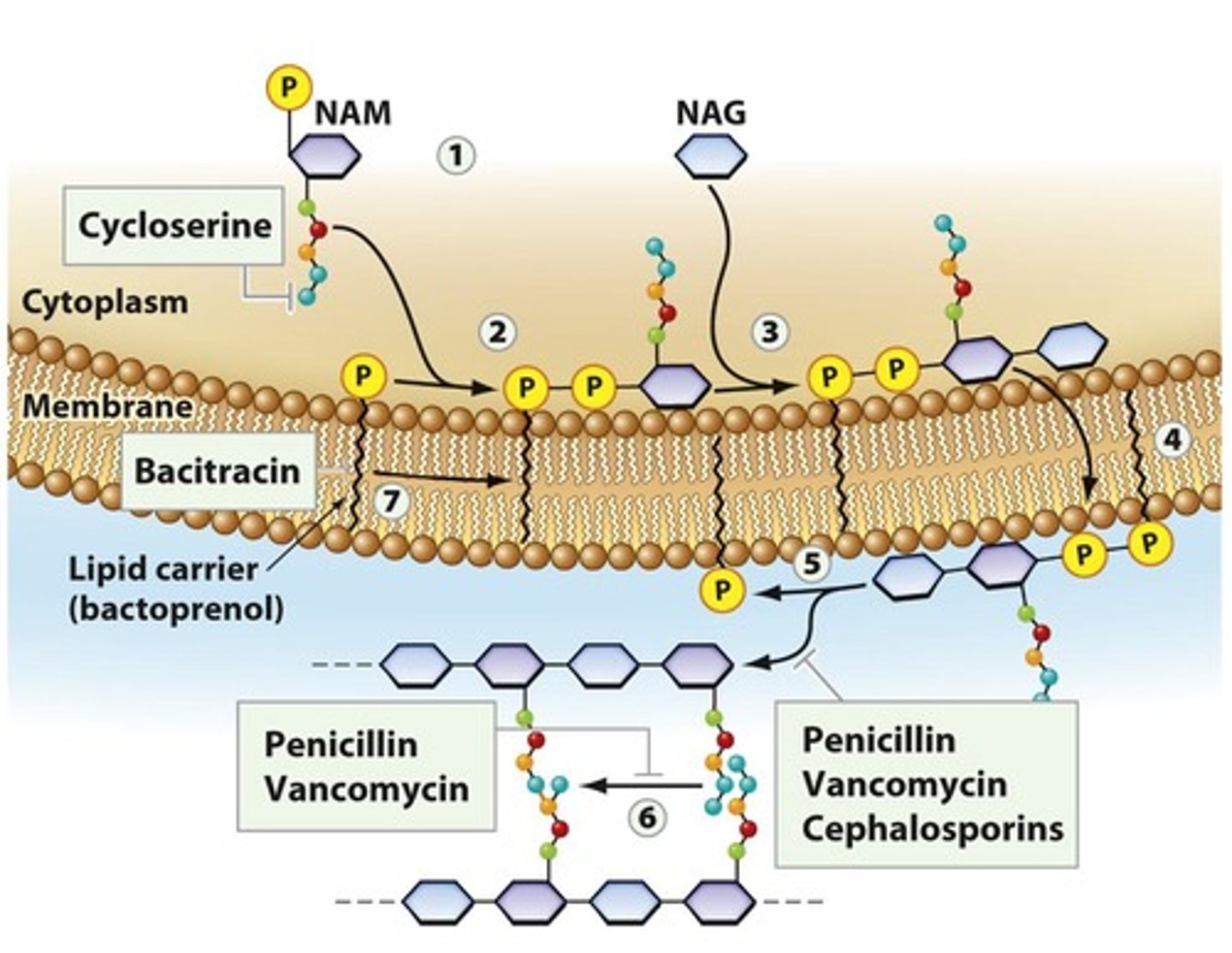
Penicillin-Binding Proteins (PBPs)
Enzymes crucial for bacterial cell wall synthesis.
Bactericidal Drug
Causes bacterial cell death.
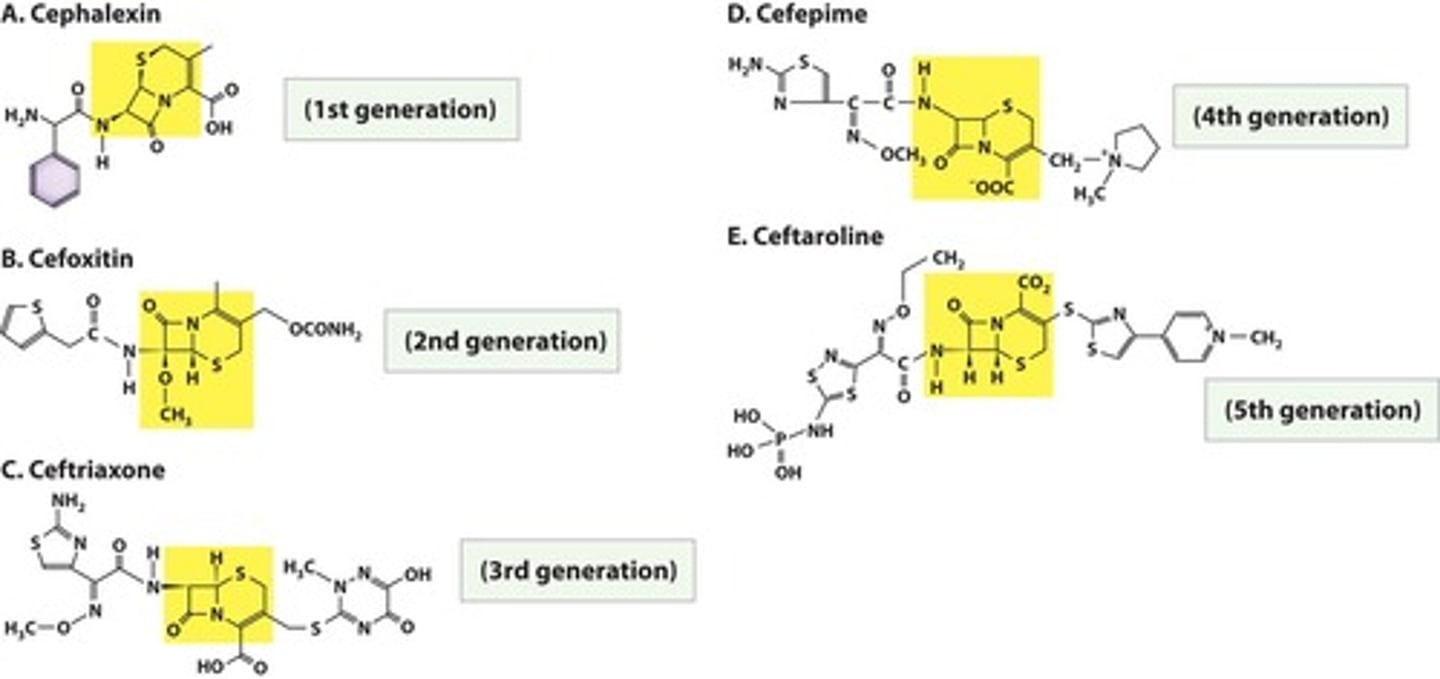
Cephalosporins
Beta-lactam antibiotics with multiple generations.
Bacitracin
Topical antibiotic effective against gram-positive bacteria.
Vancomycin
Last-resort antibiotic against resistant S. aureus.
Isoniazid (INH)
Inhibits synthesis of mycolic acid in bacteria.
Ethambutol
Prevents incorporation of mycolic acid in bacteria.
Polymyxin
Disrupts bacterial membrane, highly toxic.
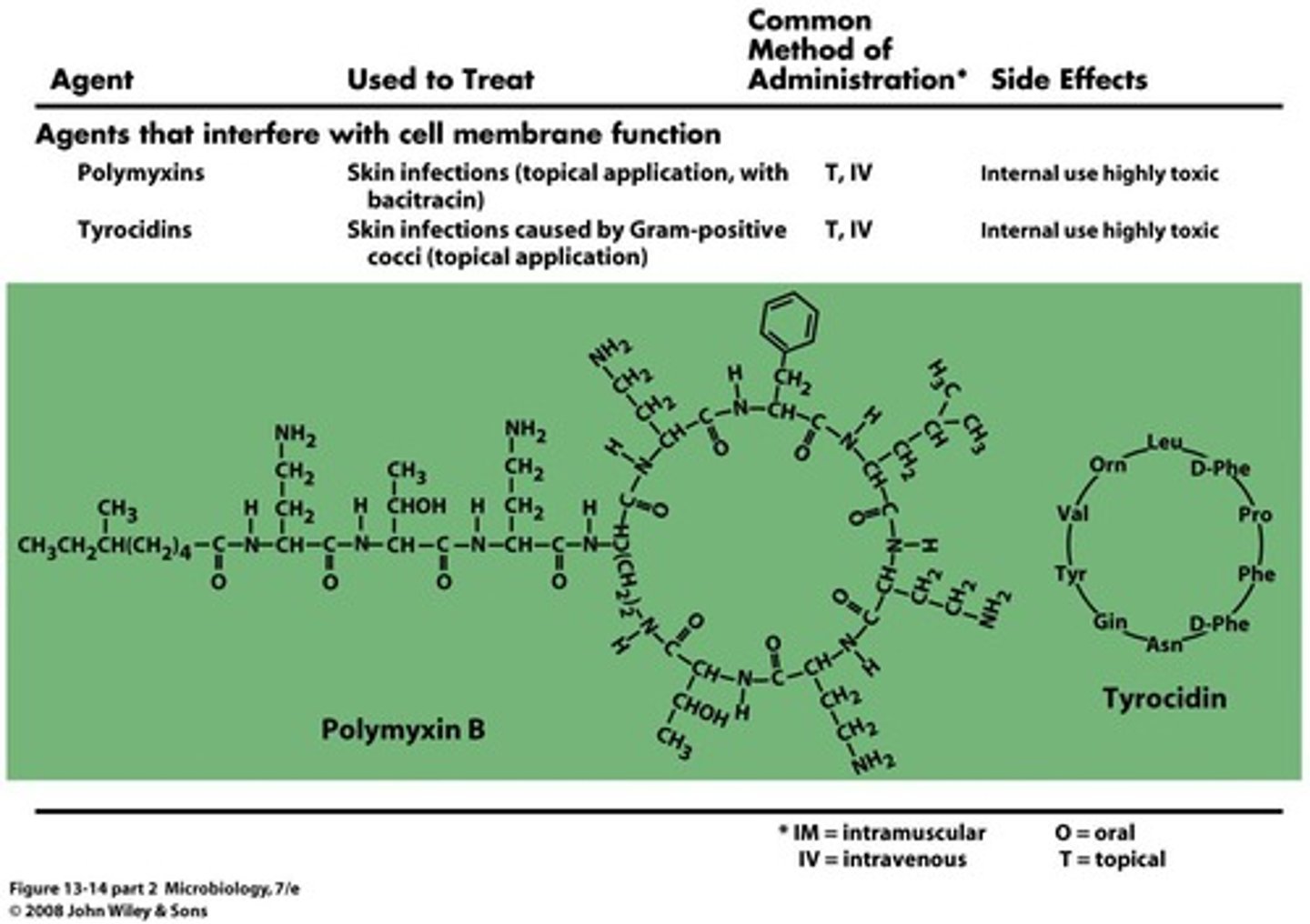
Gramicidin
Cyclic peptide that disrupts gram-positive membranes.
Metronidazole
Activated by anaerobic bacteria for DNA targeting.
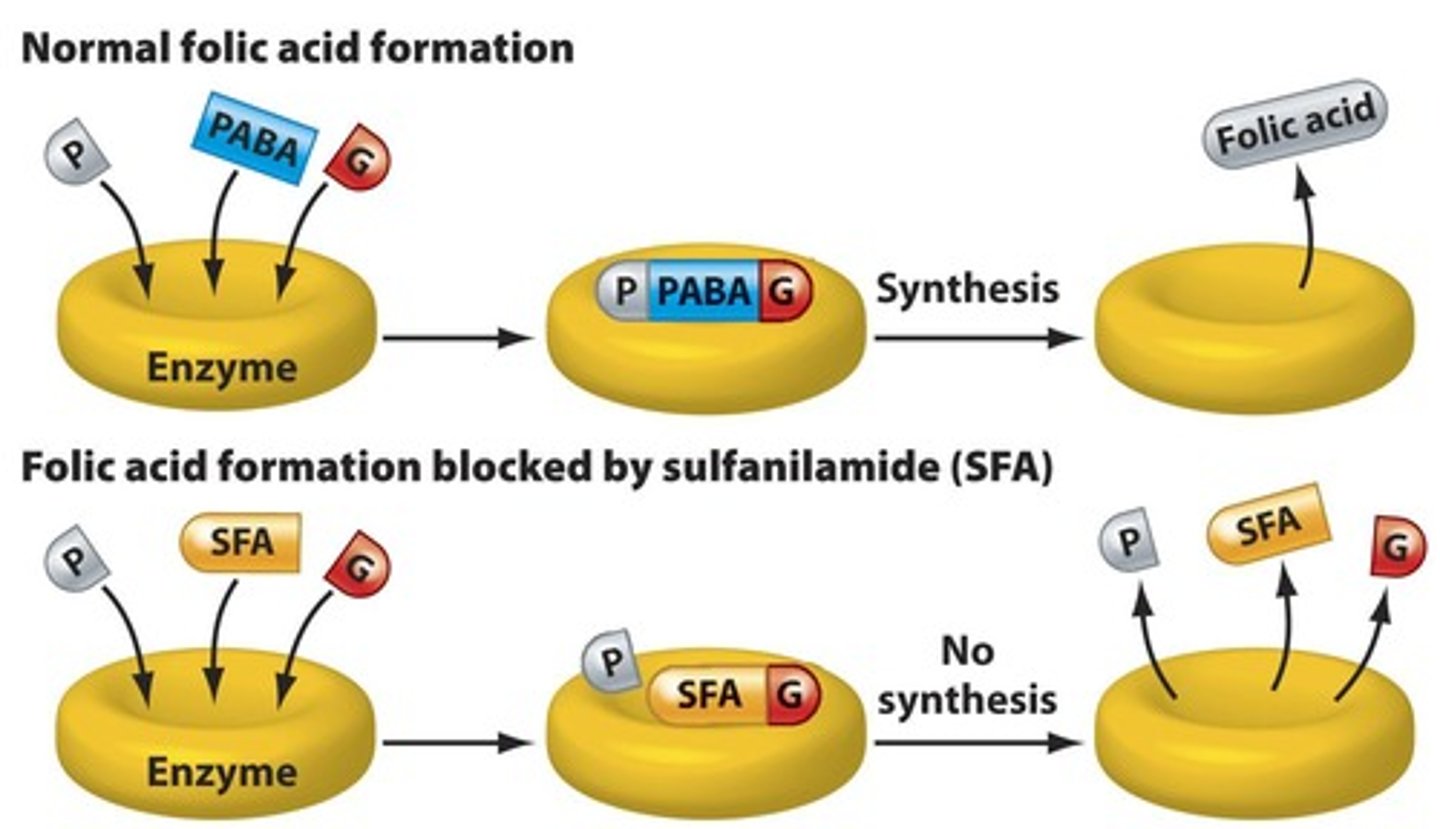
Sulfonamides
Inhibit folic acid synthesis in bacteria.
Quinolones
Inhibit bacterial DNA gyrase, blocking replication.
Antimicrobial Resistance
Bacteria's ability to resist effects of antibiotics.
Antimicrobial Combinations
Using multiple antibiotics to enhance treatment efficacy.
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
Antibiotics that disrupt bacterial cell wall formation.
DNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Target bacterial DNA replication processes.
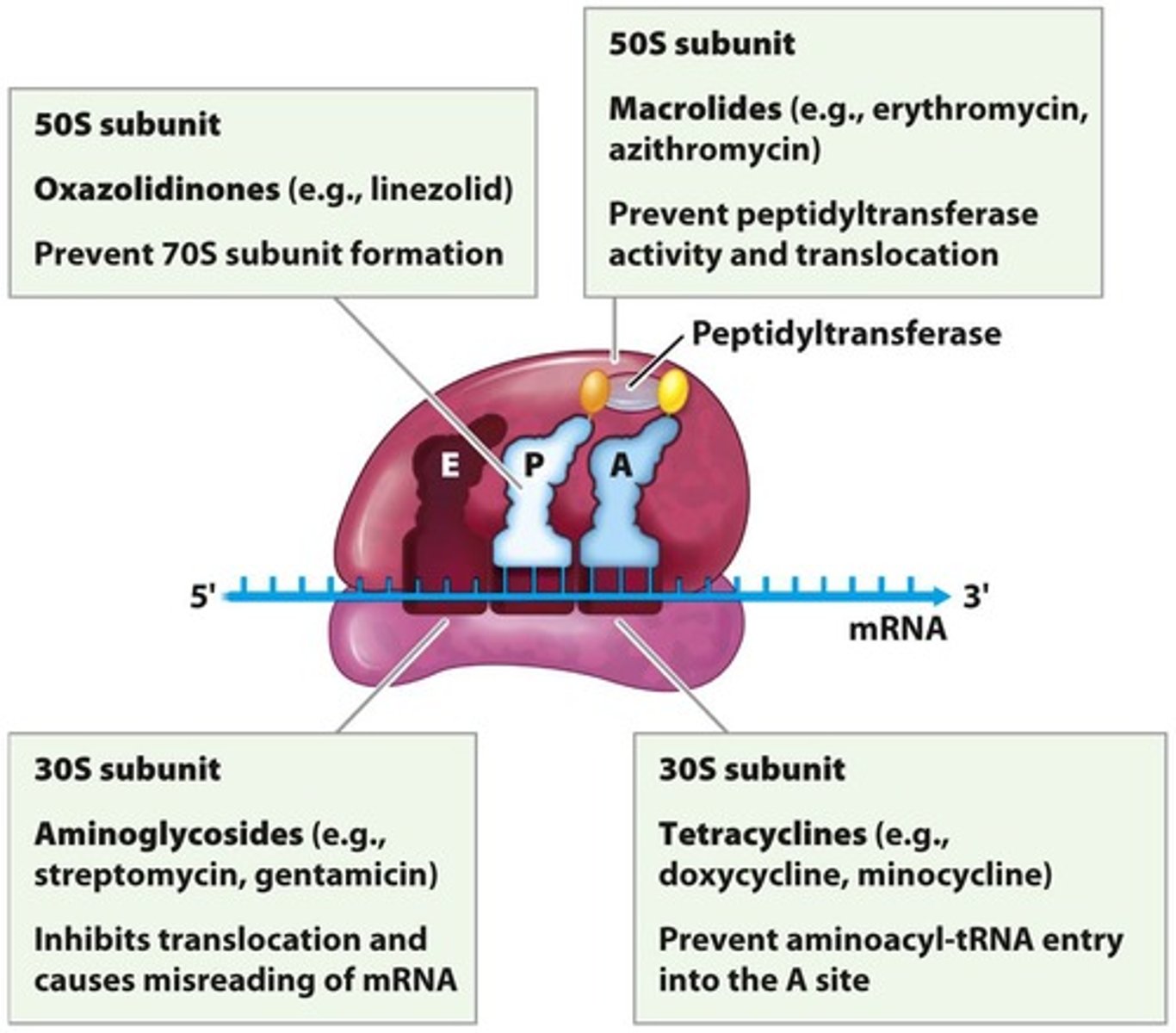
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
Antibiotics that block bacterial protein production.
RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
Interfere with bacterial RNA transcription.
Metabolism Inhibitors
Disrupt bacterial metabolic pathways.
Rifampin
Antibiotic that inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase.
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesizes RNA from DNA template.
Aminoglycosides
Class of antibiotics causing mRNA misreading.
Streptomycin
Aminoglycoside antibiotic used against tuberculosis.
Tetracyclines
Antibiotics that block tRNA entry to ribosome.
Doxycycline
A tetracycline antibiotic effective against various infections.
Glycylcyclines
Inhibit tRNA entry in tetracycline-resistant bacteria.
Chloramphenicol
Inhibits peptide bond formation in protein synthesis.
Macrolides
Antibiotics that inhibit tRNA translocation in ribosomes.
Erythromycin
A macrolide antibiotic used for respiratory infections.
Lincosamides
Prevent peptide bond formation in bacterial ribosomes.
Oxazolidinones
Block assembly of the 70S ribosome.
Streptogramins
Block tRNA entry and protein exit from ribosome.
Drug modification
Enzymatic alteration rendering antibiotics ineffective.
Efflux pumps
Transport proteins expelling antibiotics from cells.
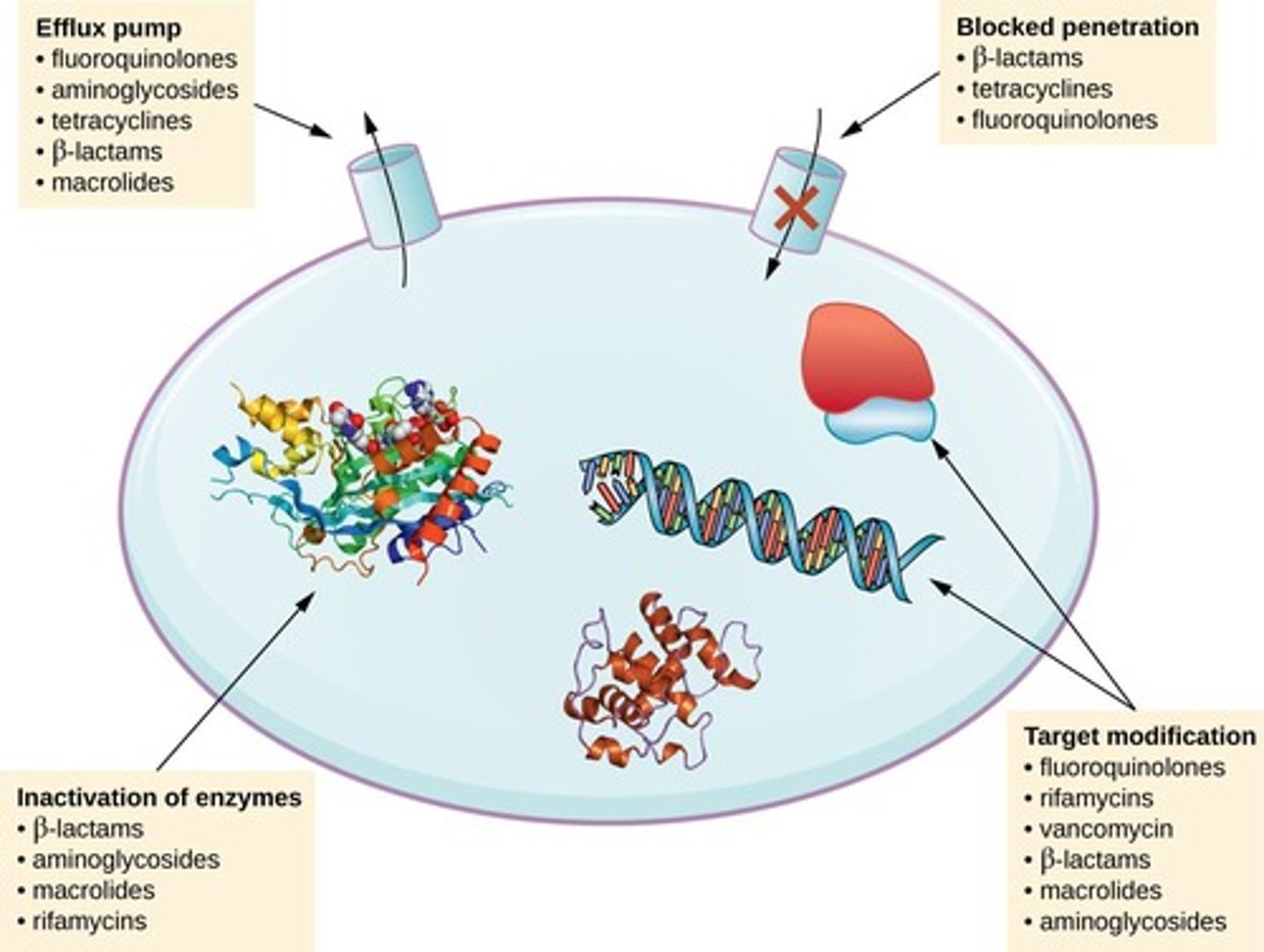
Target overproduction
Microbe produces excess target enzyme to resist drugs.
Enzymatic bypass
Microbe circumvents need for functional target enzyme.
Target mimicry
Production of proteins that sequester antibiotics.
Clavulanic acid
Inactivates beta-lactamases from resistant bacteria.
Amantadine
Prevents influenza virus uncoating and exit.
Neuraminidase inhibitors
Prevent virus particles from leaving infected cells.
Nystatin
Antifungal that disrupts fungal membrane integrity.
Metronidazole
Antiprotozoan causing DNA breakage, treats giardiasis.
Ivermectin
Paralyzes intestinal roundworms in antiparasitic treatment.