Math Terms Quiz chapter 4ab and 5
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Biostatistics
is the application of statistical
principles to questions and problems in
medicine, public health, and biology
The discipline of biostatistics
provides
tools and techniques
for collecting data and
then summarizing,
analyzing, and
interpreting it.
statistics
It is the practice or science
of collecting and analyzing
numerical data in large
quantities, especially for
the purpose of inferring
proportions in a whole
from those in a
representative sample.
plural sense: Statisticss
numerical facts, e.g. NBApoints
per game, pesodollar
exchange rate
singular sense: Statistics
scientific discipline
consisting of theory
and methods for
processing numerical
information that one
can use when making
decisions in the face
of uncertainty.
“ratio status”
The term statistics came from the Latin phrase______which means study of practical politics or the statesman’s art.
statistik
In the middle of 18th century, the term_____(a term due
to Achenwall) was used, a German term defined as “the
political science of several countries”.
correct, valid, reliable information
Correct statistical process
leads to?
published data
survey result
research output
What are the 3 examples of information on statistics?
news and information
making decisions
Everyday we use_________sources to
gather facts that we need in_____
Agriculture
comparing
the effects of five kinds of
fertilizers on the yield of a
particular variety of corn.
Economics
determining
the income distribution of
Filipino families.
Health
comparing the
effectiveness of two diet
programs.
Physical Science
prediction
of daily temperatures.
Education
evaluation of student performance
AIMS OF STATISTICS
uncover structure
in data to explain variation
Descriptive Statistics
methods concerned
with collecting,
describing, and
analyzing a set of data
without drawing
conclusions
(inferences) about
a large group
Inferential Statistics
methods concerned
with the analysis of a
subset of data
leading to
predictions or
inferences
(conclusions)
about the entire set
of data
universe
is the collection of things or
observational units under consideration
variable
is a characteristic observed or
measured on every unit of the universe
population
is the set of all possible
values of the variable.
sample
is a subset of the population
parameter
descriptive measure
of the population
sampling
process of collecting
a sample from a
population
statistic
descriptive measure
of the sample
inferential statistics
make generalizations
about parameters
using statistics
Variables
any characteristic that
can vary in measure
example:
age
sex
blood type
data value
a number or text response
obtained upon measurement
example:
54 years
female
Type A
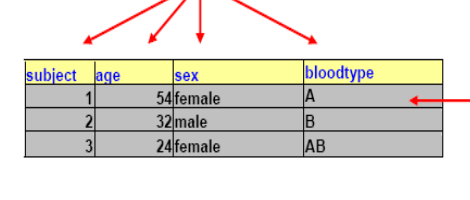
Variables
are the column headings – “subject”, “age”,
“sex”, “bloodtype”
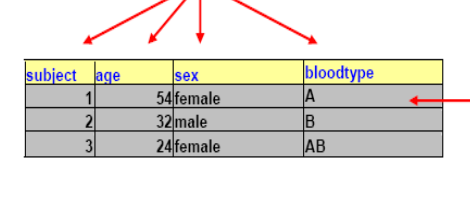
Data values
are the
table entries – “54”,
“female”, “A”, etc.
Qualitative
Quantitative
-discrete
-continuous
what are the 2 types of variables?
QUALITATIVE
categorical responses, non-numerical
characteristics or label
QUANTITATIVE
numerical responses, measurements,
or quantities
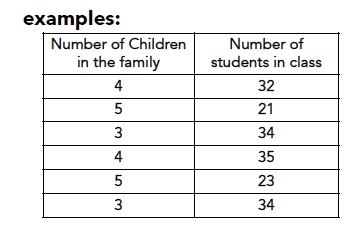
discrete
assumes a finite number
of values
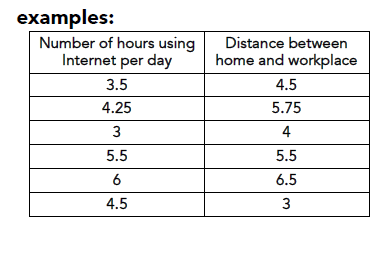
continuous
assumes an infinite number of values
associated with values within an interval
Nominal
consists of finite set of possible
values in terms labels or categories
which have no particular order.

Ordinal
consists of finite set of possible values
in terms labels or categories which do
have a particular order.
Interval
set of data wherein differences
between measurements can be
described but NO true zero

Ratio
set of data wherein differences
between measurements can be
described and true zero EXISTS.

Independent Variables
It is the variable that the experimenter
changes or controls and is assumed to have
a direct effect on the dependent variable.
Dependent Variables
It is the variable being tested and measured
in an experiment, and is 'dependent' on the
independent variable.
Independent
-fertilizer
dependent
-plant growth
-no. of leaves
-no. of fruits
-size
What is an example of independent and dependent variables?
sampling technique
is the manner by which
the samples are drawn from the population
sampling
process of collecting
a sample from a
population
inferential statistics
make generalizations
about parameters
using statistics
Reduced Cost
A sample often
provides useful and
reliable information
at a much lower cost
than a census
Speed or Timeliness
A sample usually
provides more timely
information because
fewer data are to be
collected and
processed.
Efficiency and Accuracy
A sample often
provides information
as accurate, or more
accurate, than a
census, because data
errors typically can
be controlled
better in smaller
tasks.
Greater Scope
Sampling has a
greater scope
regarding the variety
of information by
virtue of its flexibility
and adaptability
Convenience
The use of a sample
provides greater
convenience to the
researcher as it
reduces the amount
of work to process
data.
Necessity
Sampling is an
essential tool in
statistics and
research. Moreover,
it makes reliable
inferences about
population
sampling frame
The use of a complete listing of the
elements of the universe called the_____is required.
SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING
It is the most basic method of drawing a probability
sample which assigns equal probabilities of selection
to each possible sample.
Lottery
Use of table of random numbers
Use of electronic generated random
numbers
The samples are obtained through
strata
The universe is divided into L mutually
exclusive sub-universes called
Are there different groups within the
population?
Are these differences important to
the investigation?
When thinking of using stratification, the
following questions must be asked:
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING
is done when the
population is divided into several subgroups
with common characteristics.
Examples:
The population may be divided into…
o urban and rural locations
o year level of learners;
o workers in a hospital categorized by
occupations
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING
Advantages
1. It gives a better cross-section of the population.
2. It simplifies the administration of the survey/data
gathering.
3. The nature of the population dictates some inherent
stratification.
4. It allows one to draw inferences for various subdivisions
of the population.
5. Generally, it increases the precision of the estimates.
SYSTEMATICS RANDOM SAMPLING
-It adopts a skipping pattern in the selection of
sample units.
-It gives a better cross-section if the listing is
linear in trend but has high risk of bias if there is
periodicity in the listing of units in the sampling
frame.
-It allows the simultaneous listing and selection
of samples in one operation.
CLUSTER RANDOM SAMPLING
o It considers a universe divided into N mutually
exclusive sub-groups called clusters.
o A random sample of n clusters is selected, and their
elements are completely enumerated.
o It has simpler frame requirements.
o It is administratively convenient to implement.
CLUSTER RANDOM SAMPLING
Advantages:
Less complex and relatively easier
Increase efficiency and ease of data collection
CLUSTER RANDOM SAMPLING
Disadvantages:
May not fully represent all individual elements.
The method is prone to bias.
multistage random sampling
a subset is obtained from a population using smaller and
smaller groups (units) at each stage. The data used is commonly collected from a
large disperse population in national surveys
Simple two-stage sampling (First Stage – determine a primary sampling unit)
The units are grouped into N sub-groups,
called primary sampling units (psu’s) and a
simple random sample of n psu’s are selected
Simple two-stage sampling (Second Stage – take a secondary sampling unit)
In the second stage, from each of the n psu’s selected
with Mi elements, simple random sample of mi units,
called secondary sampling units ssu’s, will be obtained
MULTISTAGE RANDOM SAMPLING
Advantages:
-A sampling frame of target population is not needed
-Other sampling methods can be used between methods
MULTISTAGE RANDOM SAMPLING
Disadvantages:
-A large sample size is needed to achieve the same statistical
inference properties.
-May have unrepresentative samples since large sections
of populations may not be selected for sampling.
NONPROBABILITY SAMPLING
-Samples are obtained haphazardly, selected
purposively, or taken as volunteers.
-The probabilities of selection are unknown.
PURPOSIVE SAMPLING
The participants are obtained based on the
characteristics that needed for the sample.
Here, the units are selected “on purpose”.
CONVENIENCE SAMPLING
This involves using
respondents who
are “convenient” to
the researcher.
QUOTA SAMPLING
The participants are selected
based on specific
characteristics, ensuring
they represent certain
attributes in proportion
to their prevalence in
the population
SNOWBALL SAMPLING
Additional sample units
are identified by asking
previously picked sample
units for people they
know who can be added
to the sample.