Cardiac Anatomy, Function, and the Cardiac Cycle
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
pericardial sac
lining that surrounds the heart and helps to reduce friction
LAYERS:
1. fibrous (outer)
2. parietal (inner cavity wall)
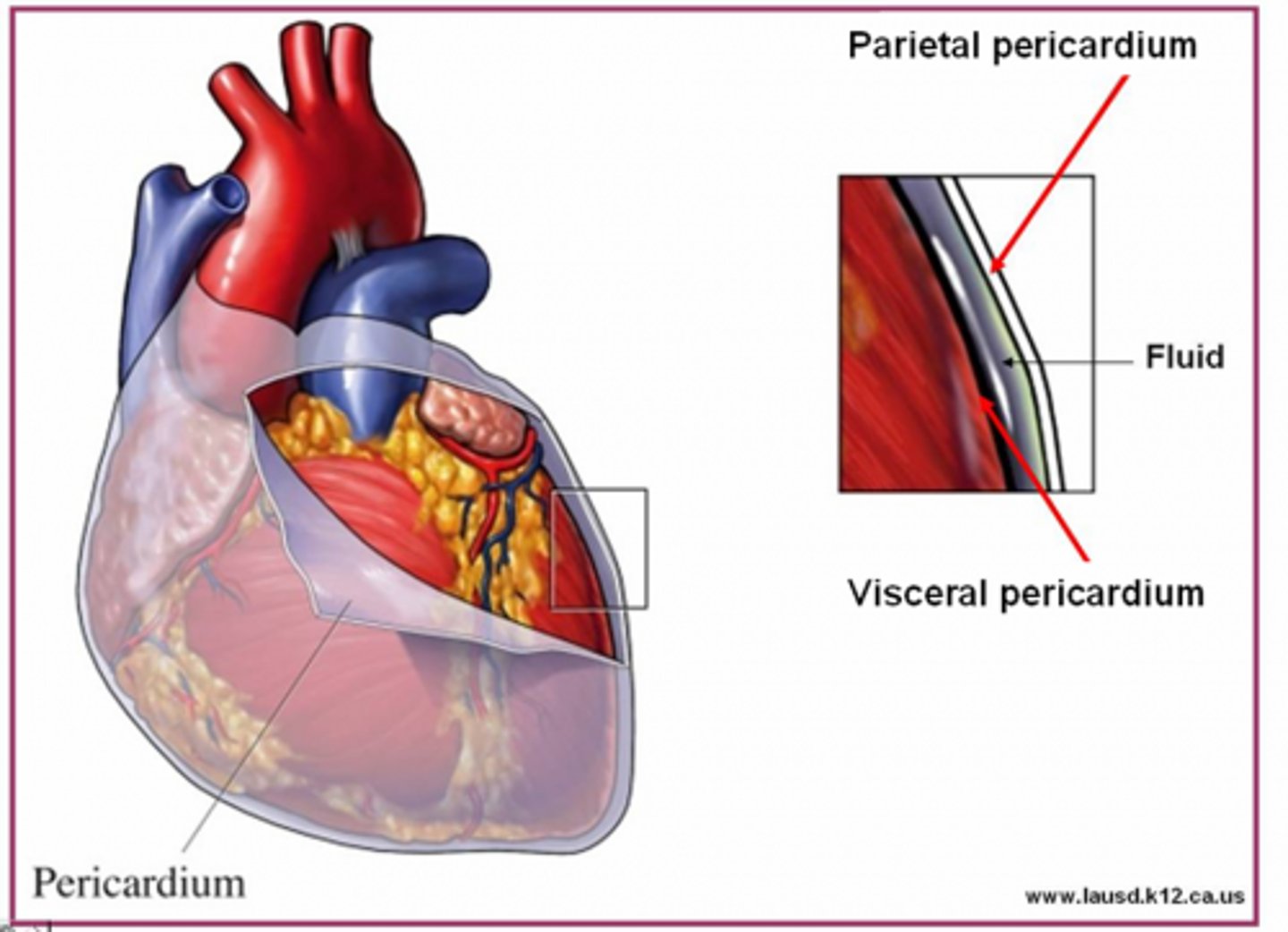
pericardial fluid
serous fluid between parietal & visceral pericardium
*reduces friction when heart beats
**contains mesothelial cells
pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardial sac surrounding the heart
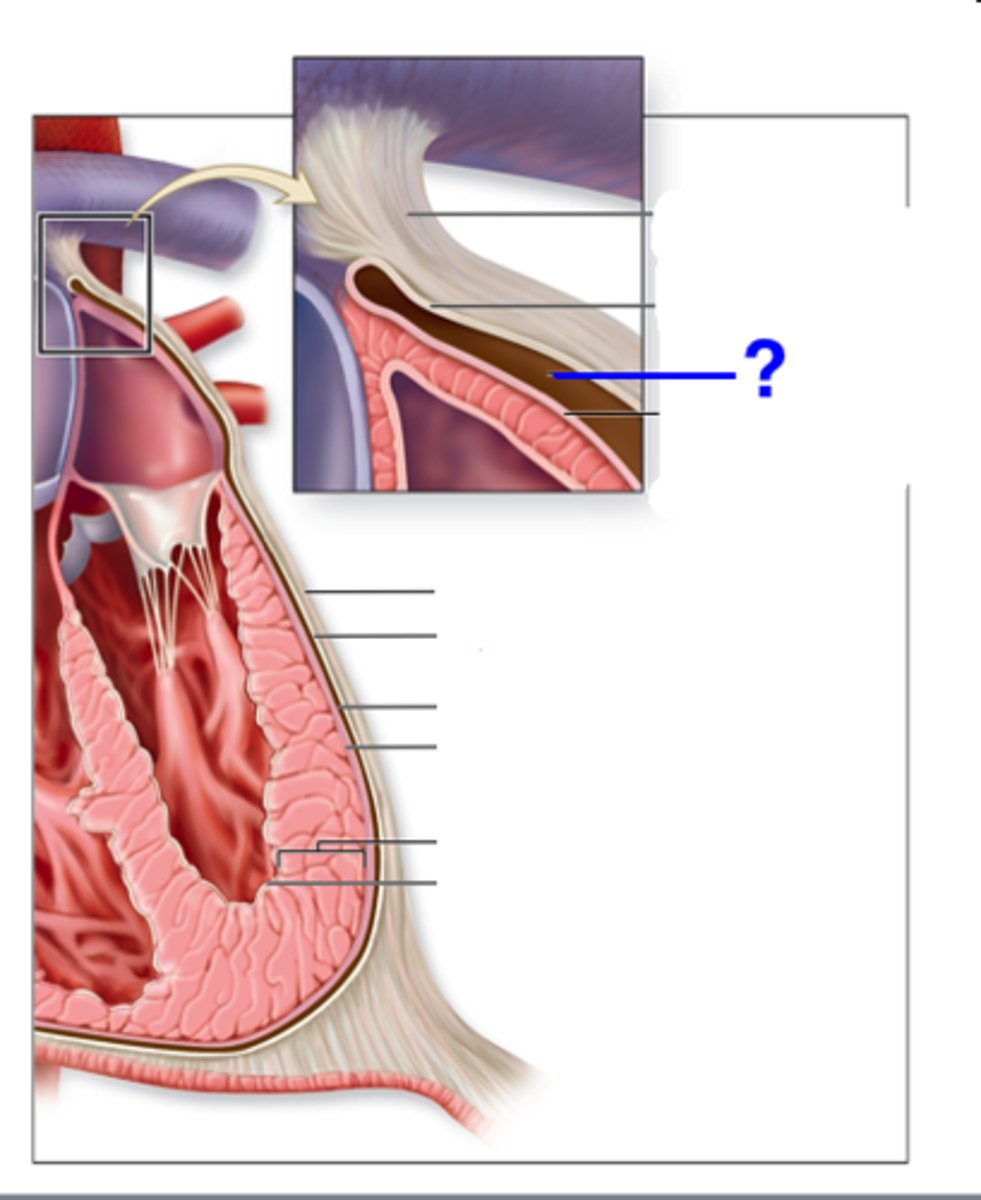
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
What are the 3 layers of the heart wall?
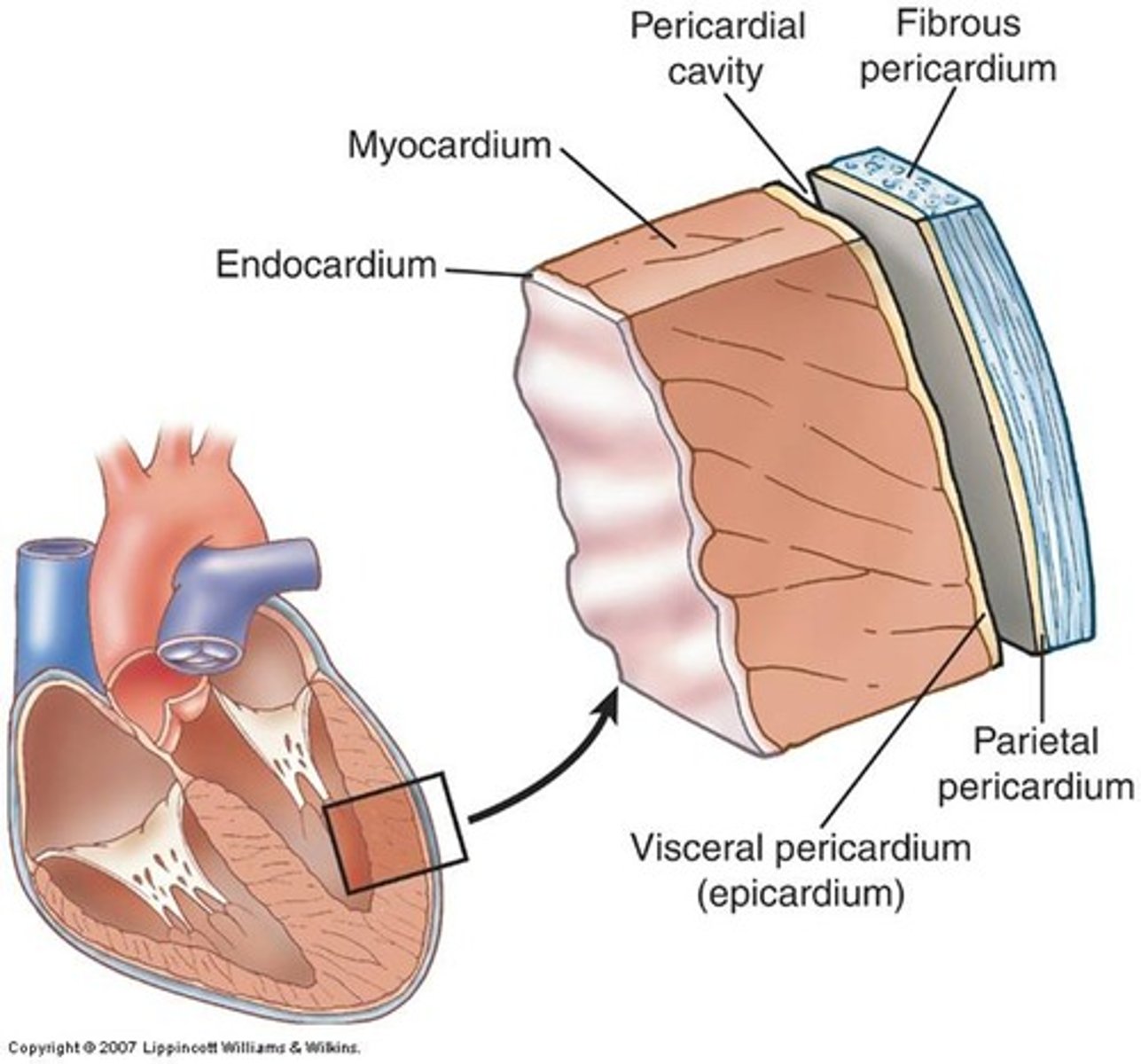
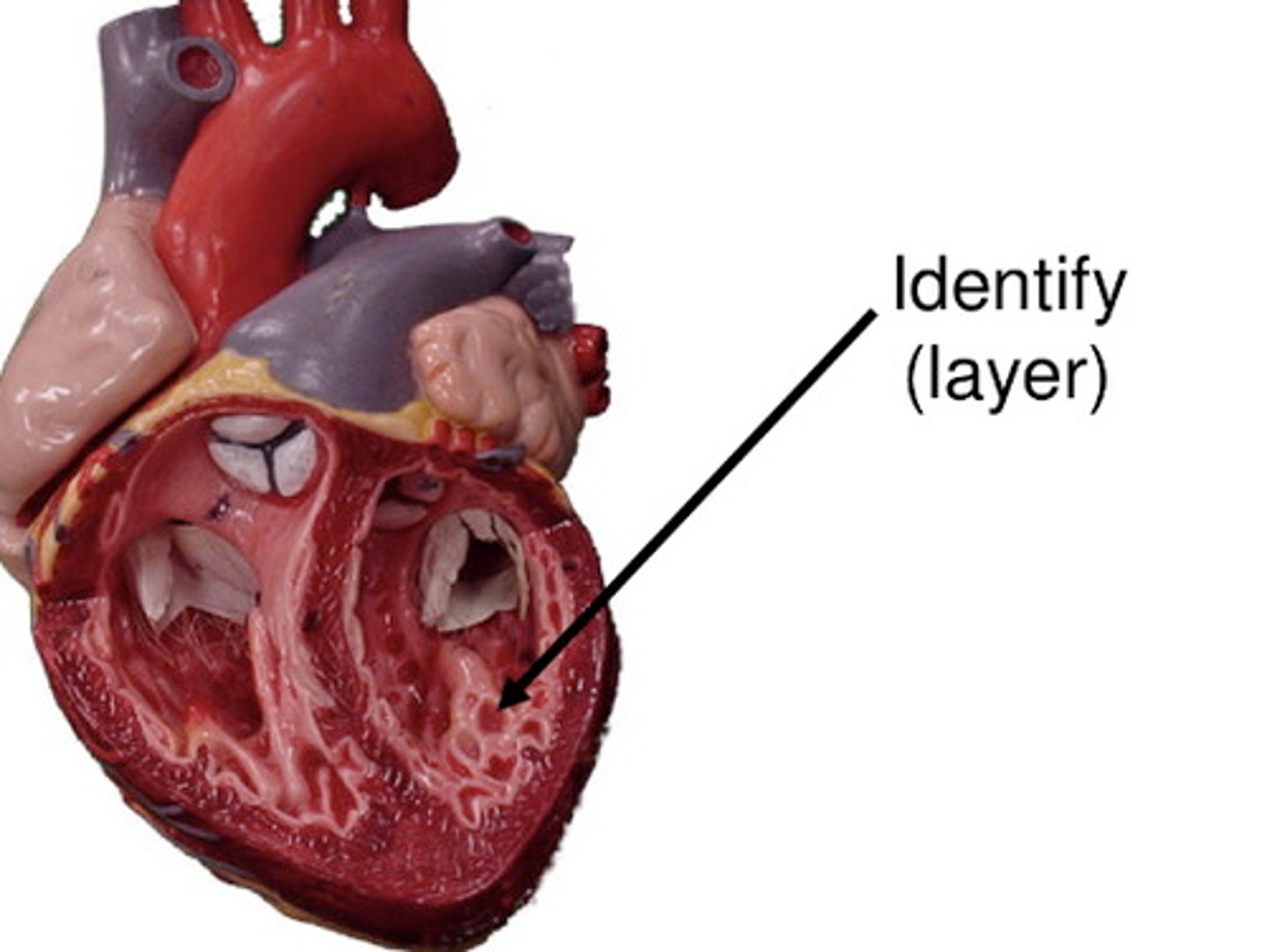
epicardium
aka visceral pericardium
outer layer of heart muscle tissue
CONTAINS:
1. coronary vessels
(supply blood to the heart muscle)
2. fat
(cushion, shock absorber)
3. loose connective tissue
4. mesothelial cells
*added protection
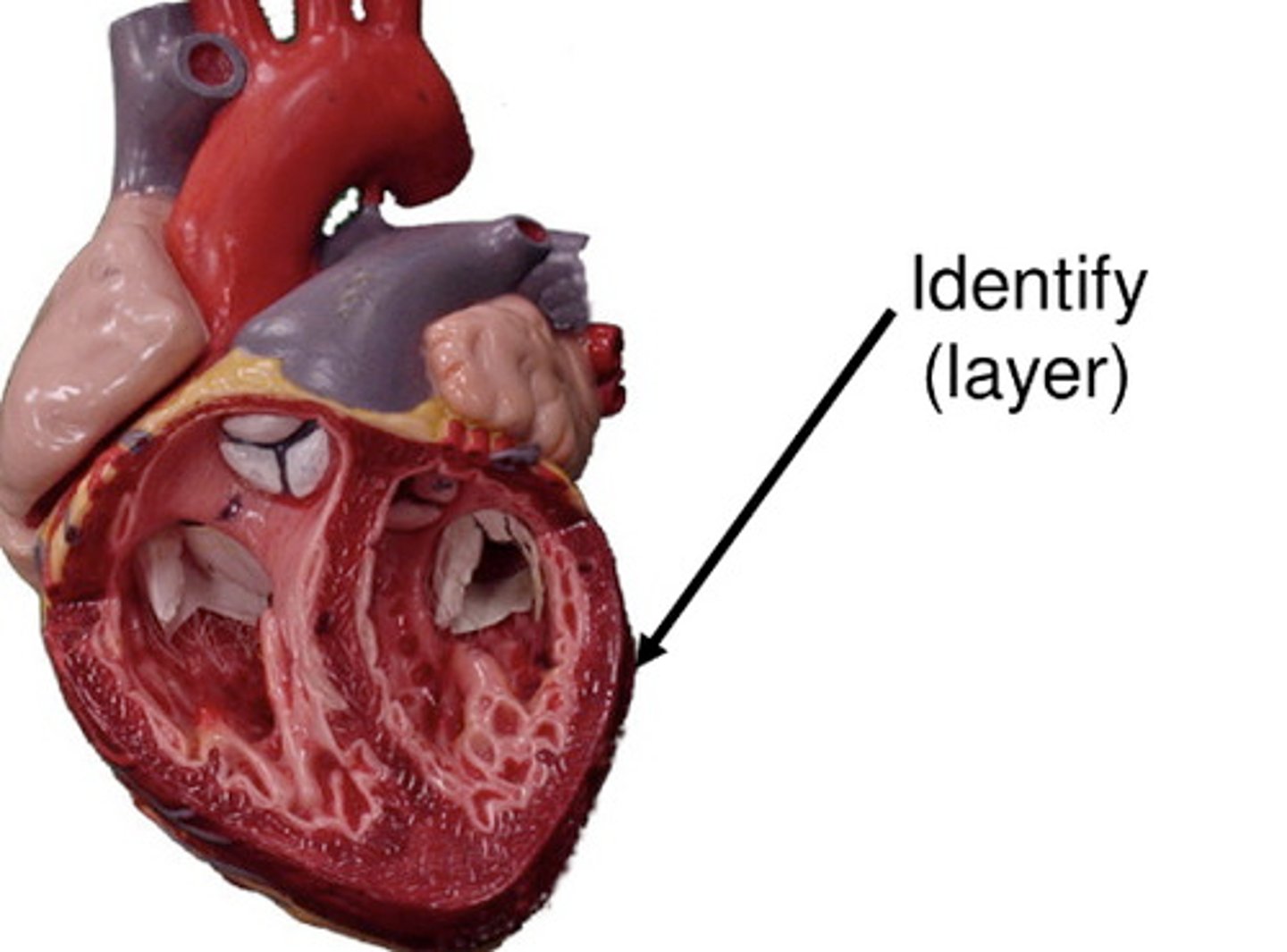
myocardium
the middle, muscular layer of the heart wall
4 chambers & 4 valves
*contains cardiomyocytes and fibroblasts
**has contractile and pacemaker function
structural integrity--> collagen production
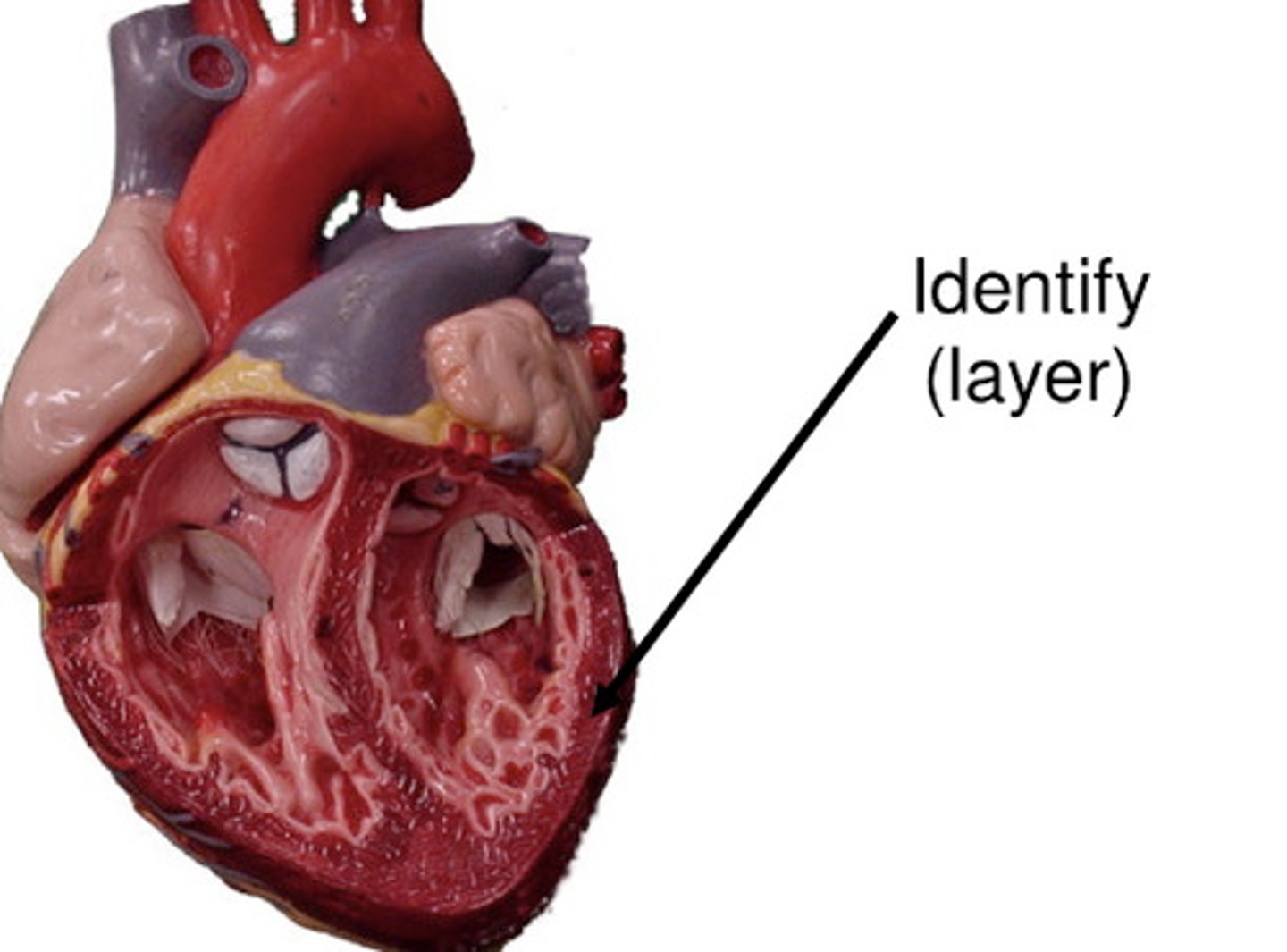
endocardium
inner lining of the heart
*contains endothelial cells
**barrier between vessels and blood
***has anti-inflammatory & anticoagulant properties
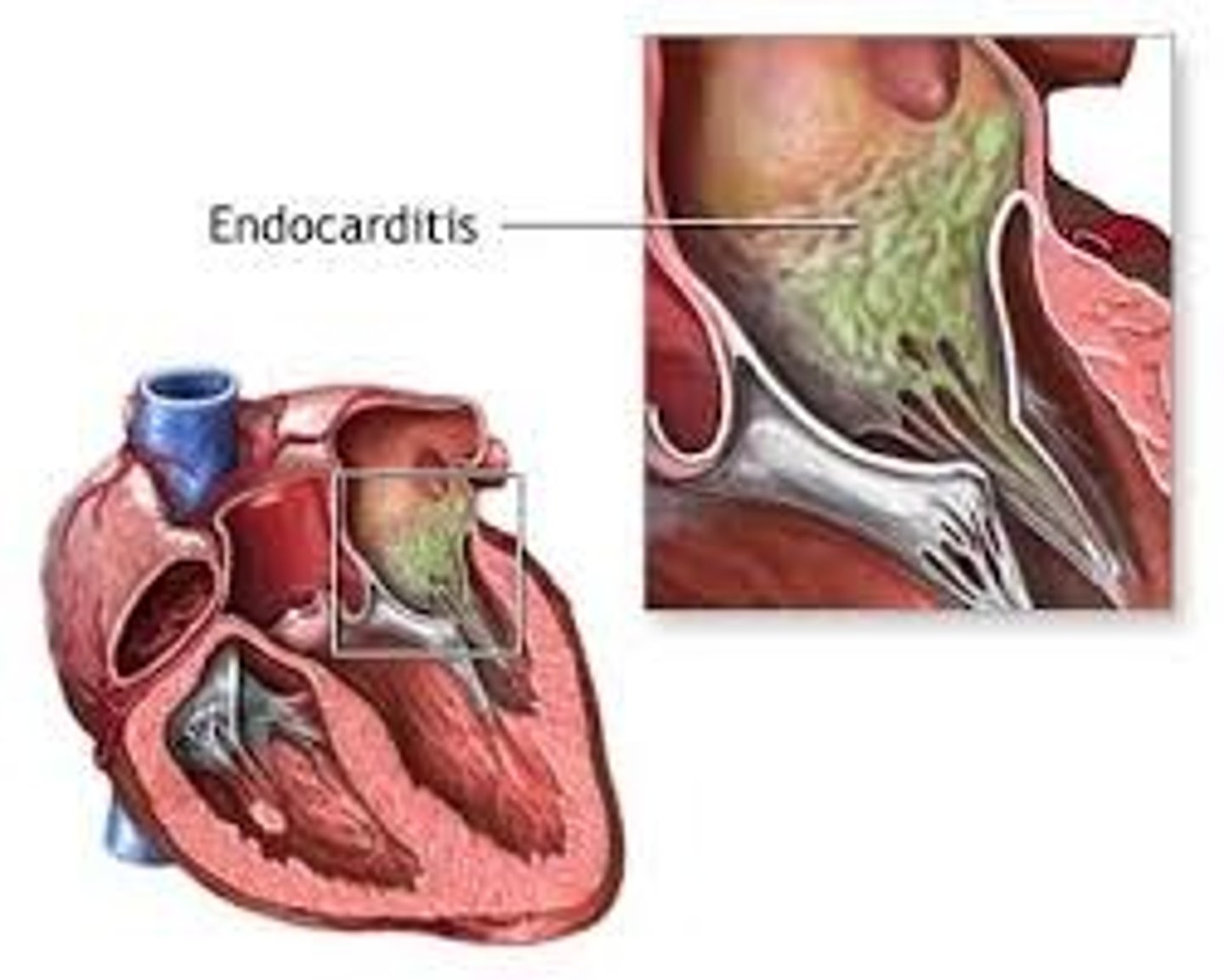
endocarditis
inflammation of the inner lining of the heart
*typically a valve issue
epicardium
The great vessels are part of which layer of the heart?
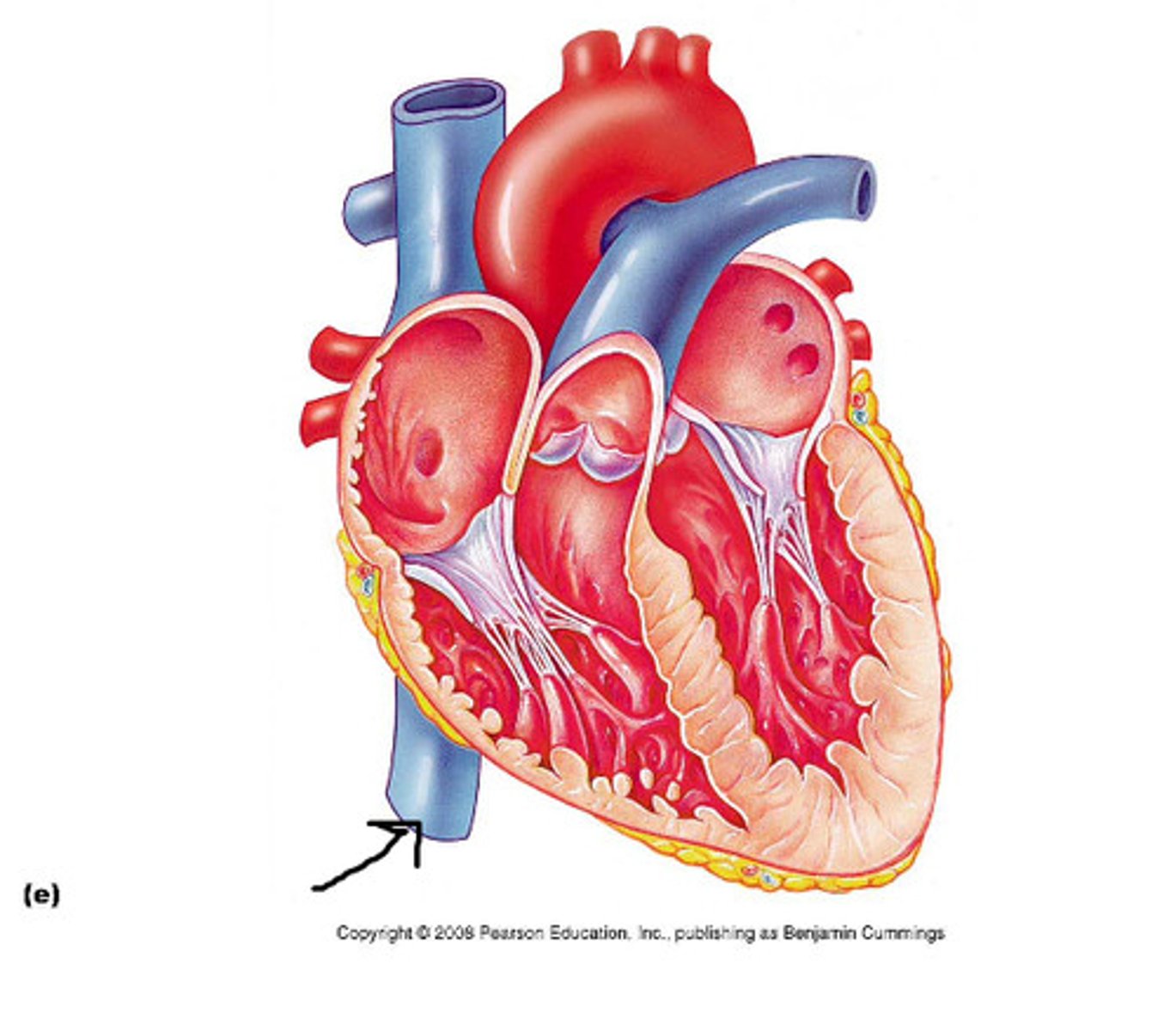
inferior vena cava (IVC)
returns blood from portions of the body below the heart to the right atrium
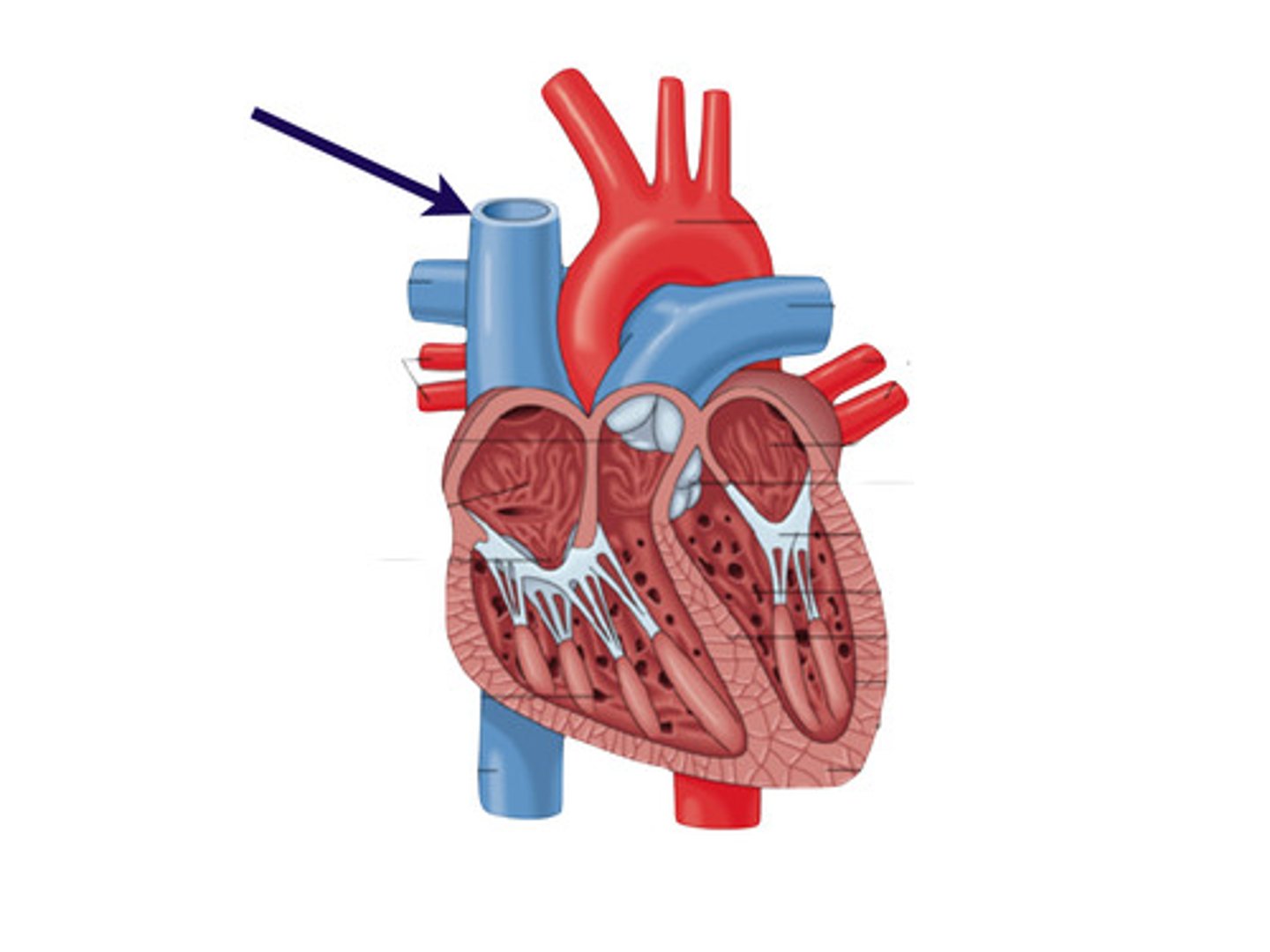
superior vena cava (SVC)
receives blood from the head and arms and chest and empties into the right atrium of the heart
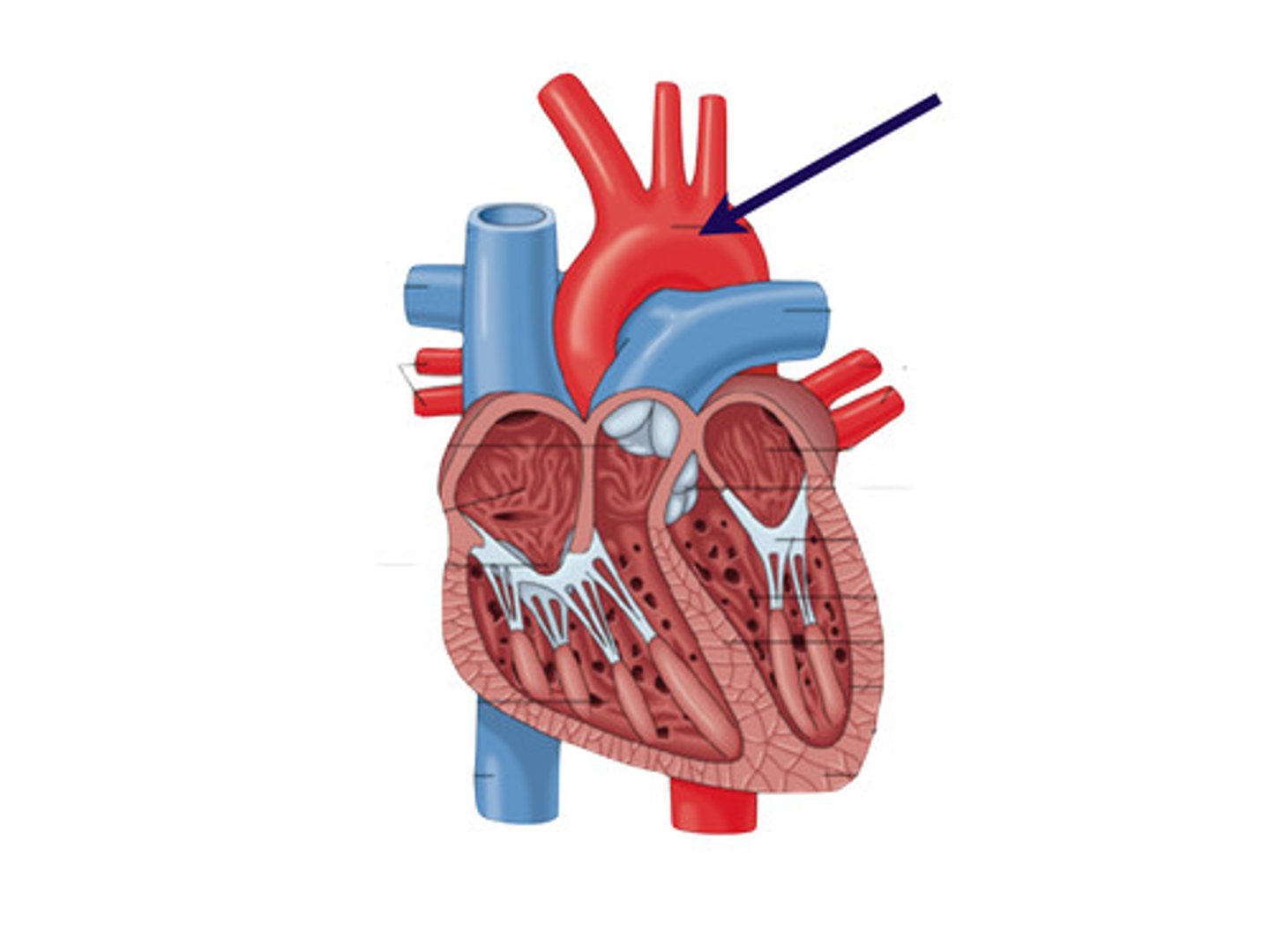
aorta
large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body
BRANCHES FROM ARCH:
1. brachiocephalic (innominate)
2. common carotid
3. subclavian
brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian
What are the 3 branches off of the aortic arch?
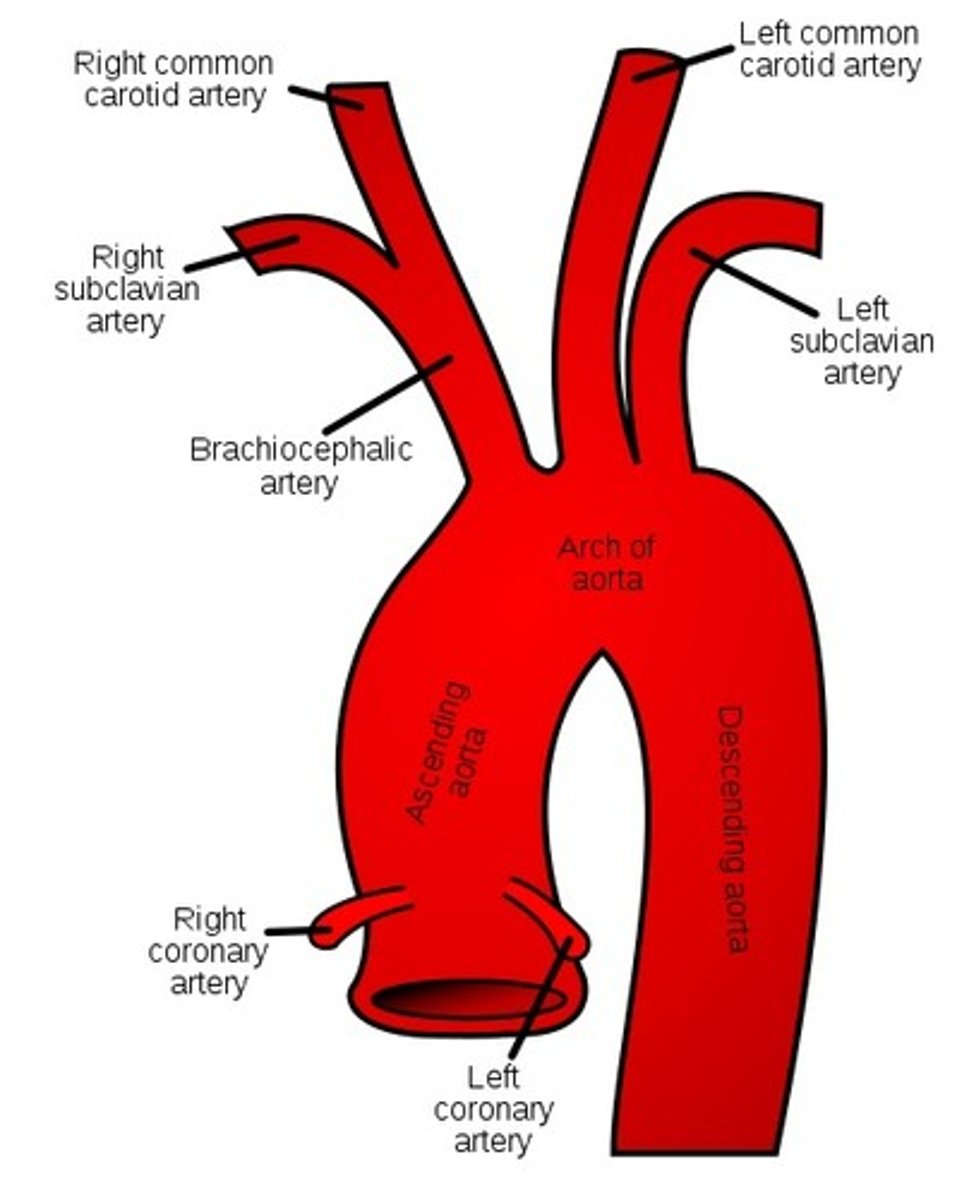
brachiocephalic (innominate) artery
the first major branch off of the aorta and the major artery to the forelimbs and head
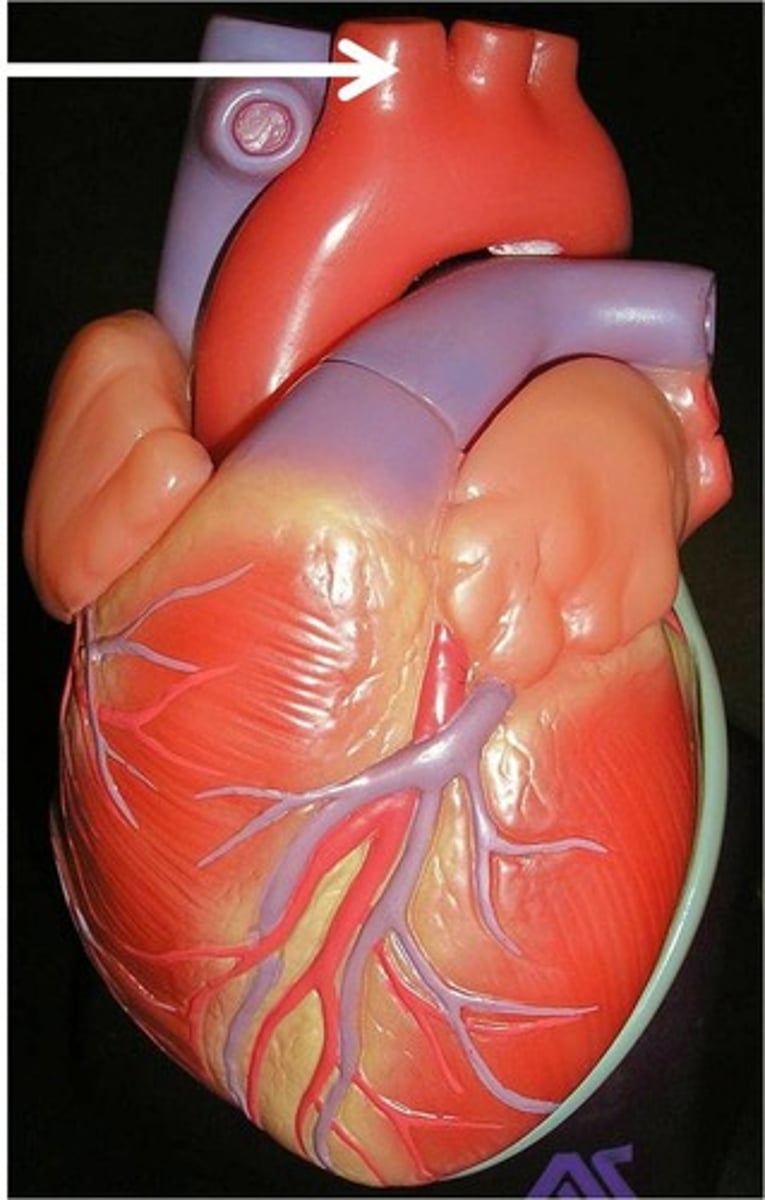
left common carotid artery
the second major branch off of the aorta that supplies the head and neck
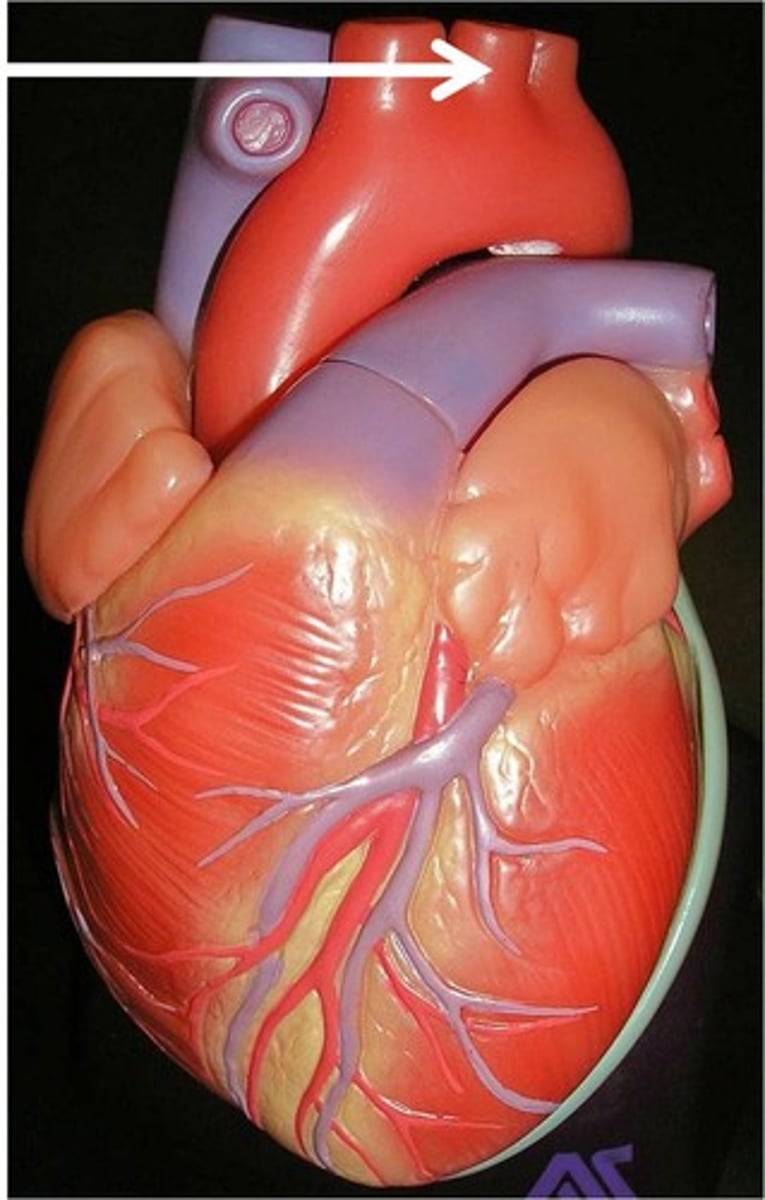
left subclavian artery
the third branch of the aortic arch that distributes blood to the left arm
*commonly utilized during bypass surgery
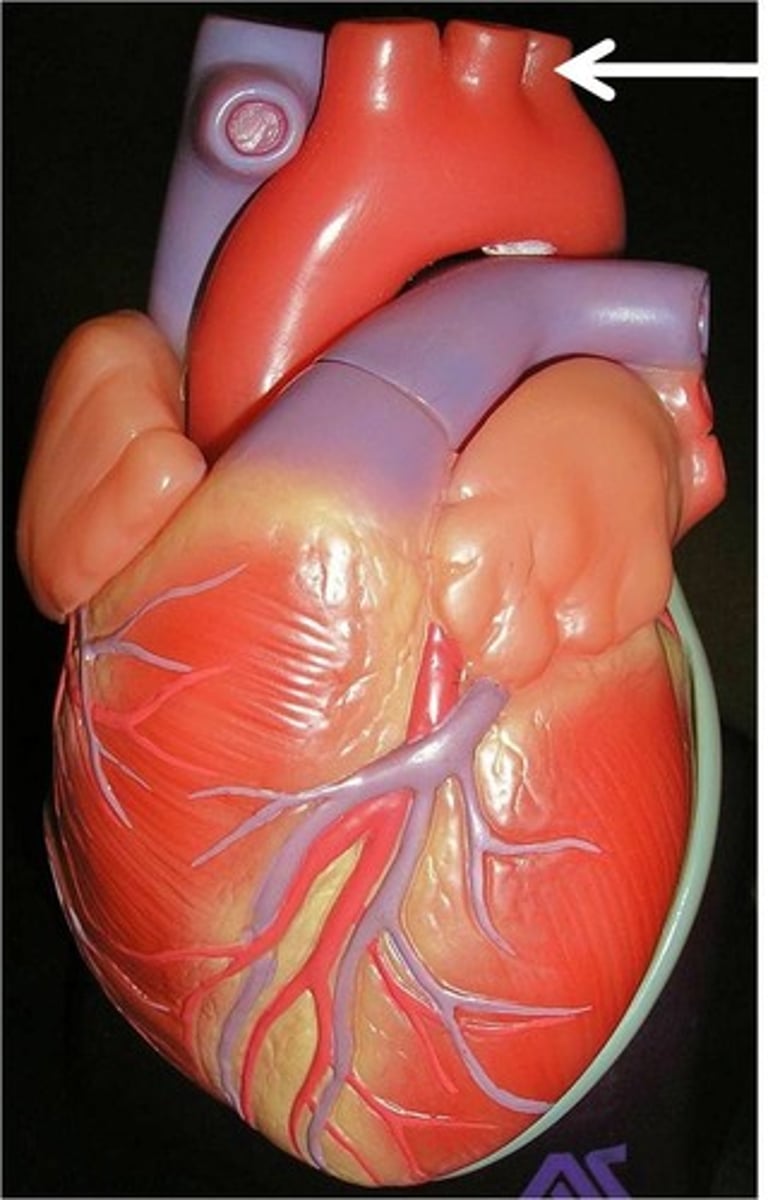
pulmonary trunk
carries blood from right ventricle to the R & L pulmonary arteries
*carries deoxygenated blood
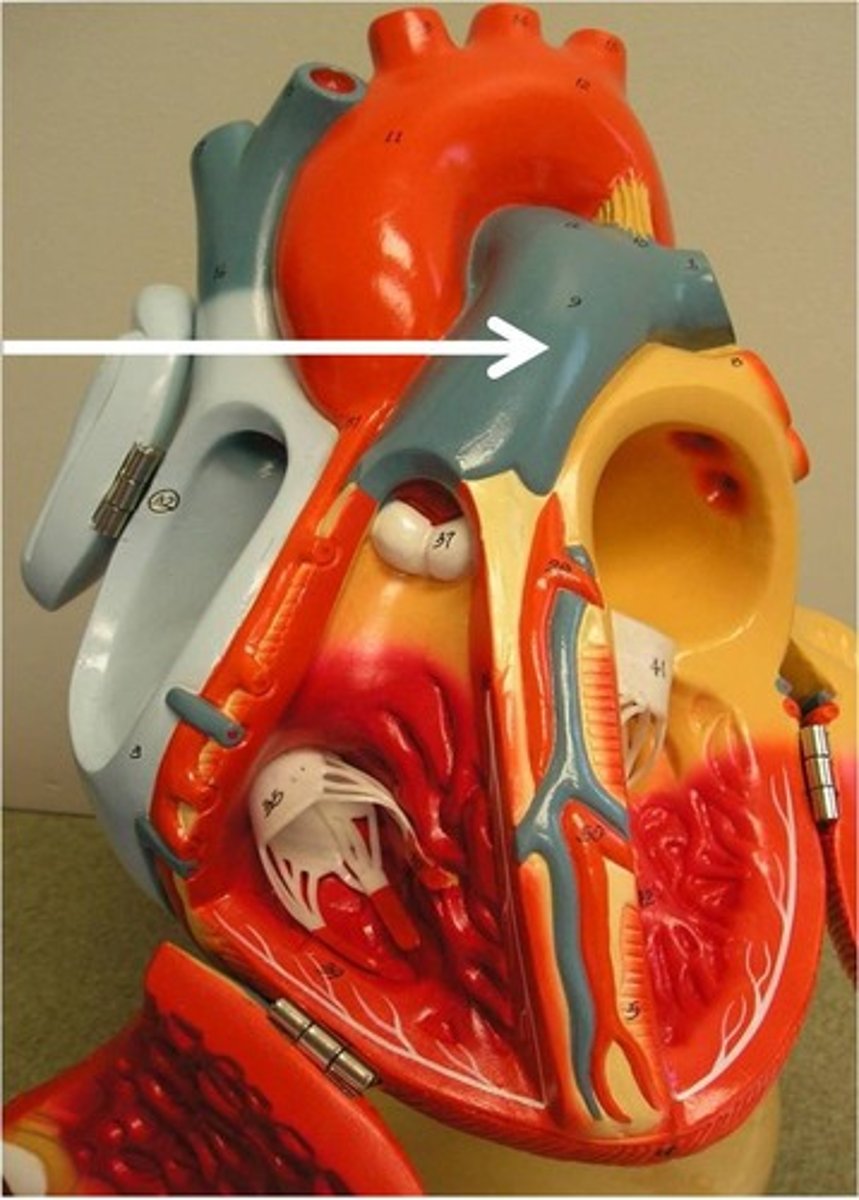
internal thoracic artery
branch of left subclavian artery that supplies the pericardium and anterior wall of the chest
aka left internal mammary artery (LIMA)
**used during bypass surgeries
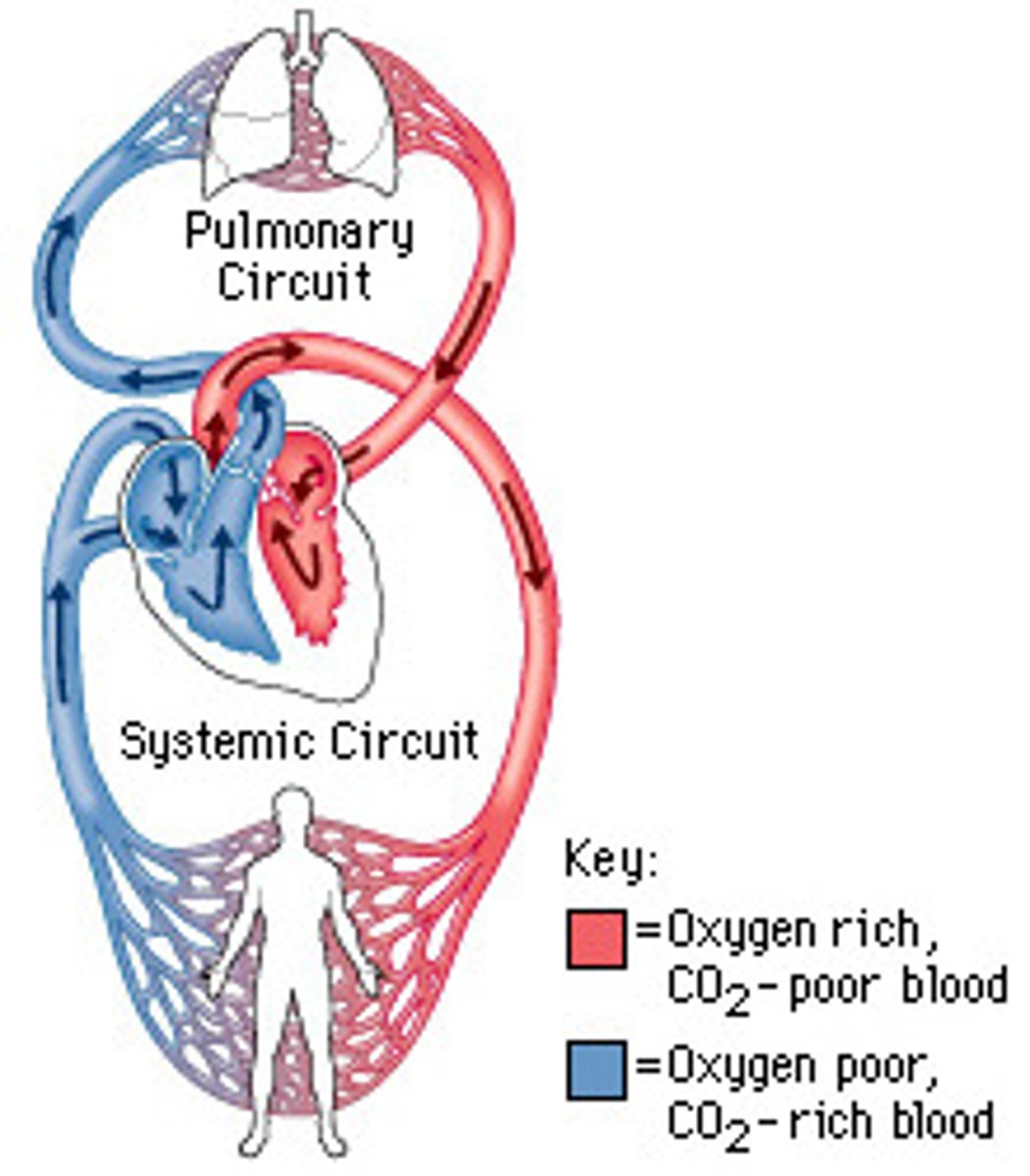
pulmonary circuit, systemic circuit
What are the 2 circulation systems of the heart?
pulmonary circuit
carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs for gas exchange and returns it to the heart
1. SVC
2. IVC
3. pulmonary trunk
RA--> RV--> lungs
systemic circuit
transports oxygenated blood to and from the rest of the body
1. pulmonary veins
2. aorta
LA--> LV--> body
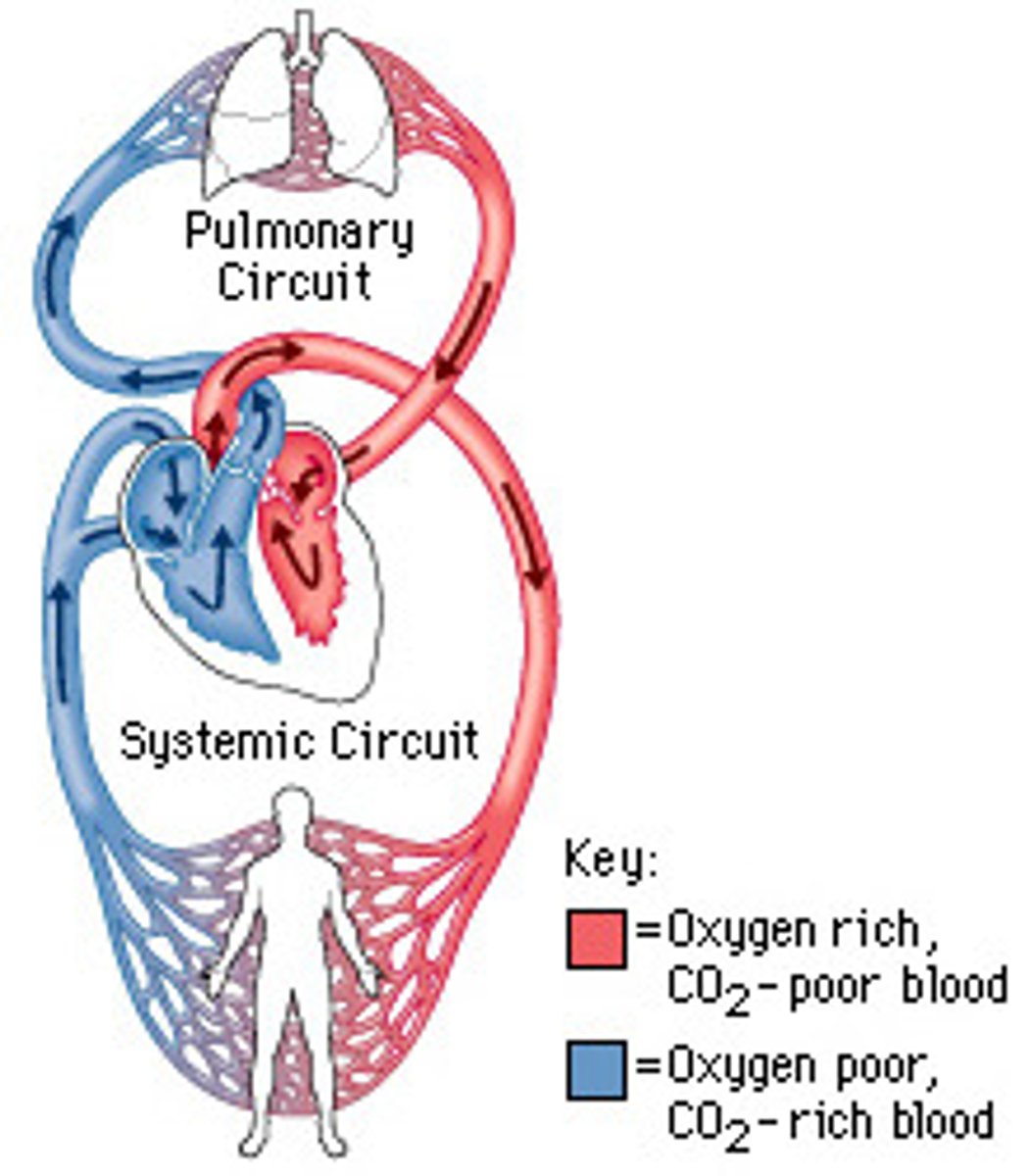
systemic (pushes blood to entire body)
Is the pulmonary or systemic circuit under a greater amount of pressure?
mitral, aortic semilunar
Which 2 valves are more commonly involved with pathologies?
HINT: high pressure
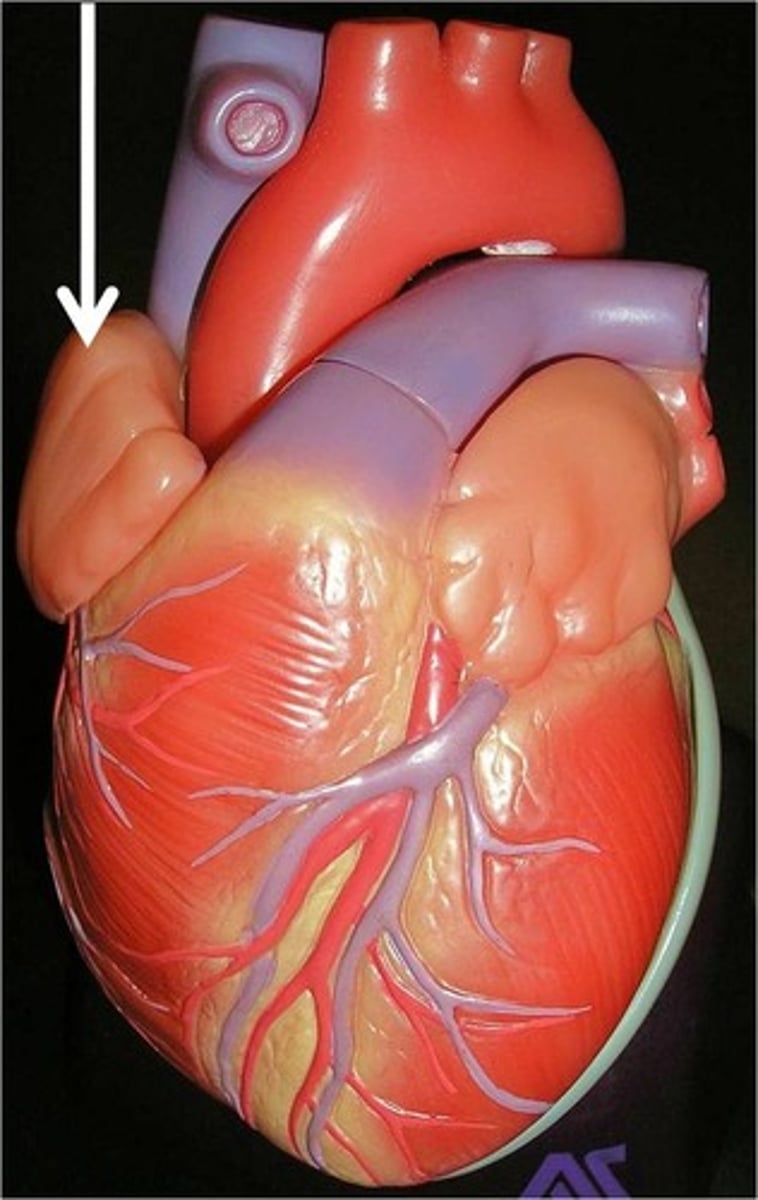
atria
upper chambers of the heart
push blood to the ventricles
(primarily gravity)
*pectinate muscle
**auricles
pectinate muscle
internal ridges of myocardium in right atrium and both auricles
*smooth lining with minimal ridges
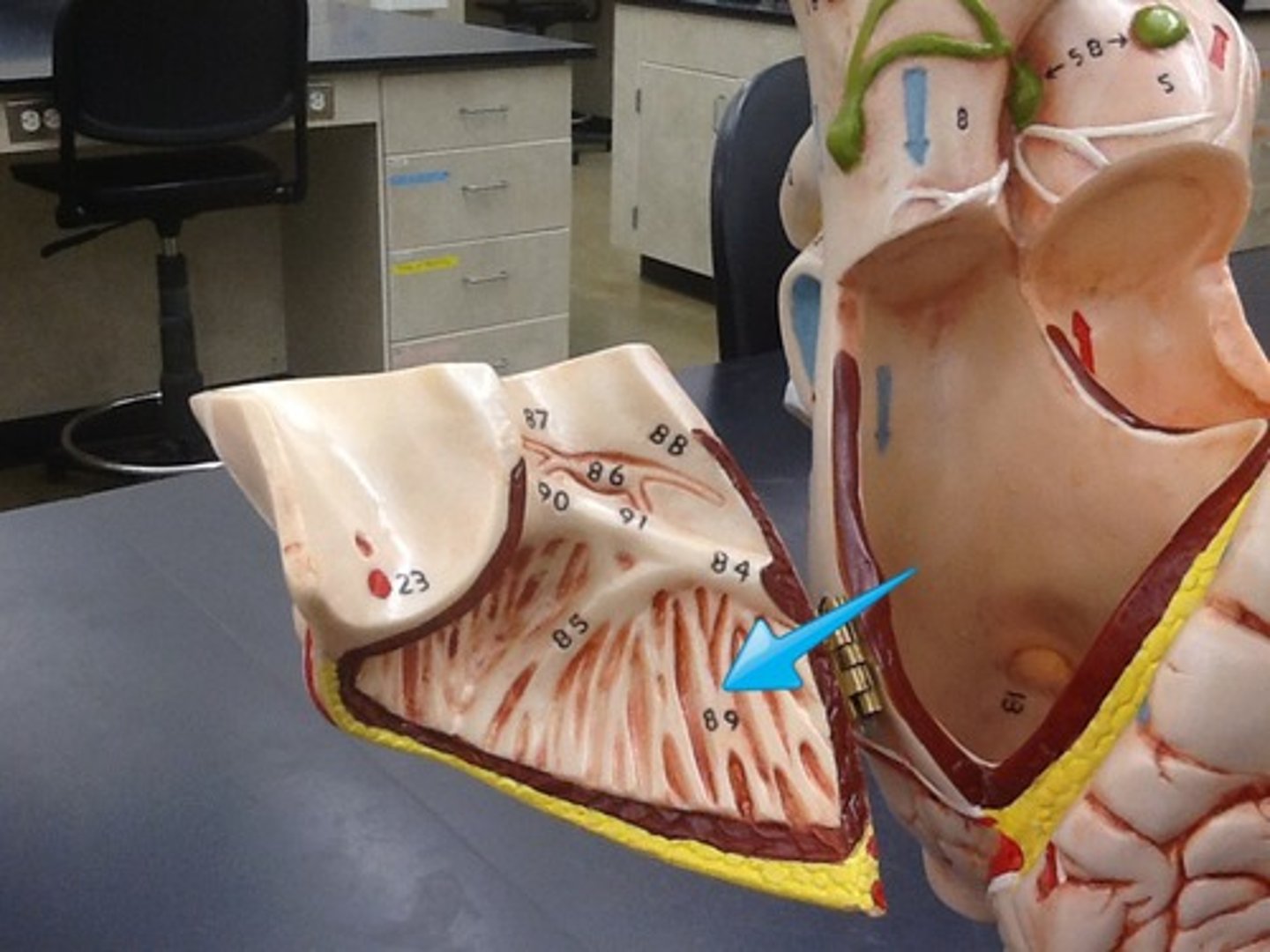
auricle
aka atrial appendages
the externally visible flap formed by the collapse of the outer wall of a relaxed atrium
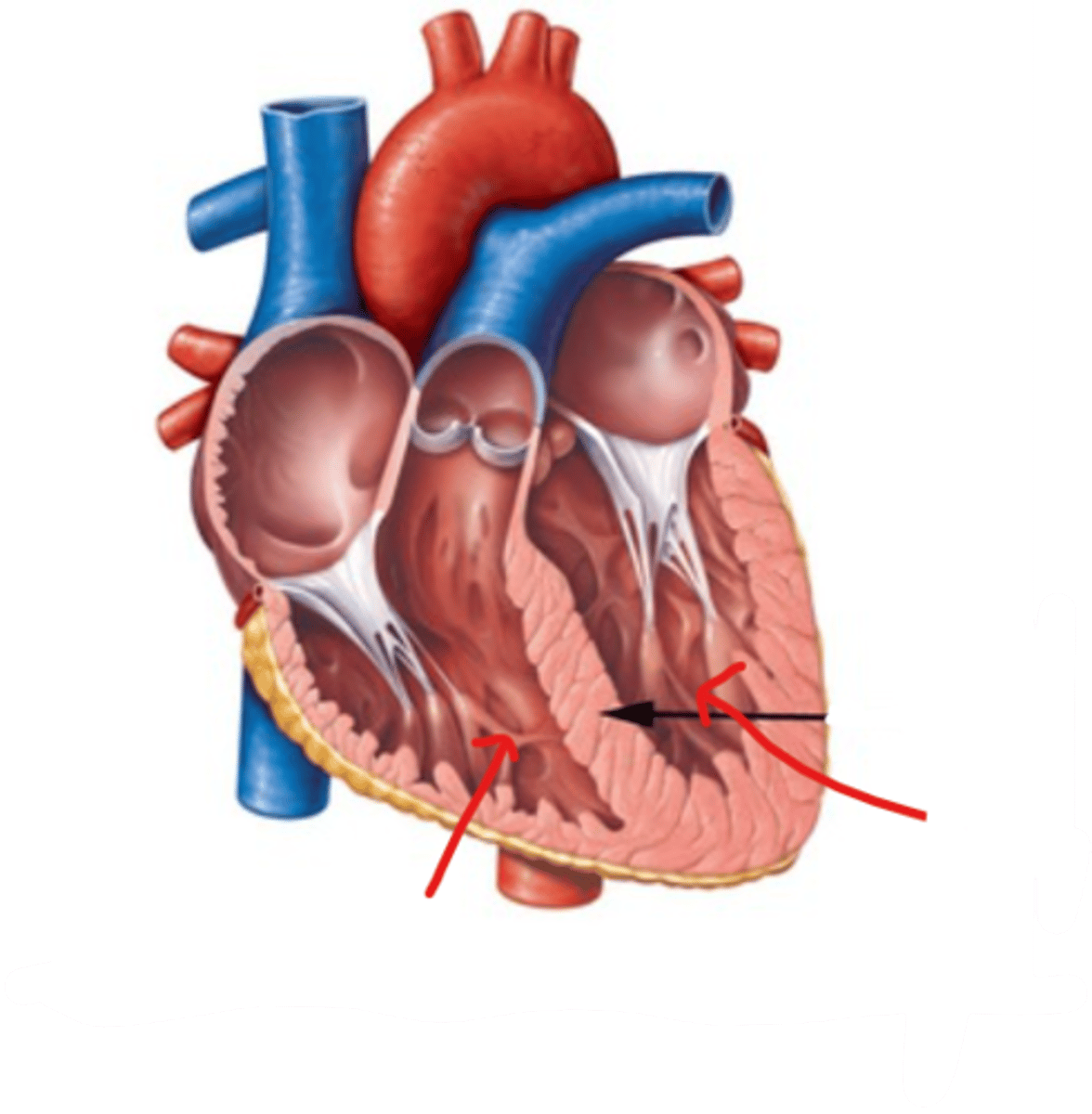
ventricles
the two lower chambers of the heart
*work anti-gravity
- trabeculae carneae
- Purkinje fibers
- interventricular septum
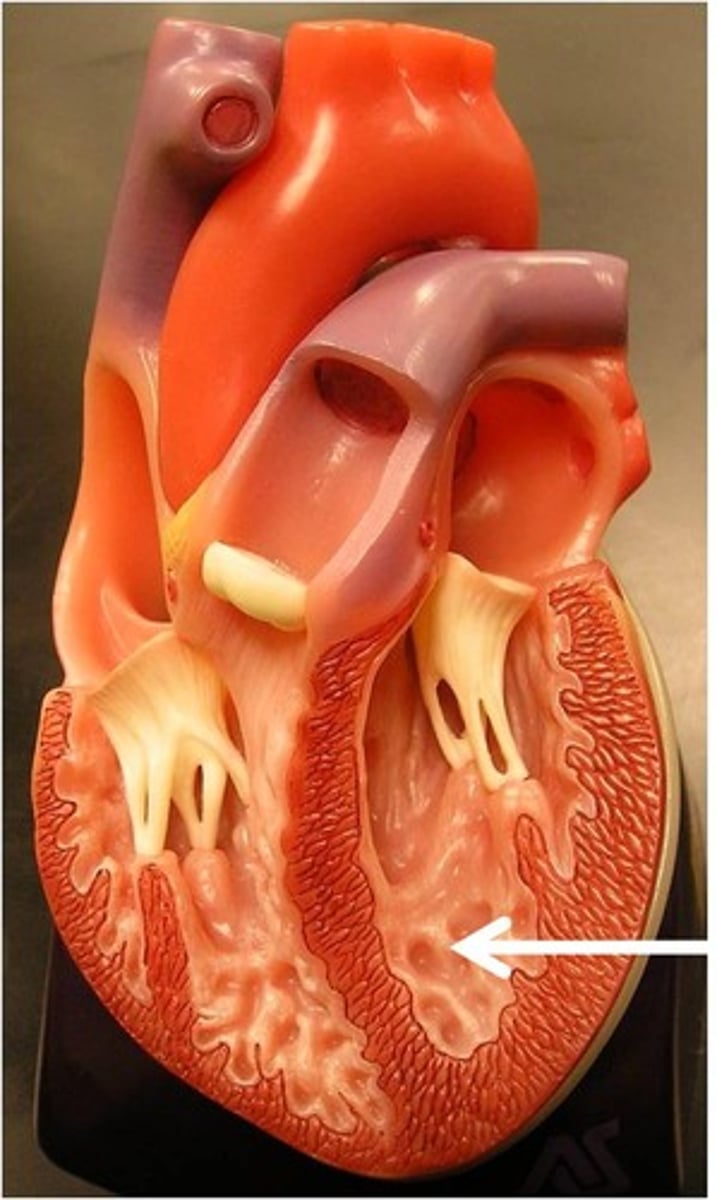
trabeculae carneae
thick muscular ridges on the internal surface of the ventricles
*main contractile tissue
**decreases suction chance
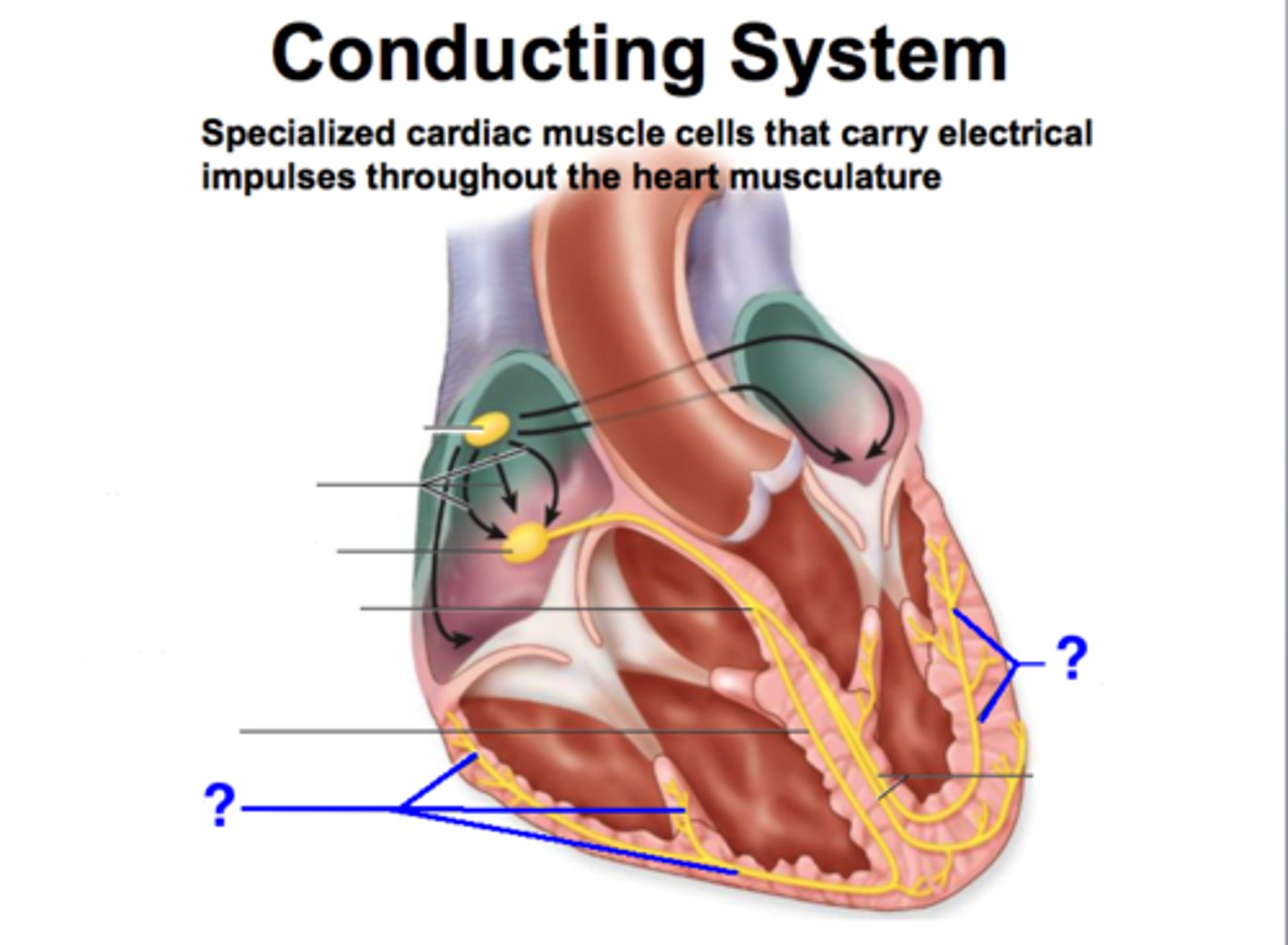
Purkinje fibers
fibers in the ventricles that transmit impulses to the right and left ventricles
*causes contraction
(<40 bpm)
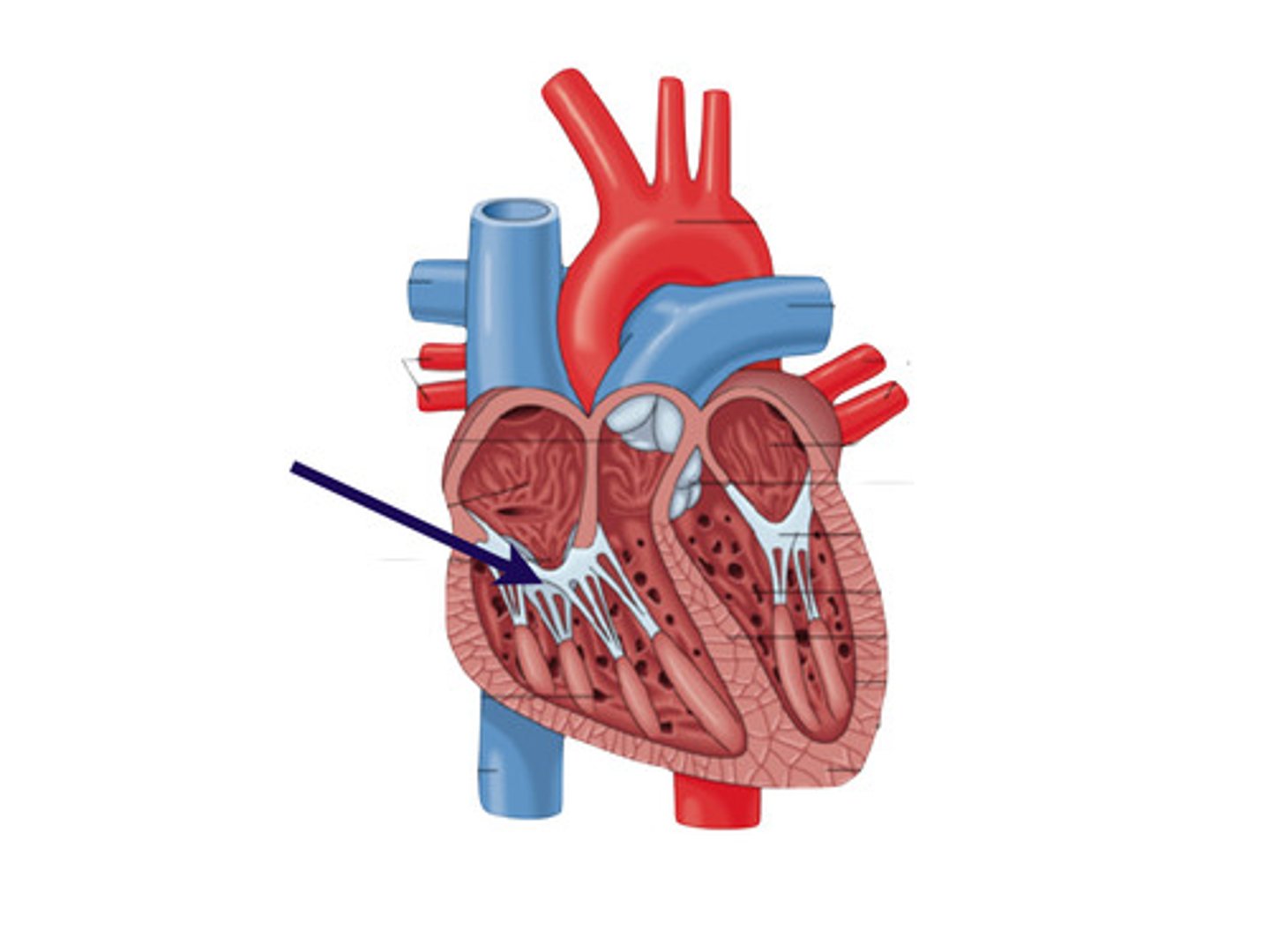
interventricular septum
partition between the right and left ventricle
*important for electrical conduction
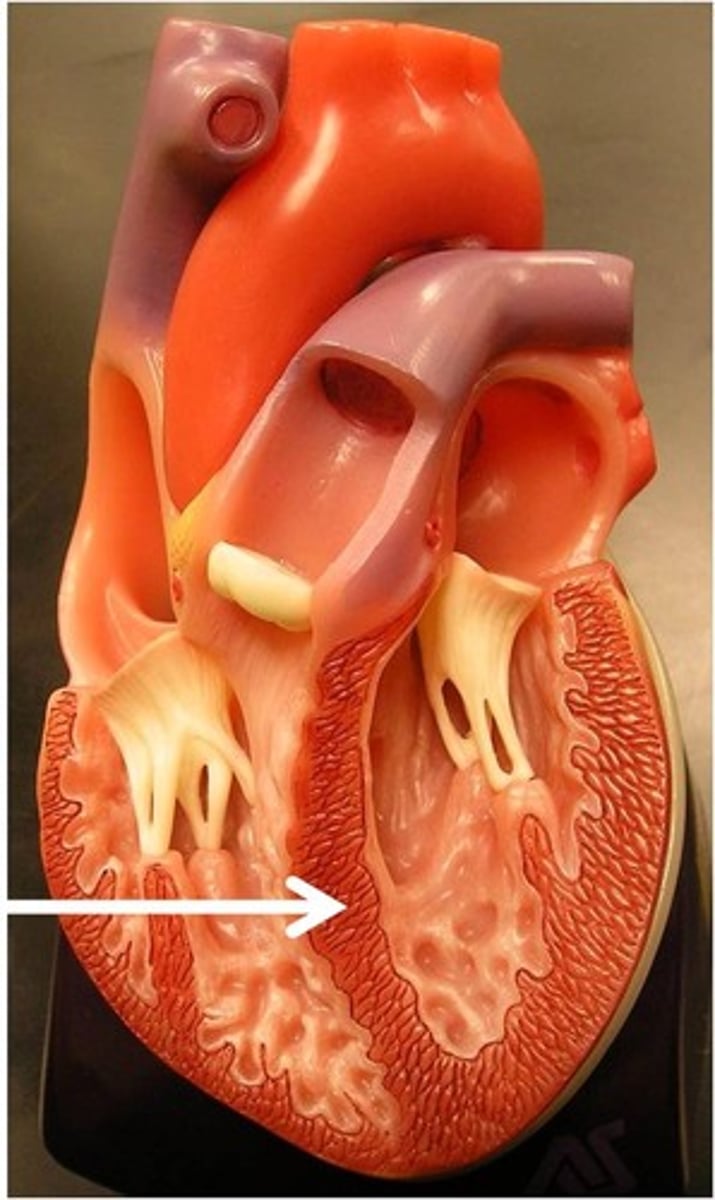
papillary muscles
responsible for pulling the atrioventricular valves closed by means of the chordae tendineae
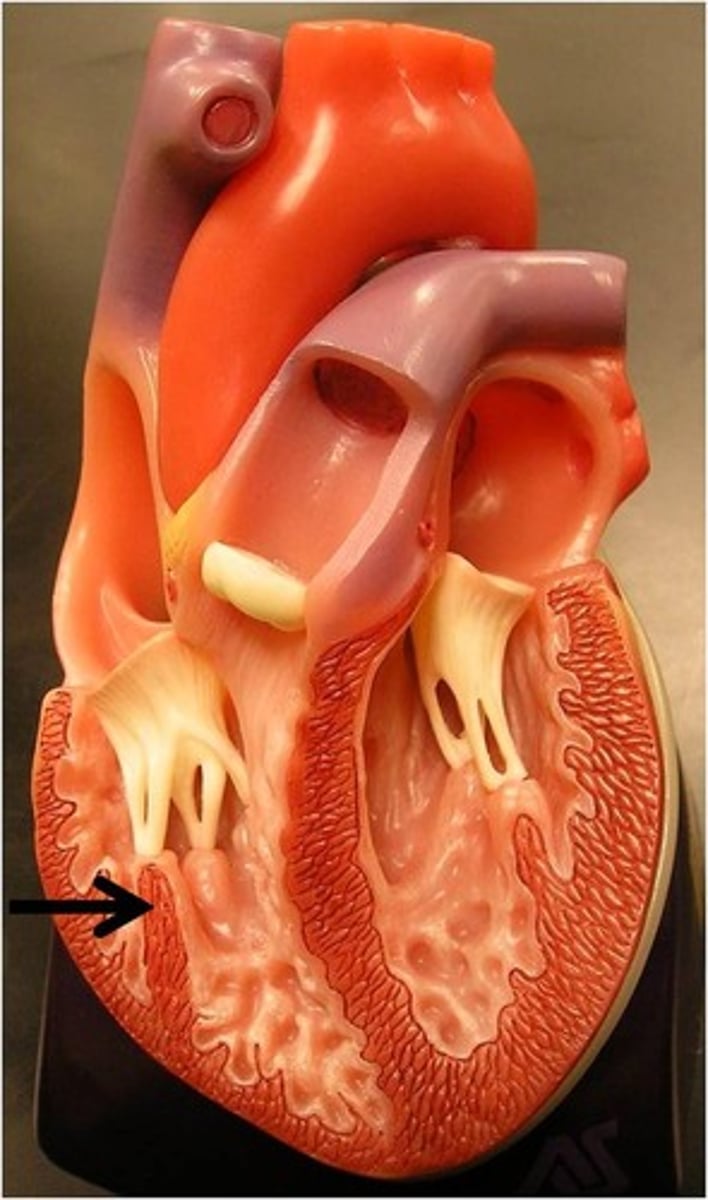
chordae tendinae
fibers attached to the tricuspid and mitral valve which pull it closed when papillary muscles contract
*preventing back flow of blood
**maintain structural support of valve
tricuspid, mitral
What are the 2 atrioventricular (AV) valves?
pulmonary, aortic
What are the 2 semilunar valves?
tricuspid valve
valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
mitral valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle
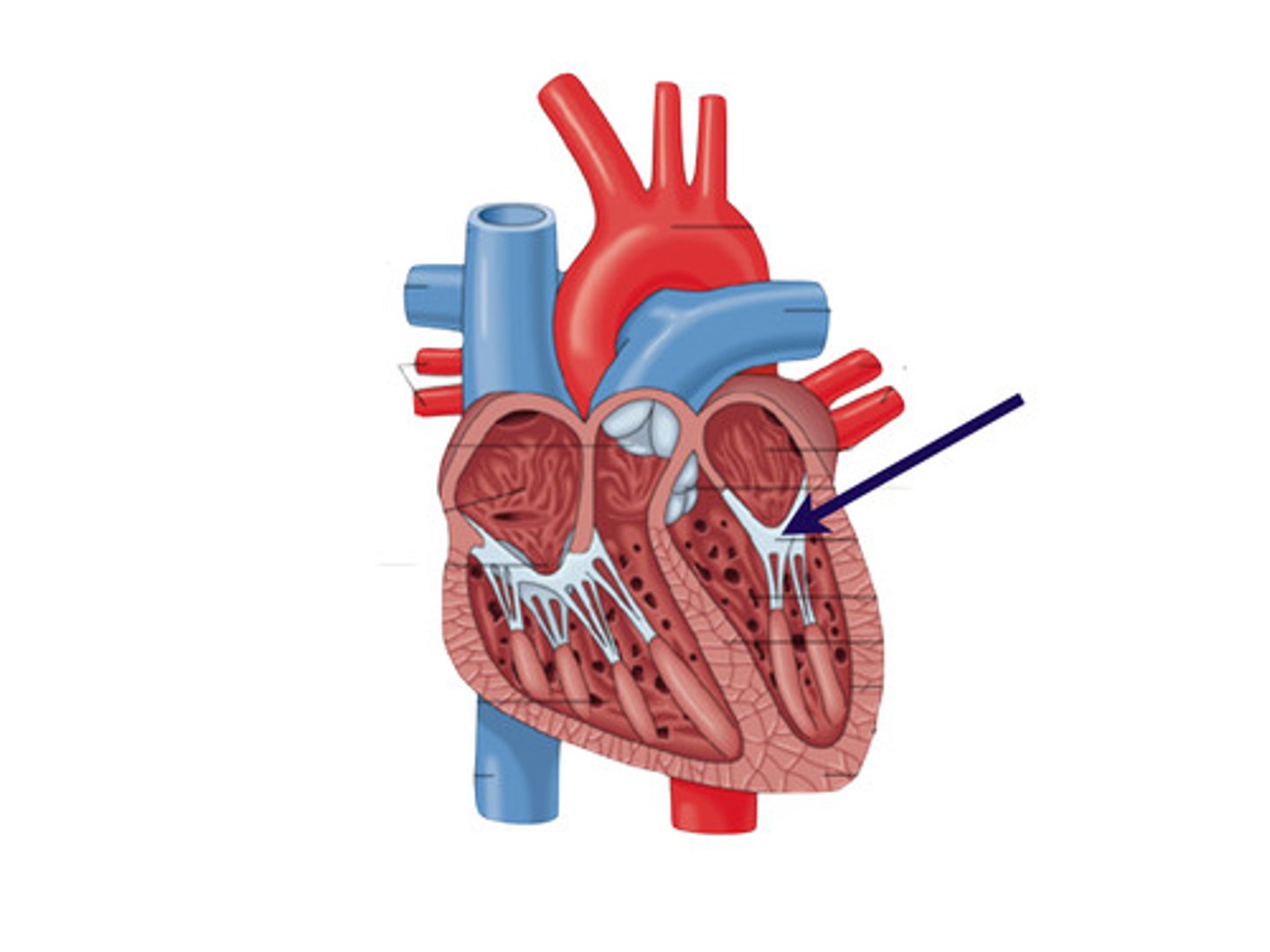
pulmonary semilunar valve
heart valve opening from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery
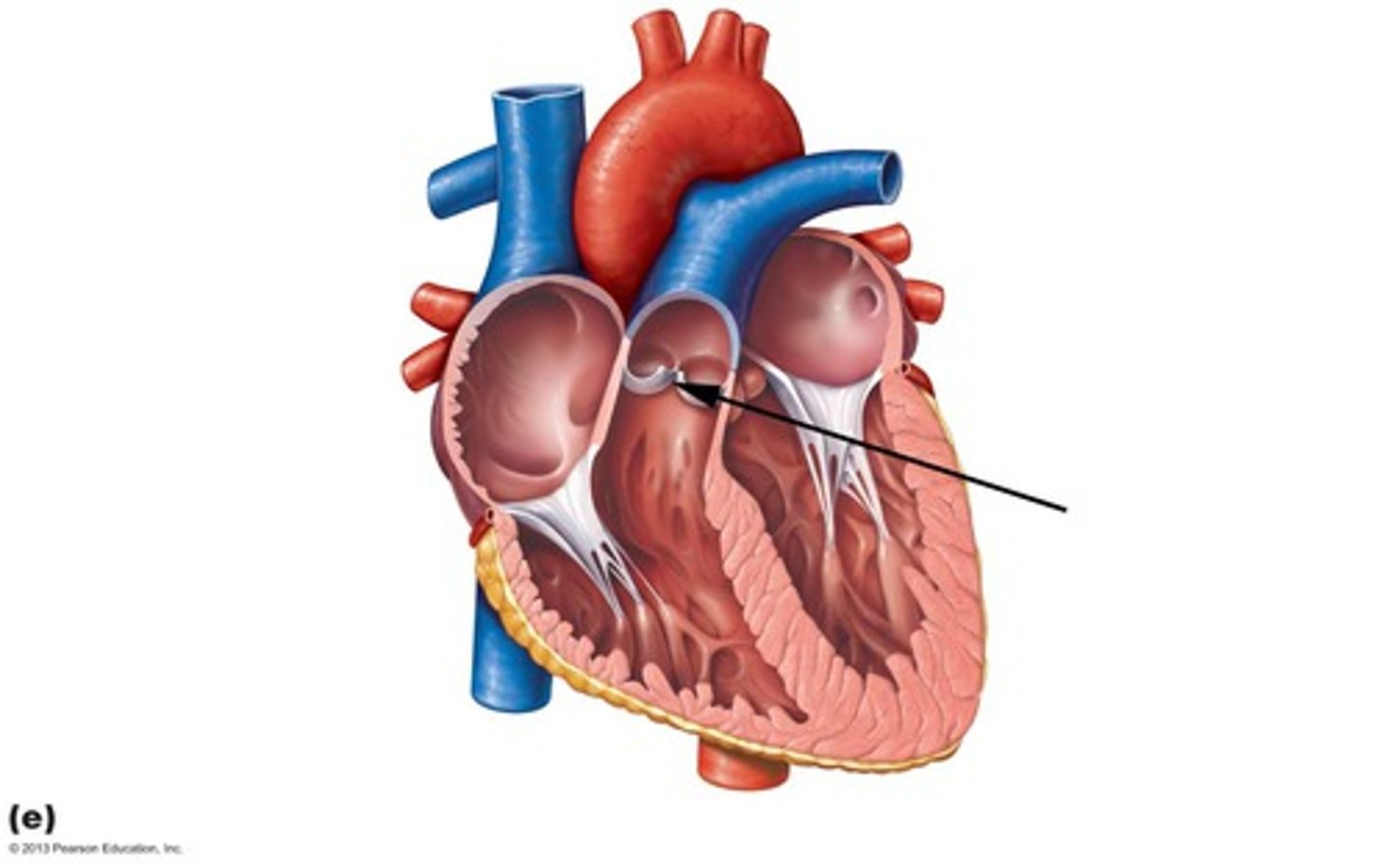
aortic semilunar valve
heart valve located between the left ventricle and the aorta
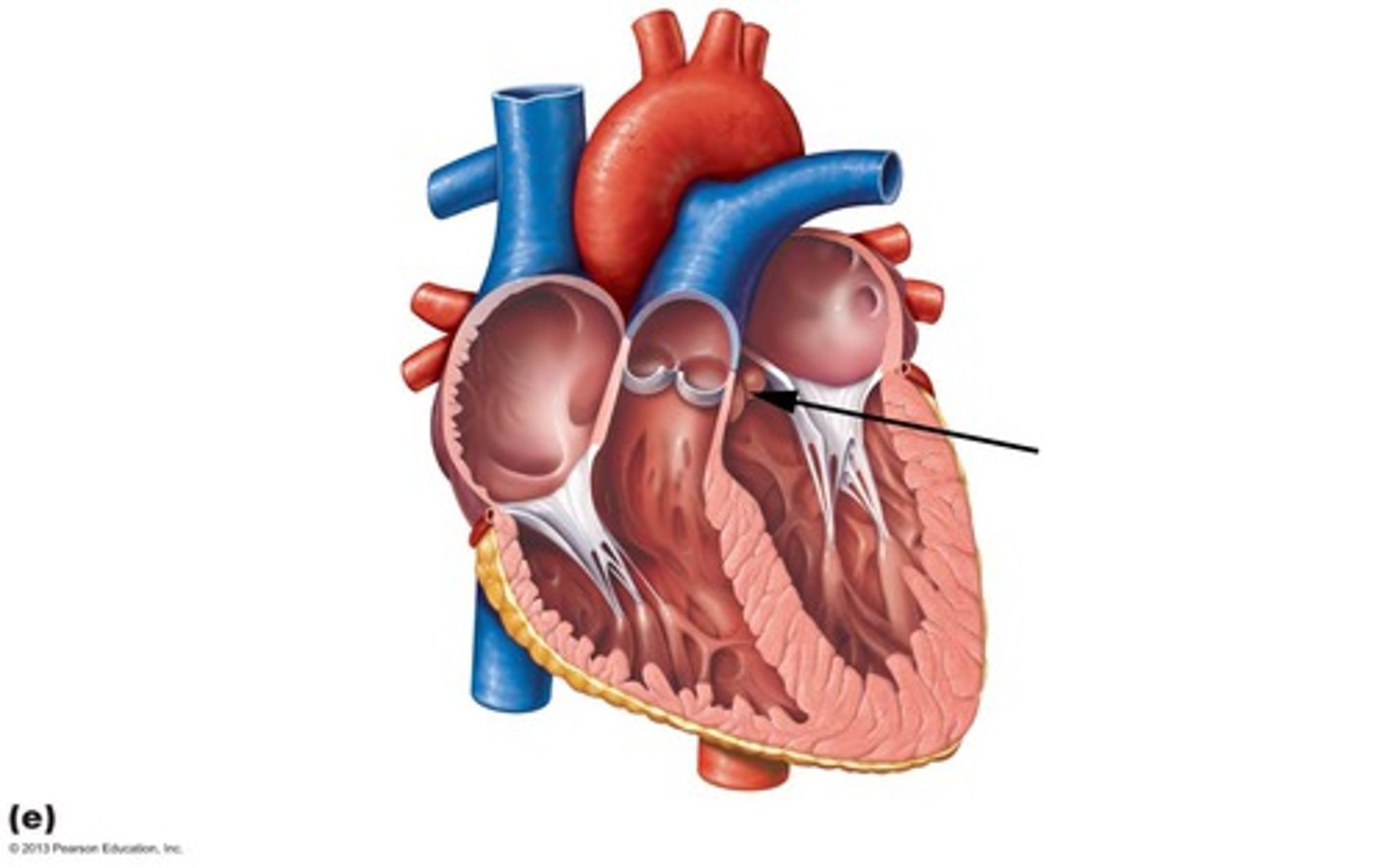
tricuspid, mitral
What valves are OPEN during DIASTOLE?
aortic, pulmonary
What valves are OPEN during SYSTOLE?
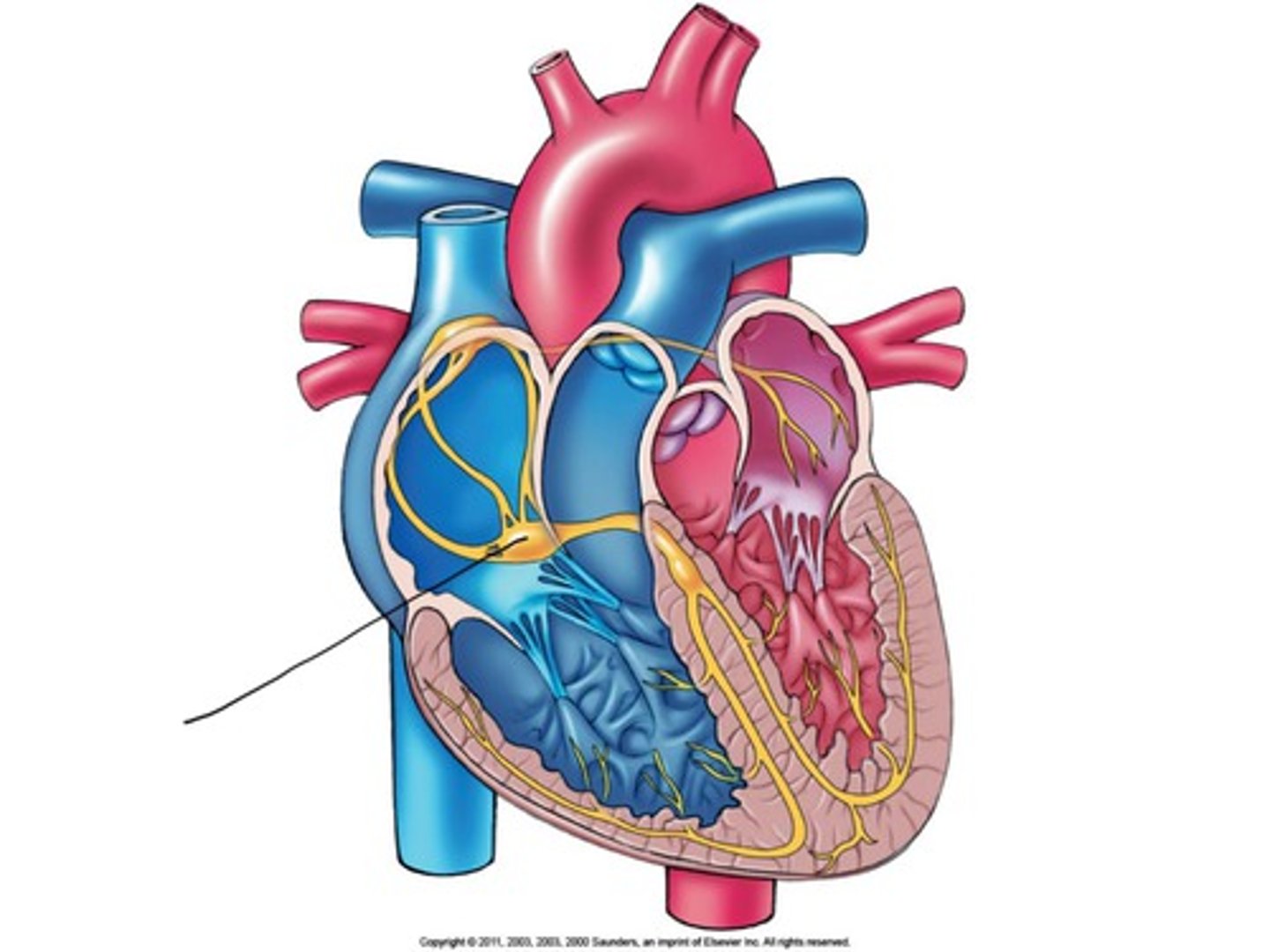
SA (sinoatrial) node
pacemaker of the heart
*60-100 bpm
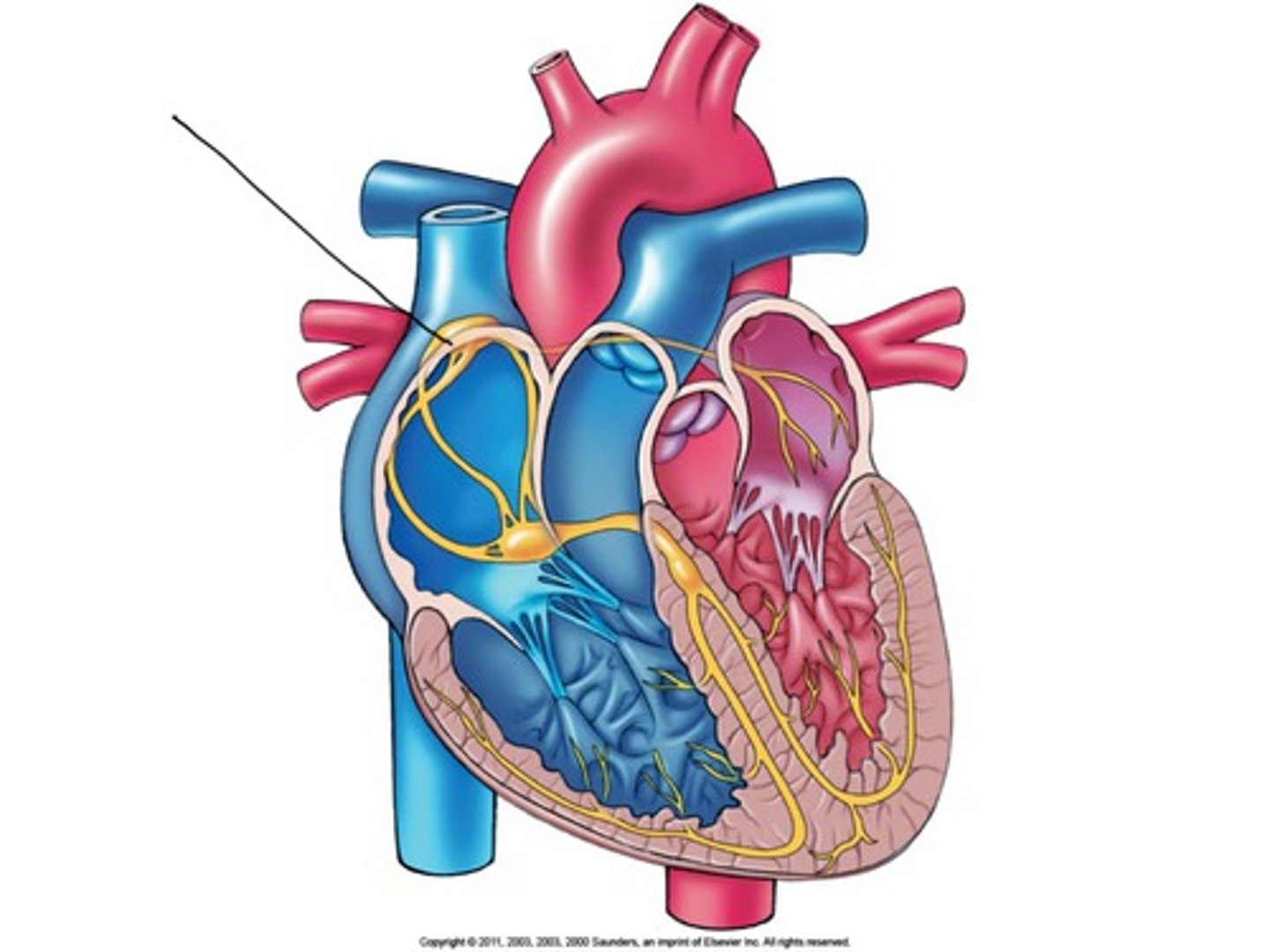
AV (atrioventricular) node
backup generator
(40-60 bpm)
conducts impulses to AV bundle in interventricular septum
*delays impulse, so that atria finish contracting before ventricles contract
increase in blood pressure
To maintain CO when HR decreases, SV must increase. How is this typically accomplished?
ECG cycle
graphic representation of cardiac cycle
2/3 = filling time (SV)
1/3 = contraction time (HR)
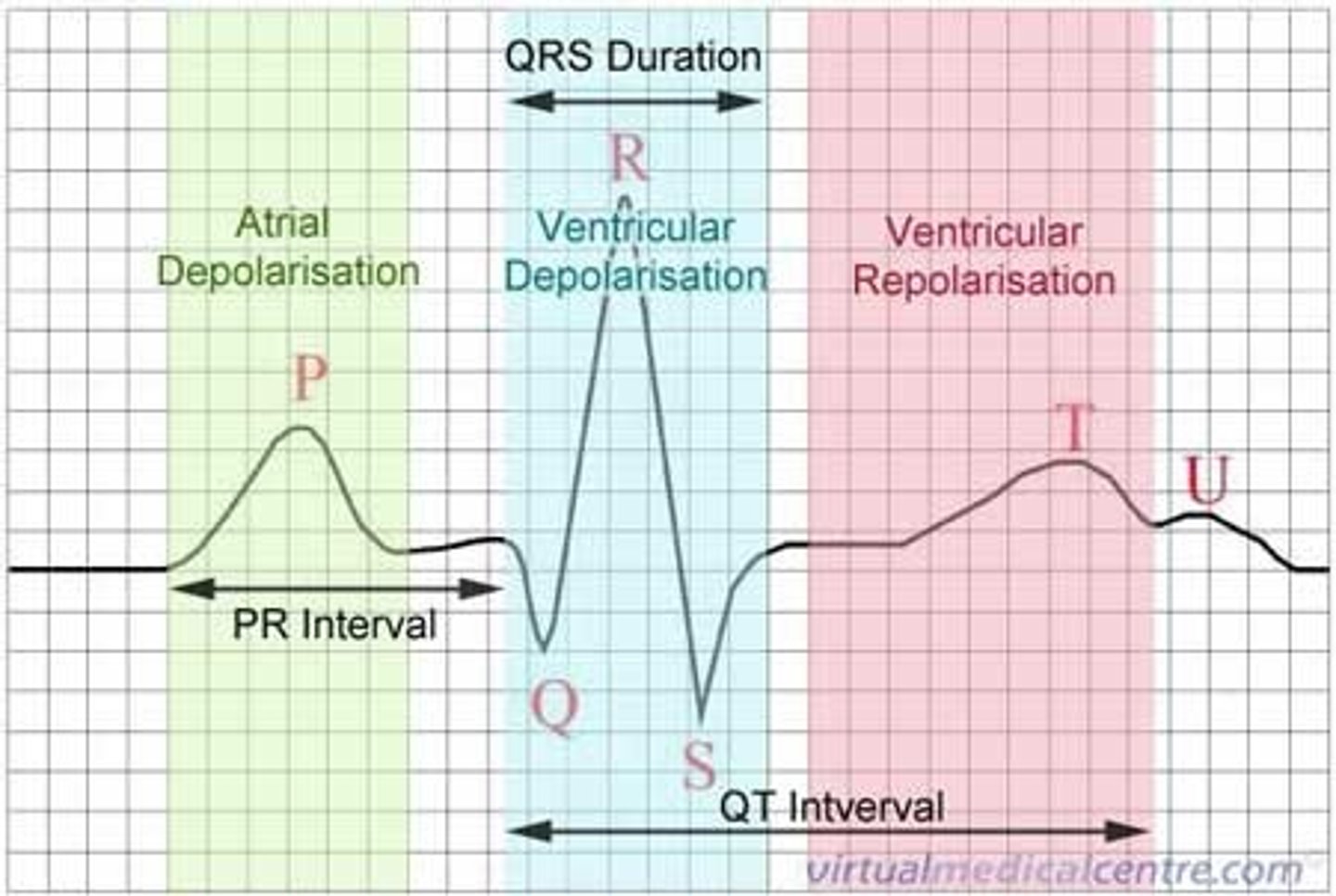
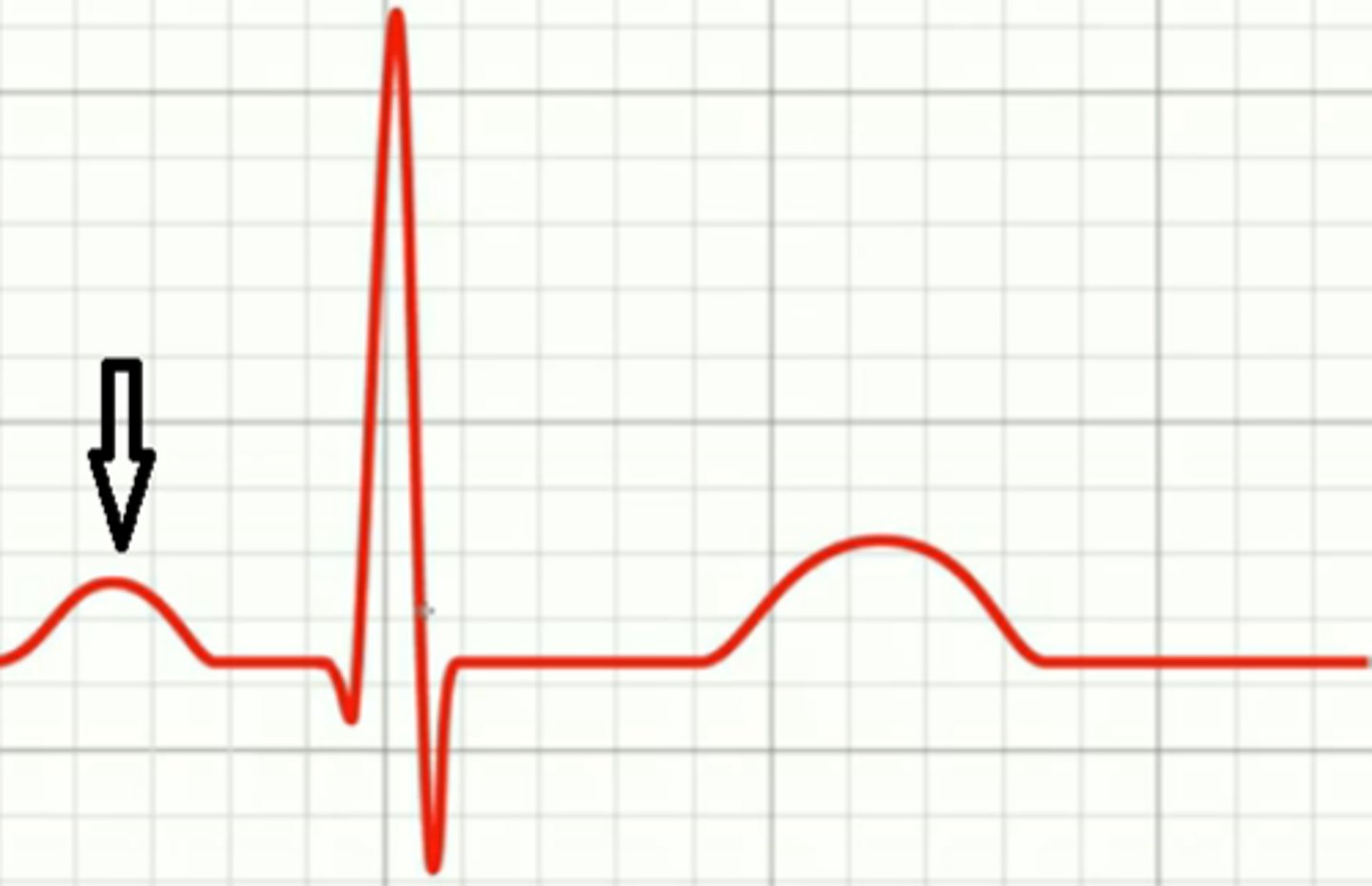
P wave
atrial depolarization
(contraction/systole)
QRS complex
ventricular depolarization
(contraction/systole)
Q wave
initial negative deflection produced by ventricular depolarization
simultaneous with blood entering ventricles
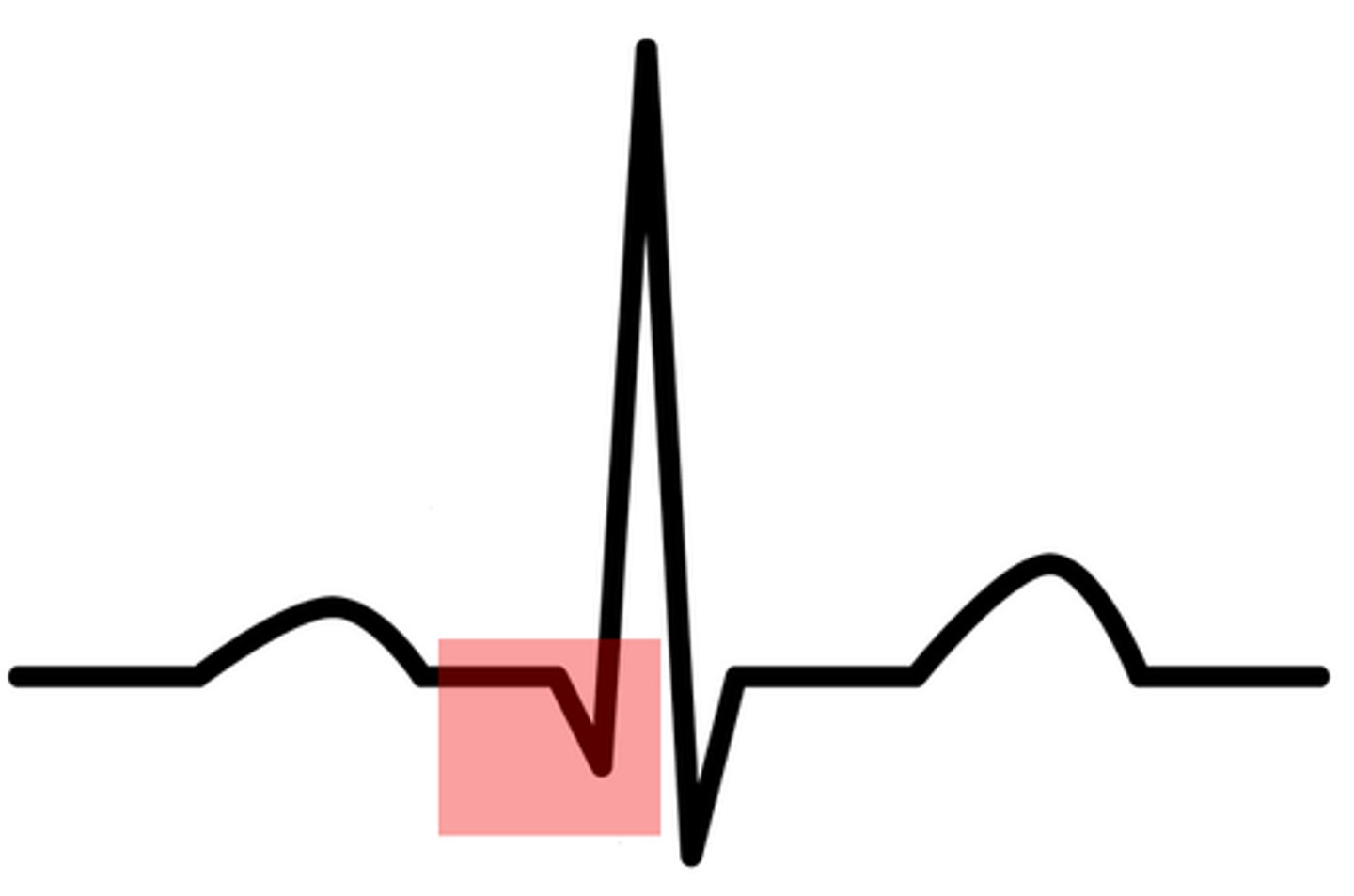
S wave
ventricular muscles begin to relax
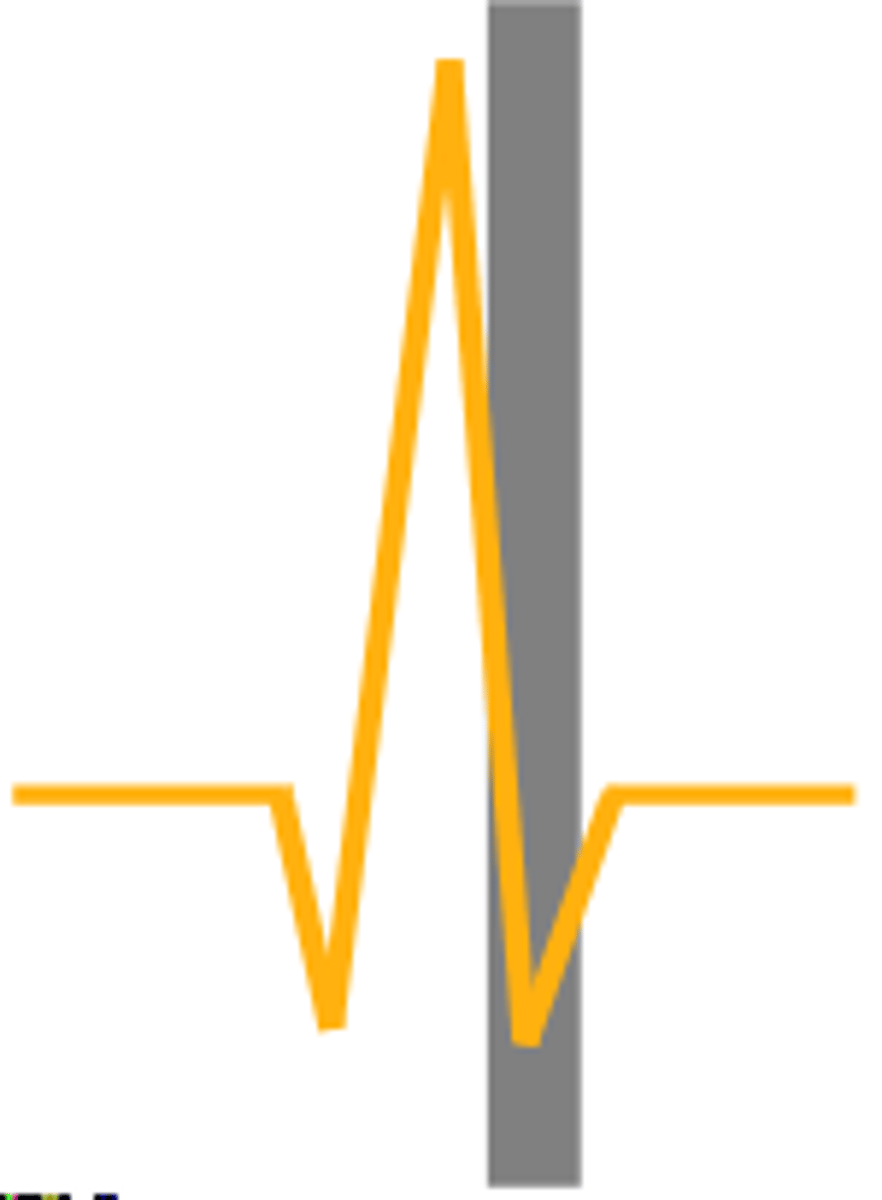

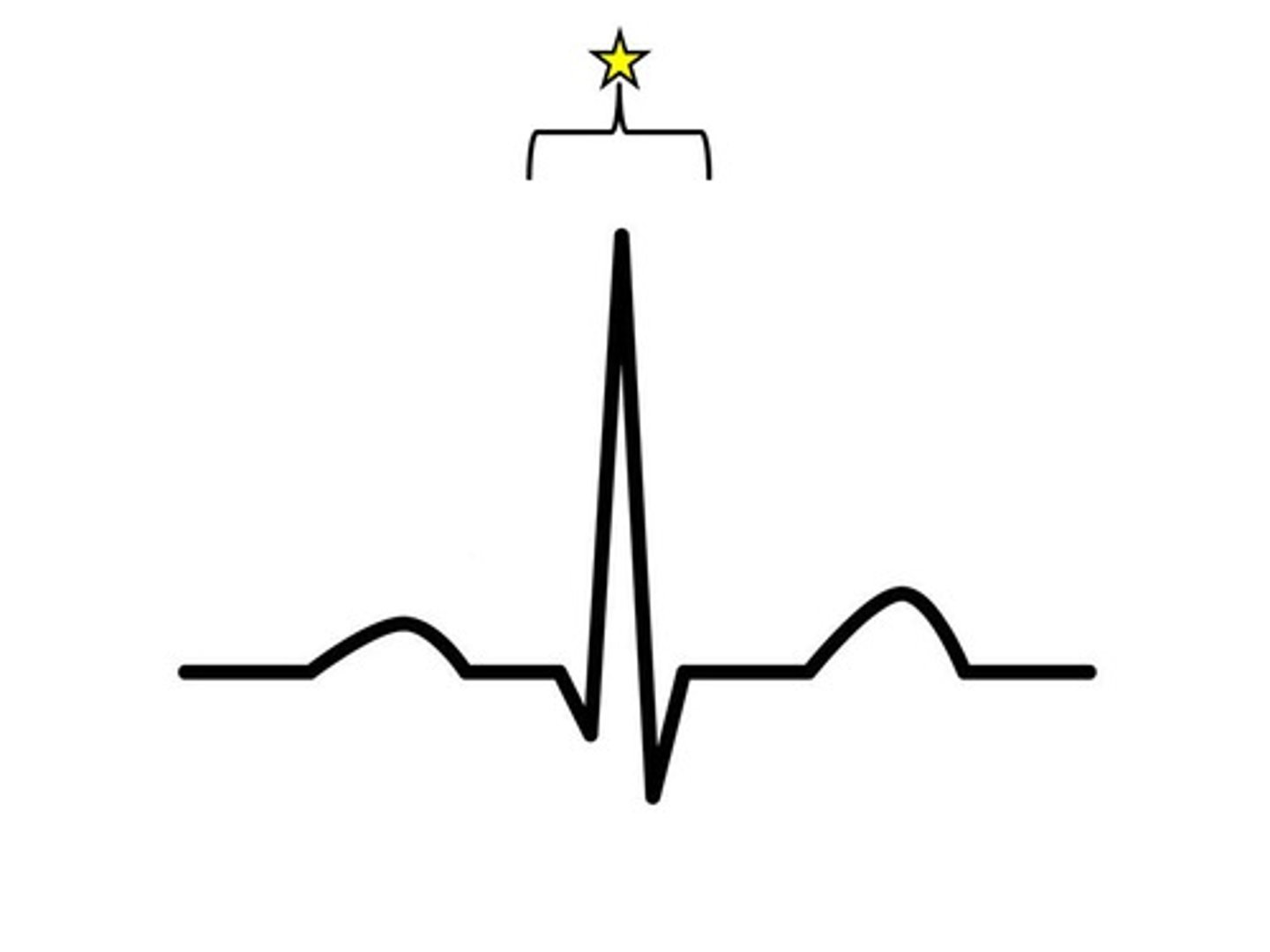
R
Problems with the ___ wave of an ECG are the most concerning.
T wave
ventricular repolarization (relaxation/diastole)
*should be bigger than P wave
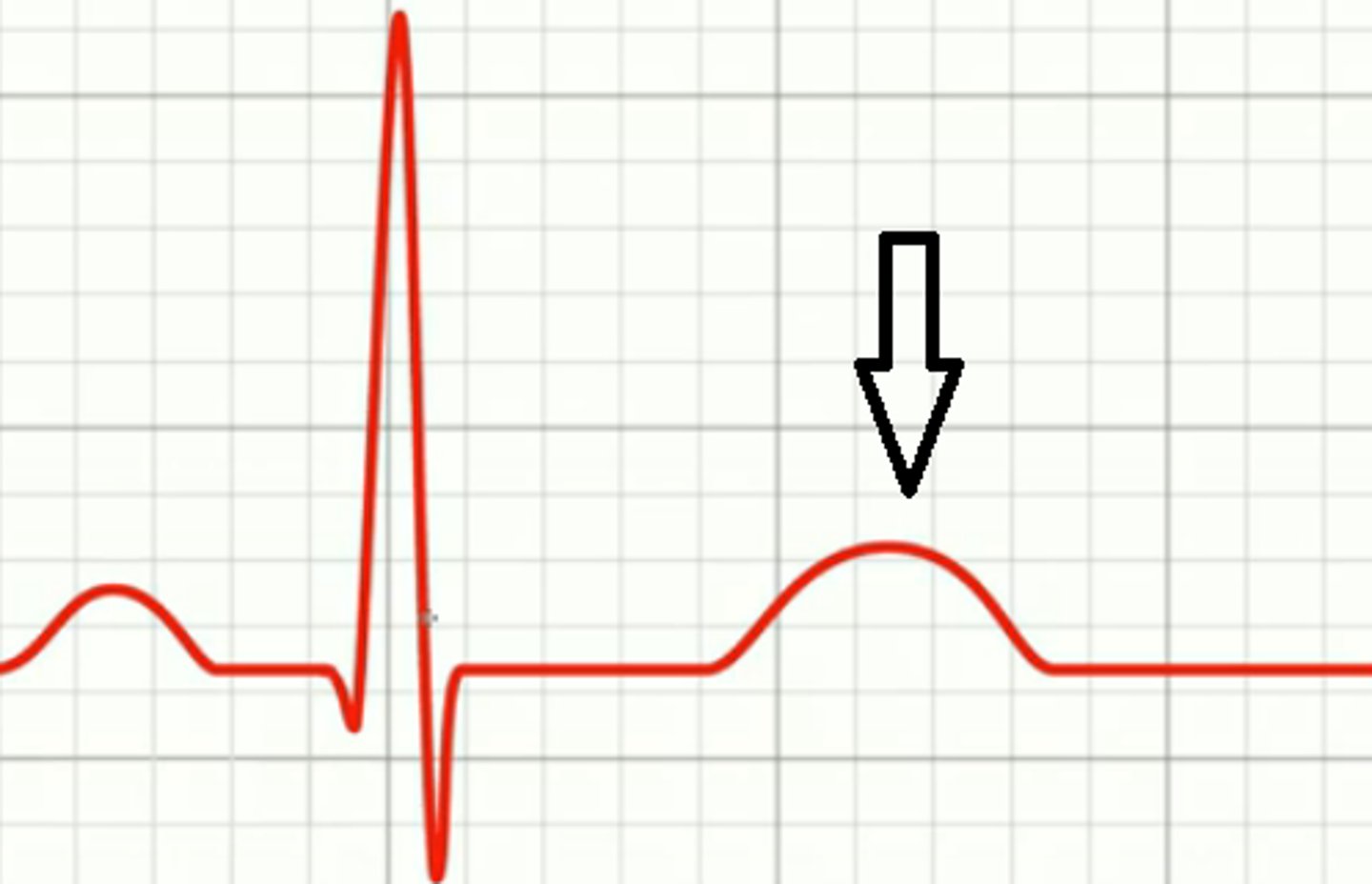
amplitude (force of contraction)
The vertical height on a ECG is what?
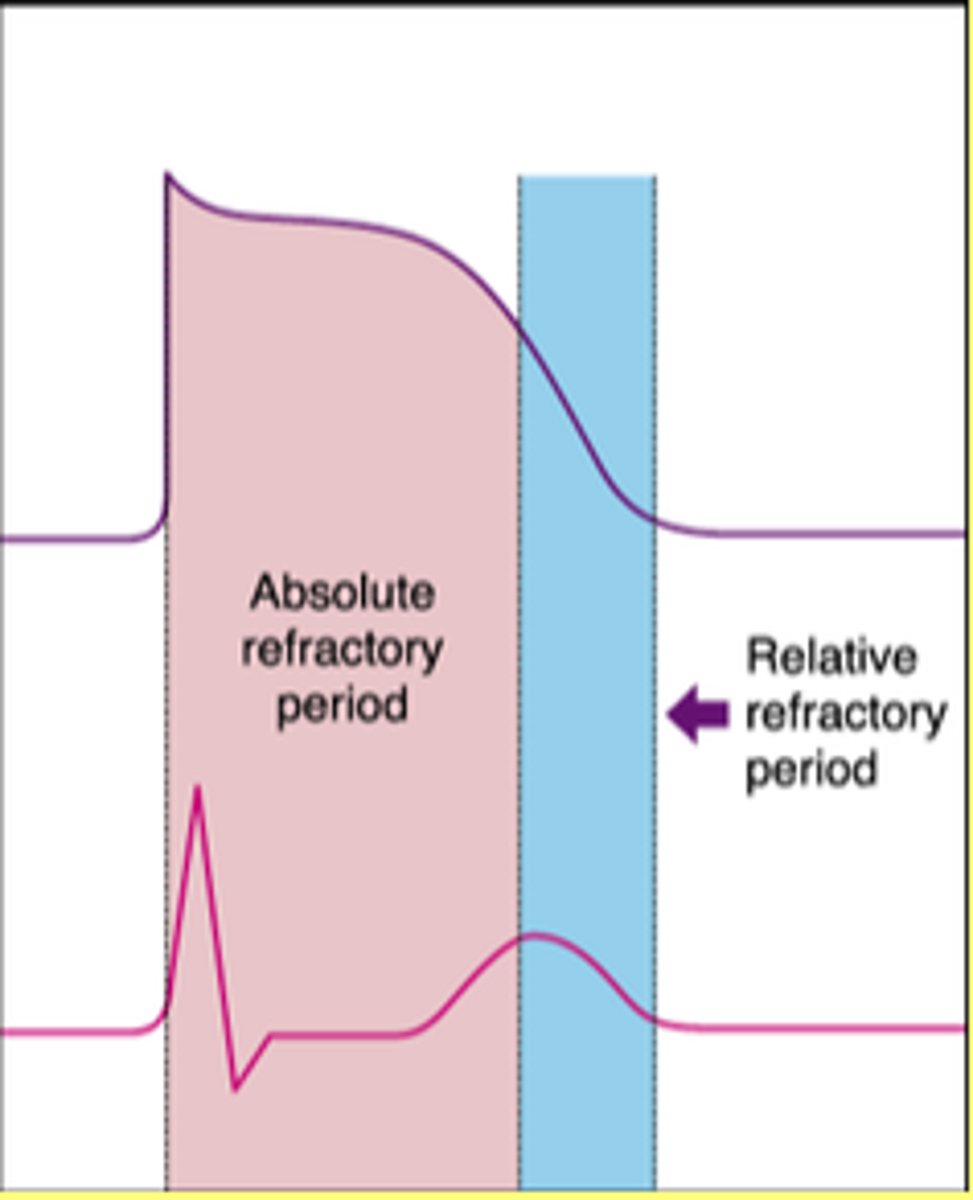
refractory period
a period of inactivity represented by horizontal line on ECG
lub
S1
sound heard w/ closing of AV valves
*occurs at ventricular systole
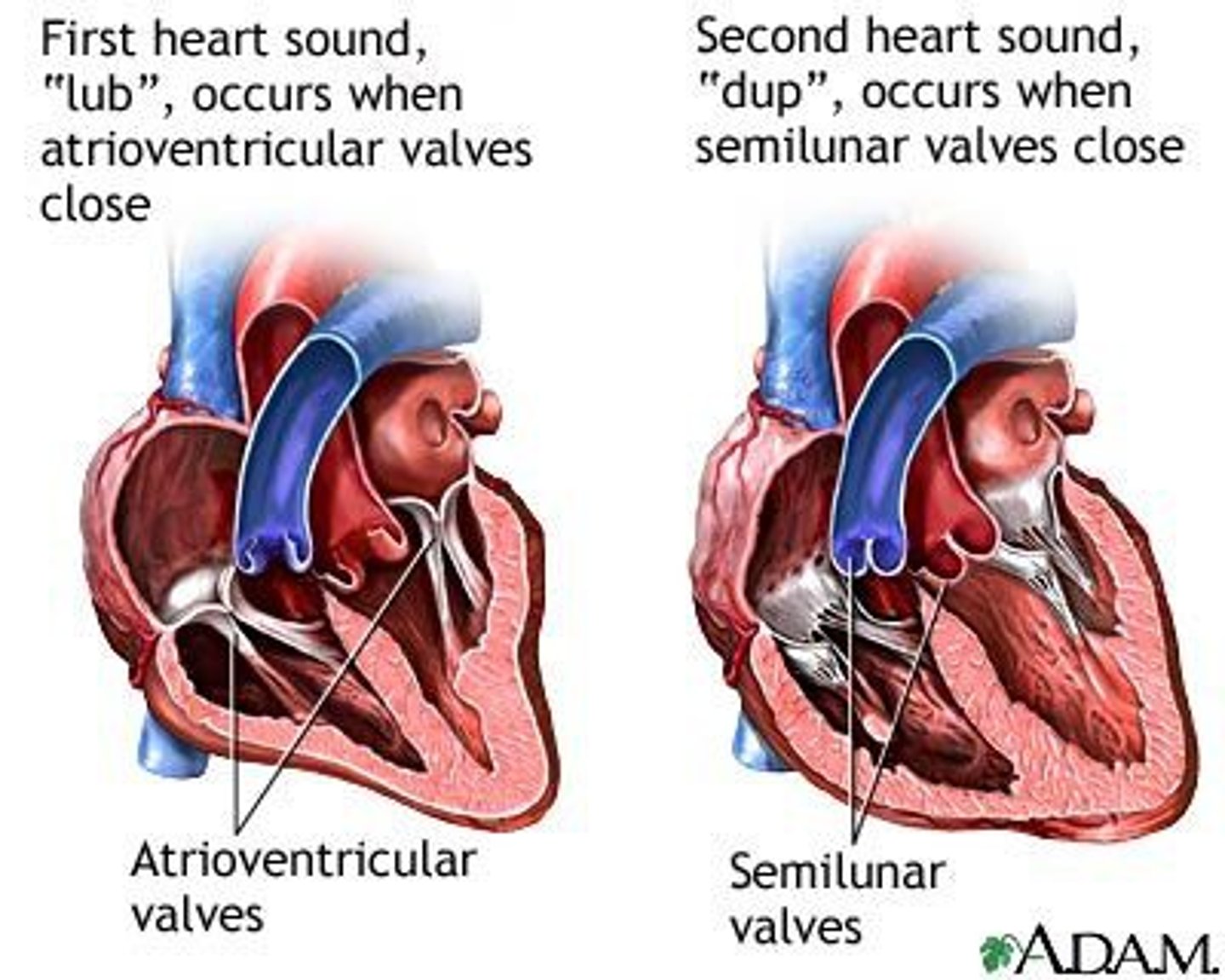
dub
S2
sound heard w/ closing of semilunar valves
*occurs at ventricular diastole
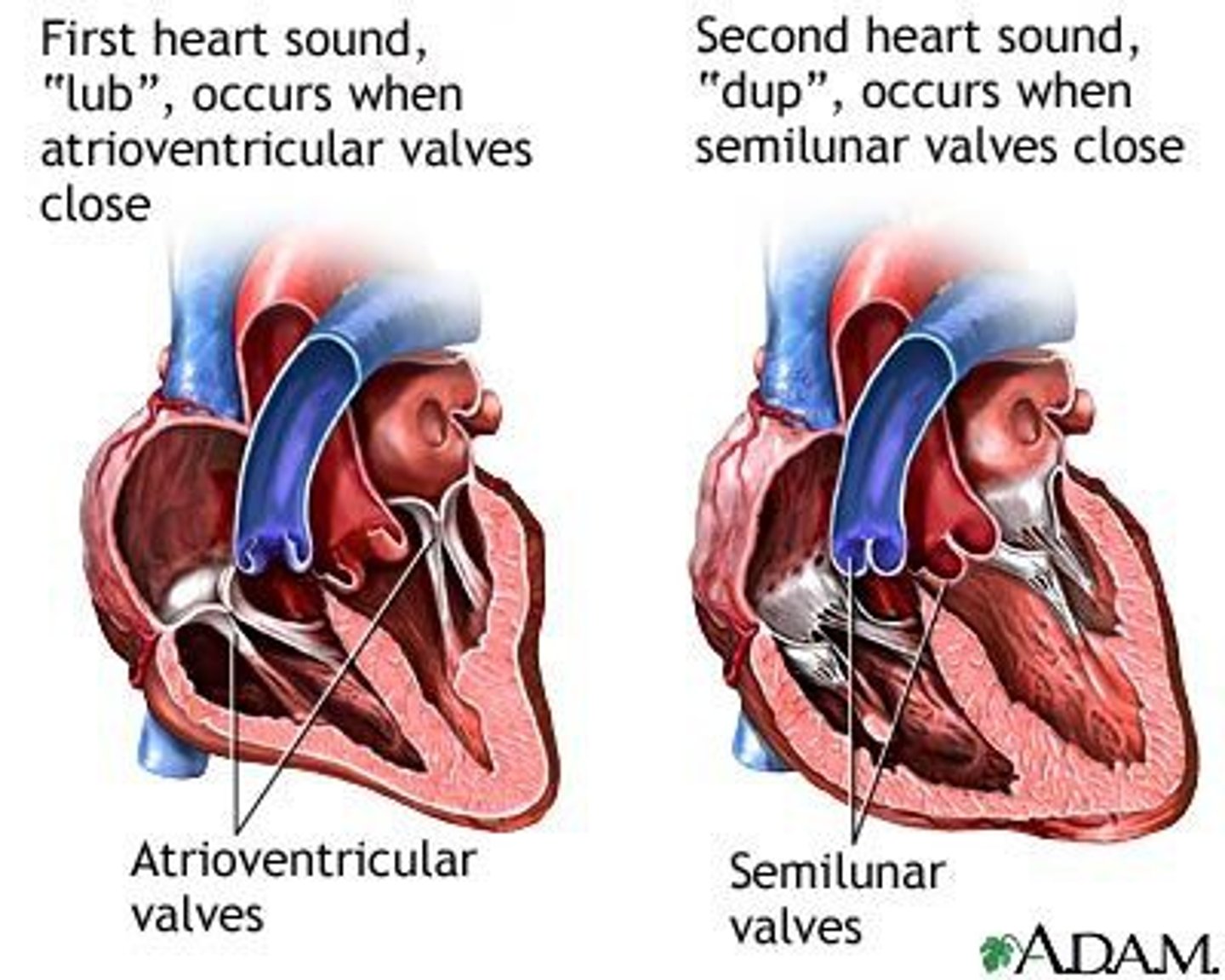
when all 4 valves are closed
The onset of diastole occurs when?
coronary arteries
blood supply to the heart muscle
*found in epicardium
1. R coronary artery (RCA)
2. L (main) coronary artery (LCA)
- L anterior descending artery (LAD)
- L circumflex artery (LCx)
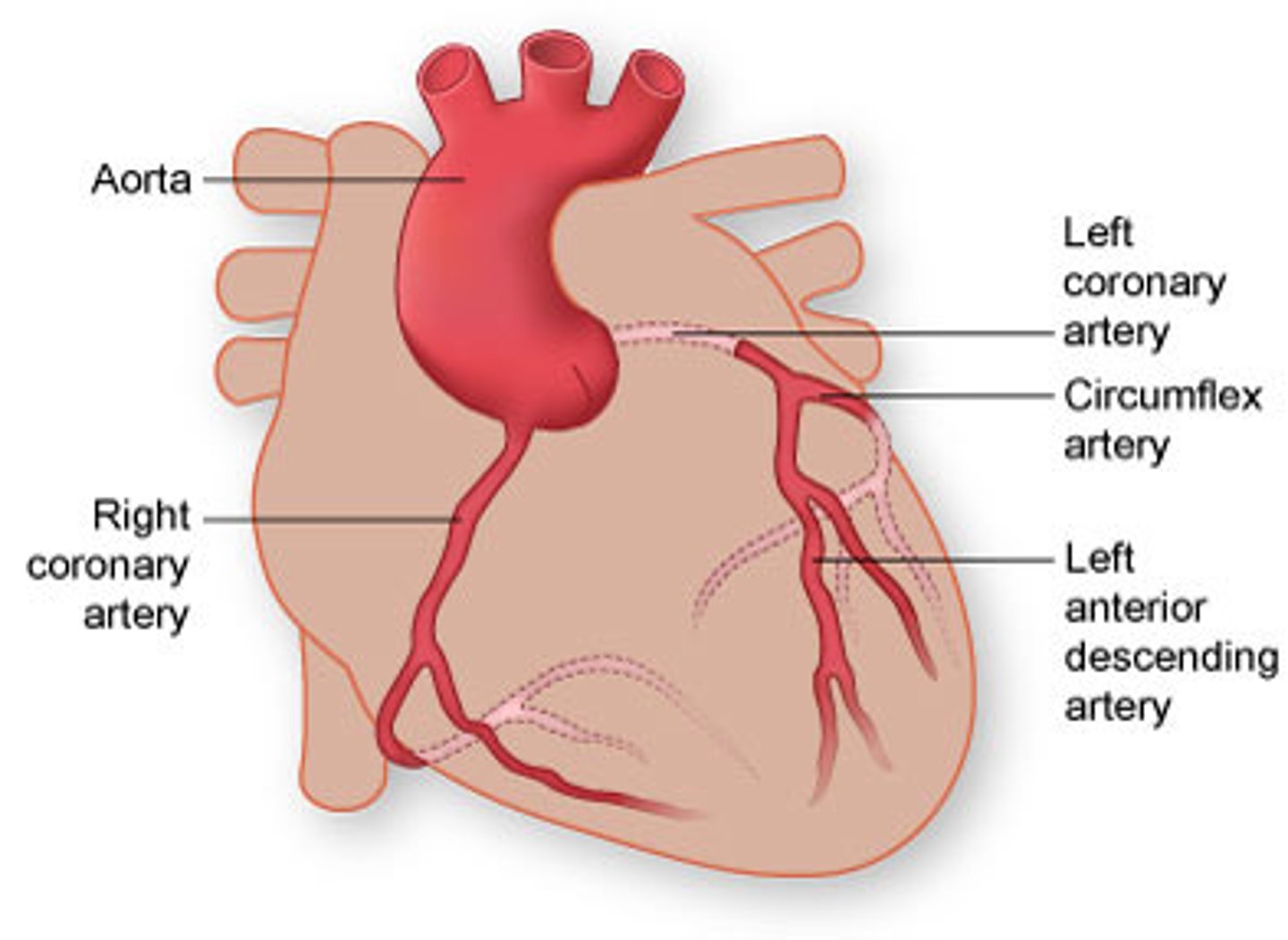
right coronary artery (RCA)
dominant supplier of heart muscle
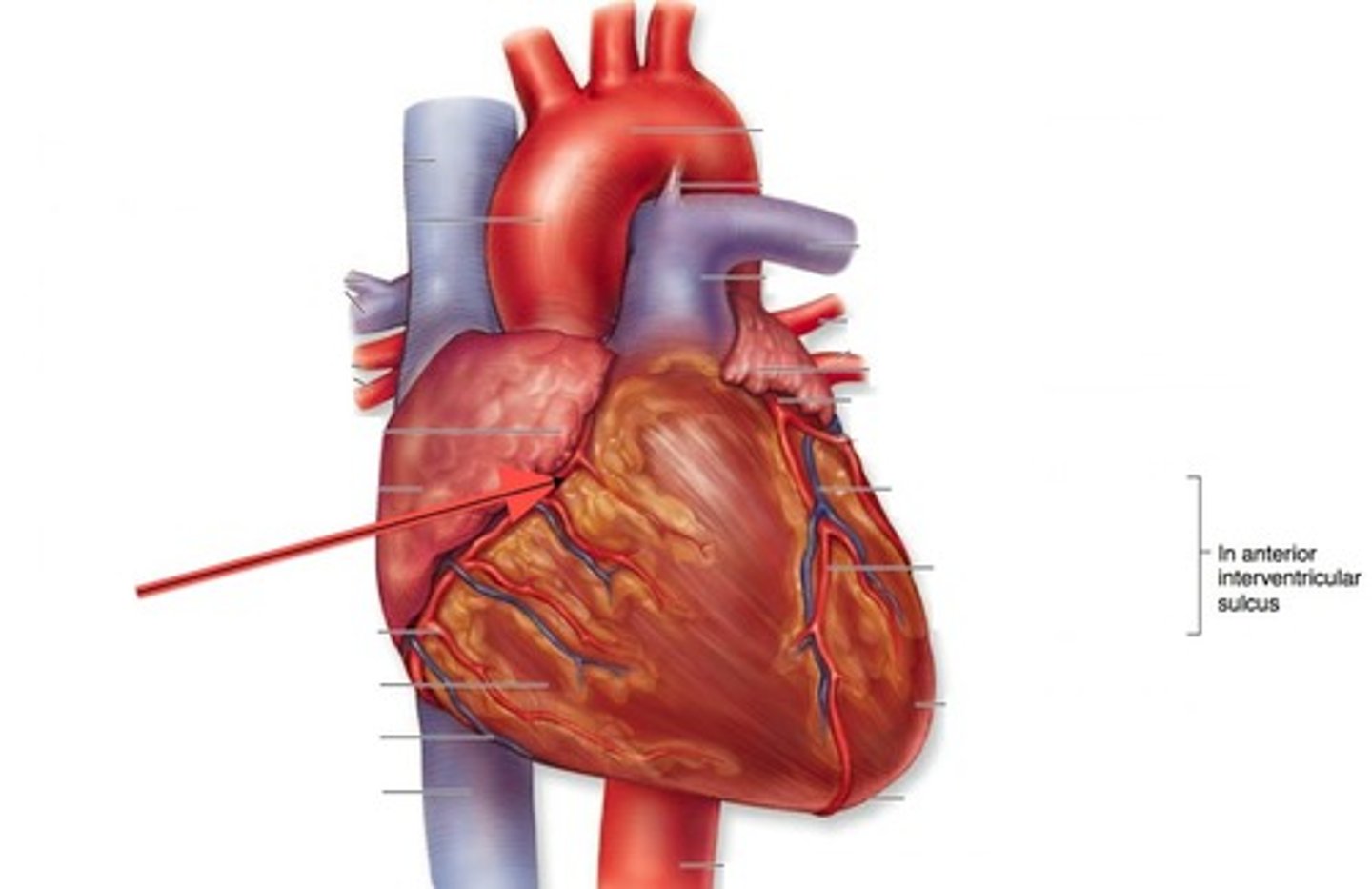
left (main) coronary artery (LCA)
devastating when occluded
"widow maker"
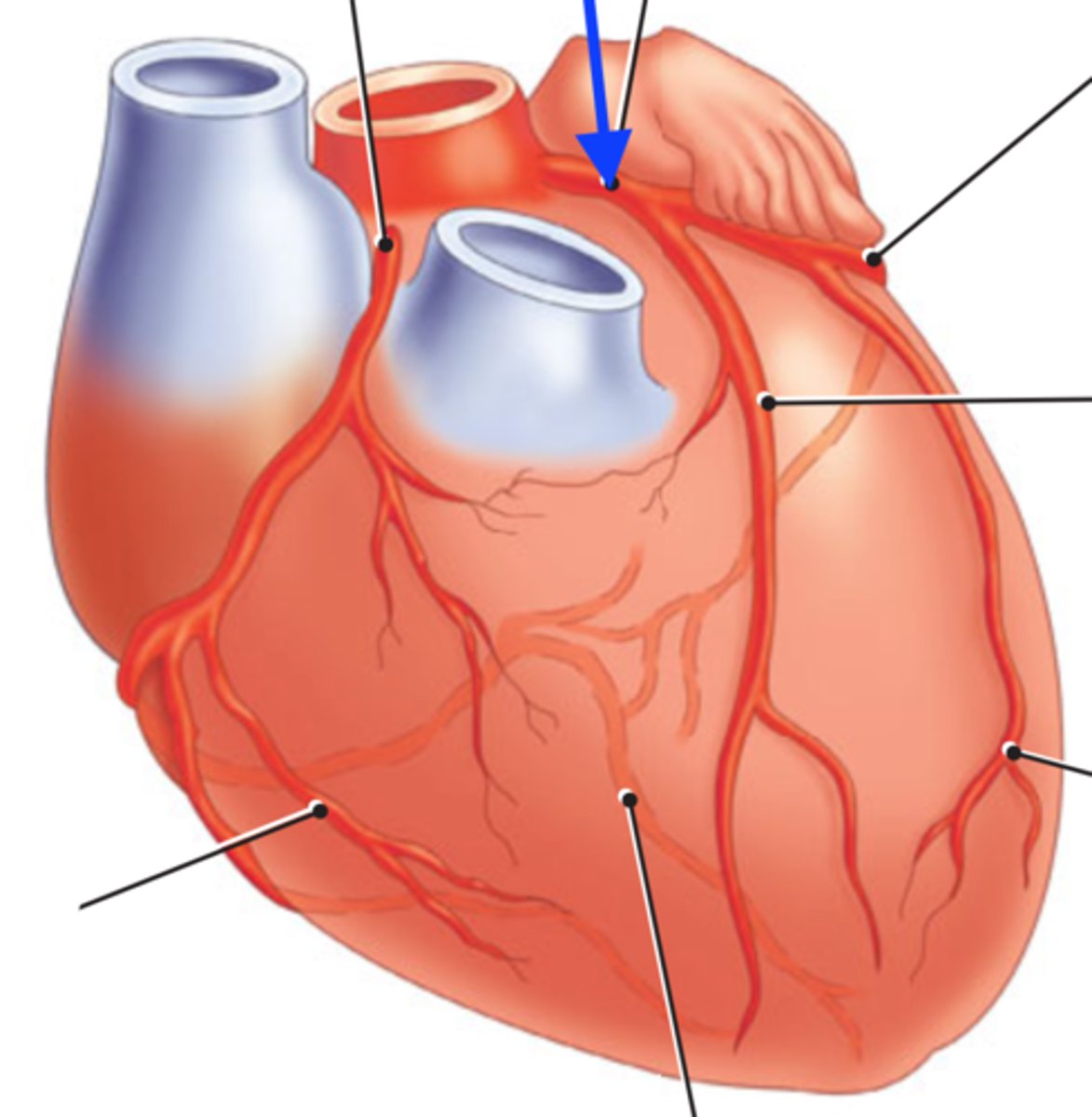
left anterior descending artery (LAD)
BRANCH OF LCA
lays over interventricular septum
*commonly bypassed
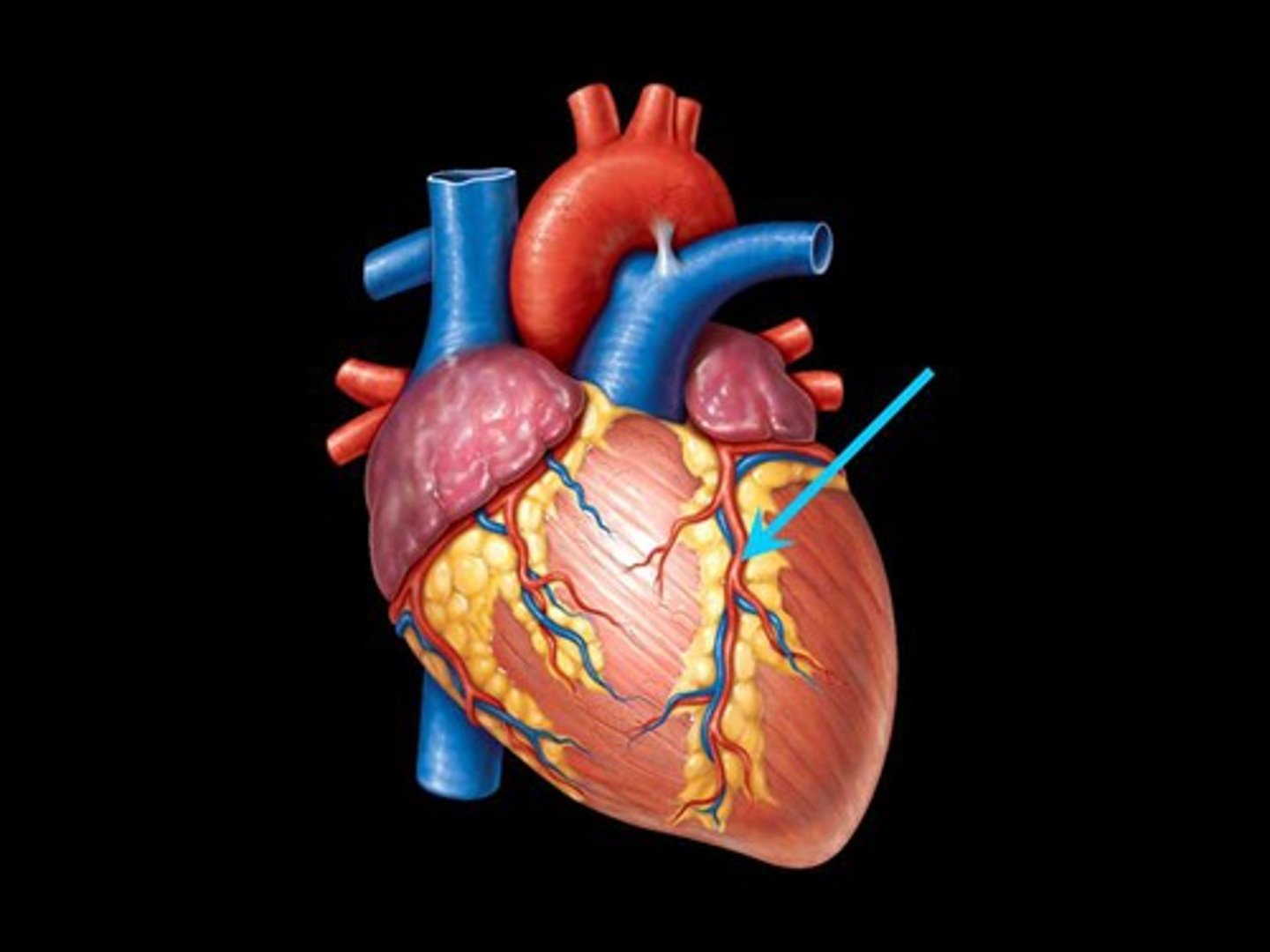
left circumflex artery (LCx)
BRANCH OF LCA
supplies left ventricular wall
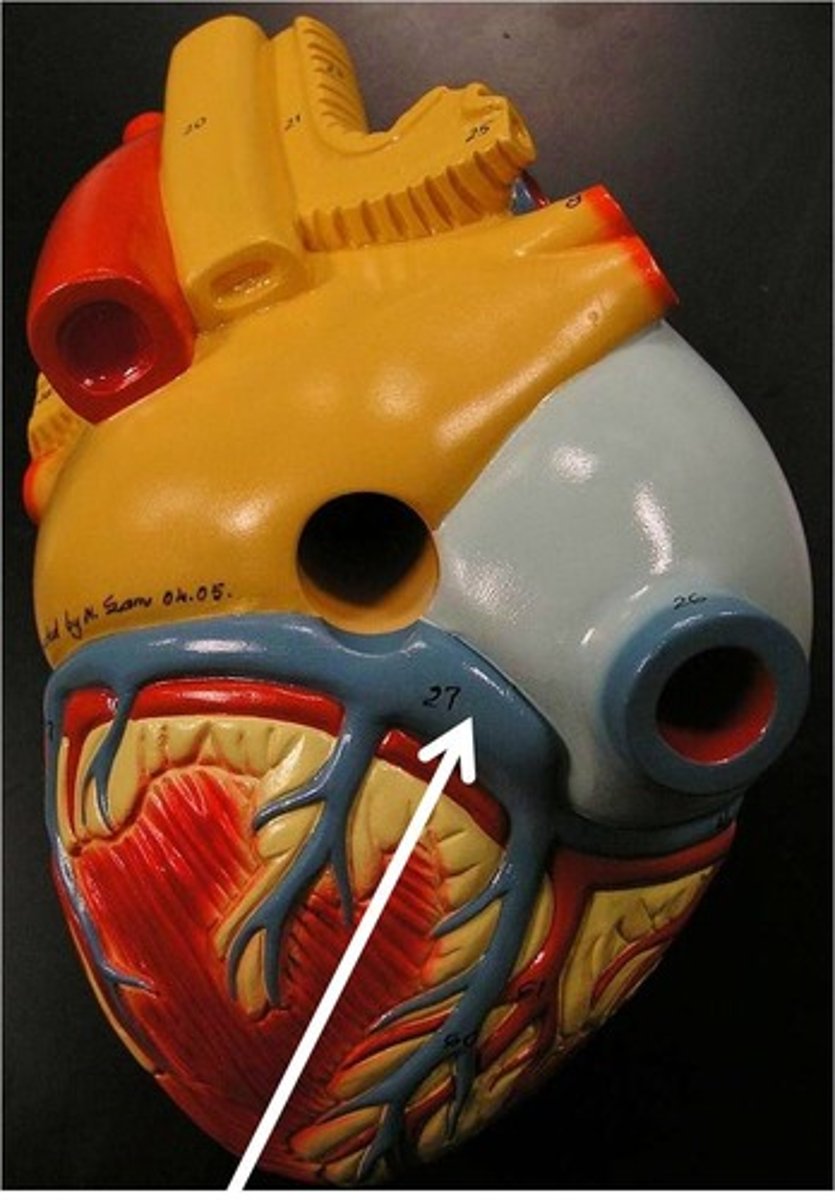
right
86% of patients have ___________ dominant coronary system.
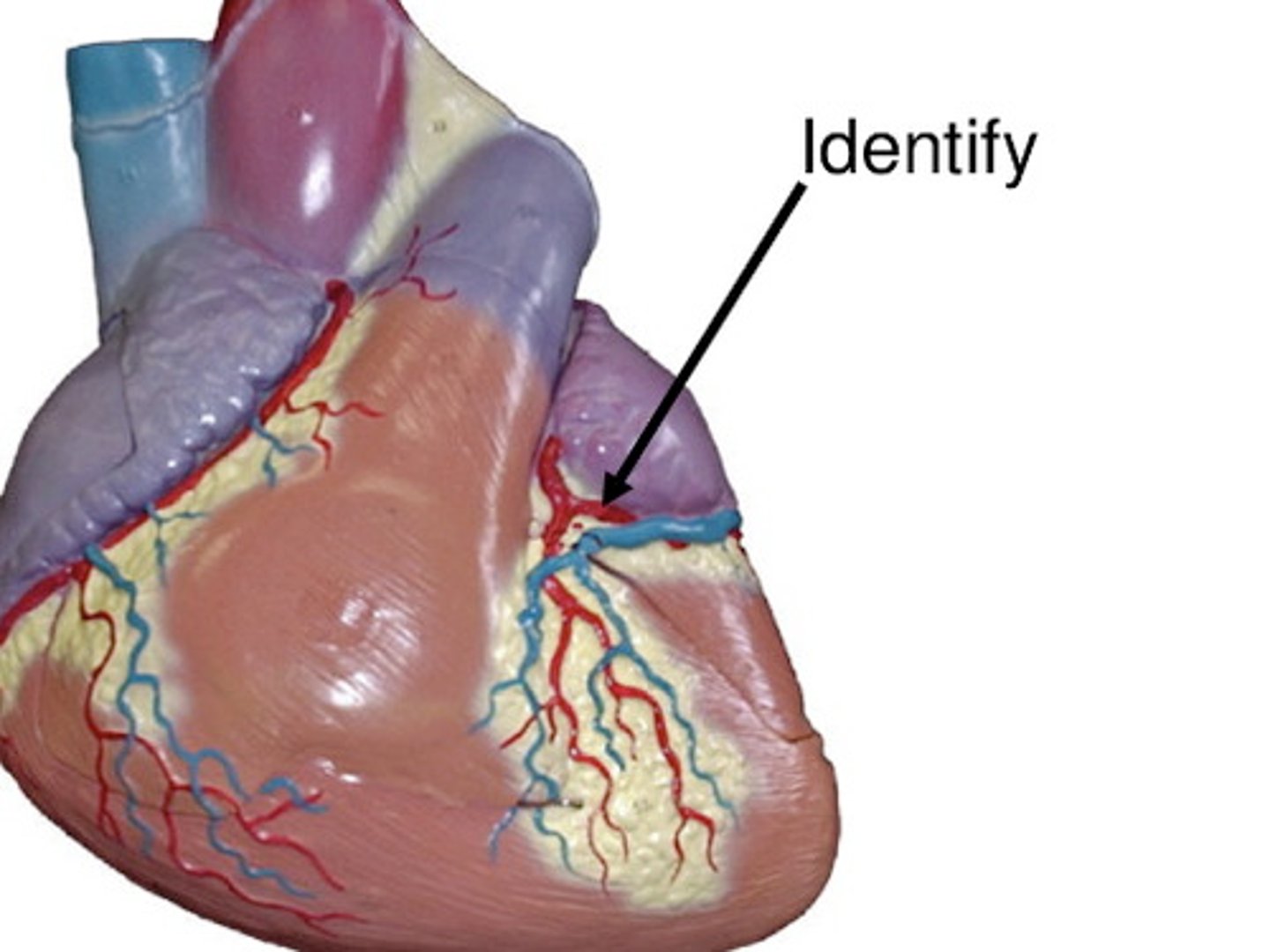
coronary sinus
receives blood from most coronary veins and delivers to R atrium
tunica externa
outer layer of a blood vessel which connects it to surrounding tissues
*collagenous, fibrous tissue with own nerves and blood vessels
**STRUCTURAL SUPPORT
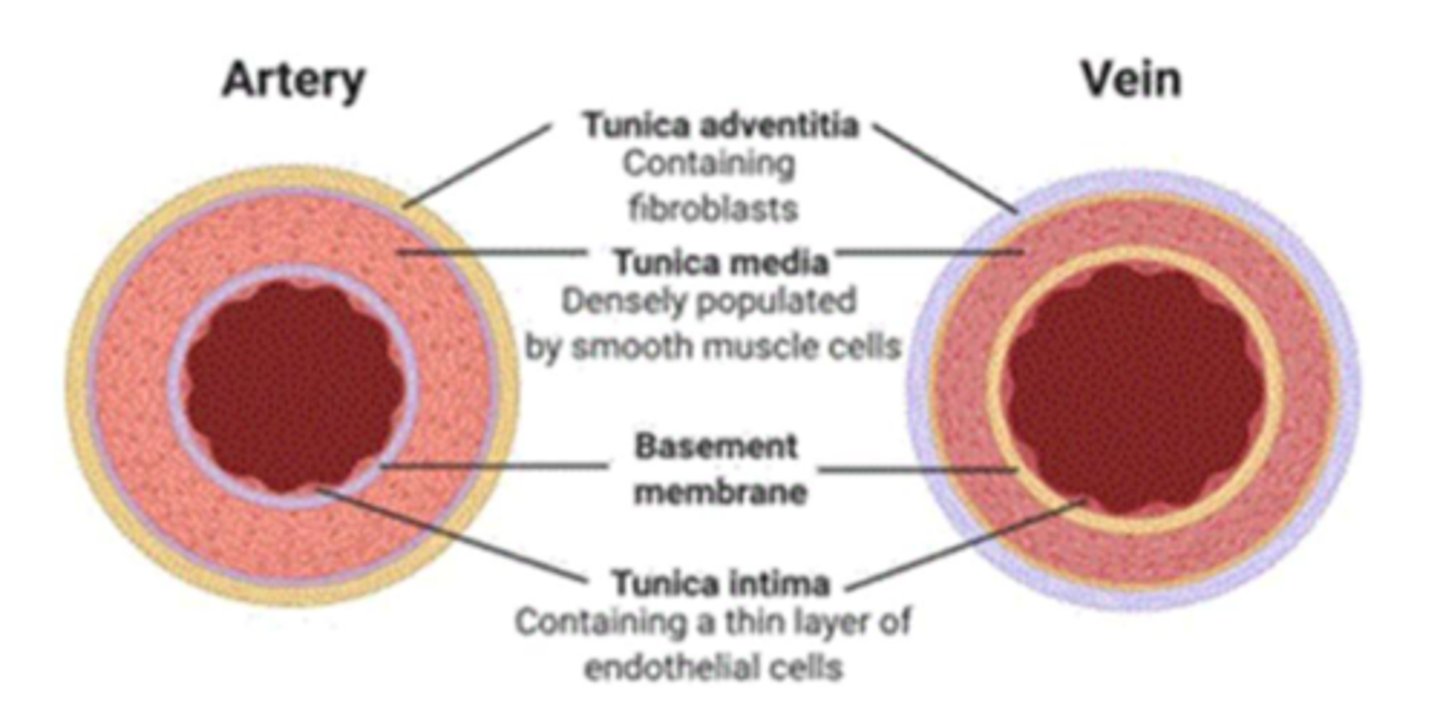
tunica media
middle and thickest layer of tissue of a blood vessel wall
*smooth muscle (contractile)
**elastic tissue
vasoconstriction/dilation by mechanical, chemical, or neurological stimulus
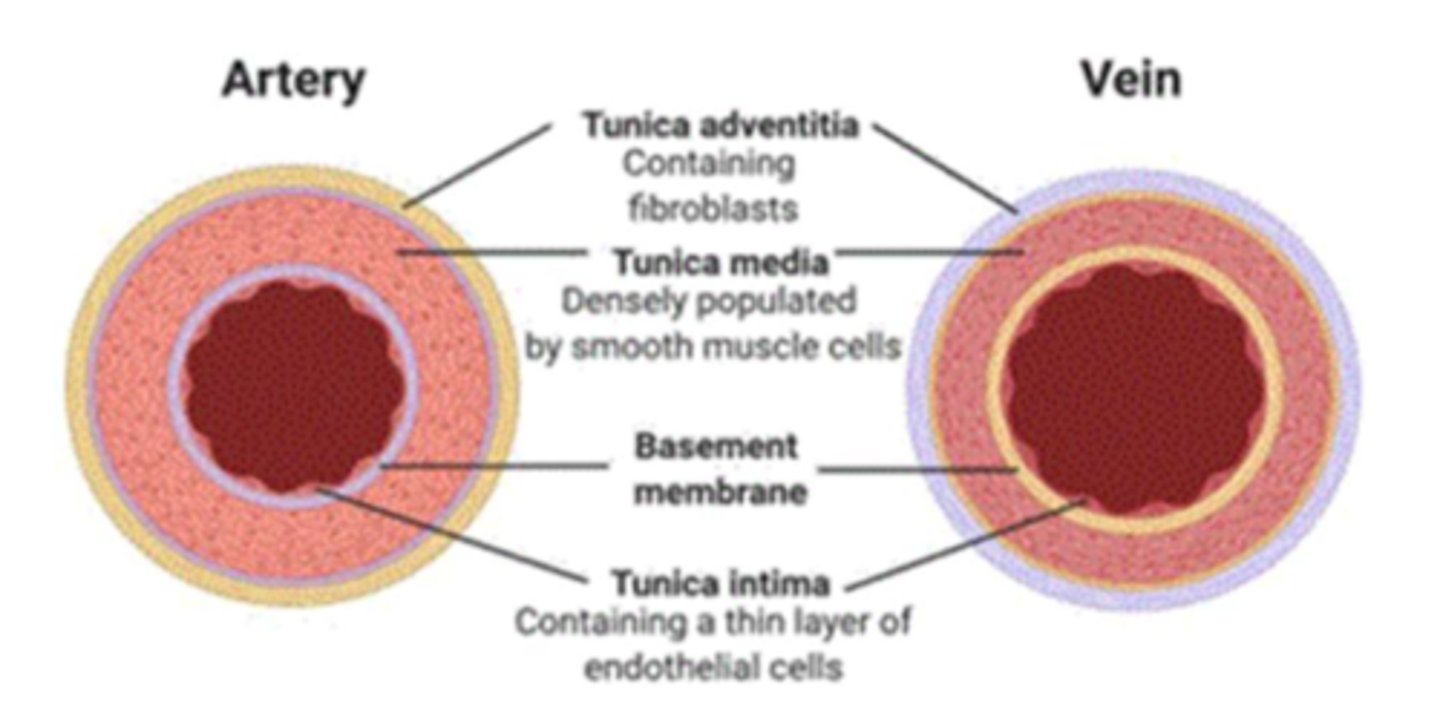
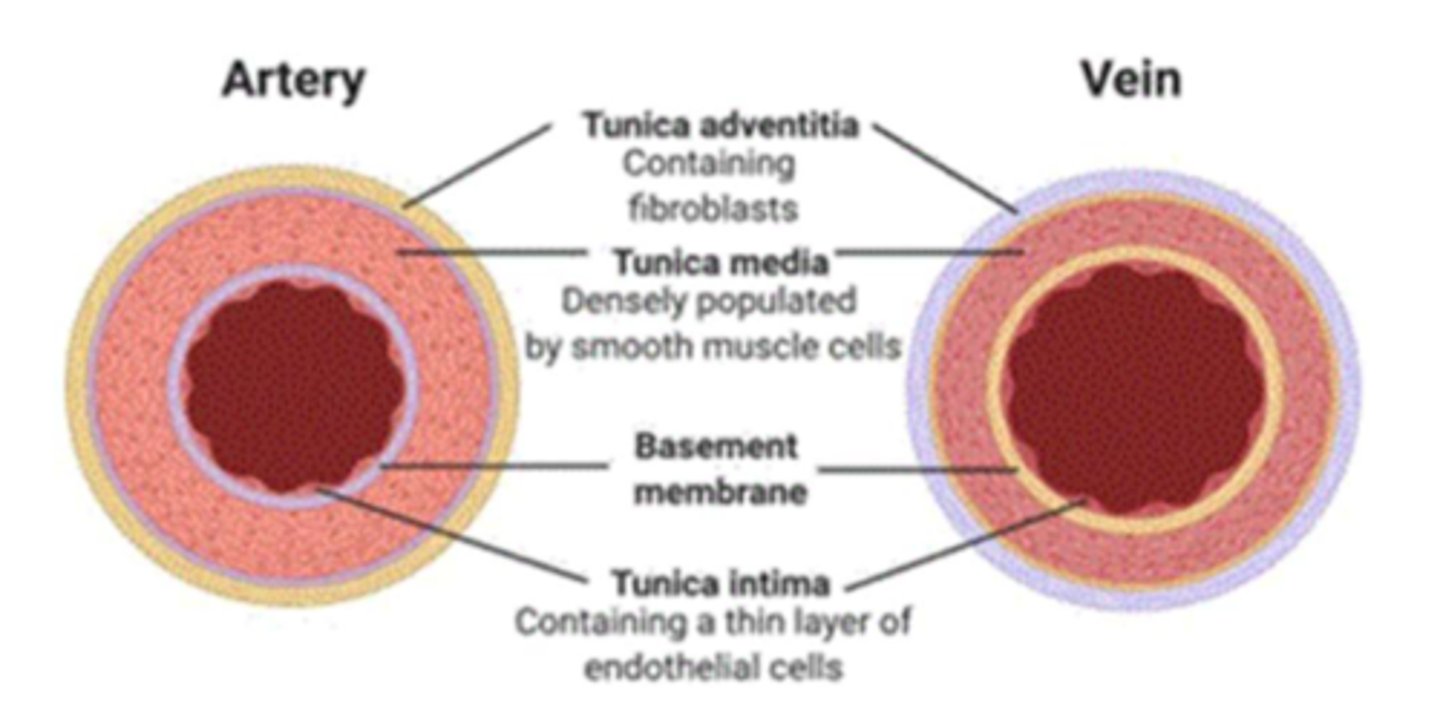
tunica intima
the innermost layer of a blood vessel
*endothelial cells
**smooth mm.
***LDL permeable
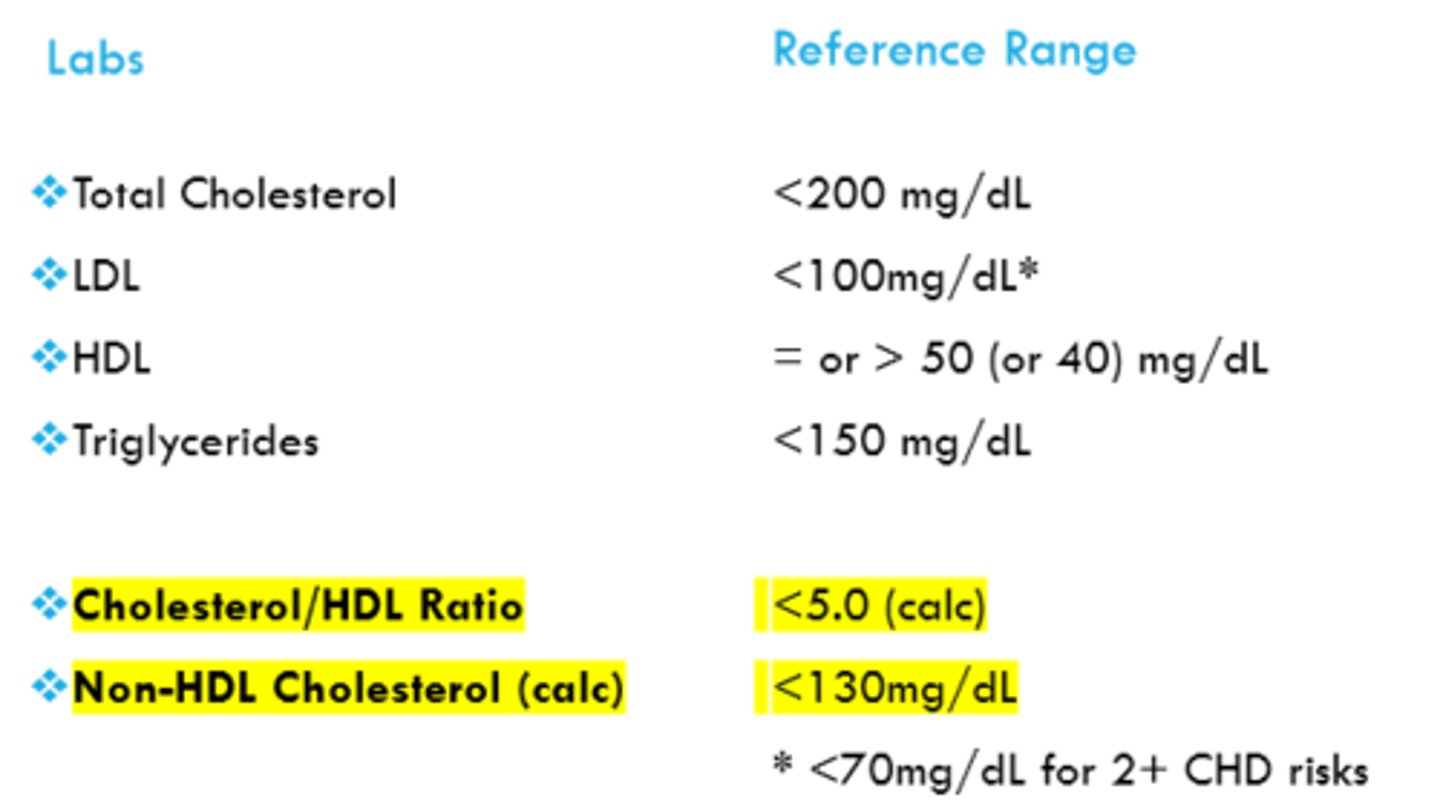
cholesterol lab guidelines
REFER TO IMAGE