spinal nerves and muscle stretch reflexes
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
what structures comprise the CNS?
brain
spinal cord
what structures comprise the PNS?
nerves that extend from the CNS
what are the three parts of a neuron?
dendrite
cell body
axon
what does a dendrite do?
receives signal/input
what is the function of the cell body?
houses nucleus
propagates info to axon
what is the function of an axon?
carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
what are the 3 types of neurons?
multipolar neuron
pseudopolar (unipolar) neuron
bipolar neuron
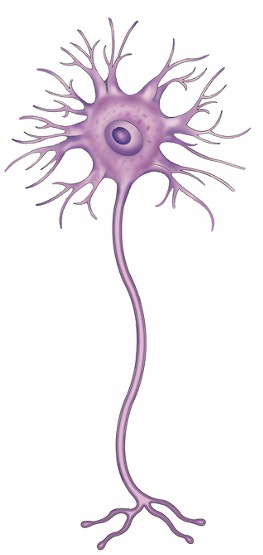
what type of neuron is this and where is it found?
multipolar neuron
found everywhere in the body
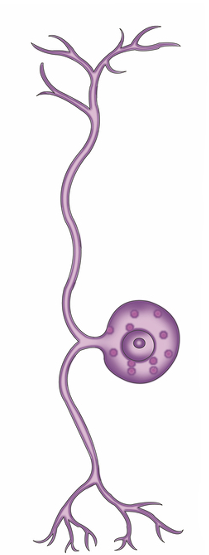
what type of neuron is this and what does it do?
what is uniquely found in these neurons?
where are the cell bodies of this neuron located?
pseudopolar/unipolar neuron
caries sensory information only
DRG: dorsal root ganglia
cell bodies located in DRG
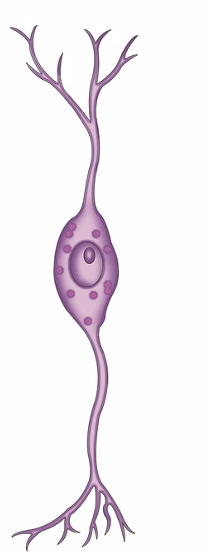
what type of neuron is this and what does information does it transmit?
bipolar neuron
special senses (vision, olfaction, and hearing)
gray matter
what is it in the CNS?
in the PNS?
collection of neuronal cell bodies
CNS: nucleus, etc.
PNS: ganglion
white matter
what is it in the CNS?
in the PNS?
bundle of axons
CNS: tract, etc.
PNS: roots, rami, and nerves
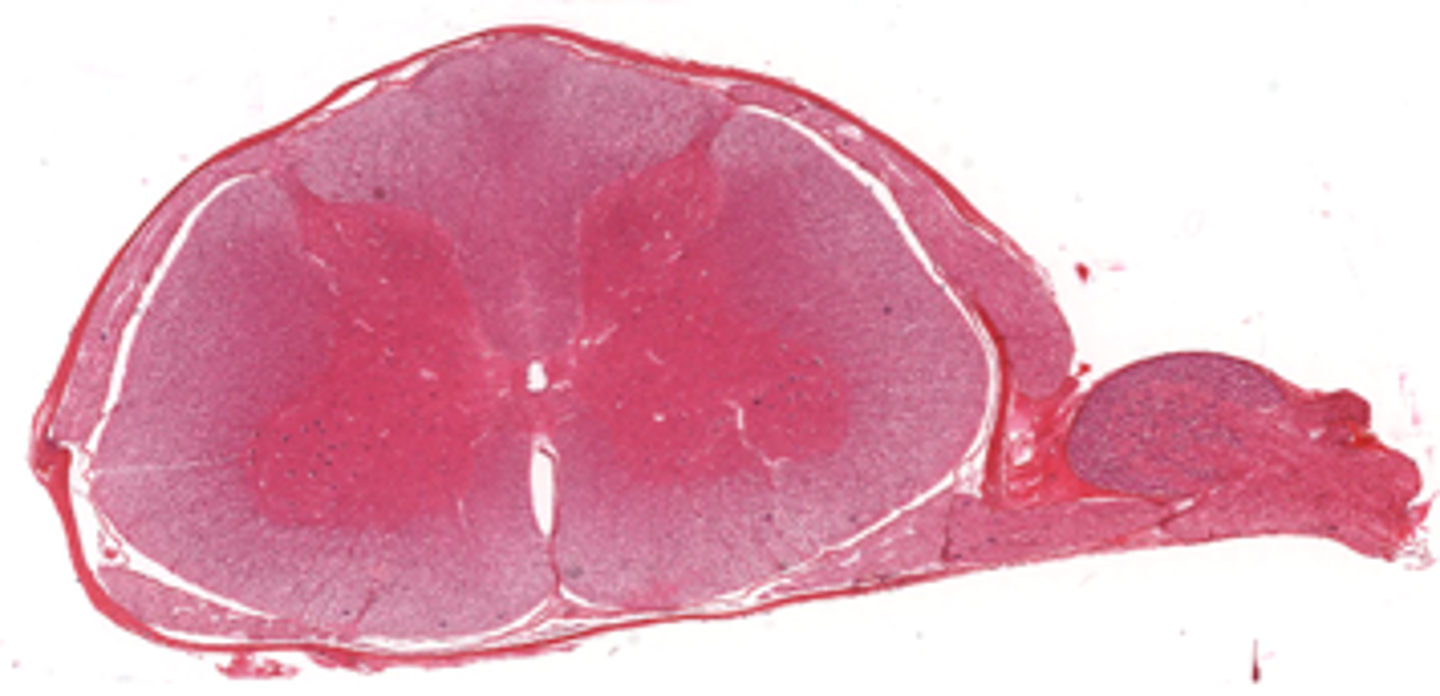
which part is white matter? which part is grey matter?
white matter: outer portion surrounding inside “bunny”
grey matter: “bunny” inside portion
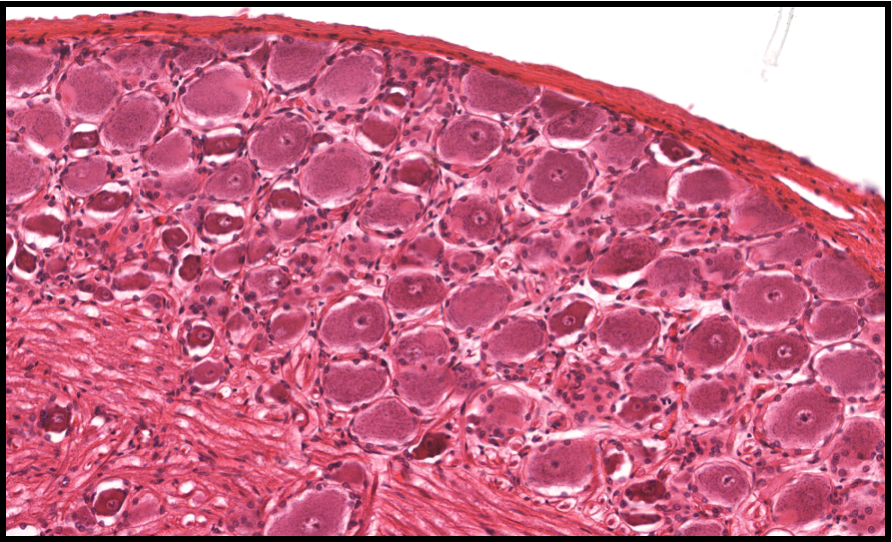
examine this DRG
what are the types of cells? describe them
ganglia cells (nucleus is in the center)
satelite cells (surround ganglia cells)
functional components of PNS axons
special
general
somatic
visceral
efferent
afferent
special PNS axons
carry info about special senses
general PNS axons
carry info about
pain
temperature
touch
vibration
somatic PNS axons
bring info from:
skin
joint capsules
periosteum of bone
muscle spindles
visceral PNS axons
bring info from
smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
epithelial glands
efferent PNS axons
carry motor info from CNS to PNS
afferent PNS axons
carry sensory info from PNS to CNS
basic functional types of axons
general somatic efferent
general visceral efferent
general somatic afferent
general visceral afferent
general somatic efferent
carry info towards skeletal muscle
general visceral efferent
carry info towards smooth, cardiac, and epithelial glands
general somatic afferent
carry sensory info from the skin
general visceral afferent
carry sensory info from the organs
any given _____ includes all four functional components of axons
spinal nerve
how many spinal nerves are there?
categorize them
31:
8 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral
1 coccygeal
what is the trend of bilateralism in spinal nerves?
In the cervical and upper thoracic regions, the spinal cord segments are almost aligned with their corresponding vertebrae. Nerves from lumbar, sacral, and coccygeal segments must descend within the vertebral canal before exiting.
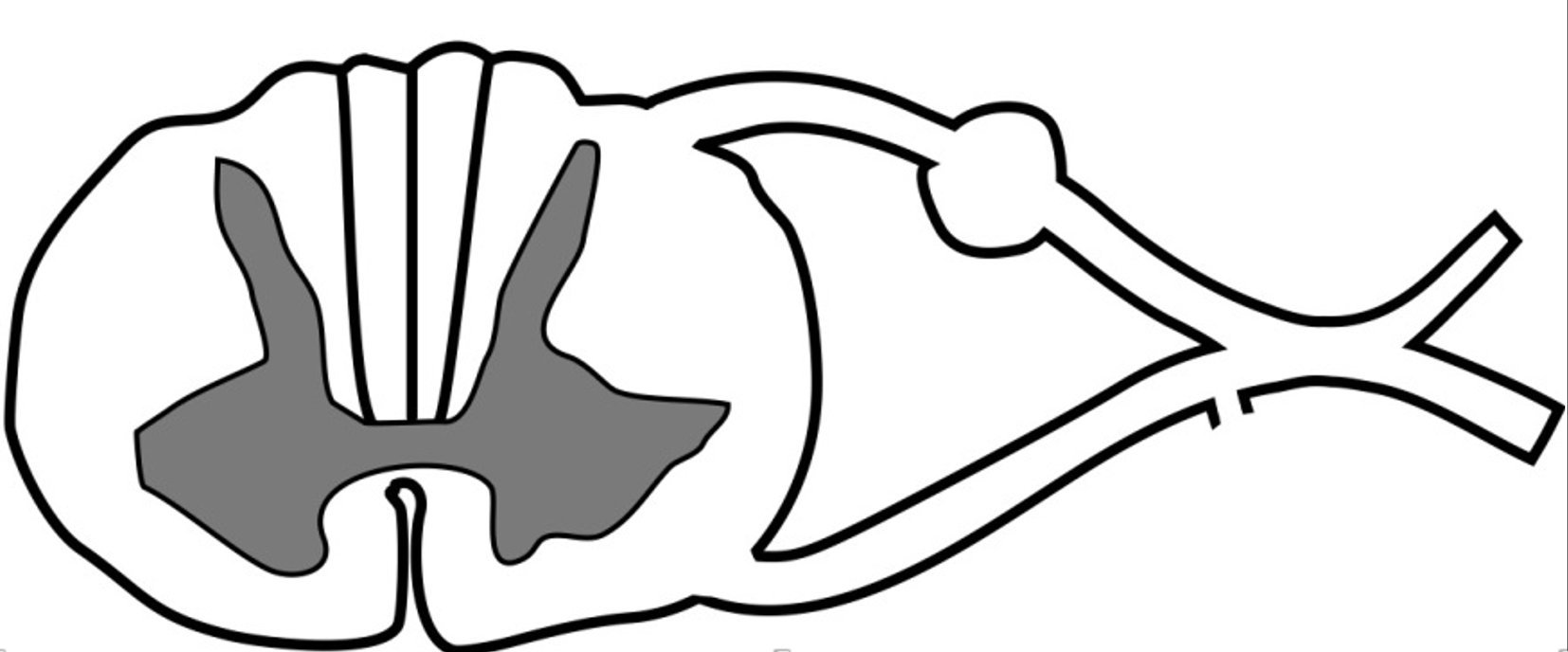
label the spinal nerve
where is the GSA located?
where is the GSE located?
posterior/dorsal horns
anterior/ventral horns (GSE location)
posterior/dorsal root (GSA location)
anterior/ventral root
posterior/dorsal ramus
anterior/ventral ramus
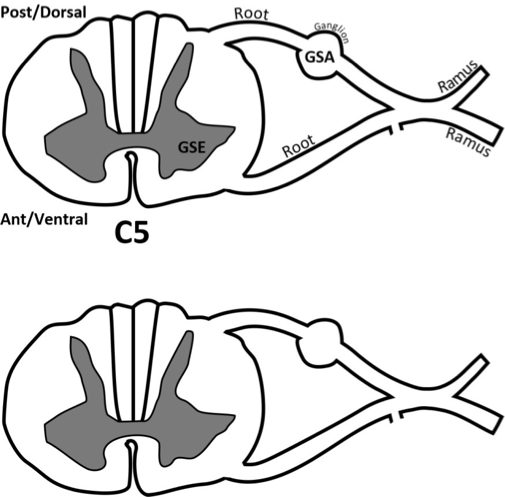
which side of the spinal nerve is afferent/sensory?
which part is efferent/motor?
DAVE
dorsal (posterior) is afferent (sensory)
ventral (anterior) is efferent (motor)
why is the ventral ramus larger in size?
ventral ramus Supplies anterior/lateral trunk and all limb muscles/skin
dorsal ramus only innervates intrinsic back muscles
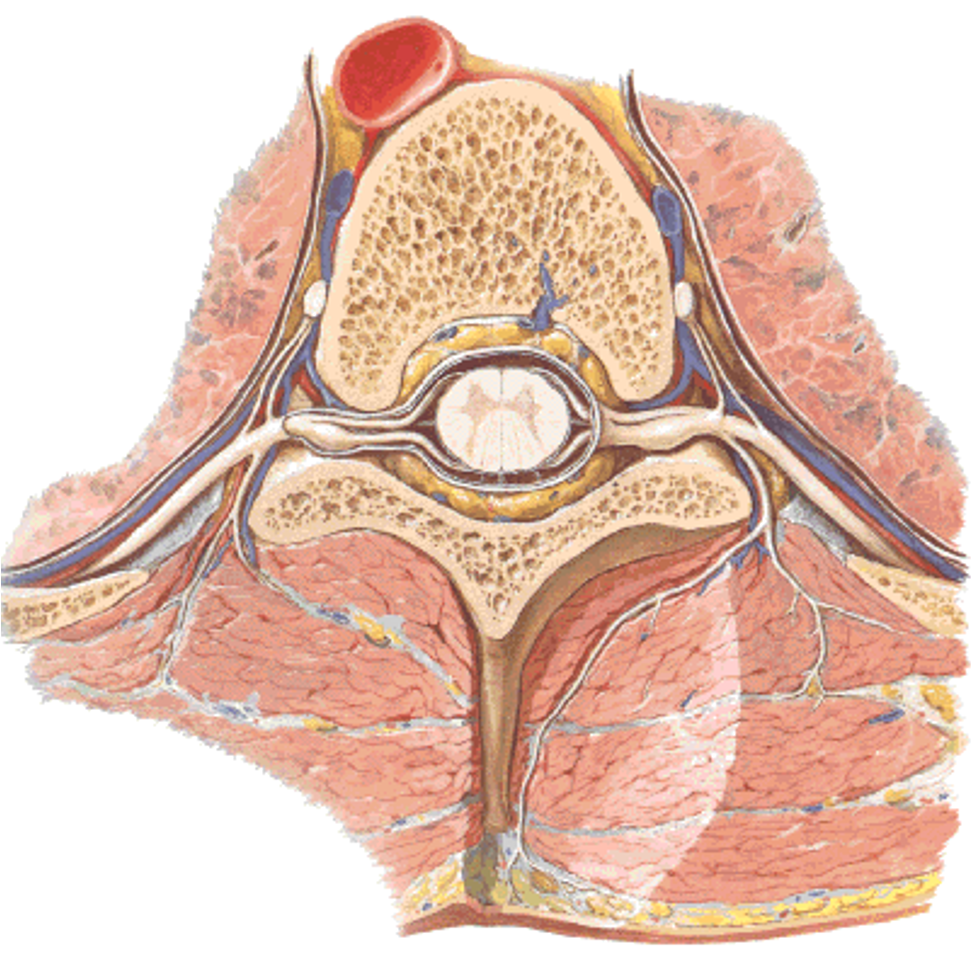
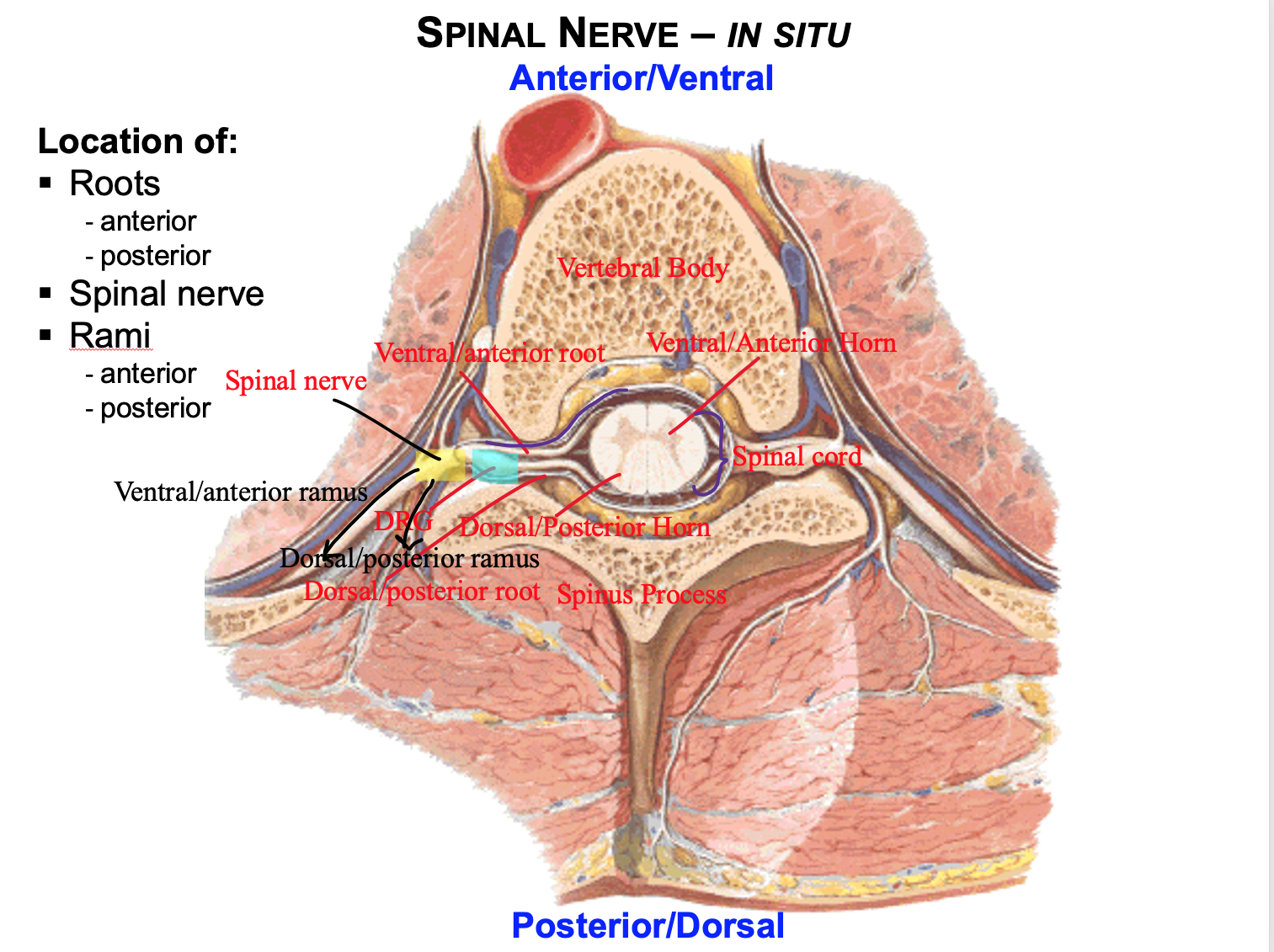
label this spinal nerve in situ
vertebral body
spinus process
dorsal and ventral roots
dorsal and ventral rami
GSE
GSA
spinal nerve
GSE
function
location of cell bodies
course of axons
innervates skeletal muscle
anterior horn
course of axons
exits anterior horn
anterior root
spinal nerve
anterior/ventral ramus: innervates anywhere else
posterior/dorsal ramus: innervates back
GSA
function
location of cell bodies
course of axons
transmits sensory info (pain, touch, vibration, teperature)
located in DRG in posterior root
course of axons
dorsal or ventral ramus
spinal nerve
posterior root
posterior horn
dermatome
specific spinal nerve responsible for skim
T1, T2, T3
built in overlap
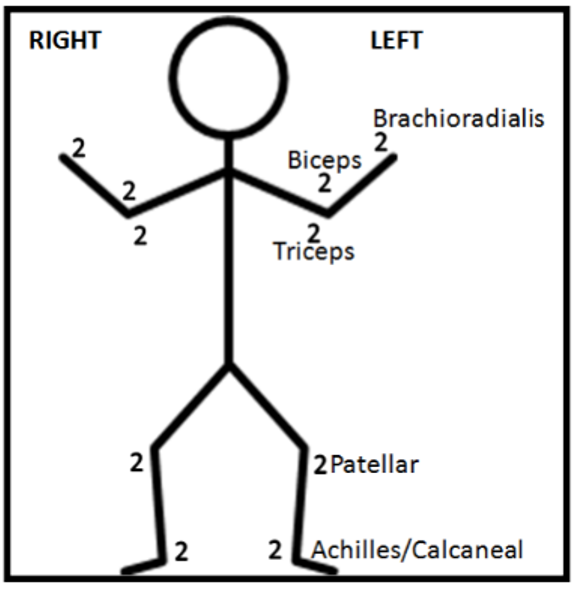
explain the Reflex Grading Scale
0/4: no response, absent reflex
1/4: hyporeflexia
¾ and 4/4: hypereflexia (ignore)
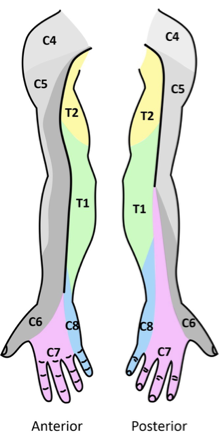
concepts of innervation: skin
see map
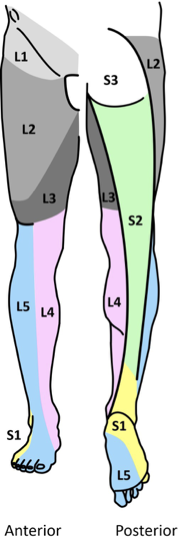
concepts of innervation: motor
Biceps – C5 & C6
Brachioradialis – C5 & C6
Triceps - C7 and C8
Patellar – L2, L3 & L4
Achilles – S1 & S2