Chromatography P2 : Applications
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the 2 planar chromo types
Paper and TLC
What are the specific stationary/mobile phases for paper and what they are used for.
Stationary Phase: A layer of water bound to the cellulose fibers of the paper.
Mobile Phase: The solvent in which the paper is dipped.
Application: Used to assess the purity of a sample
What are the specific stationary/mobile phases for TLC and what they are used for.
tHIN LAYER - DEF
Stationary Phase: A sheet of glass, metal, or plastic coated with a thin layer of adsorbent (usually silica or alumina).
Procedure: Samples are "spotted" at the base and dried. The sheet is placed in a tank with a shallow layer of solvent (mobile phase) which moves up.
Detection: Colorless analytes are visualized using UV light or specific dyes
What is general process stages for column?
: 1. Equilibration, 2. Sample Application, 3. Elution, 4. Collection, 5. Regeneration .
Simple Column Chromatography Types
Gel filtration (size), Ion exchange (charge) Affinity (shape)
Gel Filtration - principle/S.P/MECHANISN/APPLICAION
Principle: Separates molecules based on size (mass).
Stationary Phase: Porous beads/particles.
Mechanism (Crucial for Exam):
Large Molecules: Cannot enter the pores. They occupy the "void volume" (space between beads) and are washed through first.
Small Molecules: Penetrate the pores and have a longer distance to travel, so they elute last.
Applications: Fractionation (separating by size) and Desalting (removing salts from samples)
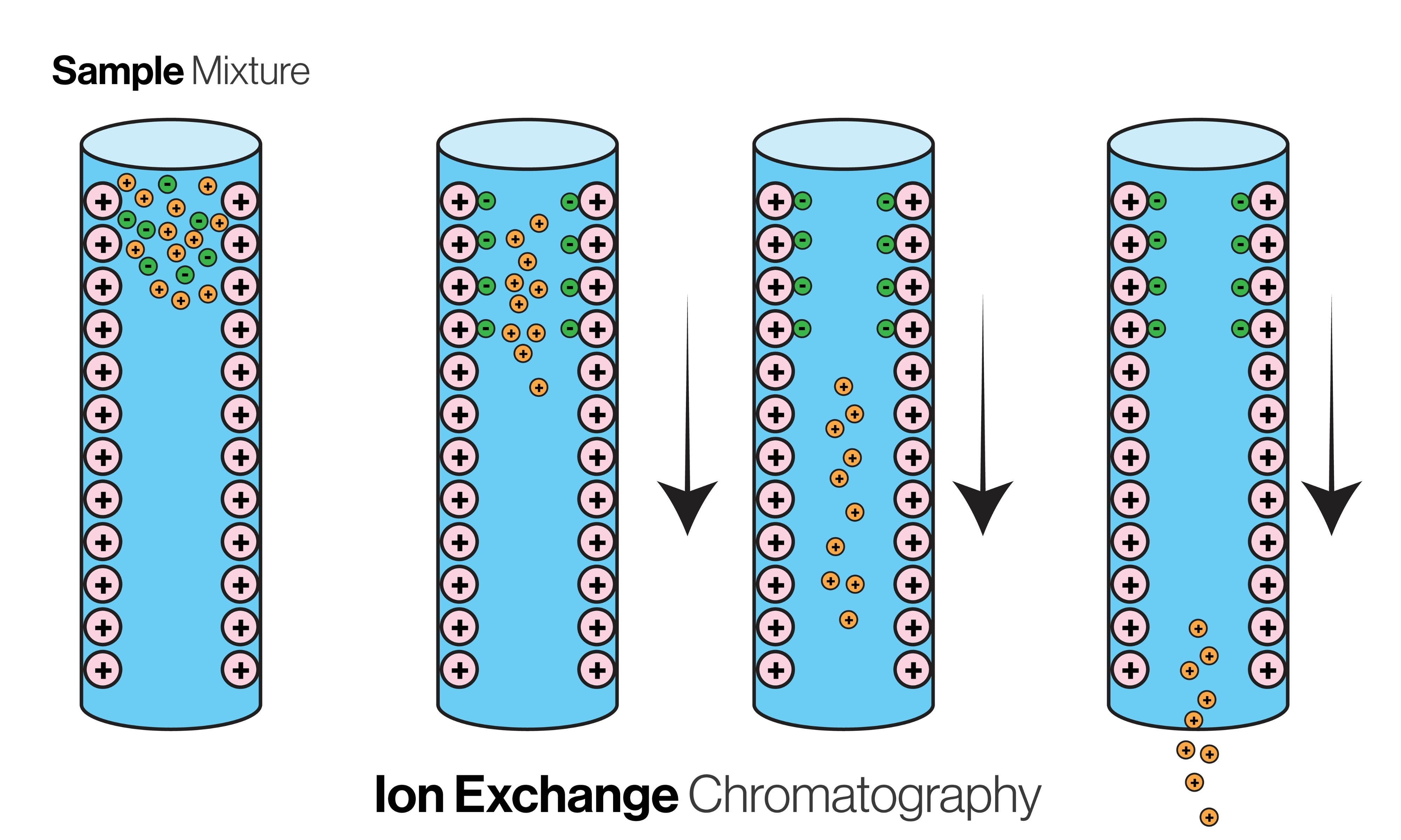
Ion exchange - - principle/MECHANISm/APPLICAION
Principle: Separates based on net charge. Relies on reversible interaction with an oppositely charged stationary phase29.
The "pI" Rule (Isoelectric Point):
pI: The pH at which a molecule has no net charge30.
pH < pI: Molecule becomes Positive (Cation) Binds to Cation Exchanger (which has negative beads)
pH > pI: Molecule becomes Negative (Anion) Binds to Anion Exchanger (which has positive beads)
Applications: Protein purification, DNA/RNA separation, Water analysis (heavy metals), Drug purification
Draw coloumn in ion exchange
Affinity - Principle/S.P/Mechanism/Application
Principle: Uses specific binding ("Lock and Key") or shape differences.
Stationary Phase: An insoluble matrix with a specific ligand attached (e.g., antibody, enzyme substrate).
Mechanism: The target analyte binds to the ligand while impurities wash away. The target is then eluted .
Applications:
Enzymes: Purified using bound substrates/inhibitors.
Antibodies/Antigens: Immobilize one to purify the other.
Hormones/Receptors: Purified from cell homogenates.
What are 2 instrumental chromo types
HPLC and Gas chromo GC
Description and Materials in hplc
Description: Uses high pressure to force mobile phase through the column for high resolution and speed40404040.
Instrument Components (Order is key): Solvent Reservoir Pump Injector Port Column Detector Recorder
Column Materials: Stainless Steel (durable, high pressure), PEEK (biocompatible), or Glass 42.
Draw HPLC

What are the S.P modes in HPLC
CHOOSE RIGHT PHASE FOR THE JOB
Normal Phase: Polar stationary phase + Non-polar mobile phase.
Reverse Phase (Most Common): Non-polar stationary phase (e.g., C18 alkyl chains) + Polar mobile phase. Separates based on hydrophobicity.
Chiral: Uses a chiral stationary phase to separate enantiomers
What are the detectors in hplc
UV/Vis: Measures absorbance (most common)47.
Electrochemical: Measures current from oxidation-reduction48.
Fluorescence: Sensitive, but limited to fluorescent compounds49.
Mass Spectrometer (MS): Separates ions by mass-to-charge ratio ($m/z$)50.
What is principle and components of GC
Principle: Partitions molecules between a liquid/polymer stationary phase and a gas mobile phase51.
Requirement: Samples must be volatile (vaporizable)52.
Instrument Components: Carrier Gas (Mobile Phase) Injector (Heated) Oven (Containing Column) Detector Waste
Draw GC
wHAT ARE THE COLOUMN TYPES IN GC
WCOT: Wall Coated Open Tubular (liquid on wall).
SCOT: Support Coated Open Tubular (liquid on support material on wall).
PLOT - Porous layer
Wat are the detectors in gc
FID (Flame Ionisation): Burns sample in hydrogen flame. Very sensitive but destroys the sample .
ECD (Electron Capture): Radioactive source. Specific for electron-capturing compounds like pesticides
Applications of GC
Applications: Environmental (Greenhouse gases, pesticides), Forensic (Arson accelerants, explosives), Clinical (Blood alcohol)