13- Nuclear Chemistry
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what's the difference between an atoms atomic weight and its mass number?
mass # = protons + neutrons
atomic weight: the weighted average of all of the atomic weights of isotopes of an element
atomic mass/mass number= an element's exact mass
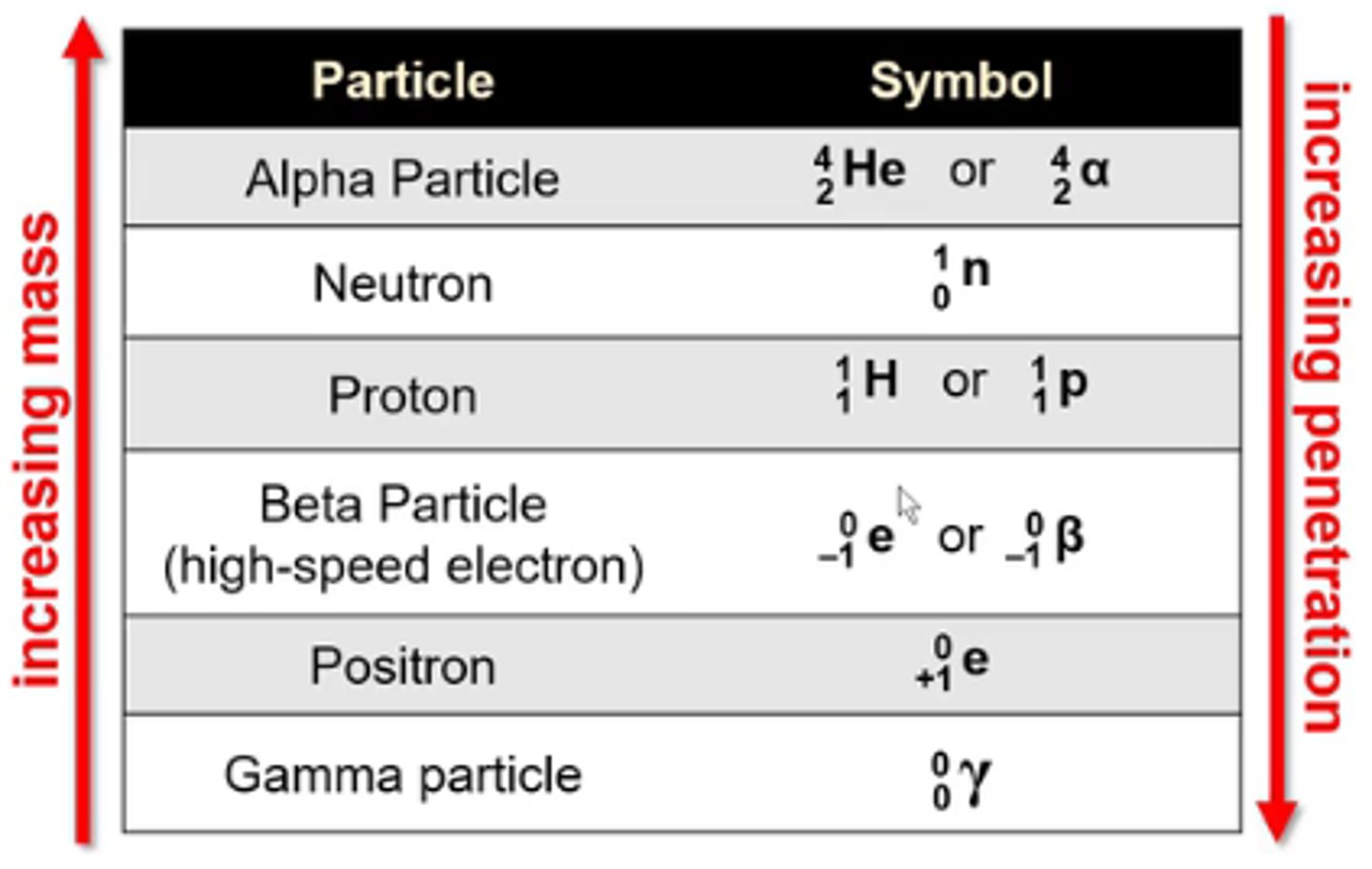
what is the symbol for the nuclear particle alpha particle?
4/2 He or 4/2α
-He is not a true alpha particle bc alpha particles don't have any e-
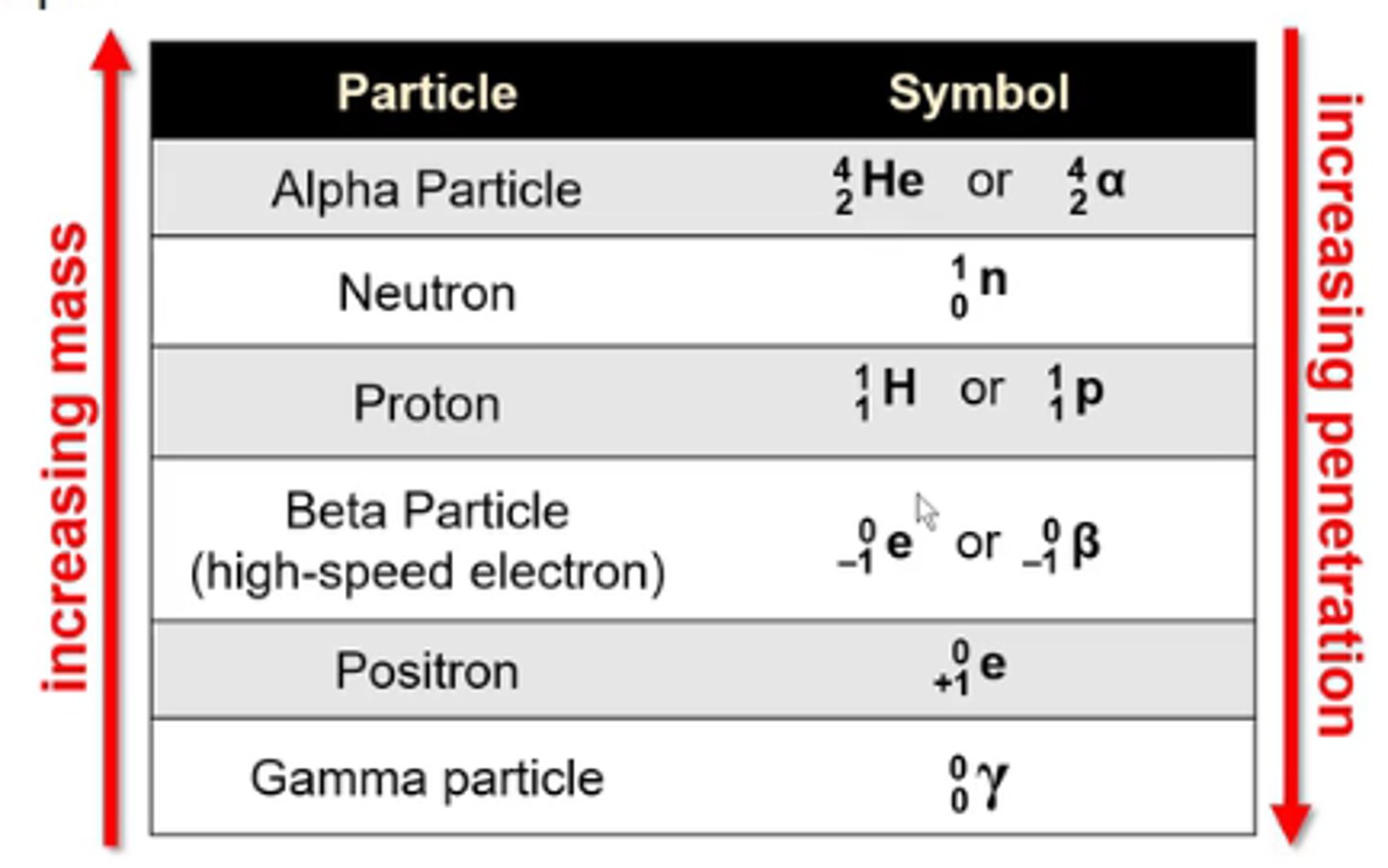
what is the symbol for the nuclear particle neutron?
1/0n
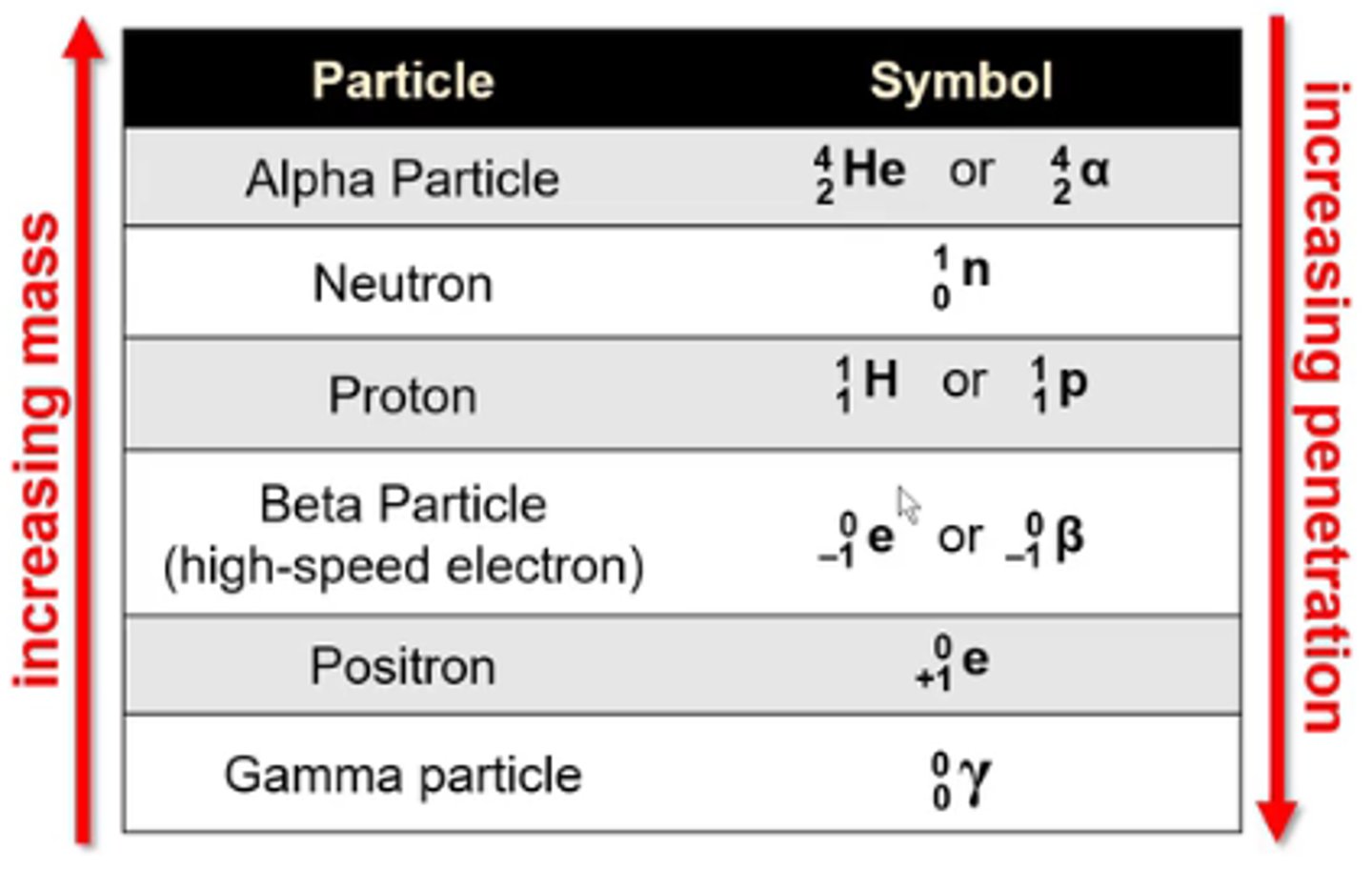
what is the symbol for the nuclear particle proton?
1/1H or 1/1p
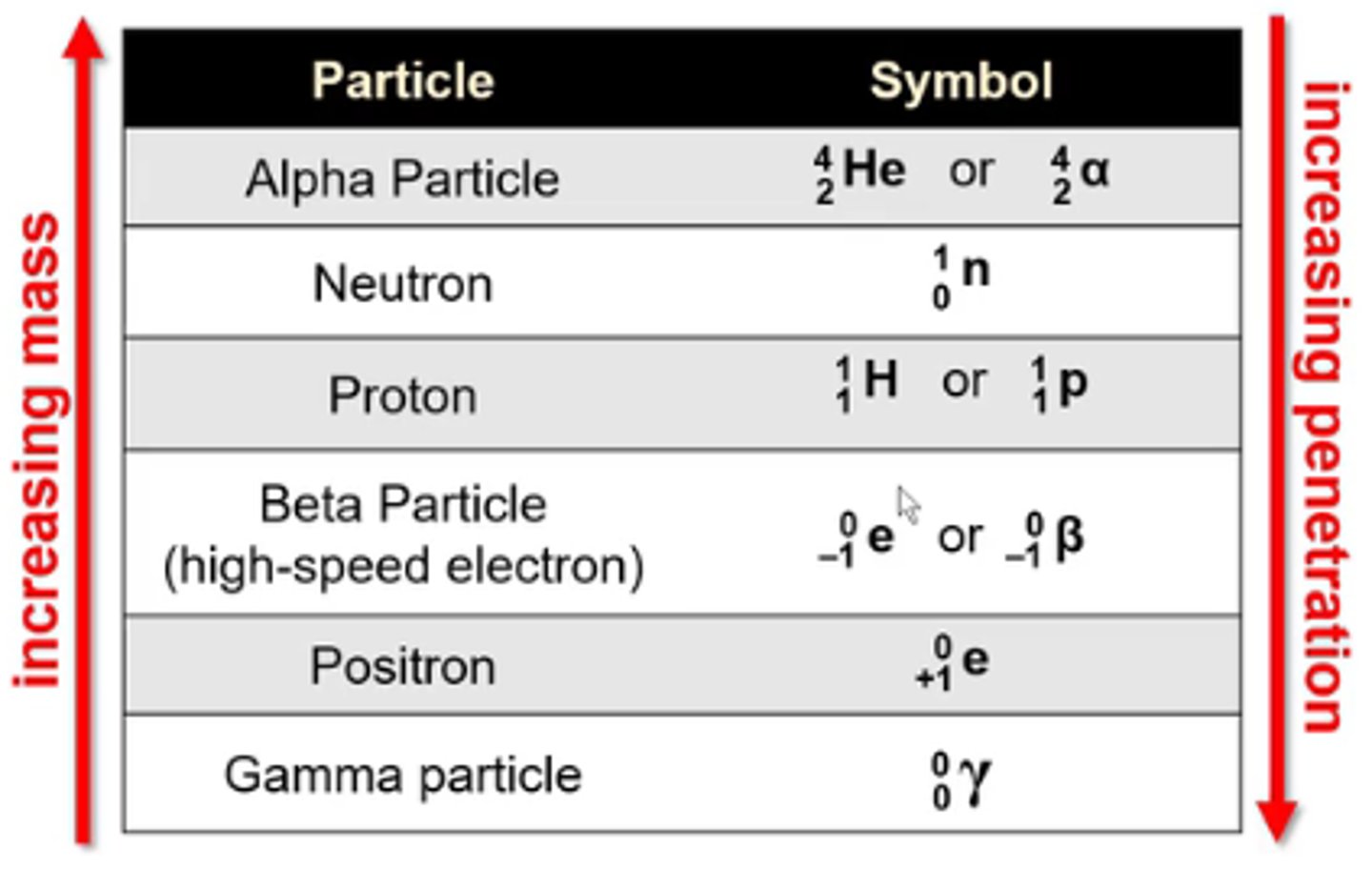
what is the symbol for the nuclear particle beta particle (high speed electron)?
0/-1 e or 0/-1β
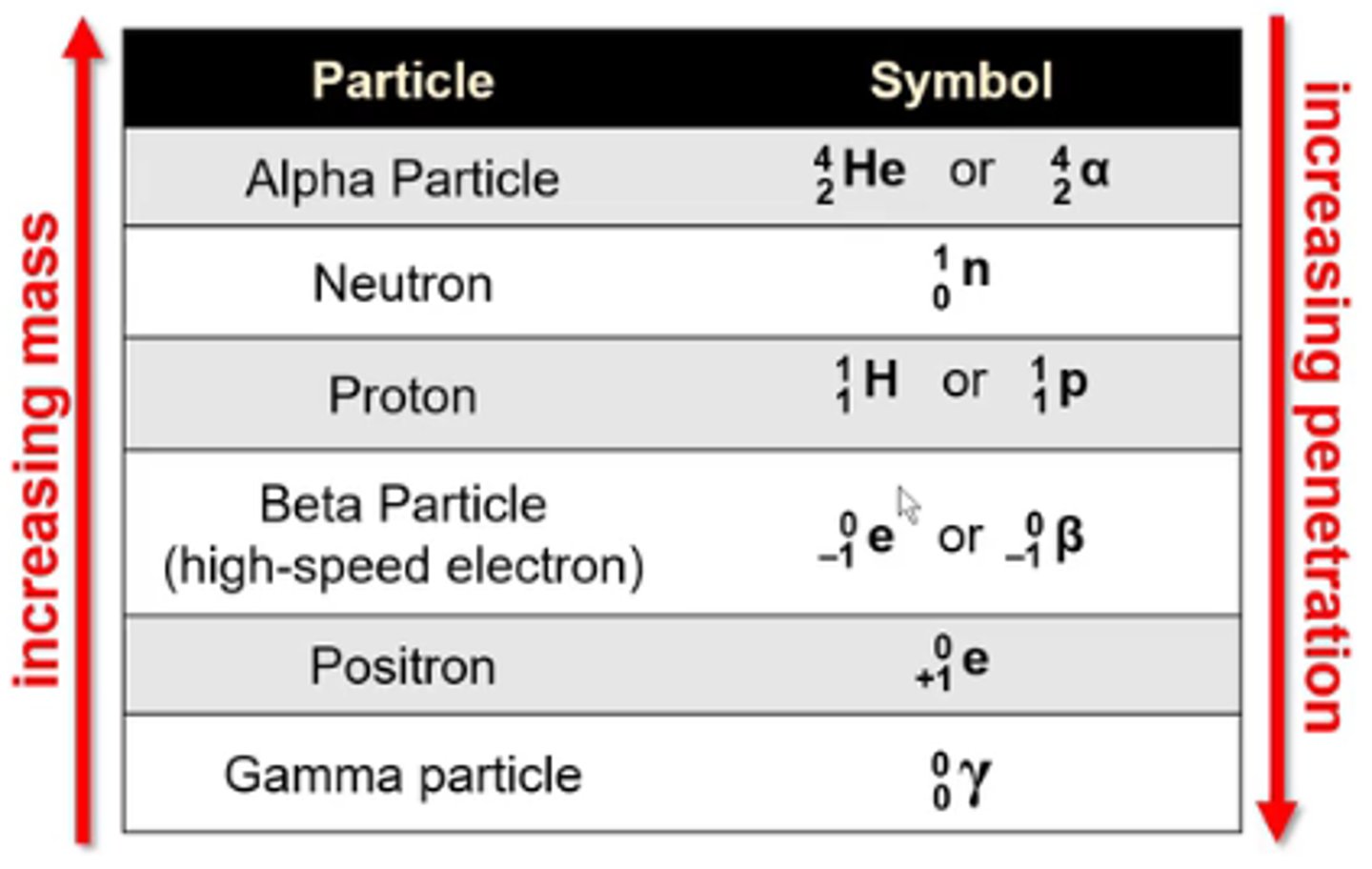
what is the symbol for the nuclear particle positron?
0/+1 e
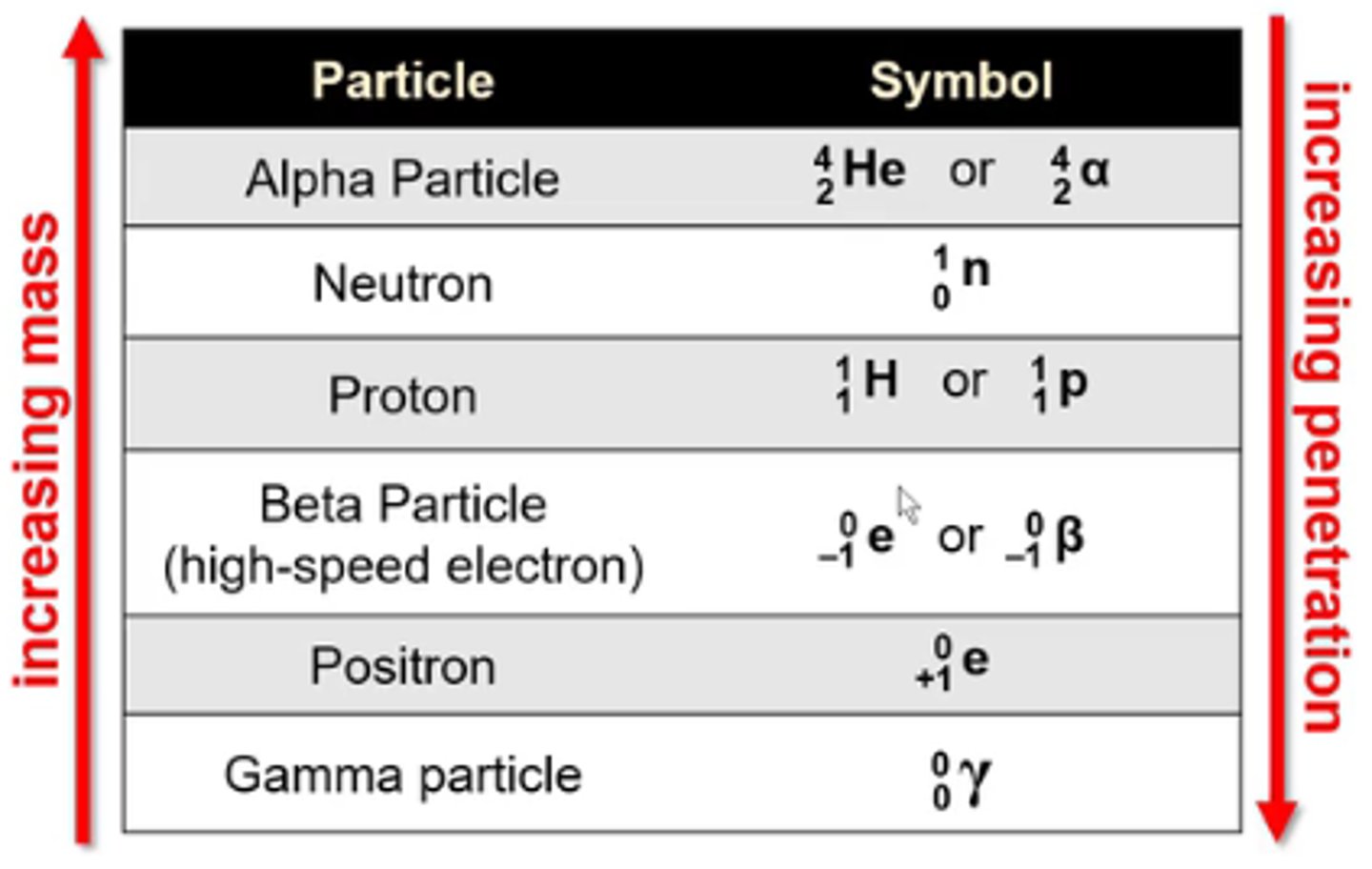
what is the symbol for the nuclear particle gamma particle?
0/0γ
what does a nuclear decay (fission or emission) reaction look like?
both fission and fusion give off energy
-mass gets converted into energy in these reactions
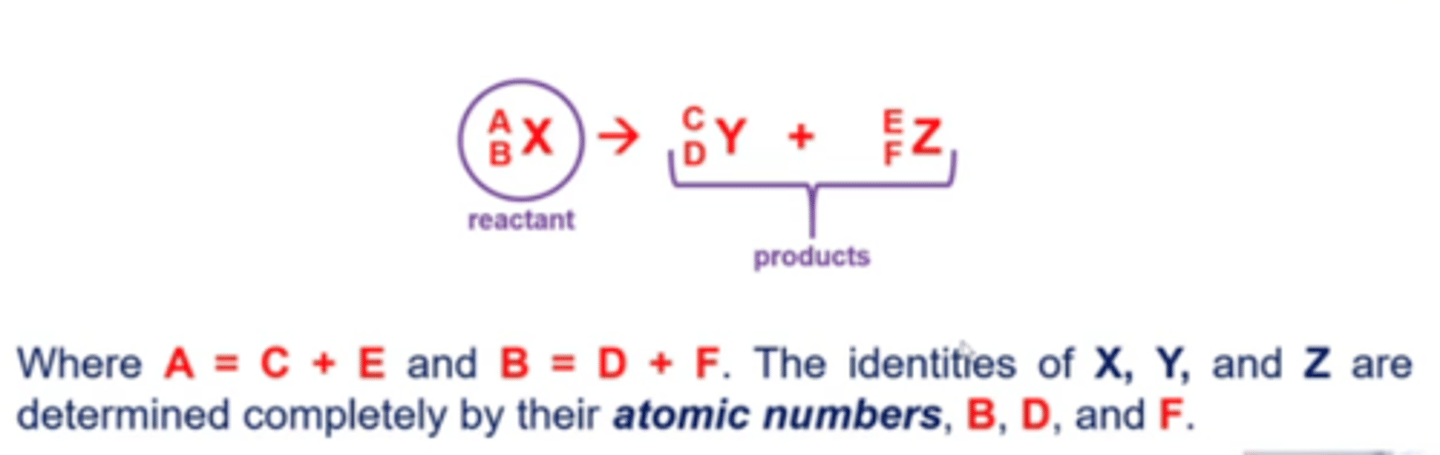
what does a nuclear capture/fusion reaction look like?
both fission and fusion give off energy
-mass gets converted into energy in these reactions

in order to be stable, what ratio of protons to neutrons must the first 20 elements on the periodic table have?
1:1
in order to be stable, what ratio of protons to neutrons must the elements beyond number 20 on the periodic table have?
their neutron number can exceed proton number, to a point
-all isotopes that fall outside this band are unstable (radioactive) and will spontaneously undergo nuclear reactions
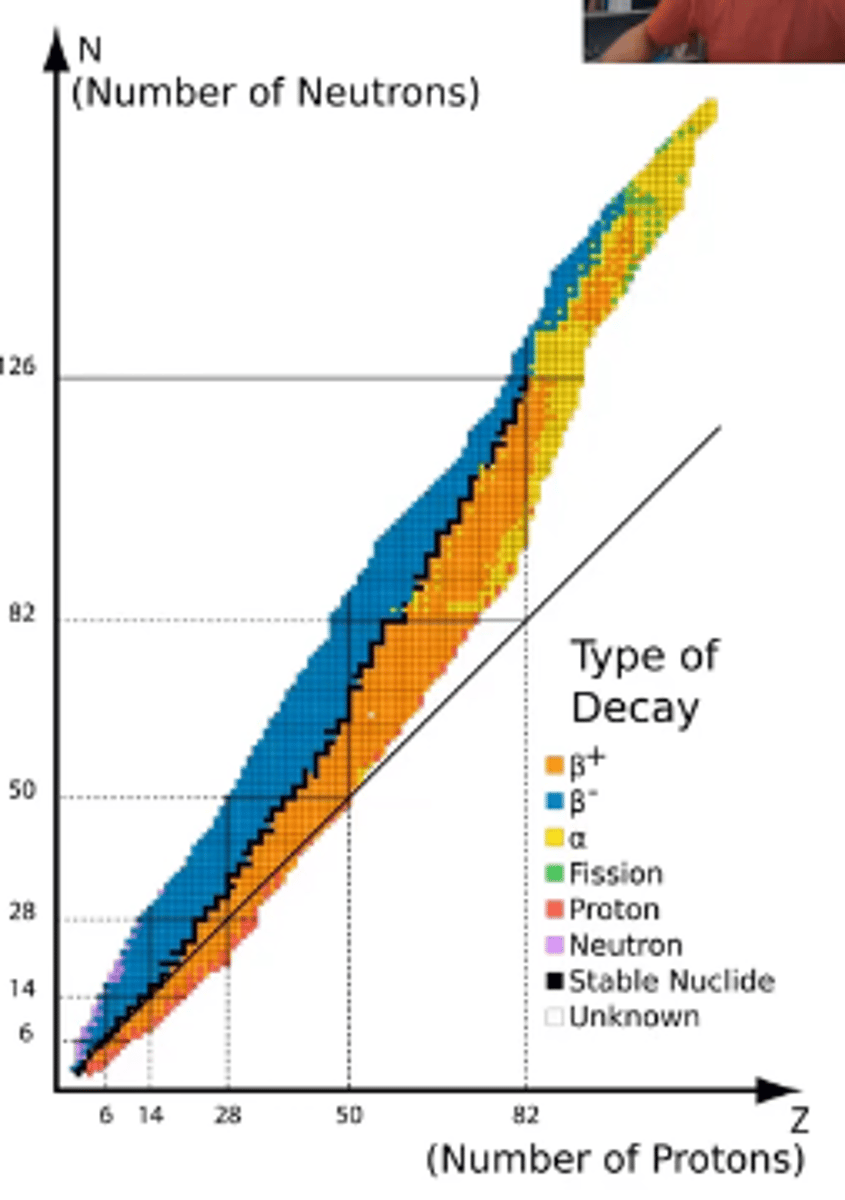
how do atoms above the band of stability (they have too many neutrons and not enough protons) react?
they decrease the neutron-to-proton ratio by emitting beta particles through beta decay, and they gain 1 proton in the process
how do atoms below the band of stability (they have too many protons and not enough neutrons) react?
their either emit a positron (positron emission) or capture an electron (electron capture)
what is the order of all radioactive decay reactions?
first order:
thus, their curved-line integrated rate law looks like this:
half life stays constant and is independent of concentration!
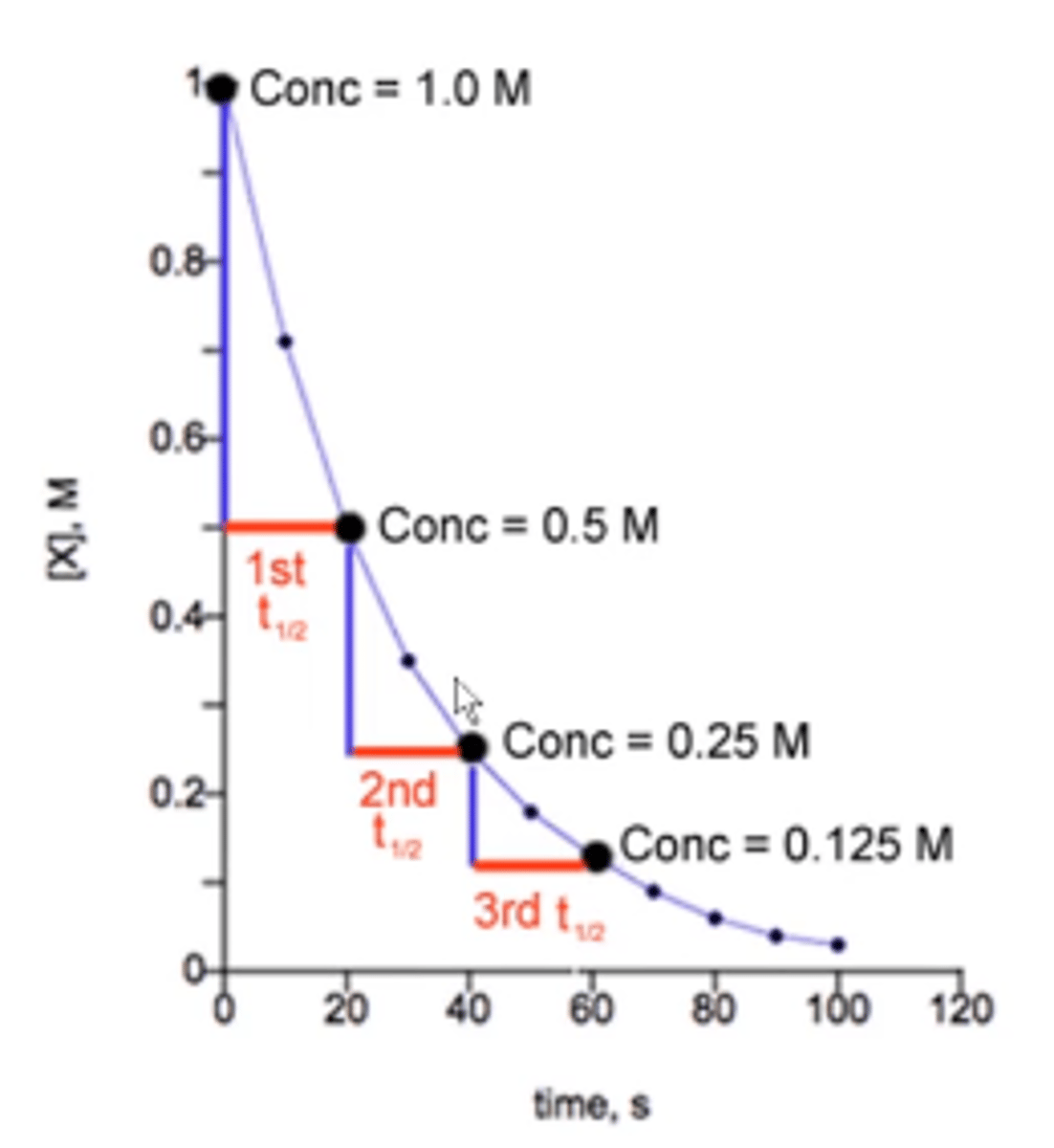
what is the equation to find radioactive decay rate constants?
t1/2 : half life
k: radioactive decay's rate constant
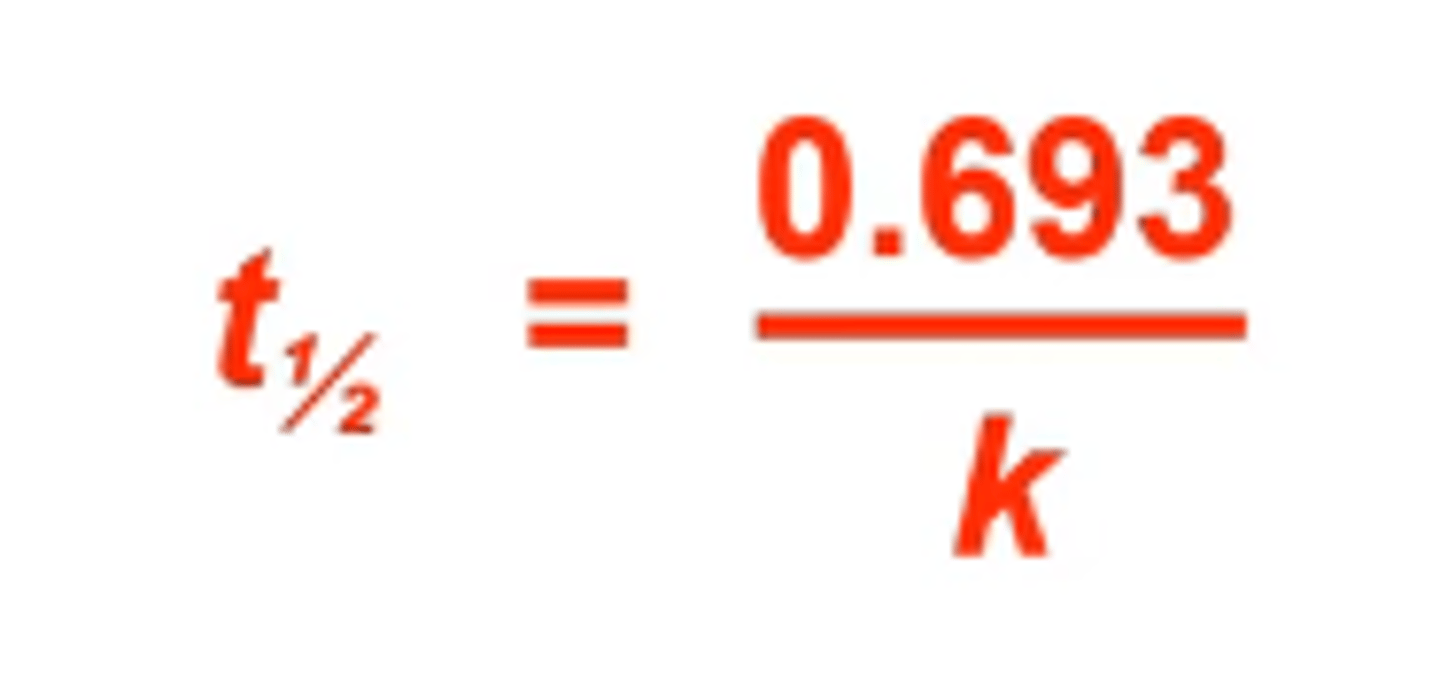
the amount of energy necessary to separate an atom's nuclear protons and neutrons
nuclear binding energy
the difference between a nucleus' calculated mass (heavier) and its actual mass (lighter)
mass defect
how do you calculate the nuclear binding energy for an atom?
ΔE = Δmc^2
c=3x10^8 m/s
m: atom's mass in Kg!!!