Biology Mod 8 - Non-infectious Disease
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
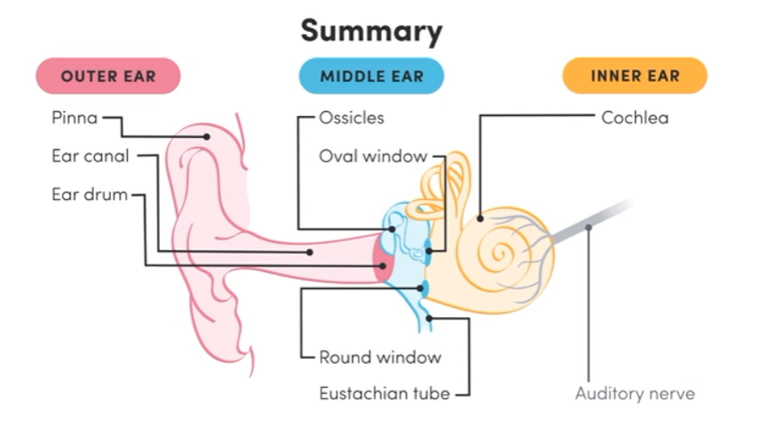
Pinna
Outer part of the ear that collects sound waves, made of cartilage and skin
Tympanic Membrane
Eardrum that vibrates in response to sound and passes on vibrations to ossicles; converts sound waves to mechanical vibrations
Ear Ossicles
Three bones in the middle ear that transmit vibrations from eardrum to oval window.
Oval Window
Structure that amplifies and passes vibrations to the cochlea
Round Window
Membrane that allows vibrations to escape from the cochlea and prevents ringing in cochlea
Cochlea
Spiral structure filled with fluid for sound transmitted to produce pressure waves
Basilar Membrane
Part of the cochlea where specific fibers vibrate
Organ of Corti
Structure containing hair cells stimulated by pressure waves to send signals to auditory nerve to brain
Auditory Processing Disorder and Cause
Inability of the brain to understand speech due to sound transmission issues, caused by birth defect or brain injury
Conductive Hearing Loss and Cause
Impairment in mechanical conduction of sound vibrations through outer and middle ear, caused by impacts to outer middle ear e.g. ear infection
Sensorineural Hearing Loss and Cause
Disruption in the pathway from the inner ear to the brain due to cochlear damage, caused by exposure to loud sounds, head injury, damage to cochlea hairs
Mixed Hearing Loss
Combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss
Cochlear Implant Function and Process
Device to stimulate the auditory nerve directly for hearing improvement in response to sensorineural hearing loss
External speech processor captures sound and transmits it to receiver, which conveys sound to electrical signal and passed to auditory nerve. alternative to damaged cochlea
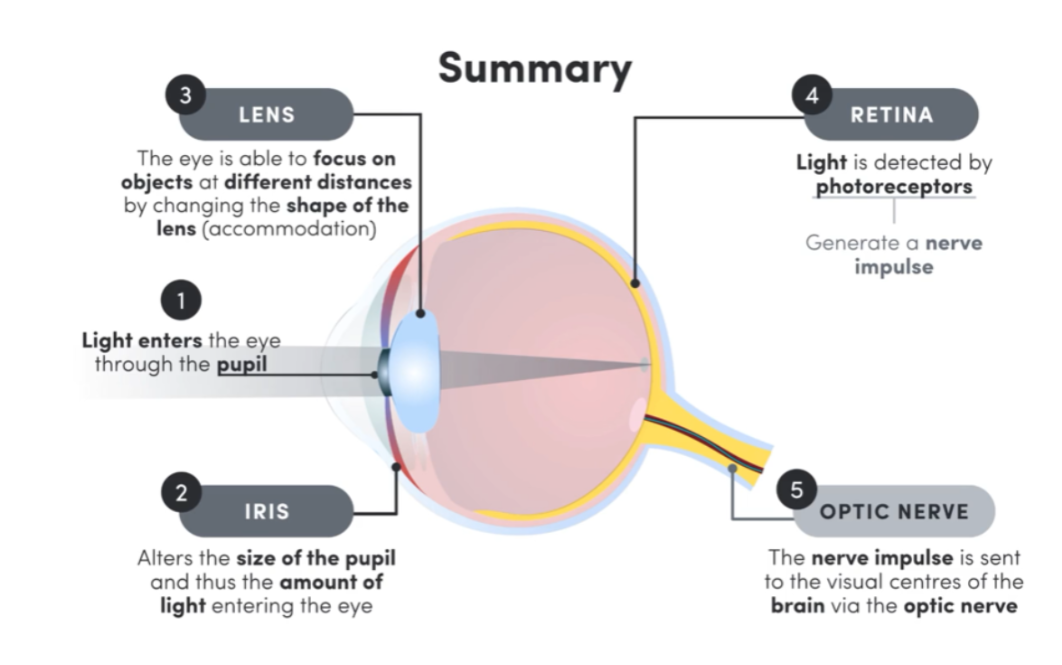
Iris Composition and Function
Muscle tissue controlling pupil size and volume of light entering eye
Lens Composition and Function
Transparent biconvex protein disk adjusts thickness to bend light directly on the retina (accommodation)
Retina Composition and Function
Layer of photoreceptor cells at back of the eye which detect light and send electrochemical signals to brain
Hyperopia, its Cause in relation to the Lens and Treatment
Far-sightedness, inability to focus on close objects
Lens of eye can no longer assume round shape required for viewing nearby objects, image falls behind retina
Glasses with convex () lens, rays bend inward to ensure they hit retina (focal point correction)
Myopia, its cause in relation to the Lens and Treatment
Short-sightedness, inability to focus on distant objects
Light from distant objects bent more than necessary, image falls before retina
Glasses with concave )( lens, rays bend outward, image falls on retina (focal point correction)
Explain the three key functions of the kidney and where they occur
Filtration (occurring in bowman’s capsule and glomerulus) to remove toxins and liquids from the blood. Non-selective
Reabsorption (occuring in the tubules) to filter essential substances e.g. salts back into the bloodstream from the filtrate via semi-permeable membranes
Filtrate → bloodstream
Osmoregulation → reabsorbs water for body
Secretion (occuring in the tubules) to remove toxic and unnecessary substances from blood and create urine to send to bladder
Bloodstream → filtrate and urine
Bone Conduction Implant Function and Process
Aids conductive hearing loss by transmitting vibrations to cochlea
External sound processor outside of ear detects and converts sounds to vibrations transferred directly through bone to cochlea
Hearing Aids Function and Process
Amplify sound for various types of hearing loss
Microphone detects sound waves which is converted to electrical energy, amplifier strengthens signals, and a receiver converts electrical signals back to sound and is directed into the auditory canal louder
Laser Eye Surgery Process and What It Helps
Uses lasers to correct refractive errors in the cornea by changing cornea curvature
can correct myopia, hyperopia
Dialysis
Machine filtering blood when kidneys fail; Removes metabolic wastes by diverting blood out of arteries into tubes with artificial semi-permeable membranes
Haemodialysis vs Peritoneal Dialysis
H —> Cannula (needle) in the arm, blood flows into the machine through a series of semi-permeable membranes. Toxins removed, clean blood returned
P —> Catheter placed in abdomen. dialysate flows through here and absorbs waste and extra fluids from body, and the solution is emptied from body every few hours
Describe the order sound travels through the ear
pinna
auditory canal
tympanic membrane (eardrum)
ear ossicles
oval window
cochlea
basilar membrane
organ of corti
auditory nerve
round window (vibrations escape from cochlea)
Auditory Canal
transmits sound waves from pinna to tympanic membrane
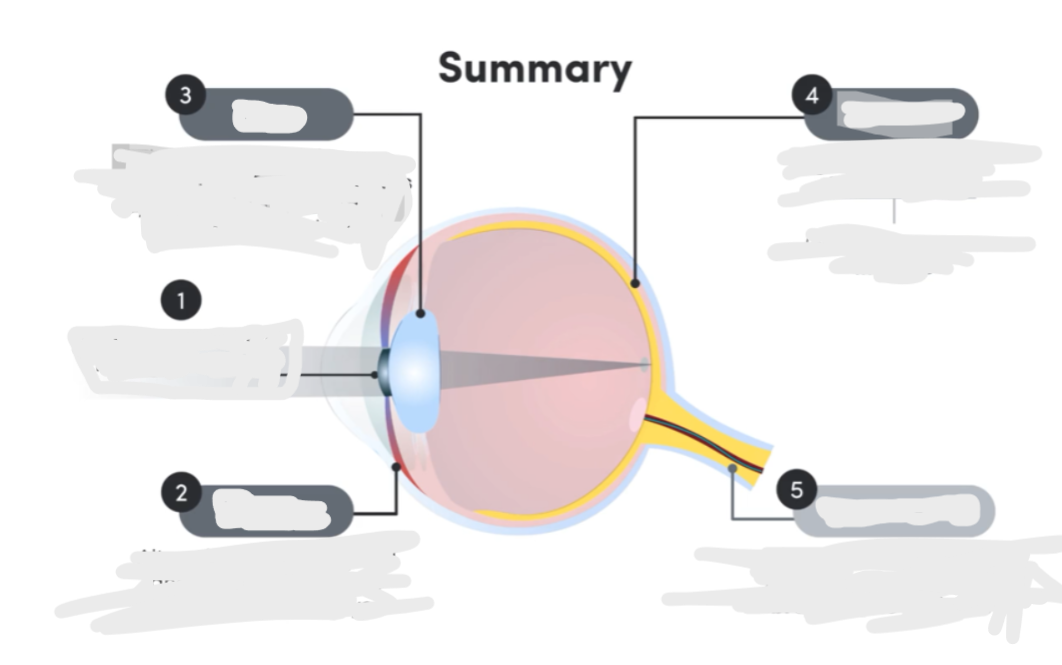
Label the eye
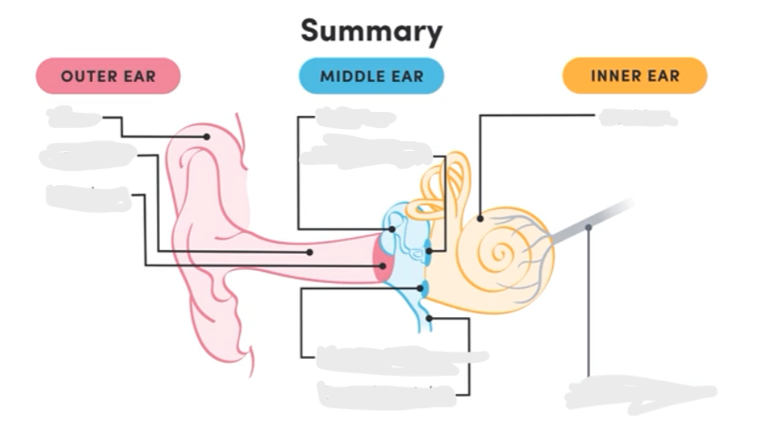
Label the ear
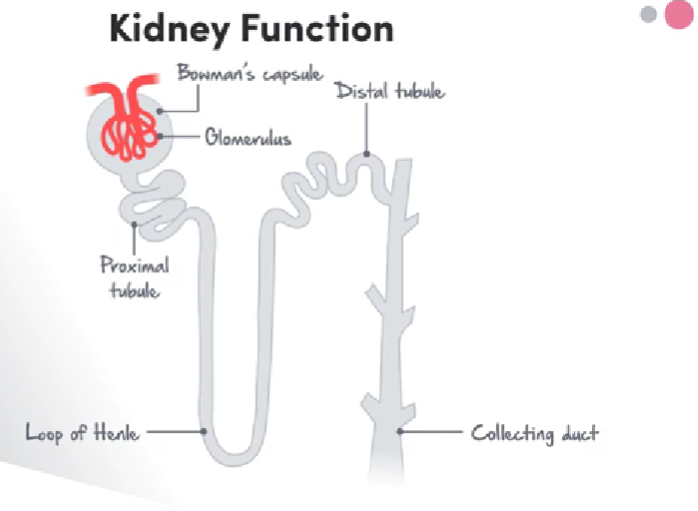
Label the nephron
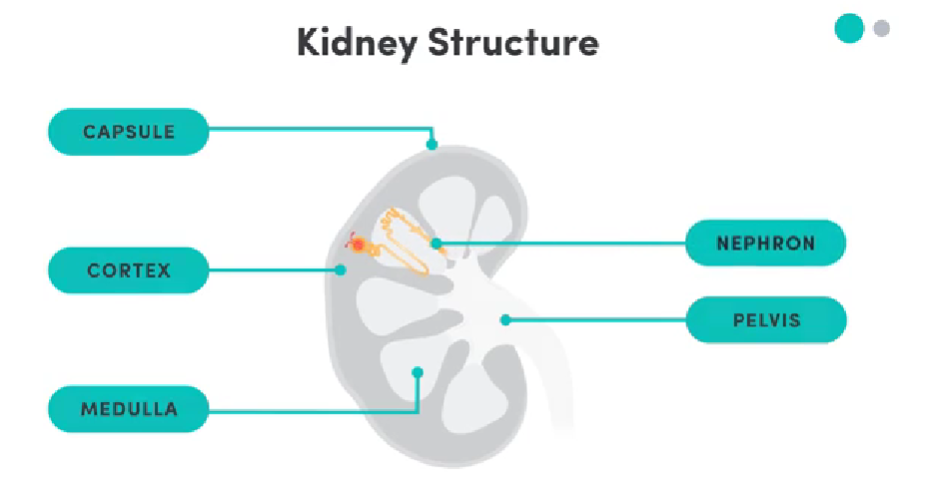
Label the kidney
Describe the order light travels through the eye
pupil
iris
lens
retina
Pros Cons Cochlear Implants
PROS: effective
CONS: invasive surgery, expensive
Pros Cons Bone Conduction Implants
PROS: comfortable, no blocking ear canal
CONS: expensive, inflammation risk, invasive
Pros Cons Hearing Aids
PROS: inexpensive, no surgery
CONS: visible, uncomfortable, all sound amplified
Pros Cons Renal Dialysis
PROS: efficient (done at home), effective (clean blood returned), no surgery
CONS: time consuming, expensive, uncomfortable
Explain the functions of the parts of the nephron
Bowman’s capsule → encapsulates glomerulus and collects filtrate from glomerulus to sends it to rest of nephron
Glomerulus → set of tight capillaries designed to increase pressure of blood and squeeze out unnecessary substances and plasma through non-selective filtering from blood into Bowman’s capsule
Proximal Tubule, Loop of Henle, Distal Tubule → semi-permeable tubules responsible for reabsorption and secretion of filtrate into and out of blood to reabsorb necessary substances and clean blood further from toxins
Collecting duct → semi-permeable tube that reabsorbs water from filtrate via osmosis and manipulation of salt levels
Kidney Pelvis Function
collects urine from calyces (small tubes collecting urine) to send to ureters to bladder
Describe the movement of blood through the kidney
renal artery —> capillaries
nephron
glomerulus
tubules
capillaries —> renal vein
Glomerulonephritis Definition and Cause
Infected inflamed glomeruli → cause, results in kidney failure
Toxins and wastes not properly filtered into urine, therefore excess fluid moves into body via osmosis
Too much waste that cannot be excreted → “full of shit”
How does the negative feedback loop work?
disturbance occurs
receptor recieves change in variable and sends message to control centre (e.g. hypothalamus)
control centre sends orders to effector organs, e.g. muscles
effector organs correct issue
message sent back to control centre to stop once homeostasis is reached
Compare endotherms and ectotherms
endotherms: generate body heat metabollically (atp from consumed food goes toward creating heat)
ectotherms do not control body temp, rely on external sources (e.g. lizards on hot rocks)
- Change detected by thermoreceptors in hypothalamus (control centre)
- Regulated by electrical impulses and nervous system
- receptors send message to hypothalamus
- hypothalamus sends message to effector organs
- vasodilation and sweating occurs to cool body temp
- receptors send message back to hypothalamus to stop once homeostasis is reached
- receptors send message to hypothalamus
- hypothalamus sends message to effector organs (muscles)
- muscles shake and shiver to heighten body temp
- receptors send message back to hypothalamus to stop once homeostasis is reached
surrounding environment to decrease body temp
- seeking shade
- seeking shelter
- increasing amount of clothes worn
- sweating
- changes in metabolism and rate of cellular respiration
- piloerection
- shaking/shivering
- glucose changes with carbohydrates consumption
- Animals lick forearms (cools body temp through evaporative cooling
- Panting in hot temps (quick breathing evaporates water from tongue)
- Animals e.g. penguins huddle in cold (Decrease body surface exposed to cool temperature)
- Vasoconstriction (constrict to save body heat)
- Thirst (encourages body to drink water to protect from dehydration)
- Metabolism (maintains body temp, metabolism = heat)
- Hibernation (body temp drops and metabolism slowed to conserve energy in cold and low food sources)
- Body insulation e.g. fur, blubber,feathers (trap air/heat against skin to increase heat retention)
- Ear shapes (larger ears = hotter climate for heat loss)
Explain the endocrine system as an internal coordination system that allow homeostasis to be maintained
Secretes hormones (chemical signalling molecules produced by glands) to send messages through bloodstream to body that coordinate slower but long-lasting responses, e.g. reproduction
Transported by blood and diffusion through extracellular fluid/space
Explain the nervous system as an internal coordination system that allow homeostasis to be maintained
Central nervous system → brain and spinal cord; gathers info from body and coordinates responses
Peripheral nervous system → all other nerves; connect CNS to rest of body
Neutral pathways → direct for max speed
Neurons → high concentration of mitochondria for enough energy to maintain ion balance across cell membrane
Identify similarities between the nervous and endocrine systems
Shared homeostatic processes, different ways of going about them
Thermoregulation → endocrine system responds with secreting hormones to adjust cell metabolism for heat generation, nervous system coordinates piloerection, shivering, vasoconstriction/dilation
Osmoregulation → nervous system triggers thirst, endocrine adjusts ADH hormone
- electrical impulses vs chemical hormones
- neurons vs blood carries signals
- high vs low speed
- localised smaller response vs systematic larger response
- temporary vs long lasting
Define Hydrophytes and identify a mechanism to maintain water balance
Plants in freshwater environments (lots of available water) —> Internal enviro has low water and water moves into plant, plant must regulate to prevent tissue floods
High number of stomata + leaves with high SA
Describe 2 general mechanisms in plants which allow water balance to be maintained
stomata —> maintain water balance by opening and closing
High no of stomata → max loss of water (freshwater enviro)
Low no of stomata → minimum water loss (dry enviro)
Leaves hanging vertically → reduce sun exposure and therefore water loss via evaporation and overheating (e.g. eucalyptus)
Extensive root systems → max surface area for water absorptions from soil (dry enviro)
Guard cells → control opening and closing of stomata, close to prevent water loss
Explain the four causes of genetic disease
Single gene inheritance —> one gene is affected
Multifactorial inheritance —> multiple genes involved in a feature, comes from defects from multiple chromosome regions
Chromosomal abnormalities —> Errors in cell division leading to deletion, duplication, inversion, translocation or substitution of genes.
Mitochondrial inheritance —> Gene variants in the DNA found in mitochondria, which is provides instructions for proteins and energy creation
Explain environmental exposure as a cause for disease
Lifestyle choices influence the body and disease
for example, high exposure to the sun and UV rays can cause skin cancer
allergies are also triggered by certain environments
Explain the causes of nutritional diseases
Imbalanced diet lacks or is excessive nutrients
e.g. scurvy is due to a lack of vitamin C
overnutrition, malnutrition, undernutrition
Describe cancer and its causes
Large group of diseases involving rapid creation of abnormal cells which invade adjoining parts of body and spread to other organs
Caused by carcinogens (factors that mutate DNA), smoking, obesity, family history
- Non infectious disease is the cause of 70% of deaths globally
lifestyle diseases responsible for 63% of these
- Incidence and mortality rates decrease as knowledge of nutrition becomes widespread
• importance of fruit/vegetable nutrients → decreases prevalence
How do environmental exposure diseases relate to incidence, prevalence and mortality?
Mortality rates decrease as public health programs are created to control/prevent disease
e.g. slip slop slap campaign for use of sunscreen to prevent UV rays mutating DNA
E.g. quit campaign for effects of smoking to decrease chance of mutating DNA —> Decreased prevalence
- Radiation therapy - deliberately damages cell DNA, killing them, but kills healthy tissue
- Surgery - removes cancerous tumours, but difficult to remove all cancerous cells in just one surgery
- Monoclonal antibody therapy - mass production of antibodies which are injected into the body to aid the immune response.
Identify the three types of epidemiological studies
Analytical, Descriptive, Intervention
Explain how analytical studies work
Case control studies - compare those with disease to those without and look for differences in exposure to possible disease causes (e.g. age, diet, gender, lifestyle, occupation, location)
Cohort studies - studying two similar groups of people who are free of disease, one group exposed to possible cause of disease and other is not, and these groups followed over long period of time to compare resulting incidence of disease (tests mortality and morbidity)
Explain what features enhance the effectiveness of an epidemiological study
Conducted over long period
Study large samples (consider if the population of Australia is 28 million and a study for aus is 20,000, it's not the largest possible sample. Relative 'large')
Include people of wider population
Evaluation of treatment and control methods
Collect range of relevant data from large group of affected and unaffected population
These help grant a study validity especially
- potential prevention of exposure to disease causing elements
- early detection and treatment
- higher chance of saving lives
- save govt money and medical resources
- clear up hospitals potentially
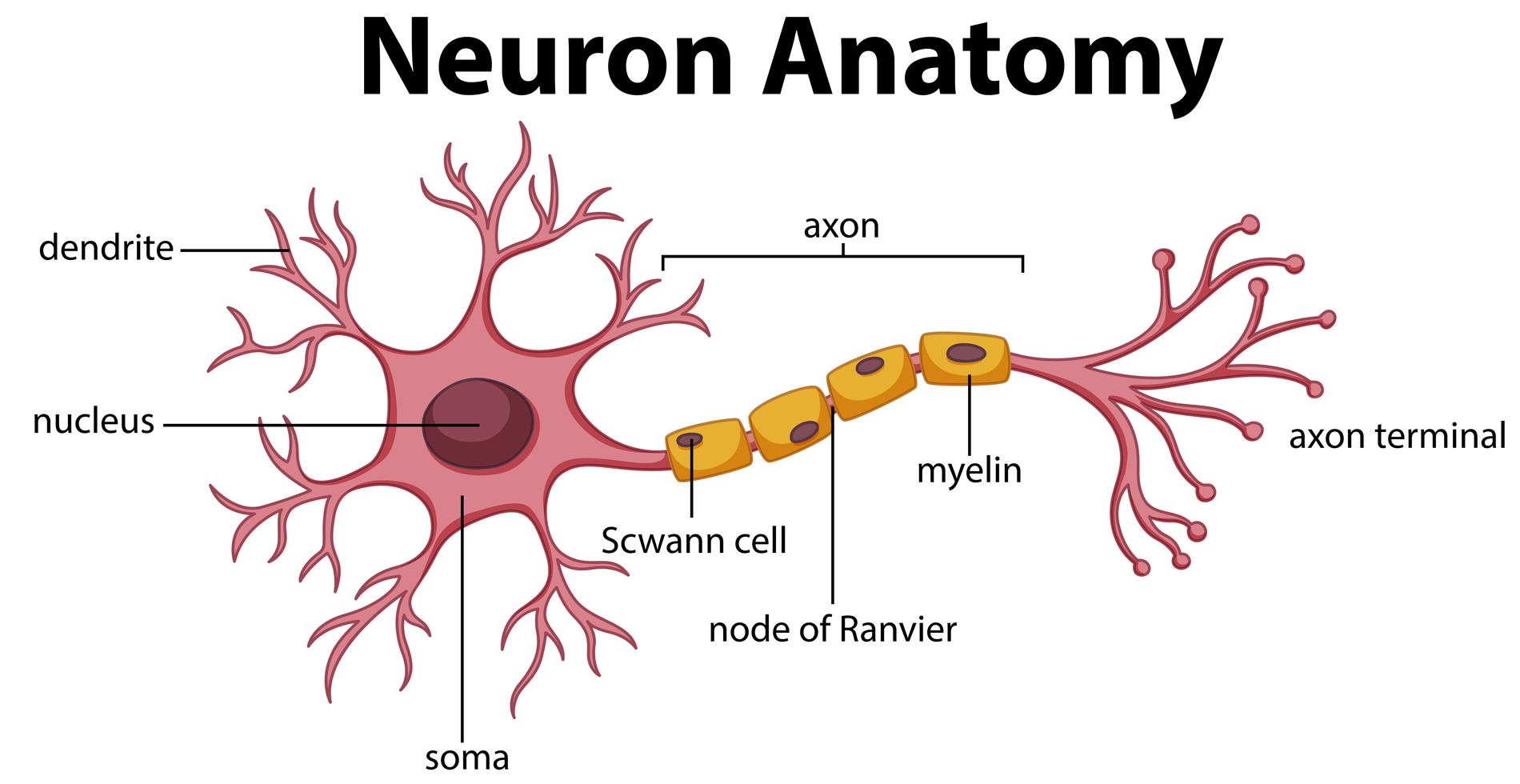
Define the function of neurons and then each part of the neuron (dendrite, axon, axon terminal, cell body, synapse)
Function → nerve cells which carry electrical signals; sending, receiving, and transmitting electrochemical signals throughout the body
Dendrites —> receptors, receive info from other neurons; branch out from cell body, carry info to cell body
Axon → tail, carries info away from cell body and has terminal area where other neurons pick up information via their dendrites; covered by myelin sheath like rubber encircles a wire
Cell body → spherical, contains nucleus
Synapse → gap between axon terminals
Define Mesophytes and identify a mechanism to maintain water balance
Land plants, adequate supply of water
Regular stomata numbers, stomata often open
Define Xerophytes and identify a mechanism to maintain water balance
Dry climates, adaptations focus on conserving water
Few stomata, thick waxy cuticles, small SA on leaves
Identify factors used to evaluate methods of epidemiological studies
Requirements for Effective Study
Conducted over long period
Study large samples (consider if the population of Australia is 28 million and a study for aus is 20,000, it’s not the largest possible sample. Relative ‘large’)
Include people of wider population
Evaluation of treatment and control methods
Collect range of relevant data from large group of affected and unaffected population
These help grant a study validity especially
Evaluate genetic engineering as a strategy to prevent disease
Genetic Engineering → insertion of genes from one organism to another; modification of an organism's genes to prevent or treat diseases, e.g. replacing faulty gene
Genetically engineering other animals (e.g. mice) to produce high volumes of monoclonal antibodies which will specifically kill cancer cells
Ethical concerns
Effectiveness: moderate (technology has not reached full potential and is not a foolproof method of eradicating cancer)
Good because reducing requirement for donors and no issues with tissue and organ rejection
Describe lung cancer as a non-infectious disease
Abnormal cells grow and multiply in an uncontrolled way, either beginning in or spreading to the lungs
Caused by carcinogens in smoking for example or exposure to chemicals
Can be treated in ways similar to other cancers - surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy
High prevalence amongst lower socioeconomic groups and rural populations due to greater rates of smoking
Identify an analytical study on lung cancer
Case control study by Richard Doll (1947) to compare smoking habits of patients with and without lung cancer → showed people with lung cancer were smokers suggesting a link
Cohort study by A Hill (1951) where 1 group of doctors were smokers and the others were non-smokers over 10 years → showed smokers had lung cancer and more cigarettes = more chance of lung cancer
Describe and evaluate an intervention study relating to lung cancer
Provide an example of a specific epidemiological study
The Quit campaign was an intervention epidemiological study through the form of an educational campaign in mass media which raised awareness of the effects of smoking to reduce the prevalence of smoking related diseases in the population
Understanding cause of lung cancer → encouraging prevention of exposure to mutagens in smoking
Used slogans, graphic images in the media and on cigarette packets, helpline and non-smoking areas
Positives: large sample size, control of variables (e.g. age, gender), long period, accurate/reliable studies
Cons: Can reliability be assessed? It wasn’t repeated
considered highly successful in decreasing smoking rates and thus the prevalence of lung cancer