BPM202: Digital Music Production II - Quiz #1: Audio Interface
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
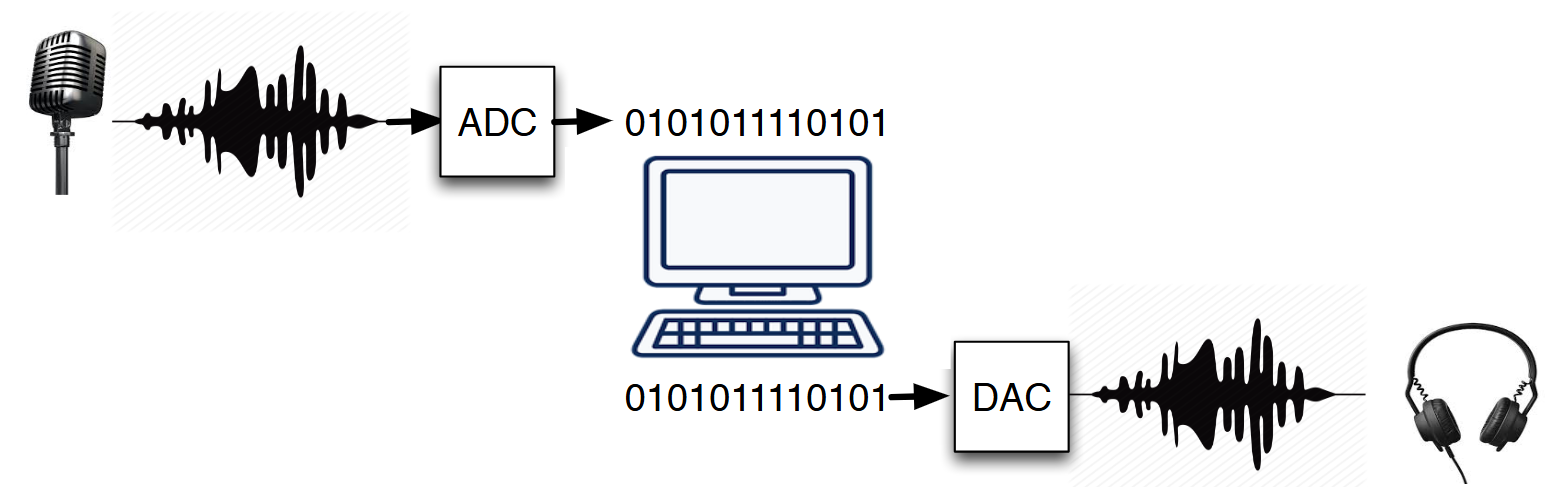
AUDIO INTERFACE
Achieves an analog audio signal converted from analog electrical information into a method a computer can understand (DIGITAL)
CONTAINS 1 OR MORE OF:
ADC: Analog to Digital Converter
DAC: An output stage that handles the reverse function (Digital to Audio Converter)
SAMPLE RATE
The analog signal is sampled at a defined interval per second
Expressed in hertz (Hz)
Most Common: 44.1 kHz (CDs) & 48 kHz (Film/TV)
The lower the sample the rate, the more grain & garbly the texture is
NYQUIST THEOREM
Reproducing an audio signal that captures the frequency range of human hearing (which is about 20 kHz, or 18-30 kHz) TO AVOID AILASING!
Laptop to replicate noise heard!
You need at least x2 (DOUBLE) the SAMPLE RATE to produce sounds for the humans (so… 20 × 2 = 40!)
Aliasing is a type of distortion that occurs when high-frequency components of a signal are misinterpreted as low-frequency components
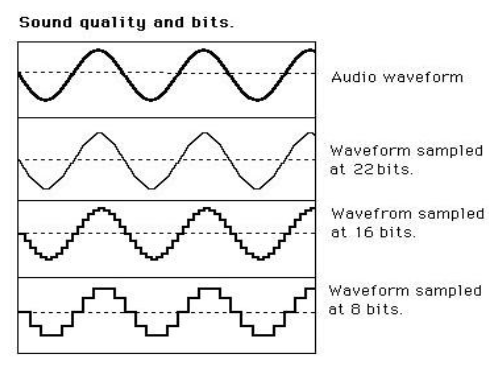
BIT DEPTH
The number of bits used during sampling
Bit too low, the audio will start to sound grainy or metallic (resulting in more square-wave type waveforms!)
“Bit-Crushing” → reducing the sample size! More degrading it is, “aylising”
ADC & DAC
Both are used to send & receive data between devices
EX: Voice calling on a cell phone
Audio signals are analog (signal’s waveform)
When someone talks into the phone’s microphone, the phone has an ADC that converts the analog signal into digital so that the other phone on the other end can receive it!
Signal sent from phone → telephone tower → satellite → another telephone tower!
ADC (ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER)
Device that takes analog signals & converts them to digital signals
Converts natural waveforms of analog into digital, binary bits
Analog signals that have a continuous sequence with continuous values
DAC (DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTER)
BLOCK —> WAVE
Device that takes analog signals and converts the signal from digital bits of data & converts it back to natural waveforms of an analog signal (so we can understand it!)
Opposite function of ADC but same clock source
Digital info from daw convertor into analog signal!
Enables sounds to be reproduced through loudspeakers/headphones
Can improve conversion of a sound
Pro Tools
EDITING MODES
SLIP MODE
GRID MODE
SHUFFLE MODE
SPOT MODE

Pro Tools
EDITING MODES
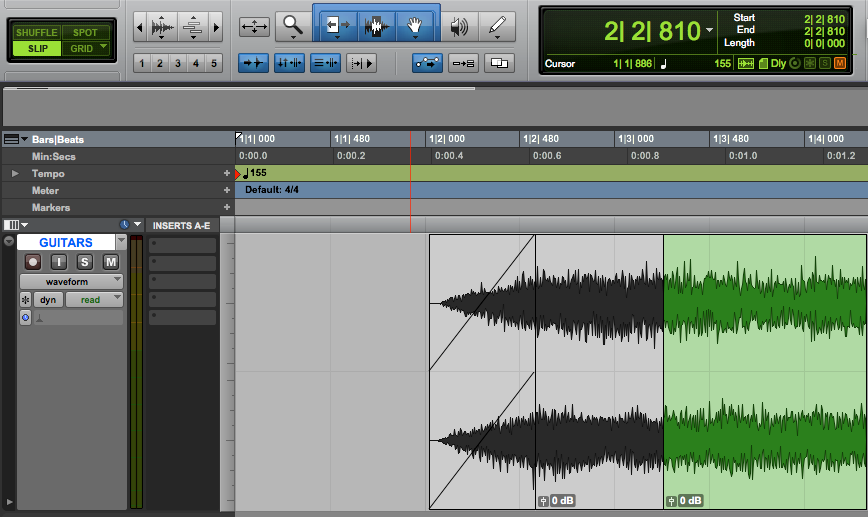
1. SLIP MODE
Allows you to manipulate audio/tracks without a grid, you can adjust it to ANY part of the pro tools, clips can freely move across timeline
Pro Tools
EDITING MODES
2. GRID MODE
Allows you to manipulate Audio and MIDI with a “Musical” timing reference → combo of Tempo & Meter, grid appears so all editing tools will “snap” to the grid
Has TWO modes
(1) ABSOLUTE MODE (Blue):
(2) RELATIVE MODE (Purple):
Pro Tools
EDITING MODES
2. GRID MODE
(1) ABSOLUTE MODE
Moving any clip snaps the clip start to Grid boundaries If a clip’s start point falls between beats, and the Grid is set to 1/4 notes, dragging the clip will snap its start time to the nearest 1/4 note (the current absolute Grid value)
Pro Tools operates in this mode by default, change it by clicking on the dropdown!
But working in the wrong mode can have dramatic results with your timing
Pro Tools
EDITING MODES
2. GRID MODE
(2) RELATIVE MODE
Clips can be moved by Grid (or Nudge) units
If a clip’s start point falls between beats and the Grid is set to 1/4 notes, dragging the clip will be constrained to 1/4 notes, preserving the clip’s relative position to the nearest beat
Ideal mode for editing drums & song structure (timing & internal edits will remain intact when moving things around)
Pro Tools
TABBING TO TRANSIENT
In Pro Tools, click Alt+Tab to see the parts of a clip you cut that are space! (So you start off well)
Pro Tools
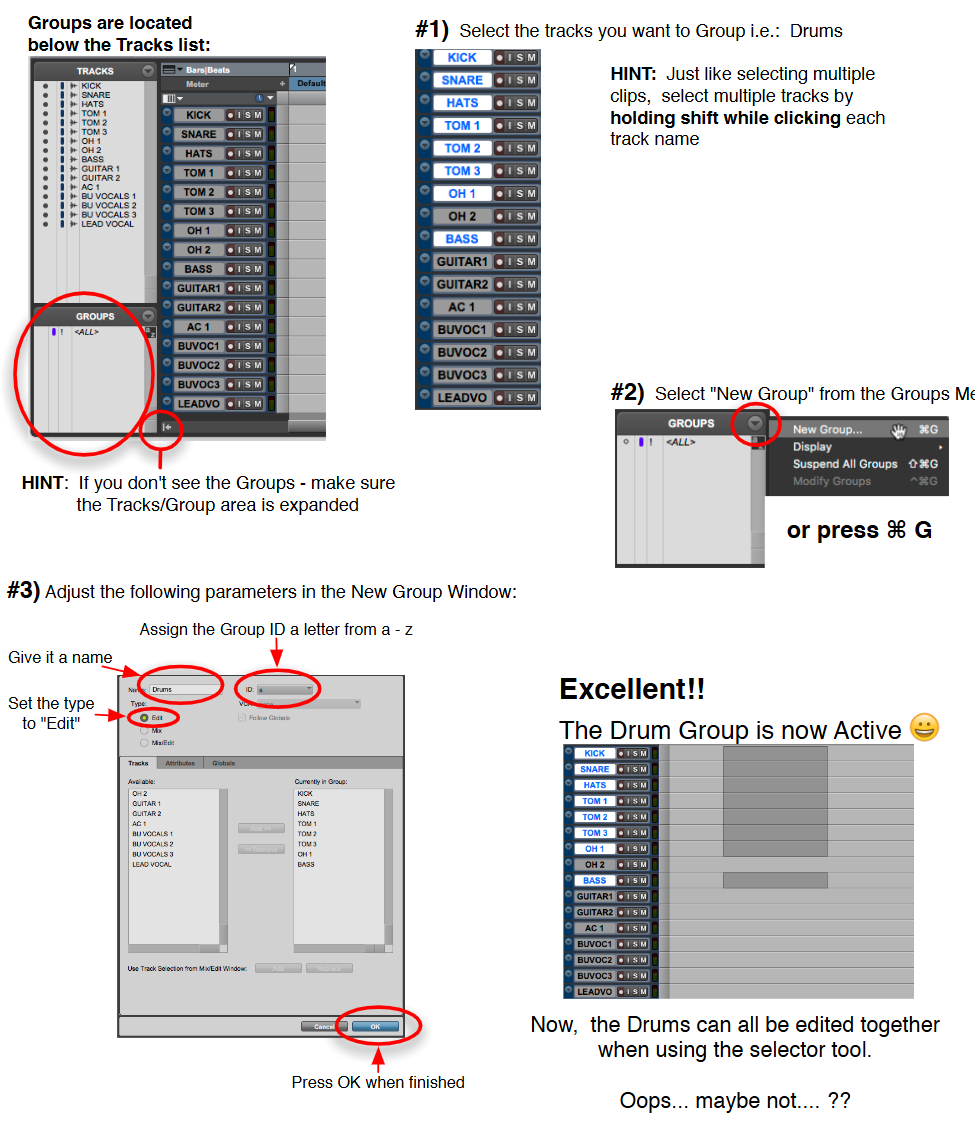
EDITING GROUPS
Pro Tools also has a helpful tool called “Edit Groups” where you can edit multiple tracks at the same time (saves time)
Located below the Tracks list
You can disable ALL groups by clicking “Suspend all Groups” or pressing shift G
You can also modify each group by right clicking the group you want and clicking modify
Pro Tools
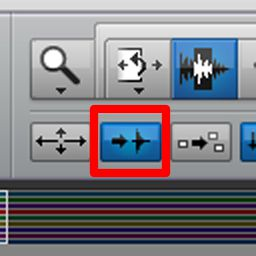
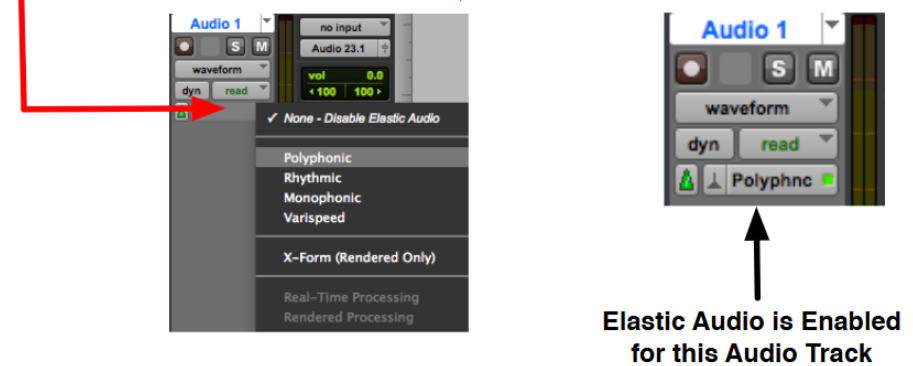
ELASTIC AUDIO
Pro Tools offers elastic properties!
Includes pitch shifting
Trimmer Tool set to TCE Mode, audio now can be extended/stretched to make the audio sound more “interesting”
Pro Tools
ELASTIC AUDIO
TYPES OF AUDIO
POLYPHONIC
RHYTHMIC
MONOPHONIC
VARISPEED
Pro Tools
ELASTIC AUDIO
TYPES OF AUDIO:
[1] POLYPHONIC
Audio with different simultaneous pitches such as piano, guitar, entire mixes
Pro Tools
ELASTIC AUDIO
TYPES OF AUDIO:
[2] RHYTHMIC
Audio with percussive elements such as Drums, Percussion
Pro Tools
ELASTIC AUDIO
TYPES OF AUDIO:
[3] MONOPHONIC
Audio with single notes at a time such as bass, vocals, trumpet etc.
Pro Tools
ELASTIC AUDIO
TYPES OF AUDIO:
[4] VARISPEED
Instead of keeping the pitch intact, Protools will lower or increase the audio speed to fit the clip boundary
This is the same concept as speeding up or slowing down a tape