AP euro unit 5 review (French revolution/ Napoleon)
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
causes/ background of French Revolution
weak french government
debt- wars of Louis XIV
inability to tax nobles
Cahier de Deleances (assembly of notables)
3 estates (old regime of France)
first- Catholic clergy
second- nobility
third- middle class, peasants, working class/ artisans
tennis court oath
- Led by Abbé Sieyés the third estate rejected the method of voting and demanded all 3 estates meet together.
- king refused and 3rd estate declared themselves true national assembly
- 3rd estate met in a nearby tennis court and took an oath not to disband until they drafted a constitution
- marked beginning of French Revolution
storming of the bastille
showed power in numbers
thought of as day 1 of french revolution
great fear of 1789
rumor that nobility was preparing to attack the third estate,
nobility flee France
night of august 4th
abolition of feudalism**
catholic church agrees to be taxed
declaration of the rights of man and citizens
- after this night all French citizens were subject to the same and equal laws
declaration of the rights of man and citizens
"all men were born free and remain equal in rights"
gets rid of titles and rights of nobility
creates equality
similar to the American Constitution
slogan of revolution
"liberty, equality, fraternity"
women's march to Versailles
during constructive phase
woman can't afford to feed their families
march royal family to Paris
legislative assembly
the governing body of France between October 1791 and September 1792. It replaced the National Constituent Assembly.
political reforms (during constructive phase)
becomes limited monarchy
most power in national assembly
voting rights based on ability to pay a fee
religious reforms (during constructive phase)
Civil Constitution of the Clergy
oath of loyalty
refractory priests- refused to take oath
- forced to go underground and upset peasants b/c most of them are devout Catholics
"underground catholic church"
economic reforms (during constructive phase)
"laissez faire" - gov had little or no role in national economy
abolished guilds
assignat- paper currency during revolution
second part of French Revolution
began August 10th 1792
much more radicalized
legislative assembly calls election for national convention who would form a more democratic gov
September massacres marked beginning of 2nd revolution
Battle of Valmy
France begins to expand empire and alert other countries (first coalition formed)
1st Coalition
Alliance of European countries (Spain, Holland, Austria, Prussia, England, Sardinia), established in attempt to defeat the growing French force
reign of terror
response to 3 fold crisis facing France
- Economic Crisis, losing war effort, counter-revolution
- led by Robespierre
- power and influence of Sans Culotte increase
Maximilian Robespierre policies
executions
levee en mass
Ventose laws
social services
conflict over
Dechristianization
levee en mass
allows government to take anything or anybody for the good of the nation, fighting the war, and to deal with the economic crisis
- created a national military based on mass participation
Ventose laws
created a system for distributing land confiscated from nobles to the peasants
law of maximum
Wage and price control
set price limits, deterred price gouging, and allowed for the continued flow of food supply to the French people
committee of public safety (institution of Robespierre)
made the laws (during the Reign of Terror)- Robespierre dominates
committee of general security (institution of Robespierre)
police force that enforced laws, (violent/brutal)- Fouche
revolutionary tribunals (institution of Robespierre)
roving street courts- punish those accused of being against the revolution
Robespierre's idea of "republic of virtue" most closely related to which enlightenment thinker's idea?
Rousseau's social contract
(sacrifice of one's self and one's interest for good of republic)
Rousseau's idea of "civic religion" that would induce morality among citizens
Jacobins
wanted to overthrow monarchy and create a republic
girondins
spread revolution outside of France to discredit monarchy (subset of Jacobins)
Sans Culotte
not part of legislative assembly
mostly working class
became very radicalized and wanted to overthrow social inequality (this group was known for taking action and sometimes violent action)
Prairial/ suspect law (made by Robespierre)
reason was defined as anyone who in thought, word, or deed was against the Revolution (i.e. Reign of Terror)
thermidor reaction
refers to the conservative reaction to the reign of terror, which ended it and saw the execution of Robespierre. (revolt against Robespierre)
(Remember Conservative as in resisting change- so the new government would want to return a little to the past).
led to a two house legislature
directory
5 member revolutionary governing body that lasted 4 years
Napoleon's early rise to power
insurrection of Vendemaire
Egyptian campaign and Battle of Nile
Coup d'etat of Brumaire
Egyptian campaign and Battle of Nile
- British victory
- French army is doing very badly, but Napoleon is reporting great success.
Coup d'etat of Brumaire
Leads to Napoleon becoming the dictator of France as First Consul.
insurrection of vendemaire
Food Riot in May of 1795, Royalists try to raid the National Assembly.
Reaction: Napoleon Bonaparte breaks it up (with his troops) "Whiff of Grapeshot"
Significance: bring Napoleon to the attention of the Directory.
Napoleon Bonaparte policies
"Napoleon was the last and greatest of the Enlightened Despots"
1) Puts down the counter-revolution in the Brittany and Vendee regions.
2) Napoleonic code
3) Maintains the abolition of Feudalism. (But offers to allow nobles back into the country and back into the government.)
4) Careers Open to the Talented"
5) concordat of 1801
6) economic modernization (industry and agriculture)
7) national bank of France: french Franc as currency
8) development of public education: Lycees
agriculture modernization
increase food production at lower cost
lead to industrial revolution
"careers open to the talented"
promotion within the government and in the military based on merit rather than birth.
concordat of 1801
an agreement between Napoleon Bonaparte and the Pope.
*The Pope recognized Napoleon's government as legitimate
*In return Napoleon recognized Catholicism as the "Majority Religion in France"
Napoleonic Code (AKA Civil Code)
-comprehensive written code of a law.
Examples: included criminal, civil law-and laws that regulated the economy etc...
-made husband/father dominant member of the family
-ENDED RIMOGENITURE
CODE APPLIED TO ANY AREA CONQUERED BY NAPOLEON, LONG LASTING EFFECTS ON EUROPE
Napoleonic wars
battle of Trafalgar
treaty of Tilsit
continental system
peninsular war
invasion of Russia
battle of nations
battle of Trafalgar
naval battle France vs. Great Britain-British victory. Admiral Nelson key antagonist (dies in battle)
Significance
Short-term: makes a direct invasion of Great Britain
Impossible **
Long term: signifies complete British naval superiority.
treaty of tilsit
-Between France and Russia
-ends war of 3rd coalition
-a. agreement between Napoleon and Alexander I (Russian Czar)
b. Napoleon gains about ½ of Prussia
c. Russia agrees to be part of the continental system
continental system
napoleon imposed an economic boycott on Great Britain
peninsular war
- continues until the end of the time period
-France had conquered Spain-Napoleon's brother had become King (gets rid of Bourbon dynasty)-the Spanish people rose up against French occupation.
Guerilla Warfare
invasion of Russia
-Russia practices retreat and burn tactics
-Napoleon goes in with 500,000 troops and leaves with 10,000
- Russia pulls out of continental system
battle of nations
(Battle of Leipzig)
- victory for 4th coalition
- first real major defeat for Napoleon (in Germany)
- Ultimately causes Napoleon to agree to abdicate the throne in return for peace.
Napoleon exiled to Elba
After loss of the Battle of Leipzig
Returns to the throne after less than a year, loses his final battle, the Battle of Waterloo, and is exiled to St. Helena, where he dies
Traditionally, men and women were in
separate spheres: Men were in public, women were in the home.
Rousseau's book
Emile (his book on education) - opposes women's education, a proper woman is in the home.
"Mother do not make a decent man out of your daughter. Make a decent woman out of her."
Active vs Passive Citizens
Active citizens can vote, passive citizens can't
Active: any man who payed a voting tax
Passive: women, servants
Marie Antoinette
Spent too much money, disliked by French people, used an example to show why women should not be in power
Given the nickname Madame Deficit
Women's clubs
began popping up across France - although they were mostly dedicated to philanthropy.
The sans-culotte and his wife supported a revolution where:
-Popular grievances were remedied
-High prices were lowered
-Government corruption was destroyed
-Petitions were used to raise awareness and inspire change
-War with Austria was going well (sending their sons to fight)
Revolutionary Republican Society
Formed by Pauline Leon and Claire Lancombe to challenge the enemies of the Republic. Were against the Girondins (moderates), loosely supported the Jacobins (Mountain).
Revolutionary Republican Society Goals
-Sought to arm themselves as a national guard (amazons) to protect Paris from Austrian invasion
-Declared war on hoarders (as in food) and inflation
-Pressed their way into Convention (government) meetings to influence Girondins
-Cockade Law - compelled all women to wear the tricolor cockade (knot of ribbons) to demonstrate their loyalty to the Republic. The cockade is the basis of the Tricolore or French flag.
Napoleonic Code & Women's Rights
Makes women second-class citizens, gave men control over them, especially married women
Olympe de Gouges
Feminist, playwright, and supporter of Girondins
Author of the Declaration of the Rights of Women and the Female Citizen
Later beheaded
Charlotte Corday
Girondin who murdered Jean Paul Marat because of his radical writings that led to thousands of executions
"I have killed one man to save a hundred thousand."
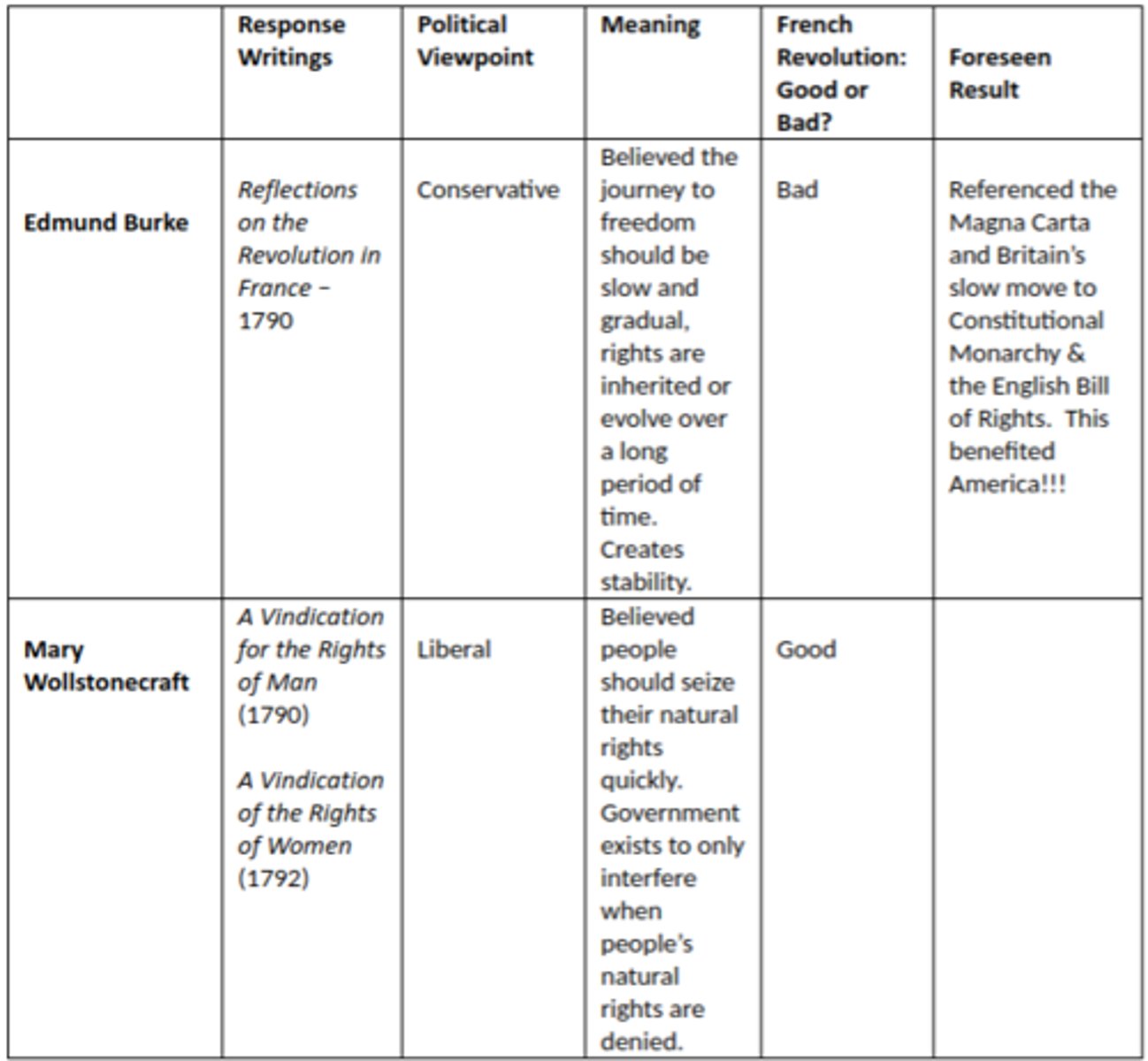
Edmund Burke
Molly Wollstonecroft