COA270: Exam II
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
random sampling
surface soil sampling
chooses random points within a plot of interest
sampled at a defined depth
transect sampling
surface soil samping
collection of samples in a single direction
Two Stage sampling
subdivision of a plot of interest into primary units
random or systematic sampling AFTER division
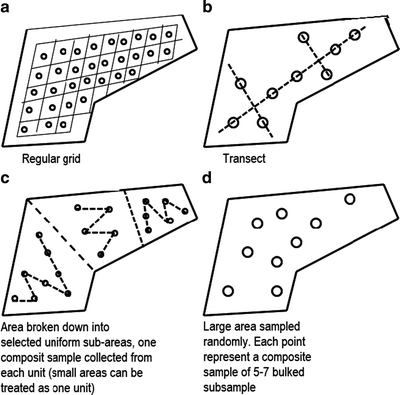
Grid Sampling
systematic sampling across regular intervals and fixed spacing
Air Rotary Drilling
subsurface soil sampling technique in unsaturated soil
→samples up to several hundred meters
→ large compressor forces air down drill pipe, out drill bit, and outside through the bore hole
→ overheating prevented by air through borehole and water/ surfactant injfection
Hollow stem Auger drilling
technique used to sample saturated subsurface soil
→ bore hole msut be kept open during sample collection
→ reaches depth up to 30 meters
→ Hollow tubes with rotating drill bit
→ reverse threaded casing hat pushes cutting up and out
Mud Rotary Drilling
technqiue to sample saturated subsurface soil sampling
depths >30 m
utilities drilling fluids to prevent borehole collapse
borehole mst be kept open during collecyion
lower colony counts
not normally exposed to atmosphere
expensive to repeat
contaimation prevention is necessary for subfurcation samples because they
Plating
culture-based anaylsis of bacteria
_> utilizes different mediums (PYTG, TSA, BEA) to select for speific populations
→ allows for enumeration
Direct counts
culture based anaylysis of bacteria
determines total bacterial number present
→ does not determine the number of populations
Air dry Sample
Filter soil through 2mm mesh to remove large drbis
store remaining sample at 4C for up to 21 days
soil sample anaylsis processess
/mass of soil
units for purified dna
Coumminity DNA Anaylsis of Bacteria
anaylsis techeniue that determines populations present an genetic potential
→ DNA extracted in situ, lysis occurs releasing DNA for extraction, cell debris, and soil particles precipitated out via centrifugation
→ DNA purification process: supernatant is transported to another container, DNA precipitated out
→ quantification UV spectroscopy and fluorometry
→ relate total extracted DNA to number of microbes in sample
lysis methodology
combintion of physical and chemical means to cause lysis
phscial: bead beating, sonification, freeze thaw cycle
chemical: enzymes(lysozyme)
Soil washing metholody
method for isolating fungal hyphae and spores
→ saturate small soil sample
→ Aggregates are teased up with fine jet of water
→ Heavier particles sediment, fine particles decant our
→ Heavy particles spread on thin film of water and observed under dissecting microscope
→ Observed hyphae extracted
storage of soil sampels with fungi
samples are stored in sterile boxes containing sieves of varying grade sizes
sample is then washed vigorously for 2 minutes
Each wash is plated onto media and results are recorded
hyphae are retained by sieves so growth on media is dormant spores from samples
sewage sludge
soil or marine sediments contaminated with wastewater or sludge
used to determine pathogen risk in environment
Viruses Sampling
collect sewage sludge and reduce pH to 3.5 by adding Hcl or AlCl3
Sludge is centrigued and soils extracted
resuspended in netural beef extraction to detach viruses
beef extract removes by flocculation of proteins and the remaning viruses are neturalized
lower
concentrations of microbes in water is ___ compared to soil
eluation
step for processing water samples
→ removal of virus from collection filter
→ virus absorption elutation filters can be electronegative or electroposotiive to attrach viruses
hose lines and pumps
tools used in collection of water samples
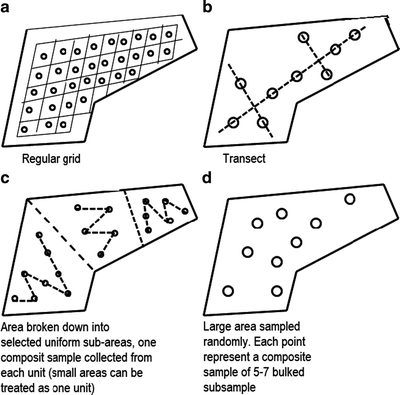
Membrane filtration
processing water samples to find bacteria
collection and concentration of bacteria via filter
cultured after completion
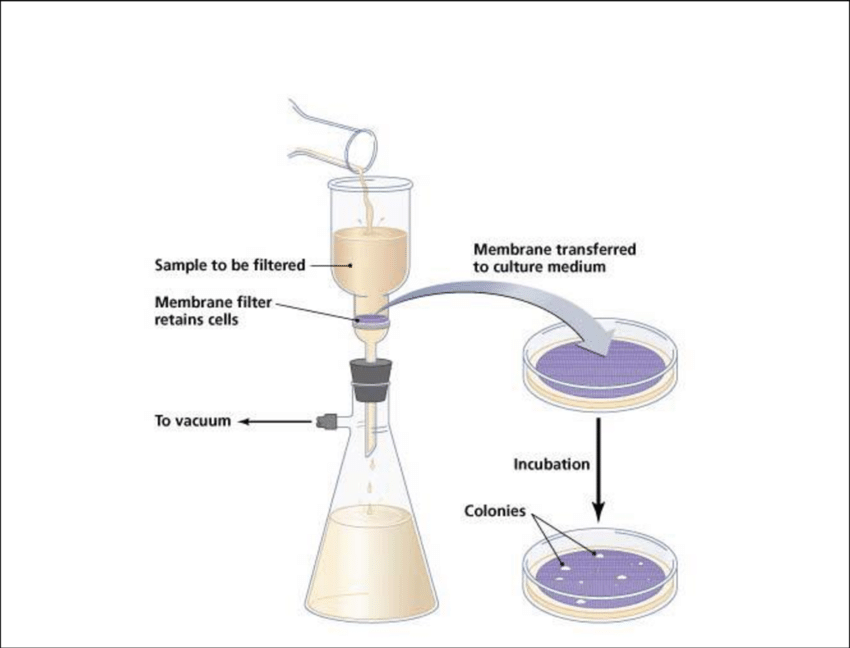
most probably number
processing water samples for bacteria
serial dilution at different aliquot levels
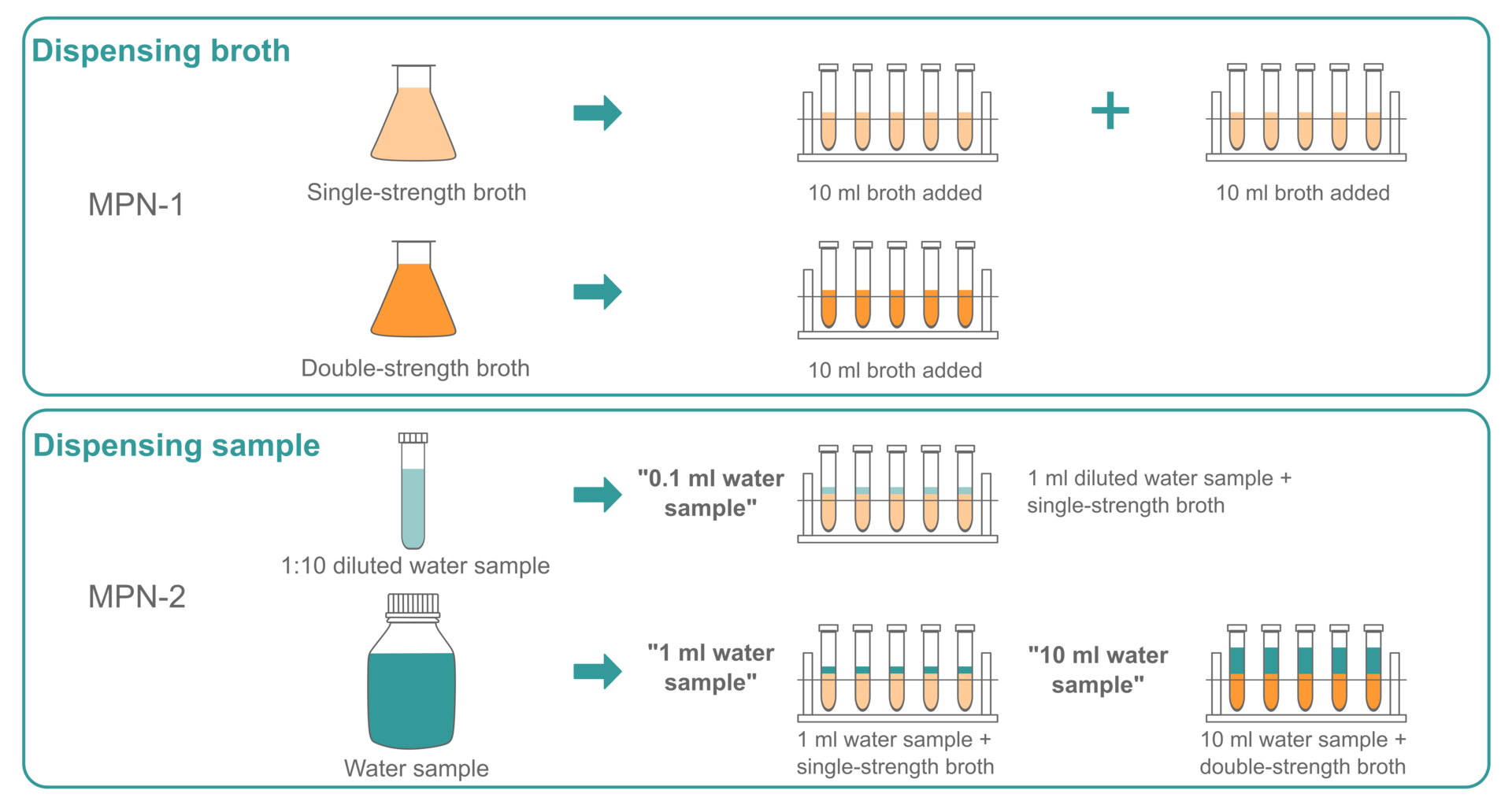
Cartridge filters
used to detect protozoan parasites in water samples
Eluation buffer is added after filtration, and the solution is agitated for 5 minutes ona shaler to remove cysts and oocysts
protozoan are pelleted by centrifugation and resuspended in buffer
size exclusion
protozoans are filtred by
foam filters
for proecessing water samples to find prpotozoan parasites
eluavation buffer added after filtration, protozoan are squeezed out with plunger
immunomagentic seperation of protozoan from partiuclate matter
stained with flursecent mono clonal antibodies
Impingement
collecting air samples; trapping airborne particles in a liquid matrix
seperate by flow rate
Impaction
air samples; forced deposition of airbones particlesonto a solid surface
size of particles and flow rate
increasing impacation potenital of airbone particles determines
centrifugation
Mechanically forced deposotion of air bone particles through intertial and gravitonal forces
FIltration
trapping of airbones particles through size exusions
→ uses vacuum and filters that can differ in pore size and flow rate
Deposition
collection of airborne particles through natural deposition forces (gravitational setting)
-< low sampling efficiency
Resolution
smallest distance between two points that are viewed
resolving power
ability to distinguish two points
Magnification
ability to enlarge the aparent size of an image
contrast
ability to distinguish an object from its surrodnings
bright field microscopy
type of microscopy where light is transmitted THROUGH specimen, producing an image
→ increases in mangfication and morphology requires staining
→ used to exam cell morphology
Positive(Basic) Stain
type of simple stained used in bright field microscopy
uses a single dye to stain cells
background is left unstained
used for determinig cell size, morphology, number present
ex: Methylene Blue
Negative(Acidic) Stain
simple stain used in bright field micrscopy
→ single dye to stain BACKGROUND
→ cells repel dye (H+) and are left unstained
→ silluthote apperance
differential stains
type of stain used in bright field microscopy
two dyes (primary and counterstain)
used to determine Gram -/ Gram + bacteria
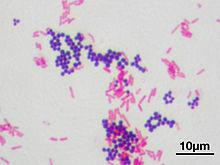
pink
stain color of gram - bacteria
purple
stain color of gram + bacteria
Dark field microscopy
type of mircoscopy
bright speciment is seen within a dark background, increases contrast of transprent organisms
determines bacterial and protozoan mobility as well as microcolony grwoth
used to visuzlie alive, unfixed cells
Phase control microscopy
type of microscopy
internal cell components are distinguished from surrodning background
differing densities of cell compenets interacted dirrectly with light → changing how they are going to be viewed on the scope
increases contrast
wet mount
suspended cells are placed between a glass slide and cover slip
cells are living and locomotion can be observed
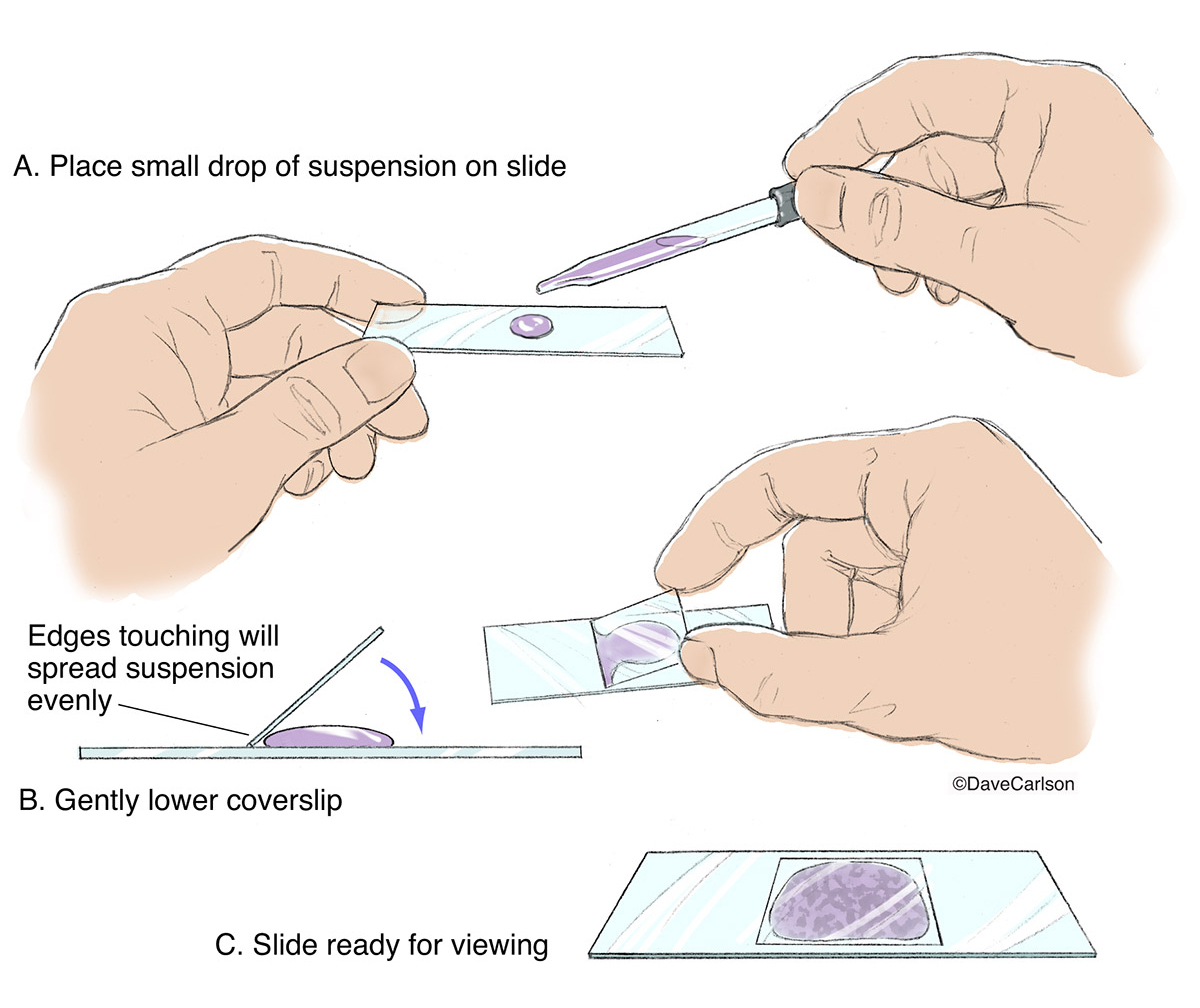
Smears
preperation for microscopy
tecnqhie better for determing cell morphology and cellualr compoents using staining
cells are air dried, heat fixed and stained→cells are killed
Buried slide tehcnqiue
soil samples for micrscopy
galss slide is inserted into sample, slide is incubated in the sample for a set time
slide is removed with least disturbance possible and observed under micrscope
Pedoscope technque
soil sample for microscopy
varation of th buired slide techniqe that contains opitcally flate capillary tubes
fluoresecent microscopy
type of light micrscopy that uses UV and a combo of fluroscent dyhes
=> Direct Count: provides number of total cells present
→ estimating bio mass
fluorescent immunolabeling
type of labeling where microbes are detected through fluorescently labled antibodies
observed by fluorescent microscopy
Flouresent in stiu hybridization
type of labeling where fluroresecently labeled nucleic acids target species DNA/ RNA sequences
universal probe
observed by fluoresent microscopy
Flow Cytometry
microscopic detection of cells perfomed as they pass a laser detector
measures flursen light emisison of cells
separate target cells/ particles from others
Scanning electron microscopy
type of electron microscopy where electrons itneract with speciment surfaces
used to produce 3d images of surface characteristcs
Transmission electron microscopy
type of electron microscope where electrons pass through speciment
used for viewing fine internal cell stucture
electron microscopy
type of microcopy that utllzies electrons isntead of ligh to form images
electron beam is focused on the specimen with coiled electromagnets in a vaccum
50%
amount of atmospheric oxygen provided by aquatic microbes
1 meter
length light can penerate in areas with high particulates
photic zone
where light is able to peneratre
aphotic zone
where light does not reach
Neustone zone
zone of thin, gel like amtrix of biomolecules at the air water interface of sea surface
high UV radiation, nutirents and chmiecals
Pelagic zone
water column./ planktonic habitat subdidied by depth
epipelagic, meso pelagic, bathypelagic, abyssopelagic
Oceans Pealgic zones
profundal
lake pelagic zone with < 1% light peneration
limmetic
lake pelagic zone that recieives >= 1 light peneration
benthos zone
sediment habitat underlying the water column
epibiotic
microroganism attached to the surface of other organisms
→ Episilon proteobacteria and euglenozoans
Endobiotic
micrograonsim living with another organism’s tissues
ex: Virbri fischeri and Hawiian Bobtail squid
Bacterioplankton
arcahe/bacteria in pelagic zone
phototrophs, chemotrophs, and heterotophs
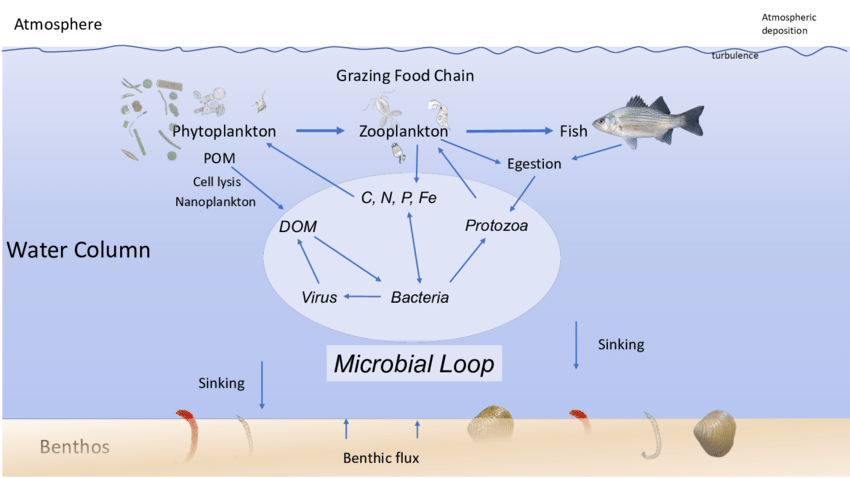
phytoplankton
photoautrophic microbes and eukayotes
(cyanobacteria and eurkaryotes)
Zooplankton
larger, hetertrophic microbes
ex: protozoan, copepods
Particulcate Organic Matter
large macromolecules (ex: polymers) that form cell structural components
prodicued by plankton
dissolved organic matter
smaller, soluble, matter that a rapidly taken up and metabolized by microbes(amino acids, carbohydrates)
→ passes thorugh filter w/ pore size of .7micro m
benthos
microbes readily grow in this oceanic zone due to nutrients and carbon sources becoming more plentiful from organic matter settlement or deposiiton from terrestial sources
Anaerobic methane oxidation
fermentation of carbon → organic acid and CO2→ methane (Ch4)→ Co2
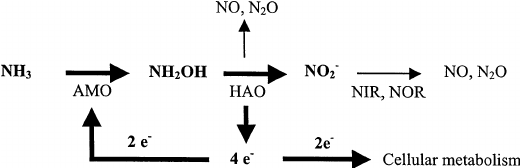
ammonia oxidation
ammonia produced by decomposer → oxidized as energy source
Nitrifciation
ammonia → nitrite → nitrate
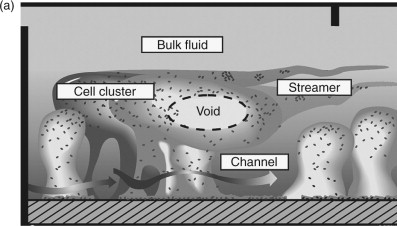
Biofilms
interfacial habit of a strong association of microbes with the surface through the prodction a polymer matrix
usally aqutic
role in water purification (removes DOM)
Reversible attachment
stage in biofilm formation
transitory physiochemical attraction from hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions
irreversible attachment
stage of bio film attached of biologically mediated stabilizaion reaction
→ attached bacteria sevrete extracellular polymers that forms strong chemical bridge with surface and allows addition of more cells
void spaces
part ot the biofilm structure that transports nutrients and icnrease biofilm surface area
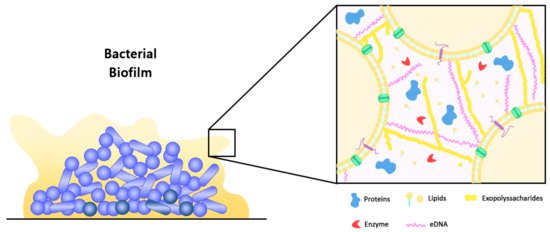
Extracellular polymer matrix
part of the biofilm structure that surrounds the cell
filters and collects essential nutrients
protection aganist enviromental stressors
barrier for antibiotic/disinfectant treaments
Microbial Mats
specialised type of biofilm that is arranged in colored stratified layers
found in extreme enviroments
self-sufficient due to use of many major biogeochemical cycles”
cycling of aerobic and anaerobic conditions partly by oxygenic photosynthesis and anaerobic sulfate reduction

inorganic nutrient availability
water temperature
turbidity of water
level of verticla mixing
enviromental factors that affect primary producers
high
coastal region production levels
POM/DOM from river outflows and upwelling
low
ocean production levels
due to lack of inorganic nutrients
DIssolved Organic matter
plantkon excretion, organic matter released during feeding and viral lysis of plankton
used in bacterioplankton biomass production (secodnary production) and the microbial loop
microbial loop
bacterioplankton remineralize DOM→ CO2 and nutrients → more primary production
Karenia brevis
dinoflagellate that produces toxic red tides in the gulf of mexico
viruses
most abundant biological entities in the ocean
limnology
study of freshwaer habitats
springs
running water that forms when subterranean water reaches surface
dominated by photosynthesis bacteria and algae
initially low heterotrophic activity, can increase with DOM additions
Gammaproteobacteria and Deltaproteobacteria
most abudant microbial phyla in soft bottom sediment communities
decreases
in soft bottom communities, thenumber of microbial cells ____ with depth
chemolithoautotrophs
in hard bottom ocean crusts, these microbes are in abudance
Rivers
running water
primary producer communities: biofilms, benthic sediment communities. aerobic/facultatively aerobic microbes
increase DOM = increase heterotrophic activity
Lakes
bodies of stagnant water
dominant microbial group: filamentous and epiphytic algae, phytoplankton dominate central area of lake
Oligotrophic lake
type of lake environment where high rates of primary production occur due to deeper light penetration
secondary production linked to amount of primary production
Eutrophic lake
type of lake where primary production is low; higher rates of secondary production
Zoophagus insidians
type of lake fungi that form fishing lines to catch rotifers
brackish waters
area in which salinity is between fresh and sal water
low primary production (high turbidity); higher heterotrophic and secdonary production