Ana - Tissue Types
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
List the four kinds of tissue
Epithelial, Muscle, Nervous, Connective
Extracellular matrix (aka ECM) Definition
Non-cellular part of tissue. It consists of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Produced largely by the tissue's cells
Epithelial tissue (definition and function)
The millions of cells that line the external and internal surfaces of the body. All epithelial tissue is nonvascular, receiving no direct blood supply. Epithelium functions as the lining of the body providing protection as well as areas of absorption and secretion.
Epithelial ECM - Called the basement membrane. Made up of two layers; the basal lamina which is superficial to the lamina reticularis.
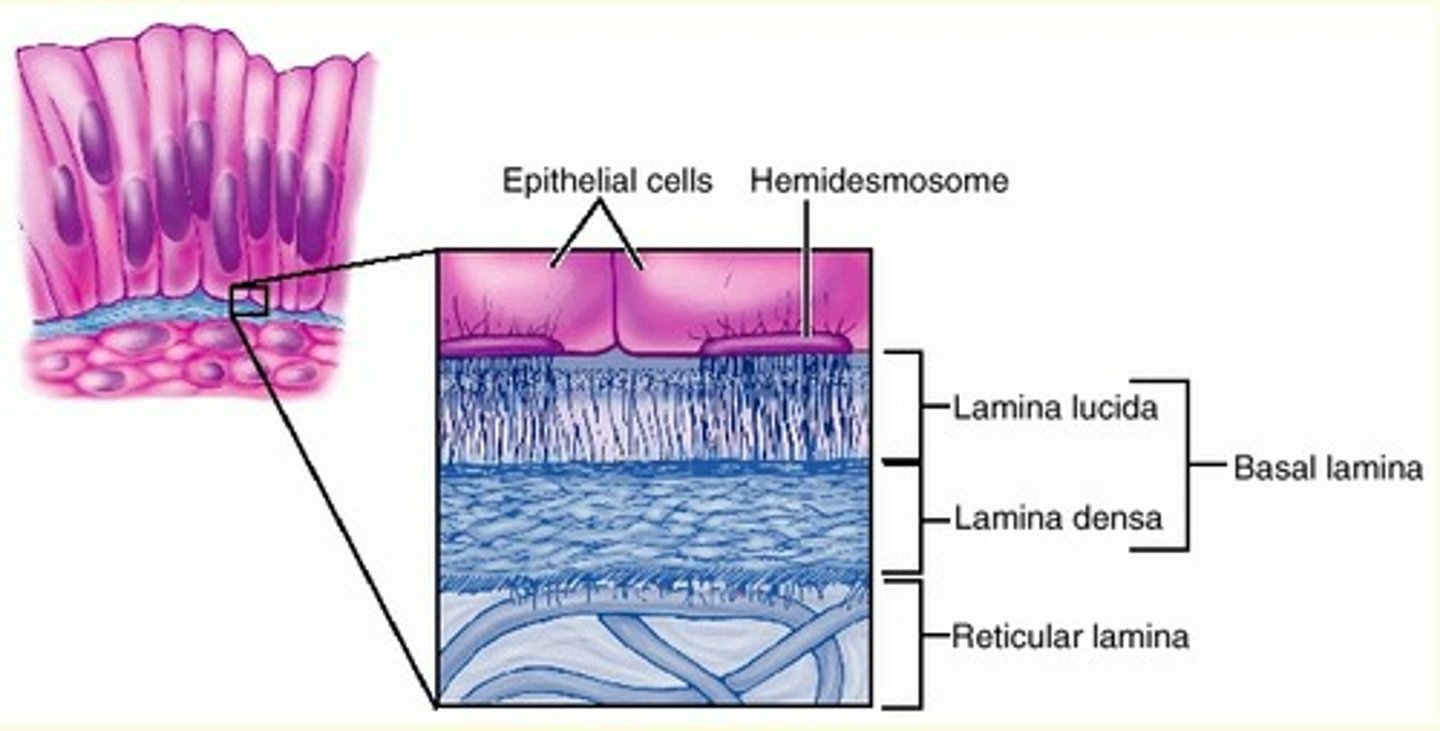
Name the types of epithelial tissue
Squamous, cuboidal, columnar. Can be simple or stratified. Also includes transitional epithelial and pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelial tissue.
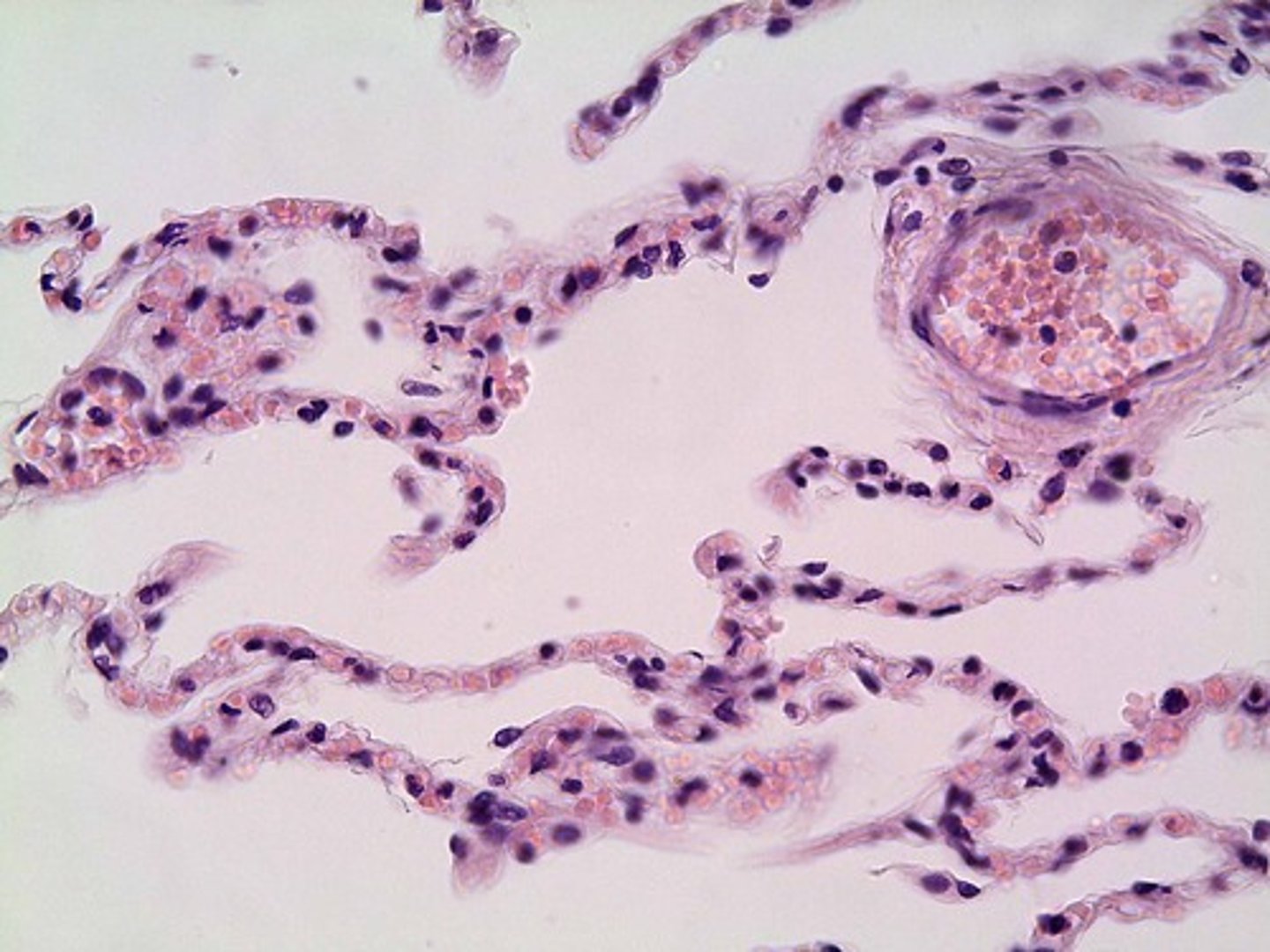
Simple squamous epithelial
location - Air sacs of lungs, lines the inside of heart and blood vessels.
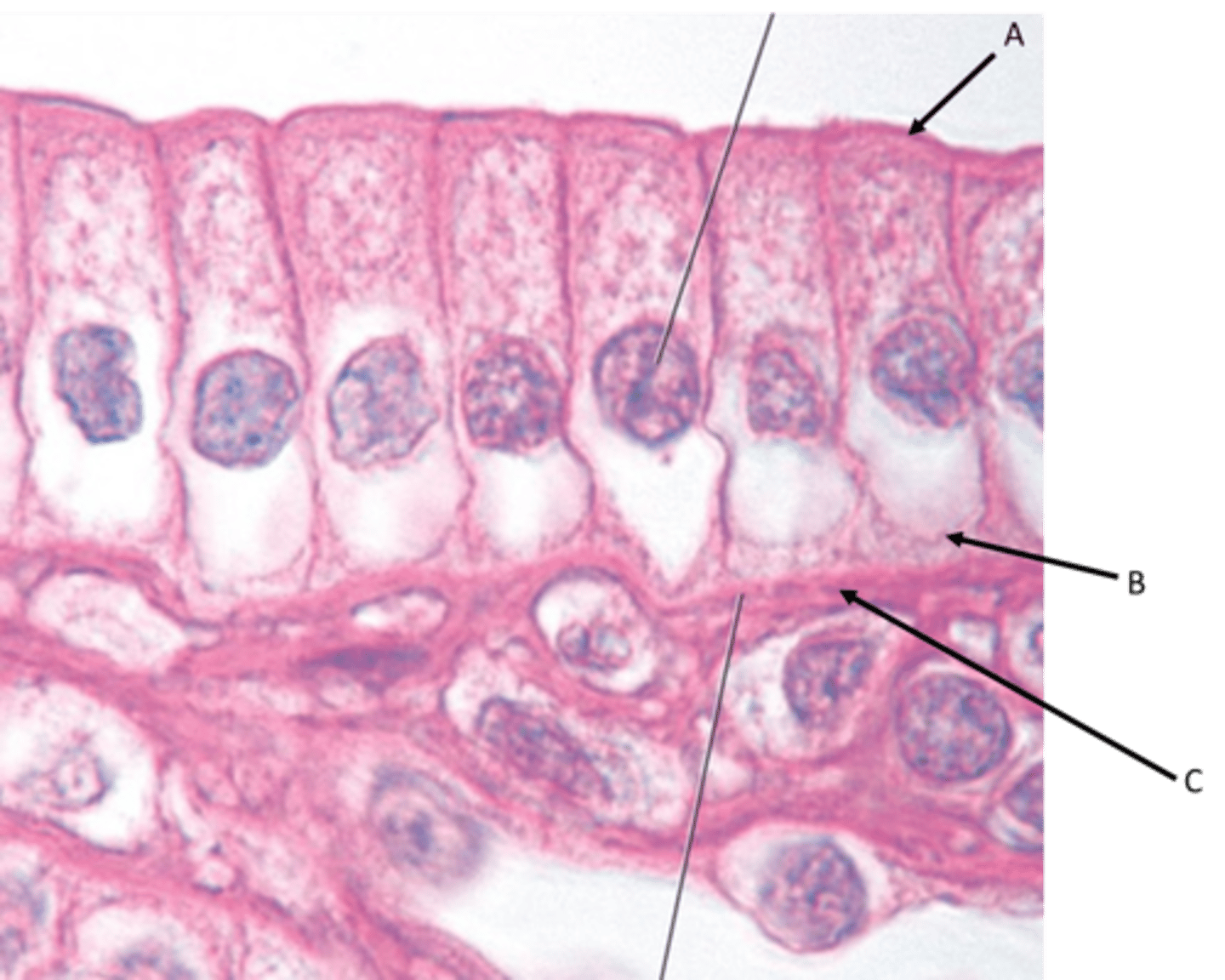
Simple columnar epithelium
Location - Lines most organs of the digestive tract including the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. Also lines the uterus.
Identify
A - Apical surface
B - Basal surface
C - Basement membrane
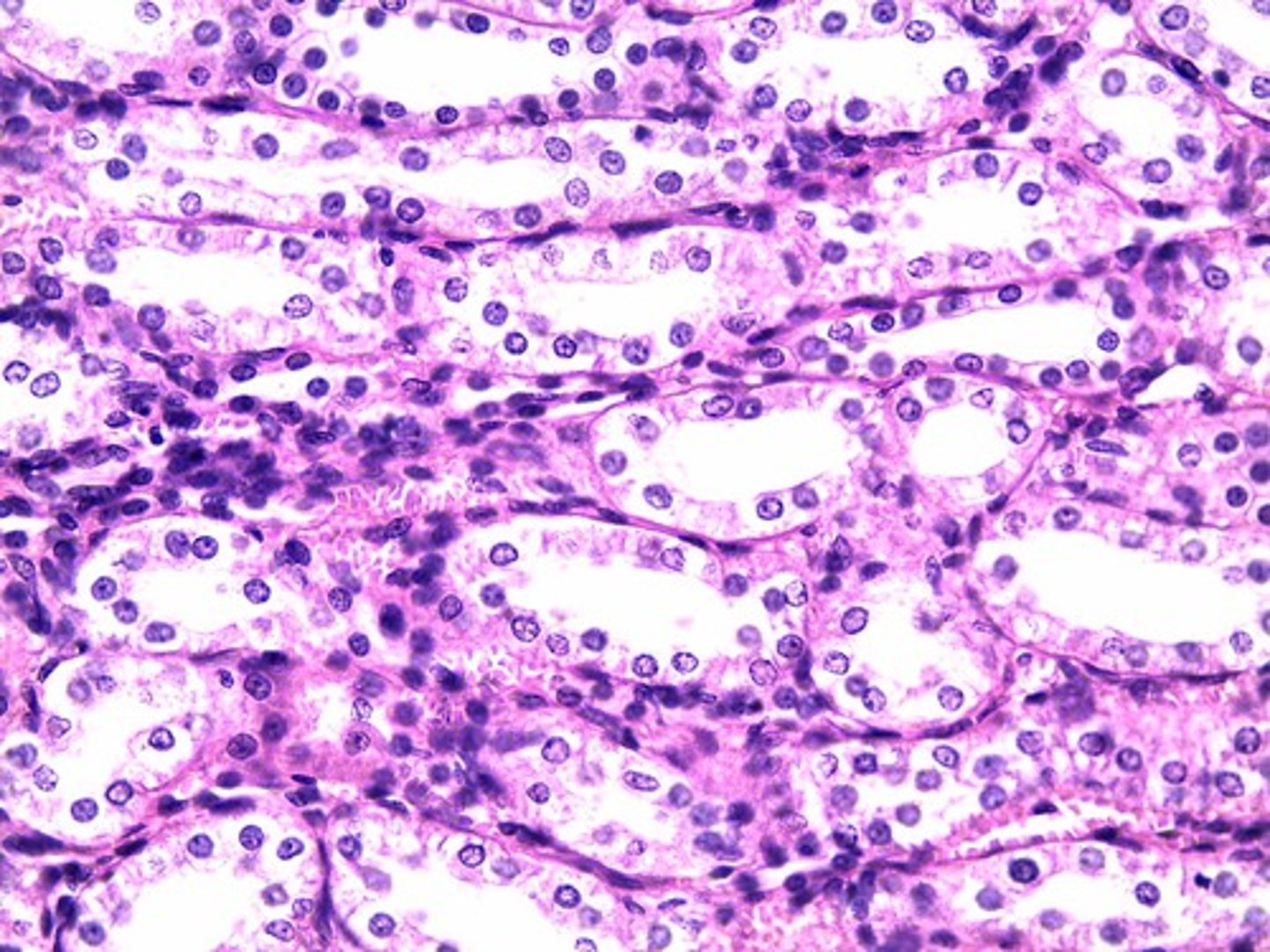
Simple cuboidal epithelium -
Location - Lines kidney tubules and the small ducts of many glands.
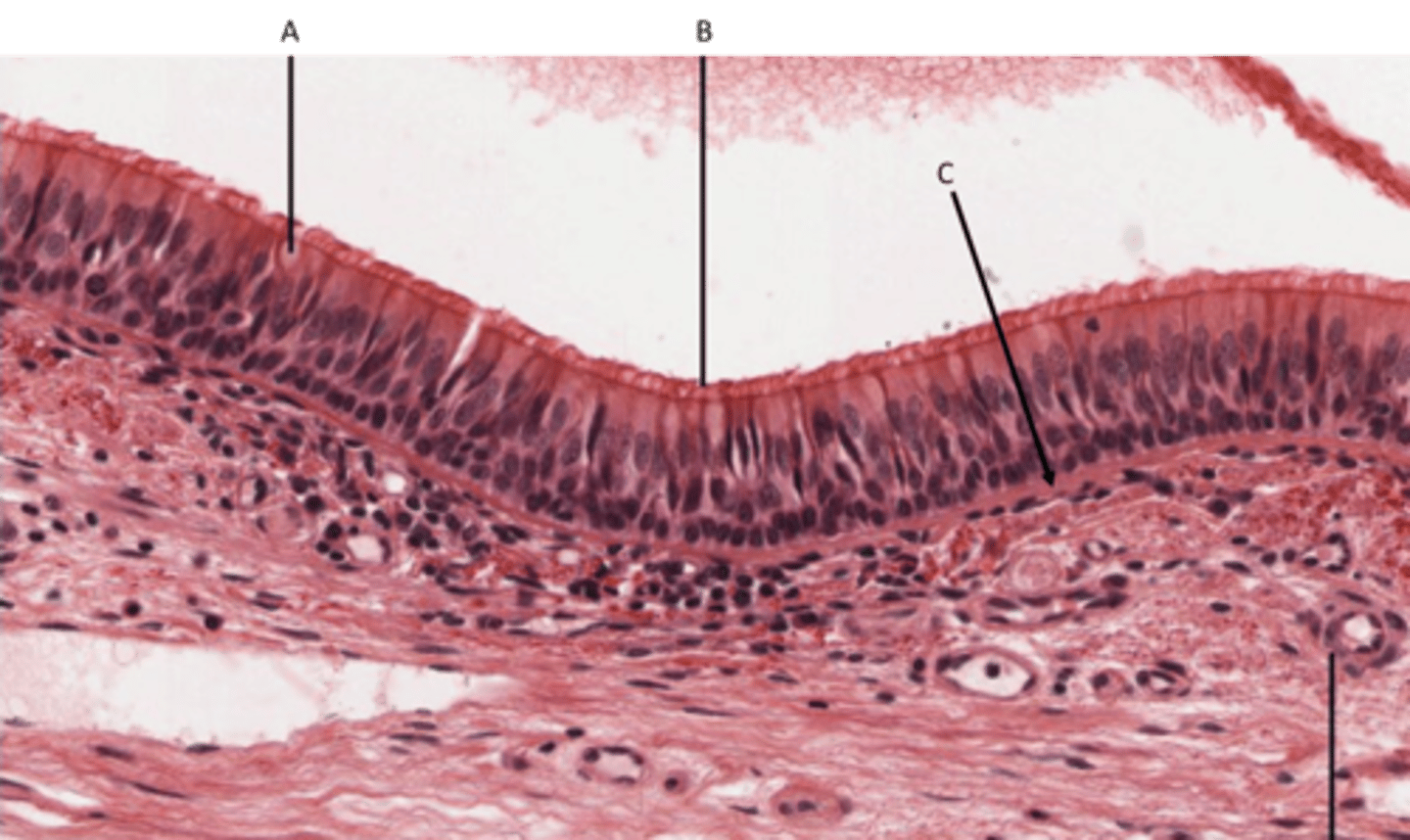
Ciliated Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
Location - Ciliated lines the trachea as well as the upper respiratory tract. Non-ciliated found in the membranous part of male vas deferens
Identify
A - Goblet cell
B - Cilia
C - Basement membrane
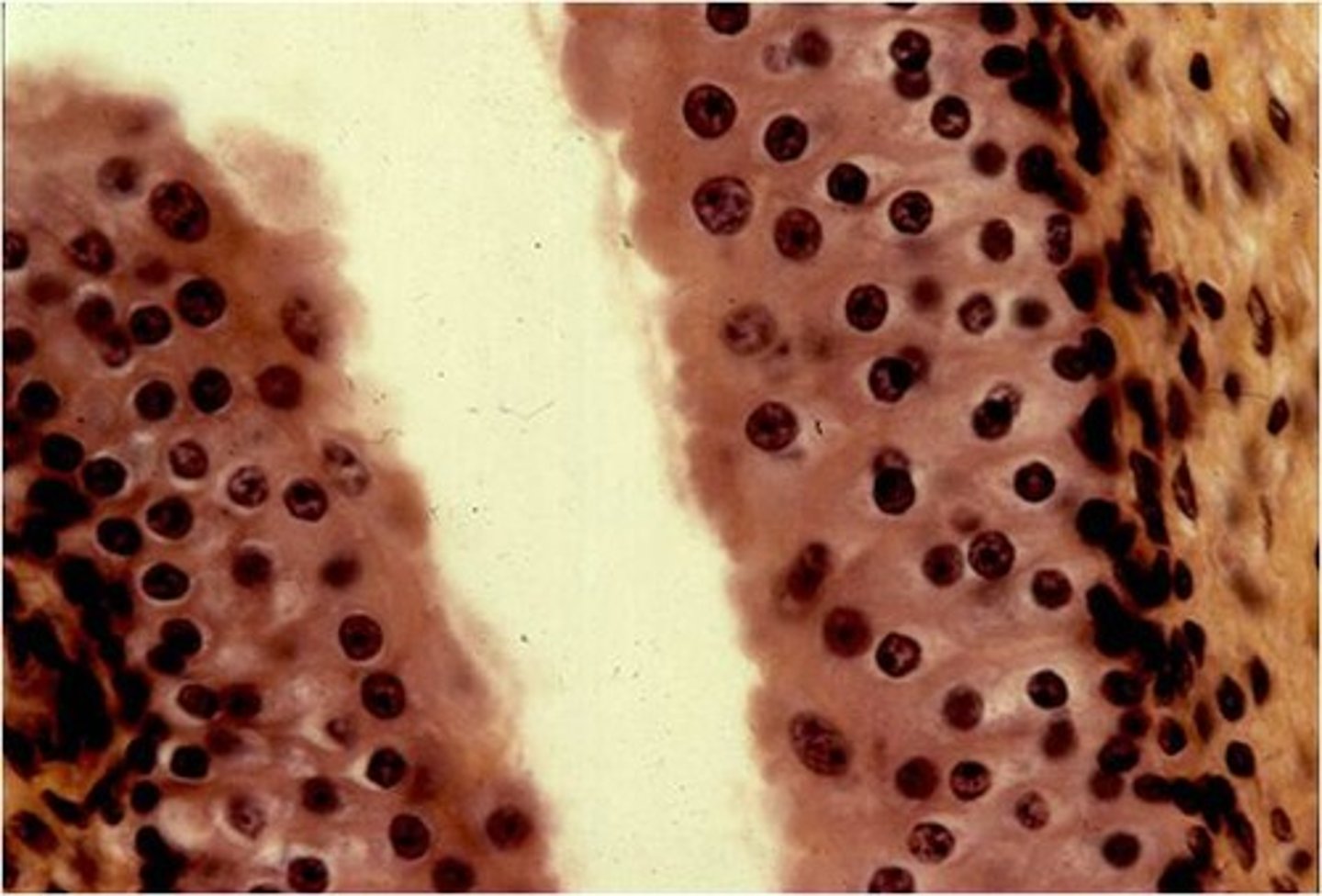
Transitional epithelium
Location - mucosal lining of your ureters, a portion of your urethra, and your urinary bladder.
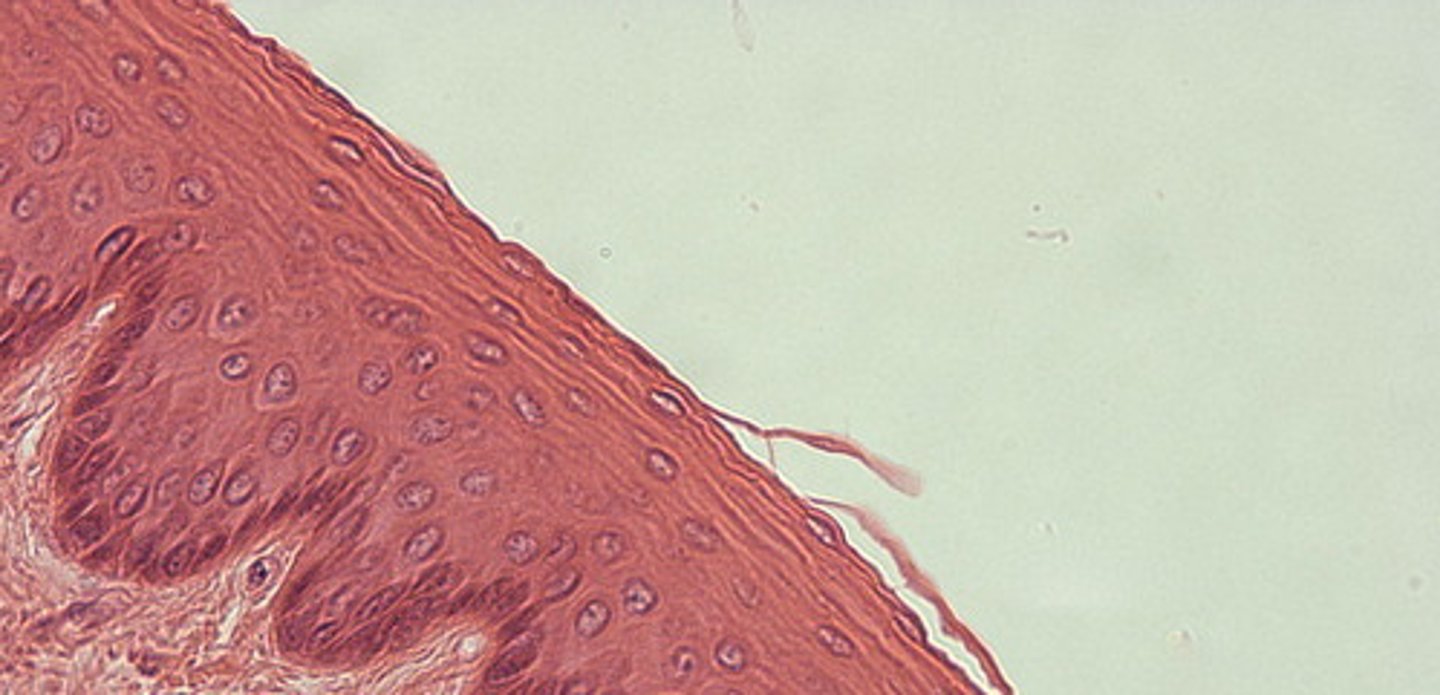
Stratified squamous epithelium - keratinized
Location - outer layer of skin
Stratified squamous epithelium - non keratinized
Location - vagina, mouth
Identify
Basement membrane
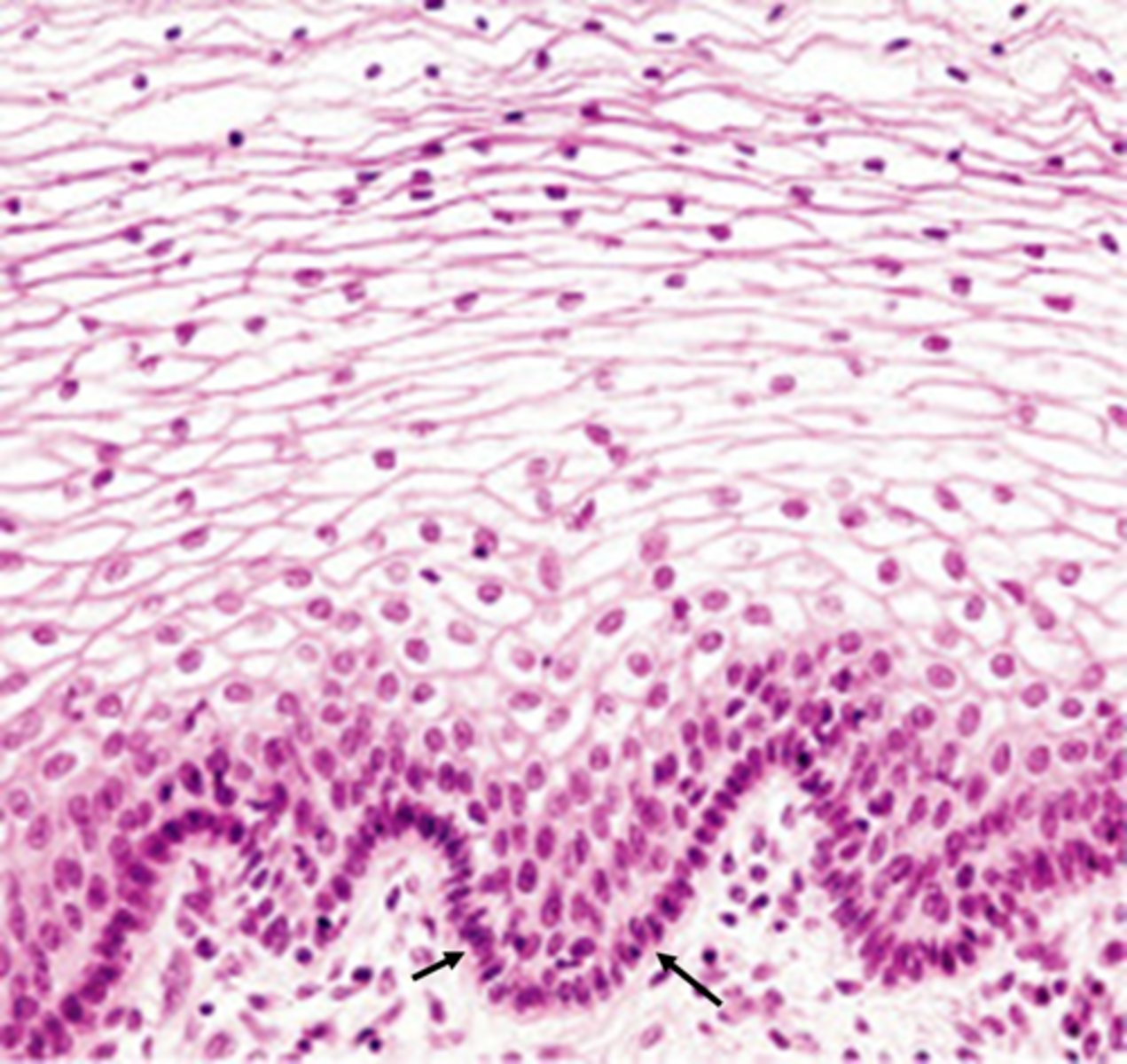
Connective tissue (definition and function)
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts
Types of connective tissue (aka CT)
Connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone and blood.
Connective tissue proper (varieties)
areolar, reticular, adipose, dense regular collagenous, dense irregular collagenous, dense elastic, hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage
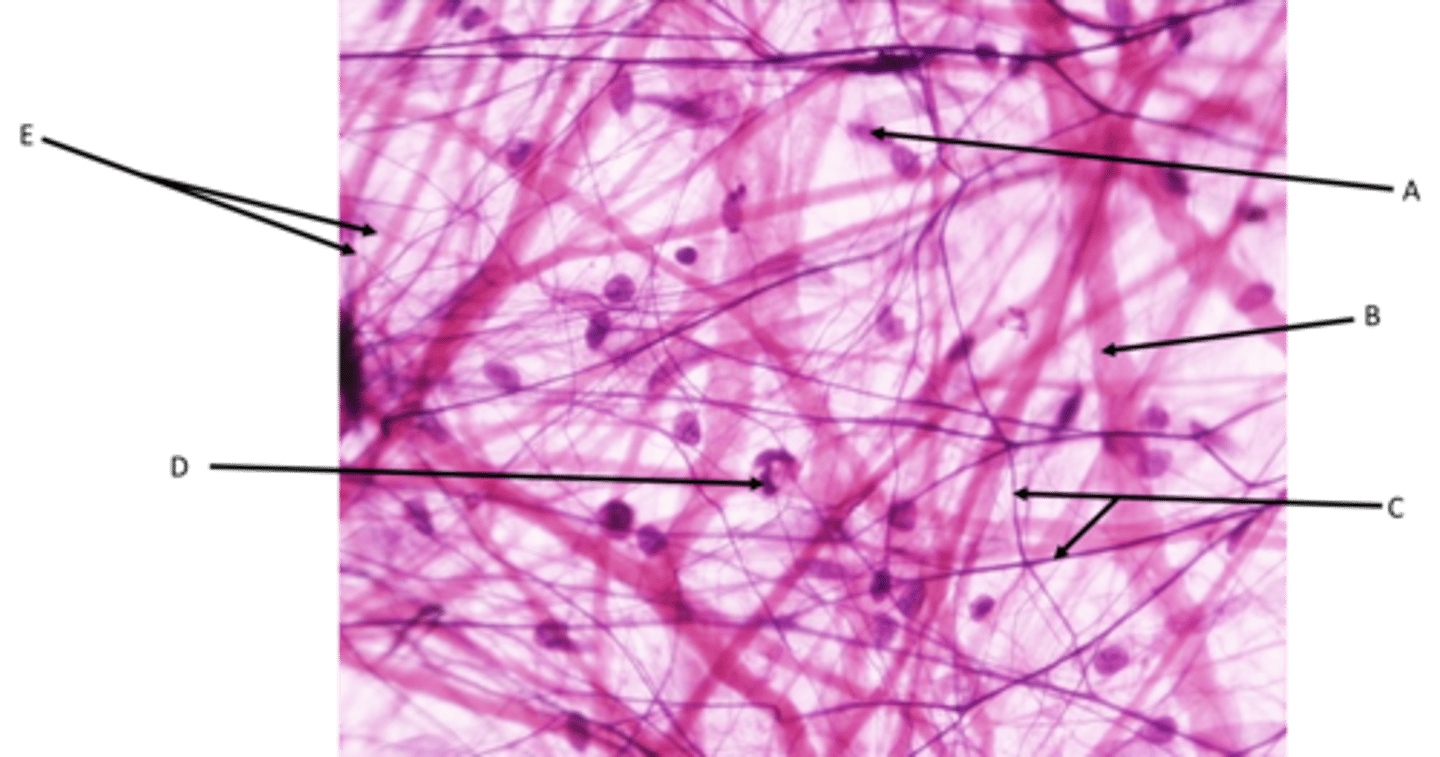
Areolar (Loose CT)
Function - Holds organs in place and attaches epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues. Almost all cells obtain their nutrients from and release their wastes into this connective tissue.
Location - Underneath nearly all epithelial tissue
Identify
A - Fibroblast cells
B - Collagen fibers
C - Elastic fibers
D - White blood cell
E - Reticular fibers
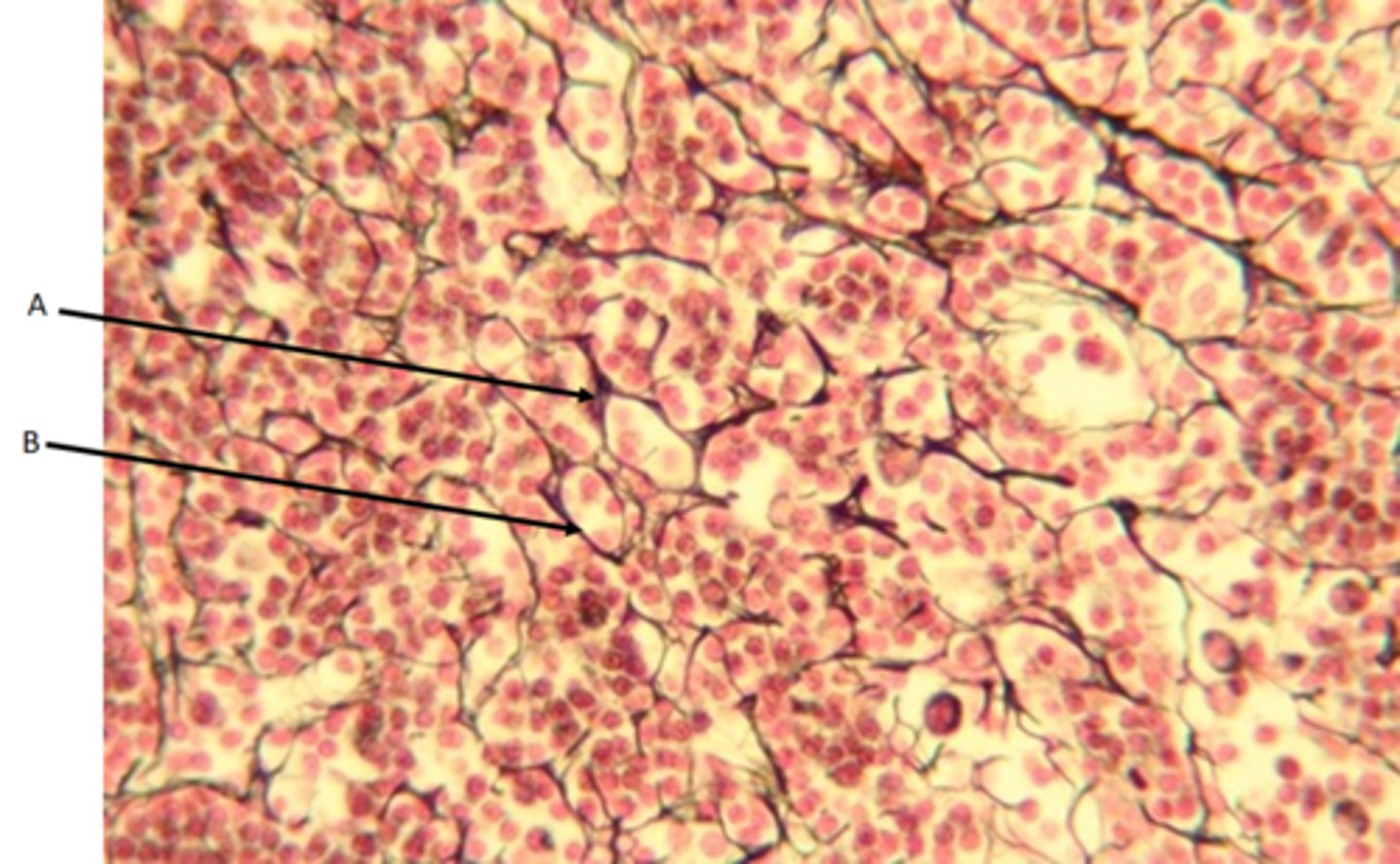
Reticular CT
Function - The abundant reticular fibers form a soft network to support organs
Location - Kidneys, lymph nodes, red bone marrow, and spleen
Identify
A - Fibroblast
B - Reticular fiber
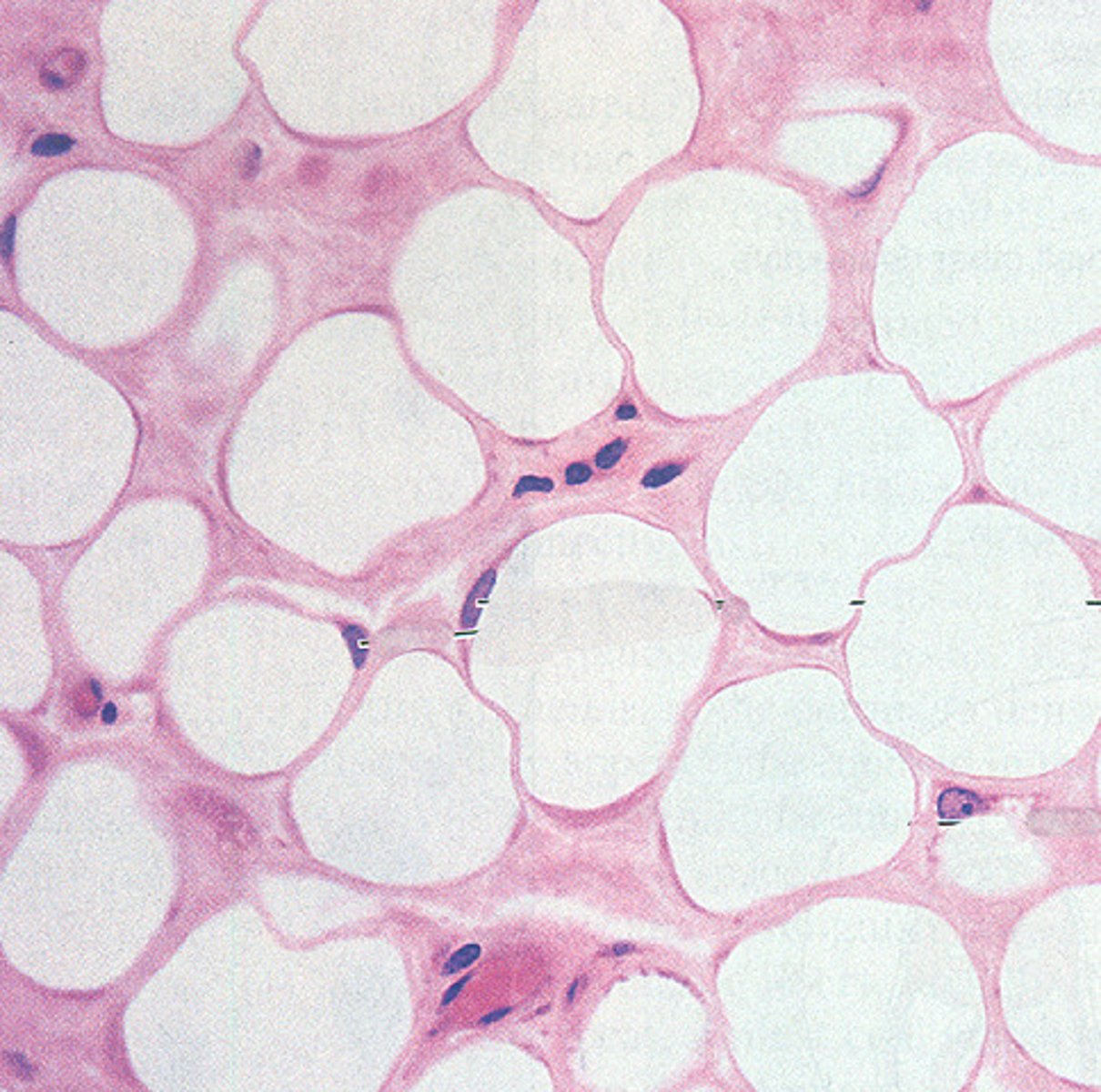
Adipose CT
Function - Acts as an insulating layer. It also has a protective function, providing mechanical protection ("padding") and support. Also functions in energy storage.
Location - Around major organs, subcutaneous layer of skin
Identify
Adipocyte
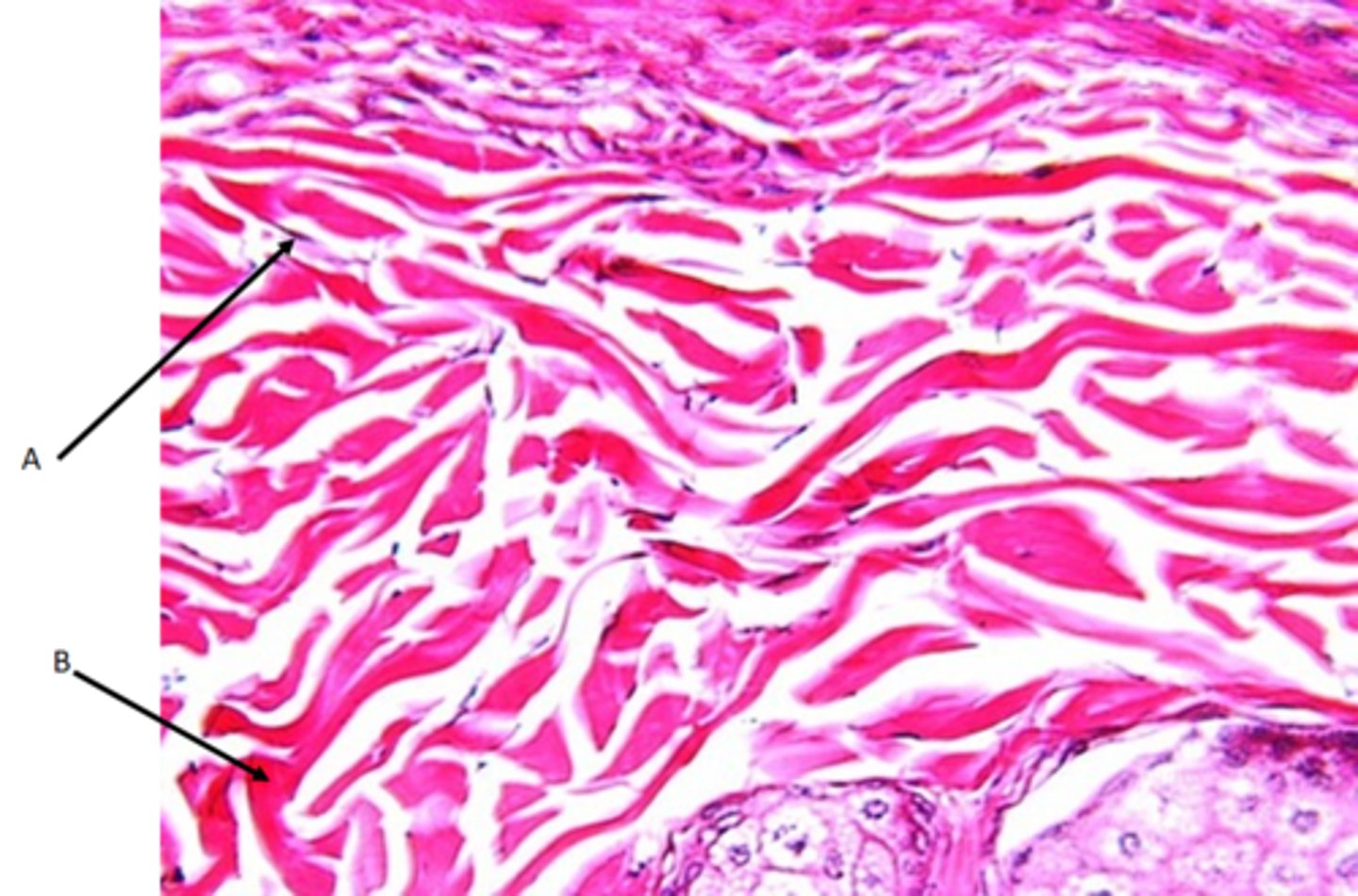
Dense regular collagenous CT
Function - Provides strength in a single plane
Location - Forms all tendons and ligaments. Coverings surrounding bone, cartilage, nerve fibers and muscle fibers (fascia).
Identify
A - Fibroblast cells
B - Collagen fibers
Dense irregular collagenous CT
Function - Provides strength in multiple planes
Location - forms the capsules that surround our internal organs such as the pericardium and the renal capsule.
Identify
A - Fibroblast cells
B - Collagen fibers
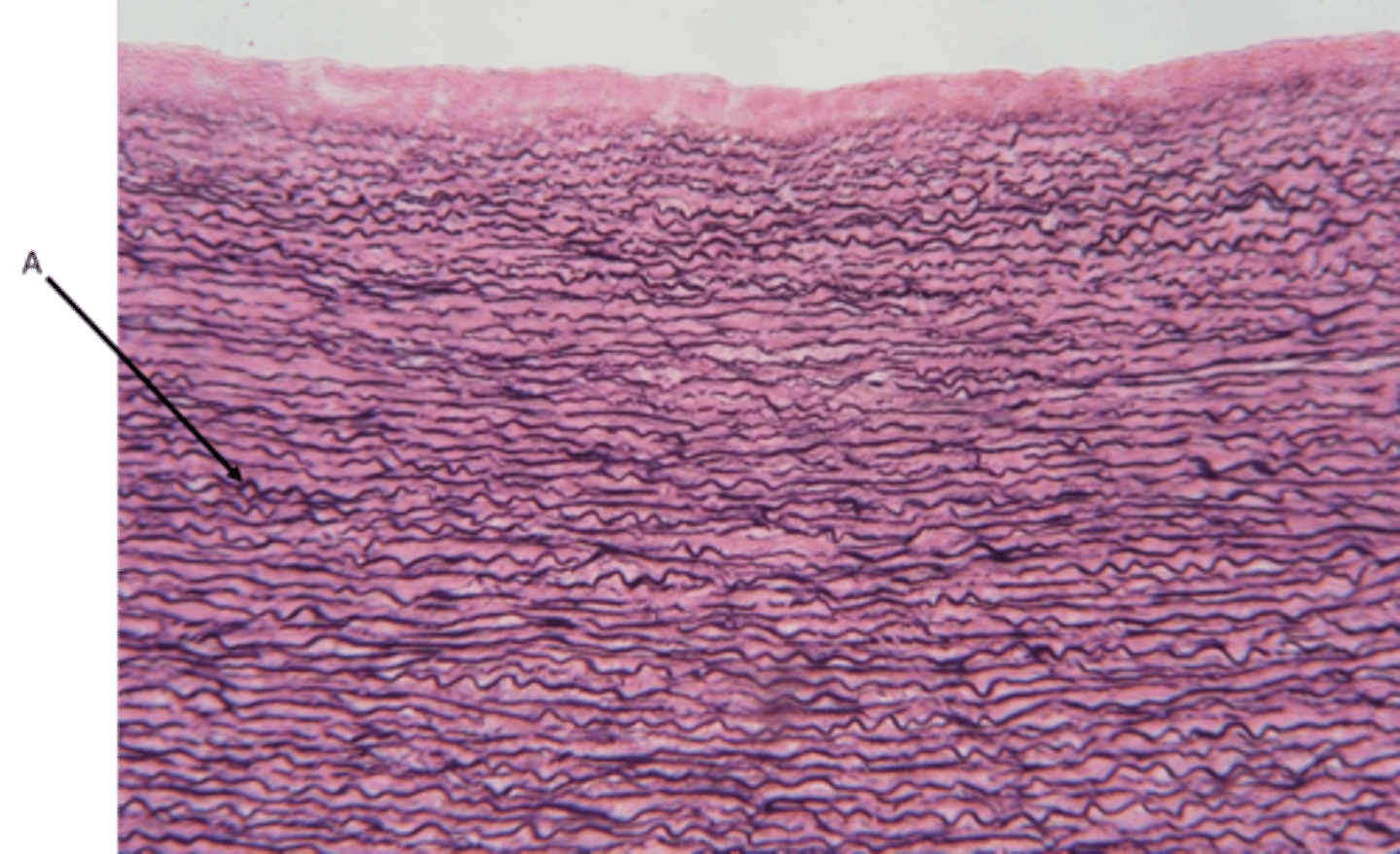
Elastic CT
Function - Allows for stretch and recoil
Location - Found in arge blood vessel like the aorta and some ligaments
Identify
A - Elastic fibers
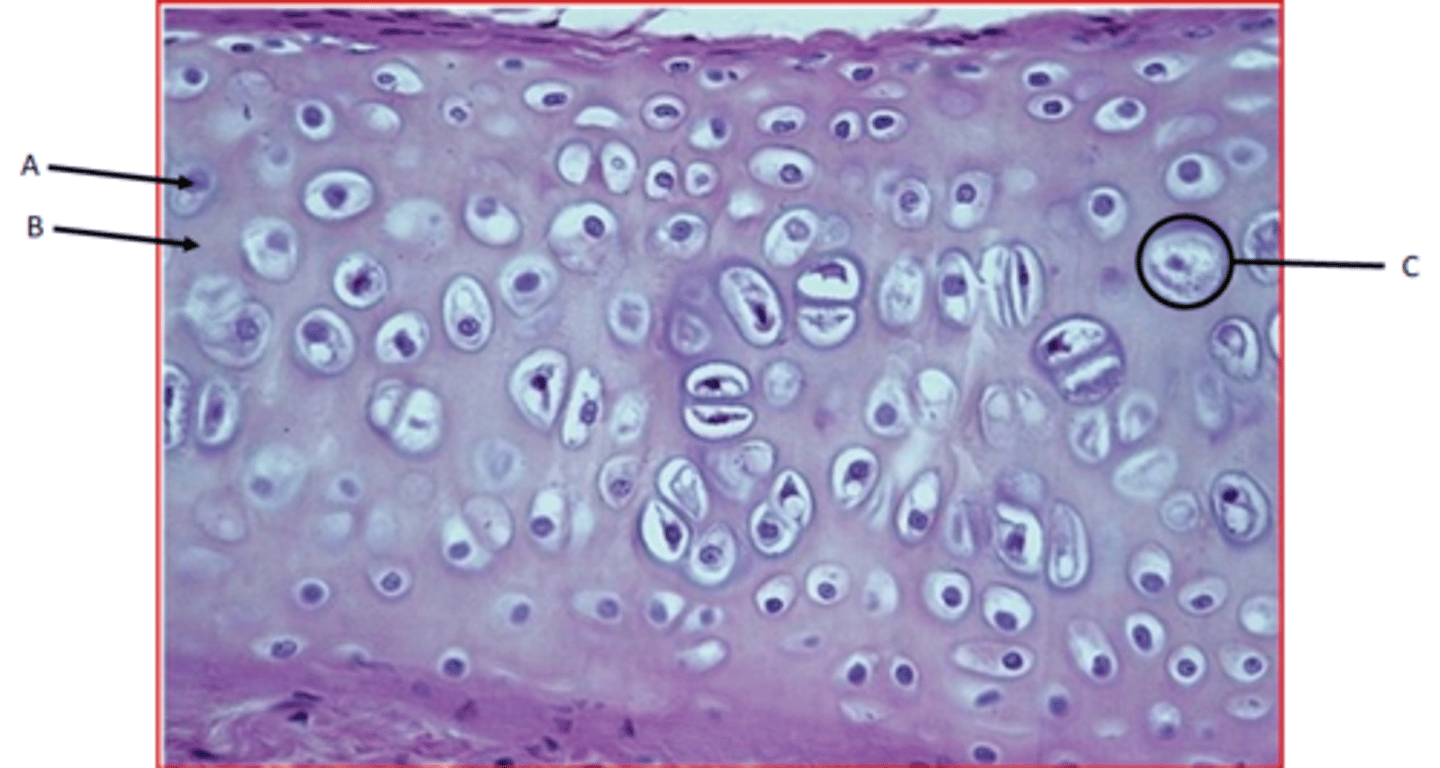
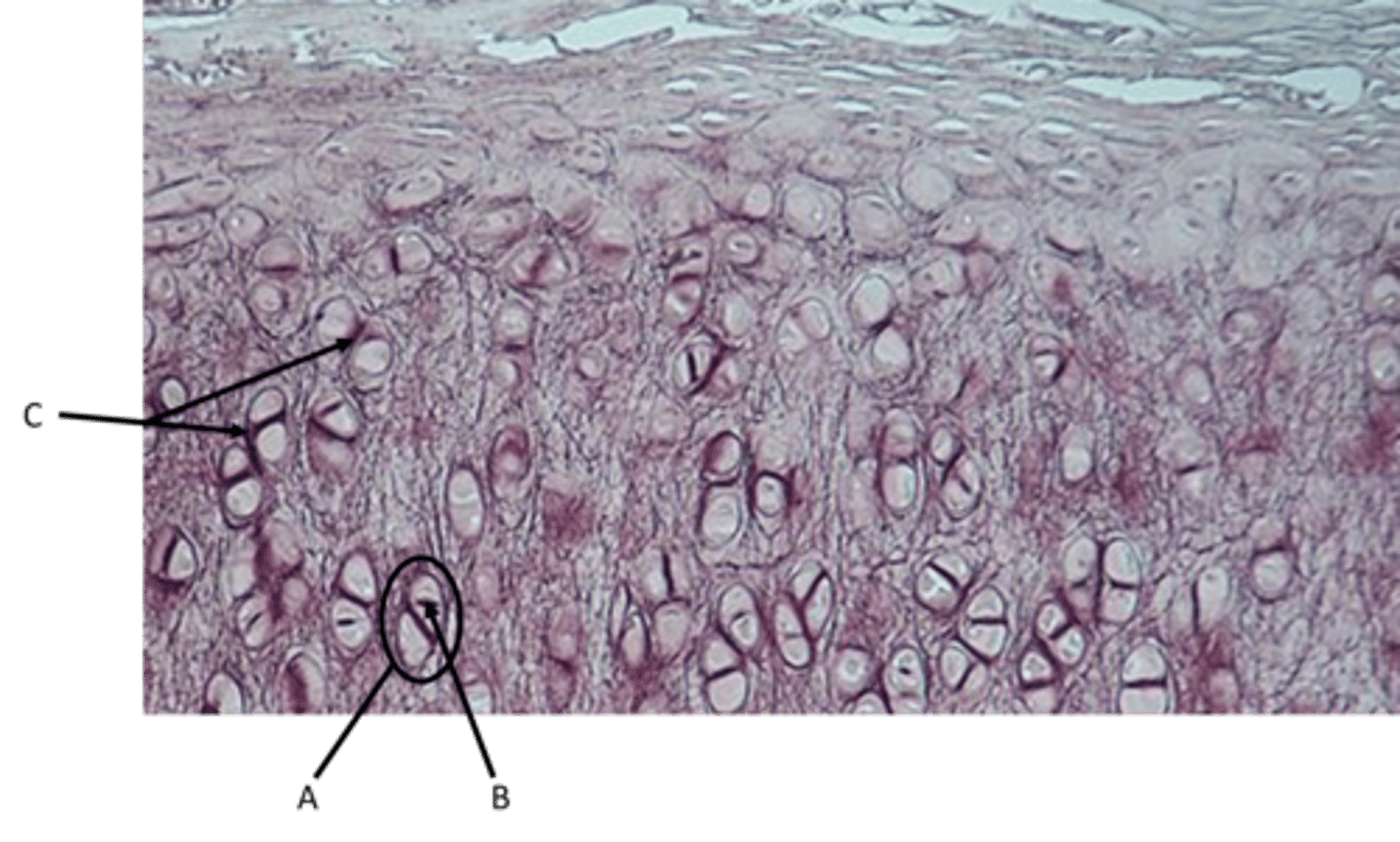
Hyaline cartilage
Function - Provides smooth surfaces, enabling tissues to move/slide easily over each other
Location - ends of long bones where they articulate with other bones, nose, ends of ribs where they meet the sternum
Identify
A - Chondrocyte
B - Ground substance
C - Lacunae
Fibrocartilage
Function - Resists deformation at great stress
Location - Vertebral discs and some bone-ligament junctions
Identify
A - Collagen fibers
B - Chondrocyte
C - Lacunae
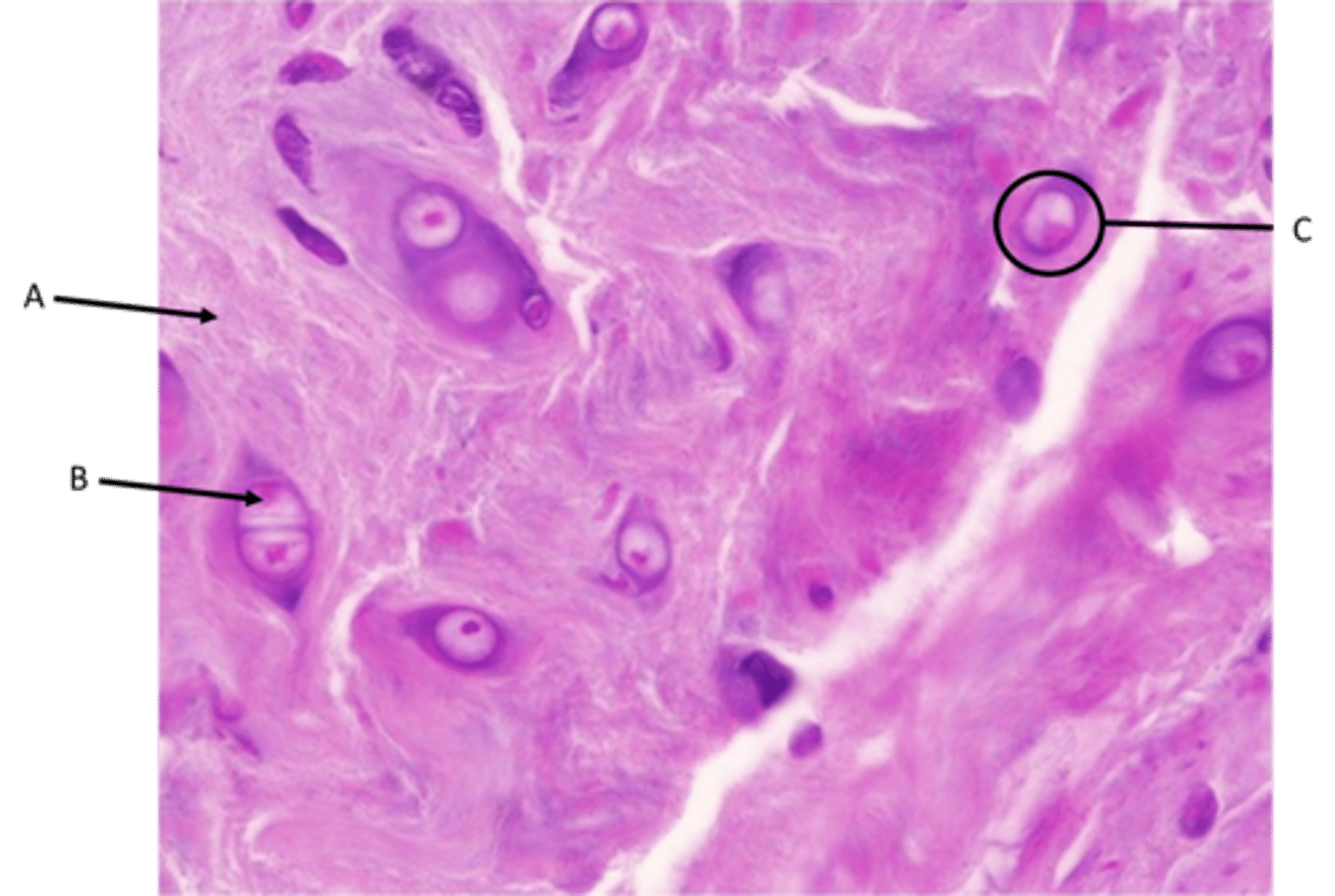
Elastic cartilage
Function - Structural support with flexibility
Location - External ear, end of nose
Identify
A - Lacunae
B - Chondrocyte
C - Elastic fibers
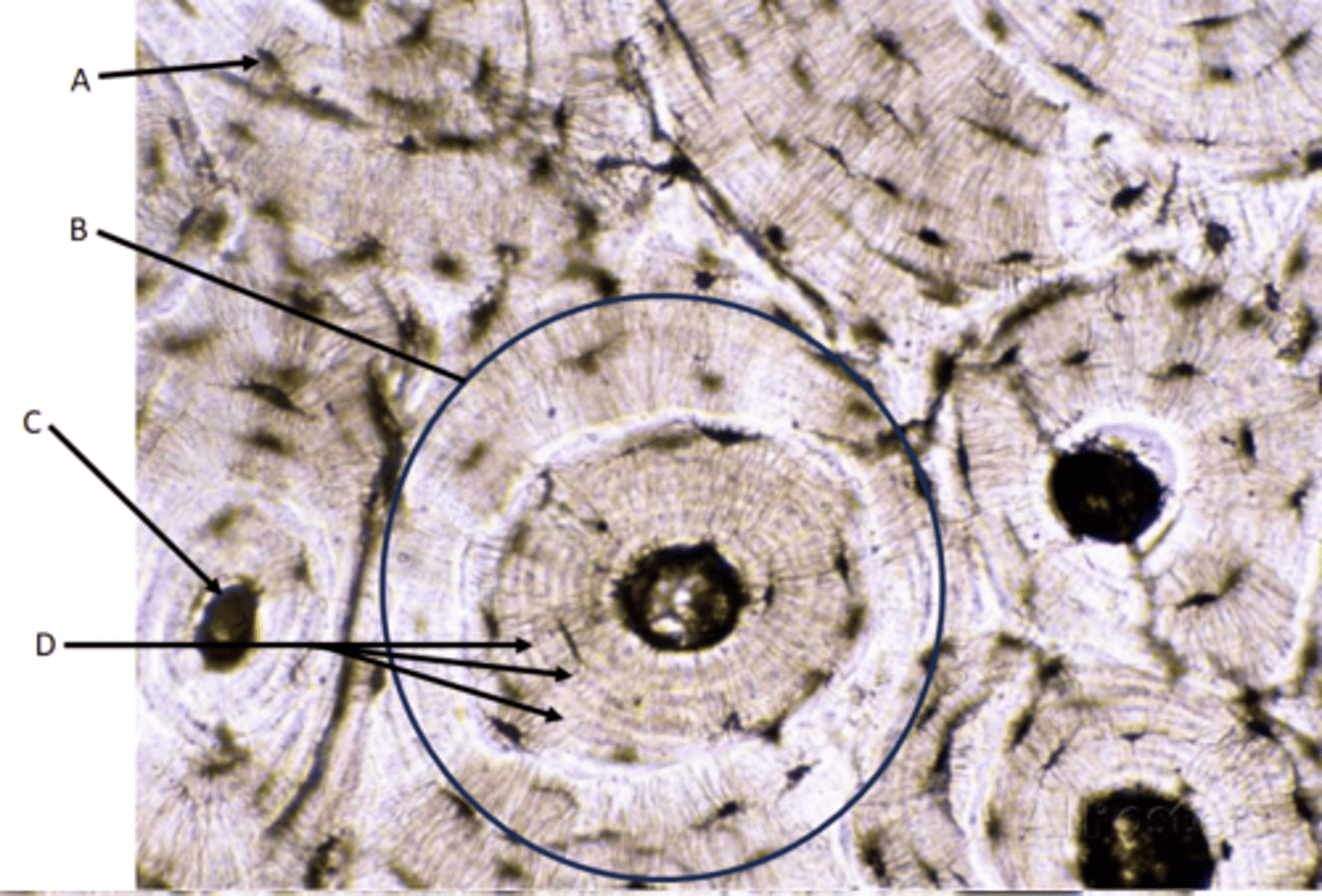
Bone tissue
Function - Attachment for muscles, movement, support, manufacture blood cells
Location - Bones
Identify
A - Lacunae
Osteocytes (found inside lacunae)
Canaliculi (small hair-like canals radiating from lacunae)
B - Osteon
C - Central canal (Haversian canal)
D - Concentric lamella
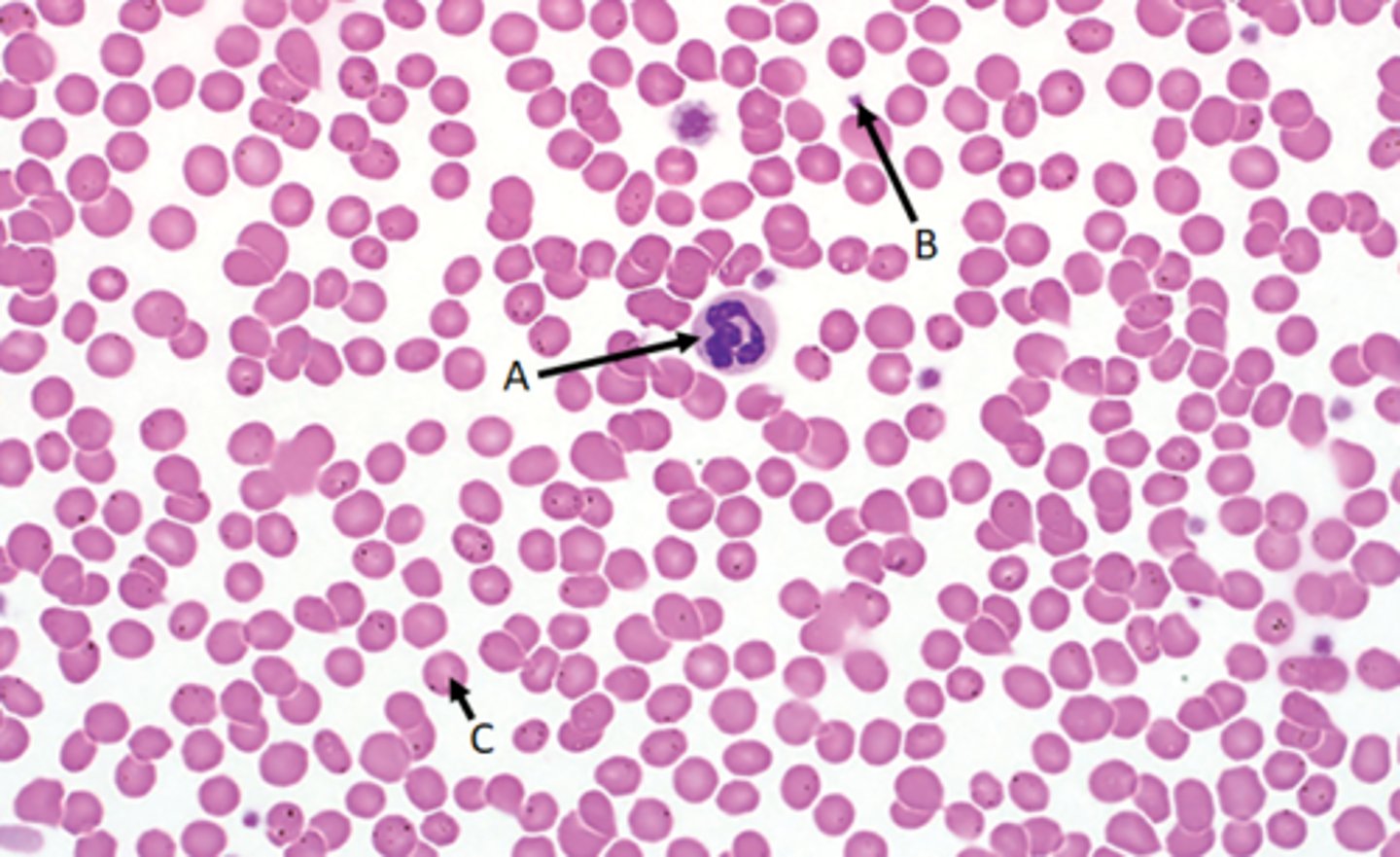
Blood tissue
Function - Transports nutrients and waste throughout the body
Location - Fluid of the cardiovascular system
Identify
A - Leukocytes
B - Thrombocytes
C - Erythrocytes
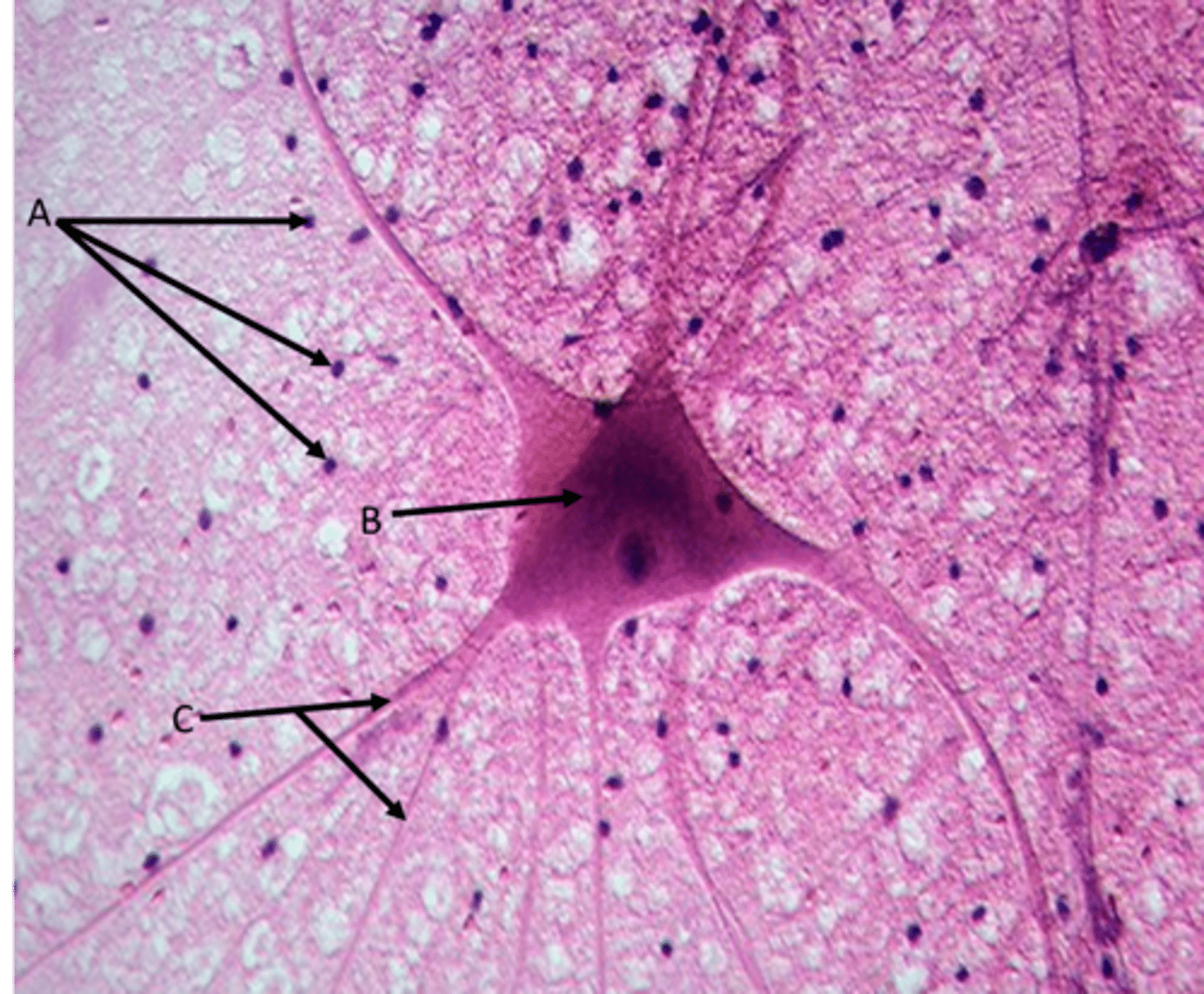
B - Neuron
Function - A cell that carries information through the nervous system
Identify
B - Cell body
C - Dendrites
A - Neuroglia
Function - Cells that support, insulate and protect neurons
Types of muscle tissue (image, function, location)
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
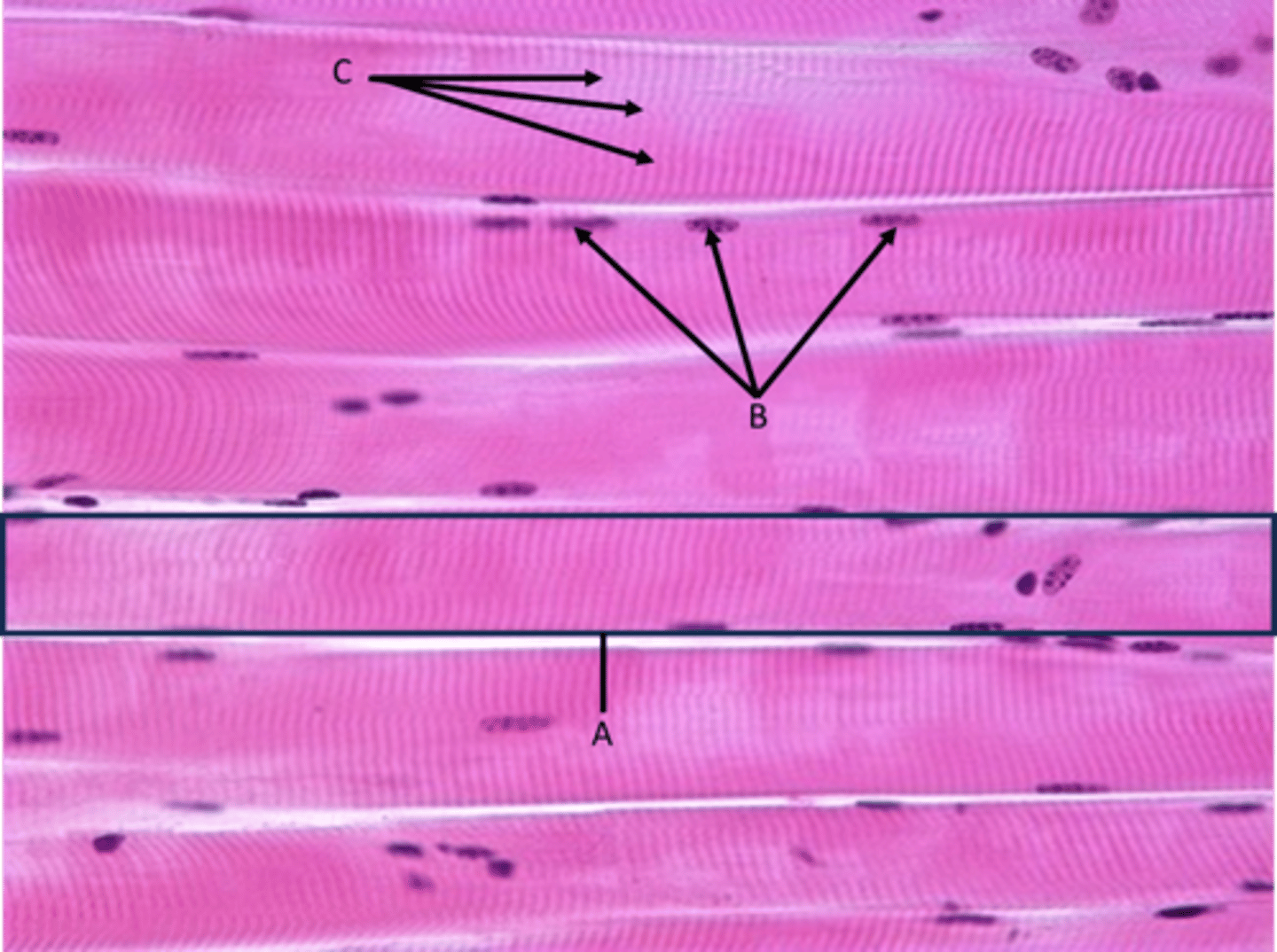
Skeletal muscle tissue
Function - Movement of skeleton, mostly voluntary
Identify
A - Myocyte (single muscle cell sometimes called muscle fiber)
B - Nuclei (myocytes are multinucleated)
C - Striations
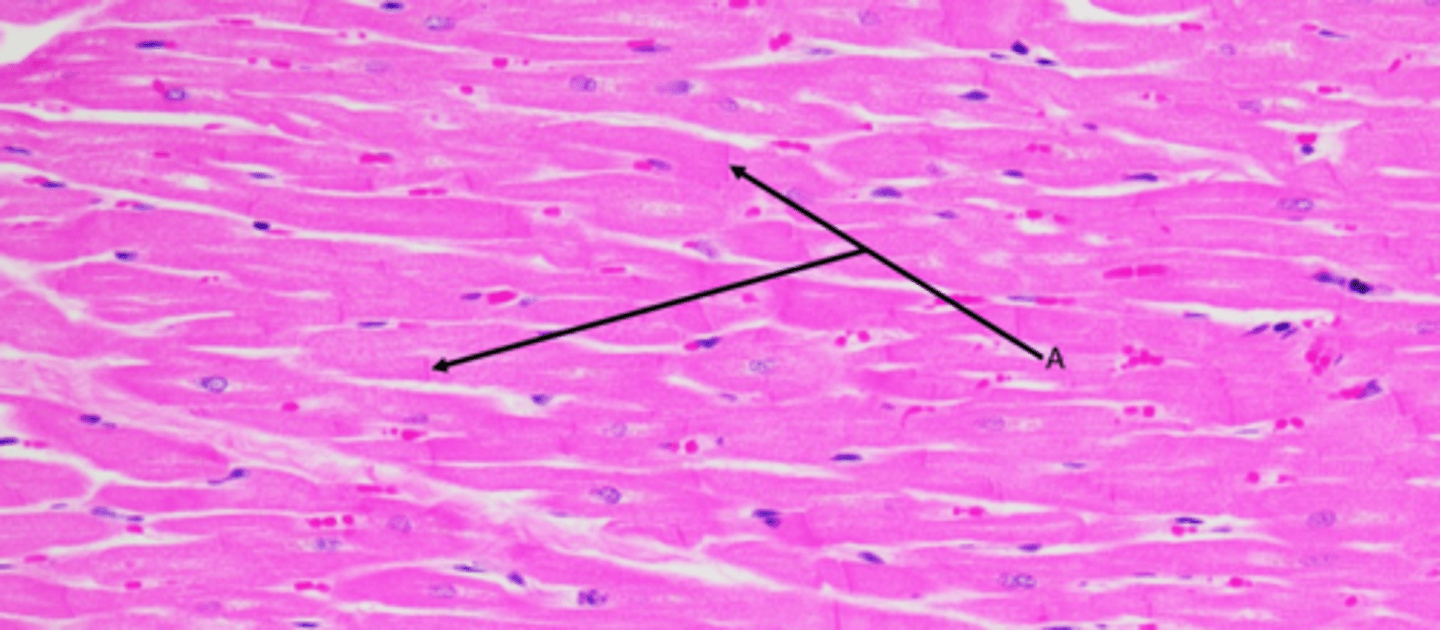
Cardiac muscle tissue
Function - Involuntary contraction of the heart
Location - Heart
Identify
Striations
Muscle fibers
Nuclei (myocytes have single nucleus)
A - Intercalated discs (gap junctions)
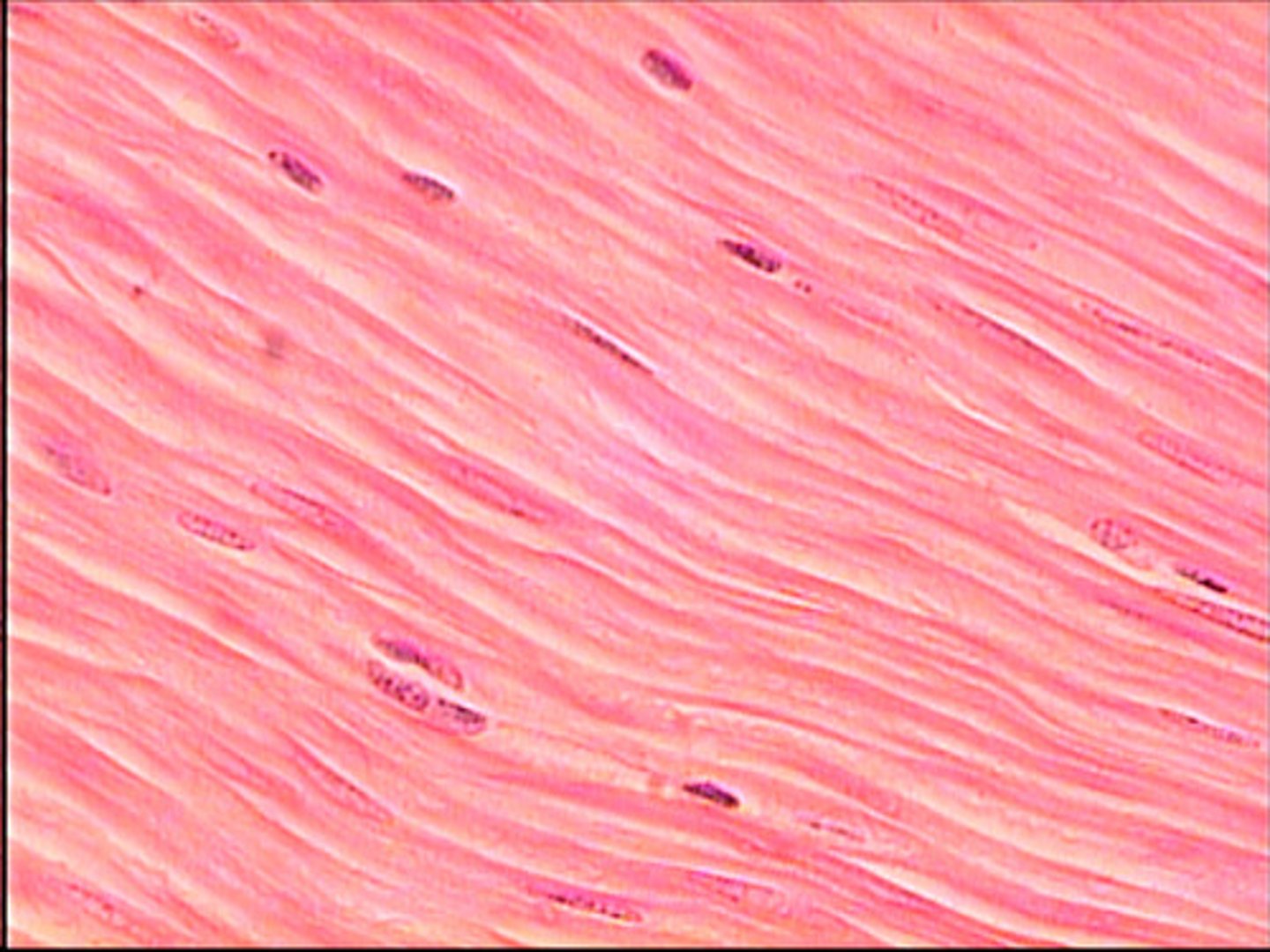
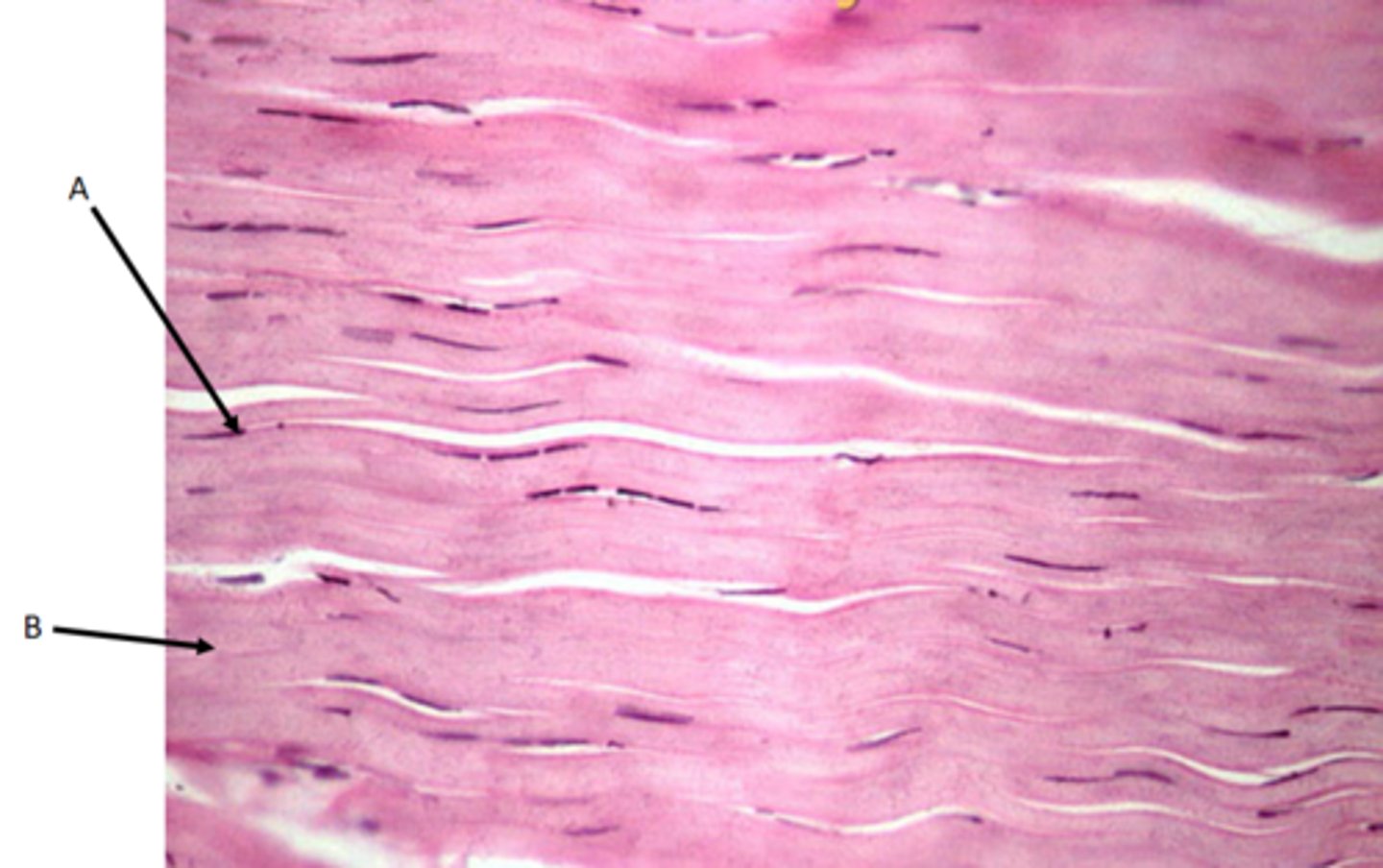
Smooth muscle tissue
Function - Involuntary peristalsis of digestive tract, also around arteries and veins
Identify
A - Myocyte (Muscle cell or fiber)
B - Nuclei