Neuro Intro LD
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
basic metabolic panel (BMP)
-kidney function and health
-blood glucose levels
-acid/base balance of blood
-fluid and electrolyte blance
glucose
blood sugar
70-115
calcium (Ca2+)
mineral critical to cardiovascular and nervous system bone health
sodium (Na+)
electrolyte
135-145
potassium (K+)
electrolyte
3.5-5
bicarbonate
electrolyte that helps measure CO2 in the blood
22-28
chloride (Cl-)
electroyte that works with K+, Na+, bicarbonate to facilitate proper water, electrolyte and acid base stats
95-105
blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
urea nitrogen is a protein breakdown product filtered out by the kidneys
7-18
-measures reabsorption of urea in kindeys
Creatinine (Cr)
creatinine is a waste material generated by normal muscle activity which is excreted through the glomerulus in kidneys
0.6-1.2
-measures how much creatinine in the blood is not being filtered out by kidneys
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
number of mL of the body fluid cleared by the kidneys per unit time
-low GFR= more waste retention
-renal function
-50% reduction of GFR = 2x creatinine
creatinine clearance
the rate of creatinine clearance by the kidneys
Complete Metabolic Panel (CMP)
BMP + Liver tests (ALP, ALT, AST, Bilirubin)
CT are used for
initial trauma evaluation/ bleeding
CT advantages
inexpensive, avaibale
exam in seconds
can be done when needed
patient can be brought in with anyhting
easy to interpret
CT disadvantage
use ionization radiation
can have unequal absorption of xrays
white matter can be seen poorly
poor resolution for lower cervical and thoracic spine
Intravenous contrast
iodinated nonionic water soluble
IV
circulated through body enters everywhere excpet within the CNS
Brain CT contraindications/precautions
claustrophobia (treated w meds)
obesity
pregnancy
unstable vitals
IV contrast dye: iodinated dye or shellfish allergy, contrast dye allergy, renal failure, glucophage
when to order CT of the brain
head trauma
acute severe headache
acute cerebral infarction
concern for neoplasm
concern for increased intracranial pressure
CT interpretation
denser tissue is brighter (hyperdense)
less dense is darker (hypodense)
bone is white, air is black
brain window- structures to be identified and differentiated
bone window- best for visualizing bone
when to use IV contrast
increase sensitivity
enhance normal and abnormal blood vessels
-aneurysms, vascular malformations, neoplasms
intravascular contrast material leaks into a lesion if the blood brain barrier is disrupted like infarction, abscess, neoplasms
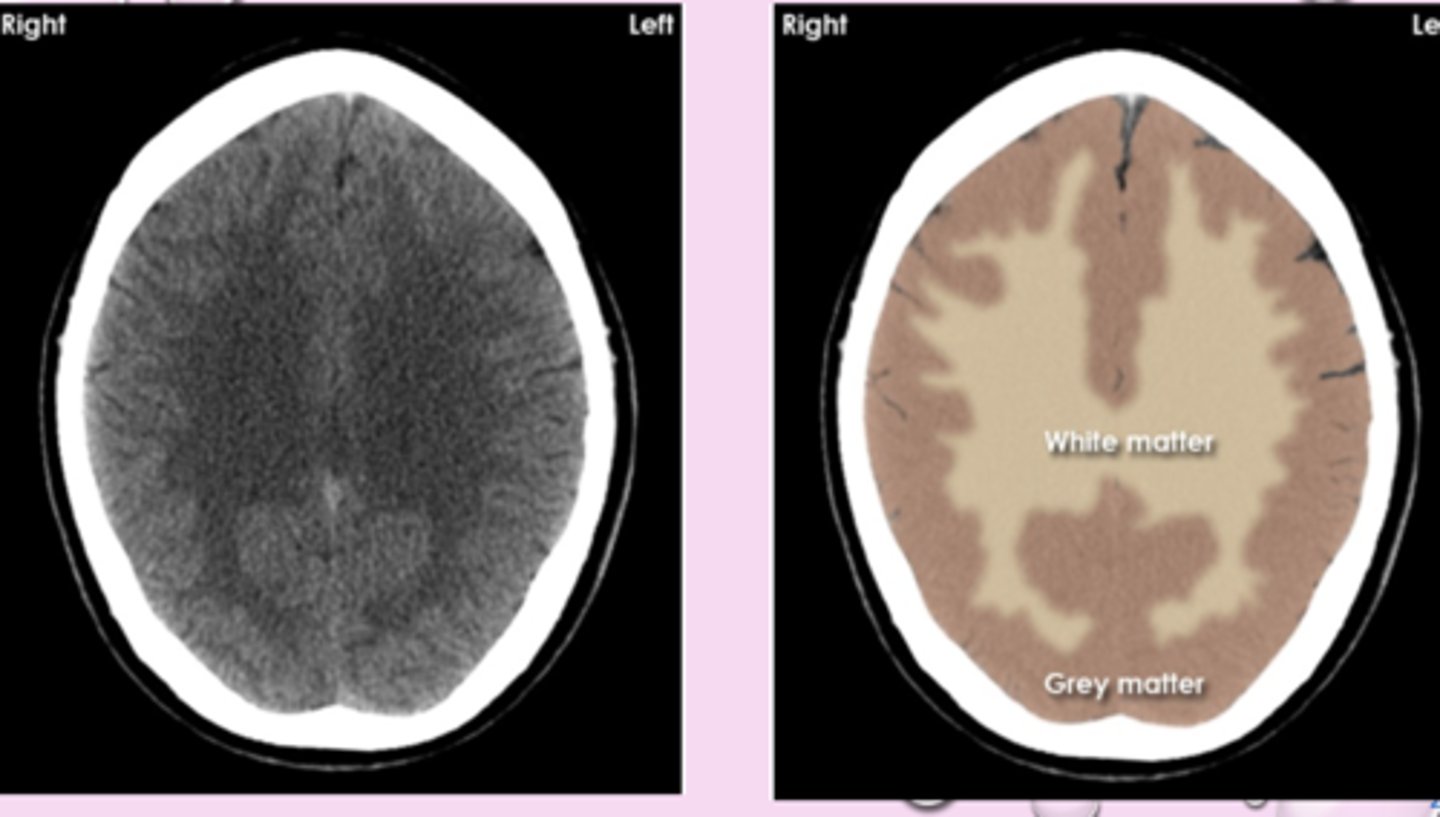
white matter appears
blacker than grey matter because it has high content of myelinated axons and lower density
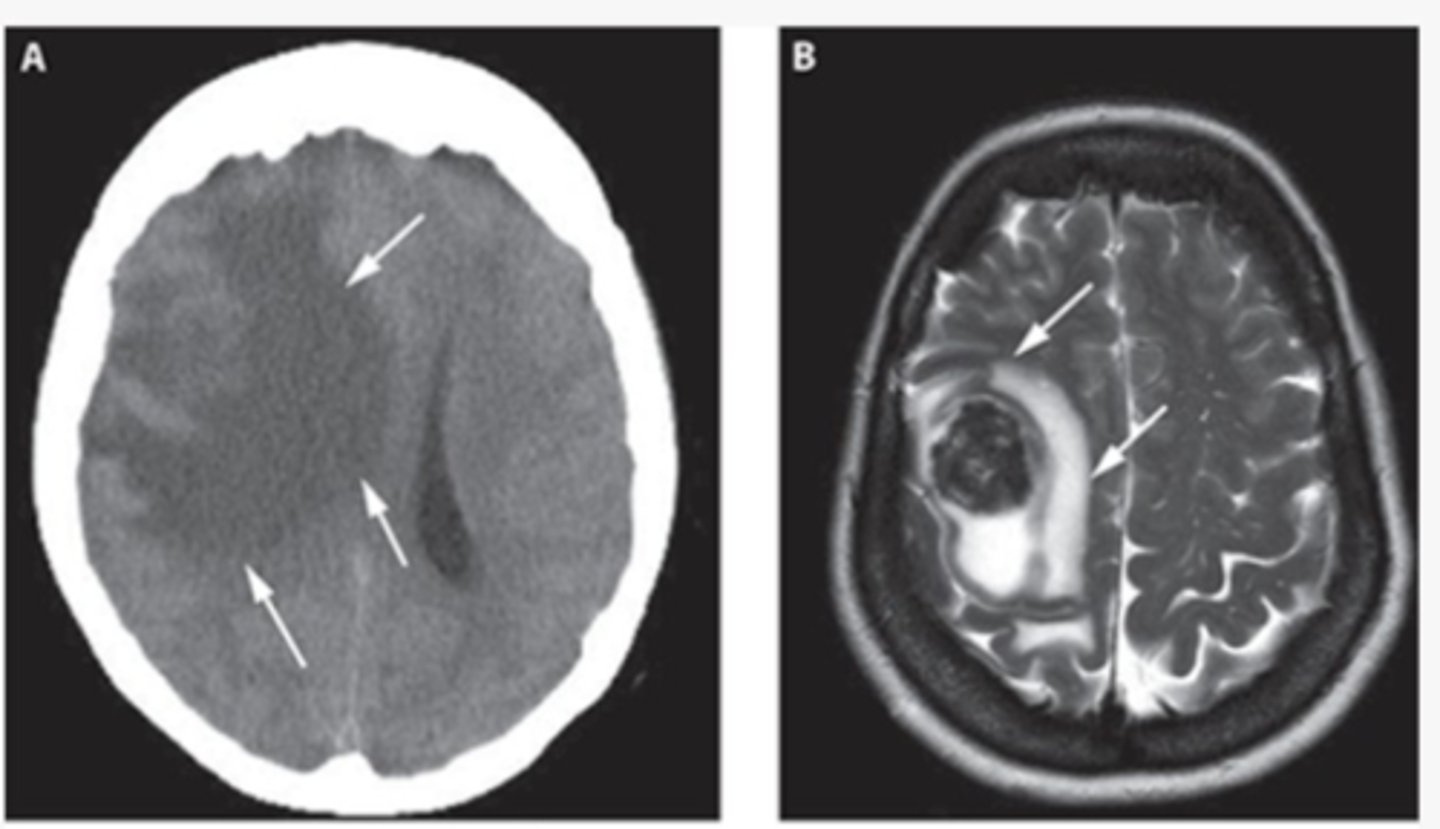
cytotoxic edema
loss of grey-white differentiation
-cant distinguish them from each other
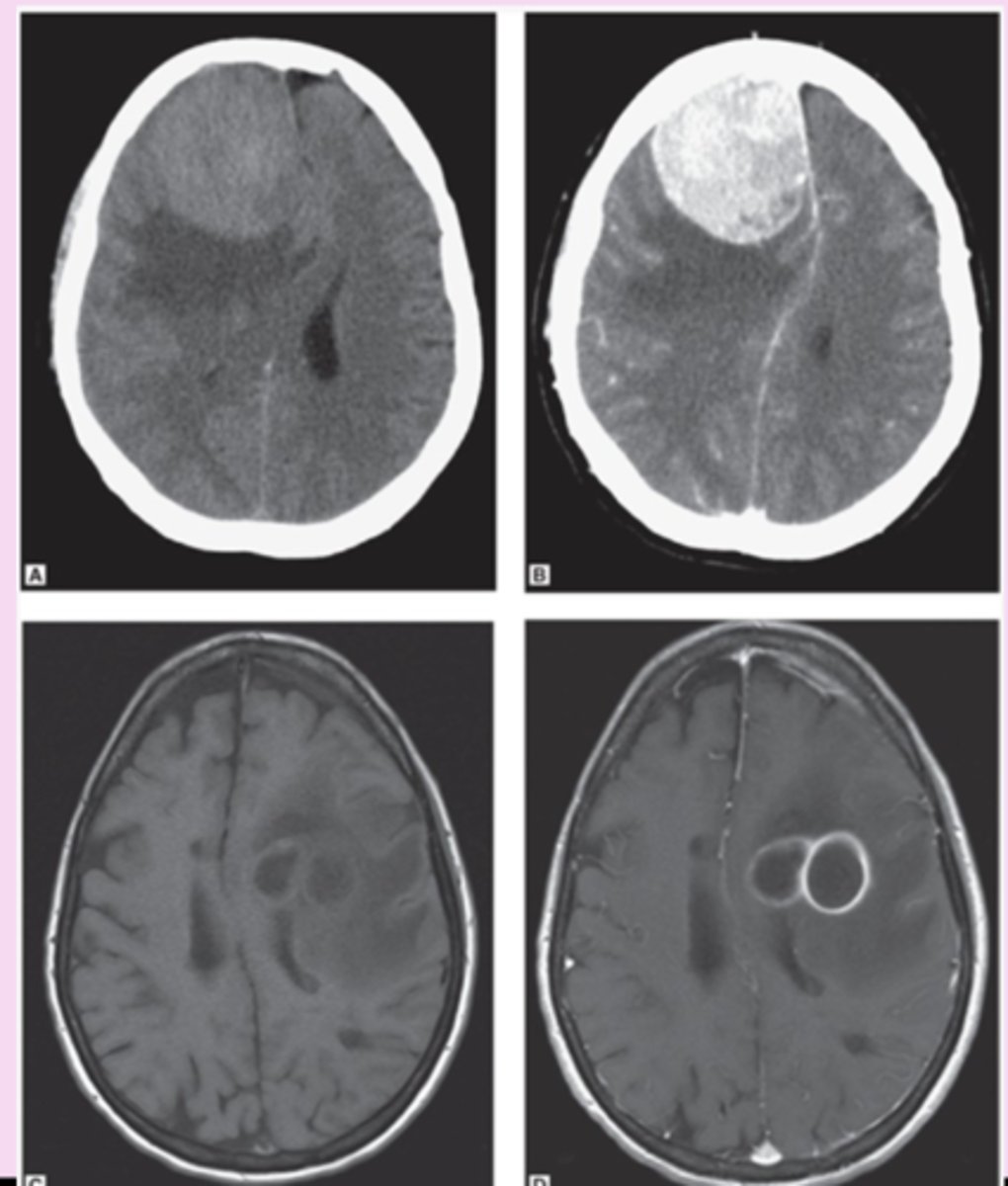
vasogenic edema
accentuation of grey-white differentiation
-tumor or abscess
MRI
A noninvasive hydrogen atoms behave in magnetic field when disrupted by radiofrequency signals
contrast MRI
chelated gadolinium -safest
-renal patients at risk
-not for pregnant
MRI advantage
increased sensitivity and specificity
sagittal and coronal image obtained without changing patient
no ionizing radiation
chelated gadolinium is safe
excellent soft tissue resolution
MRI disadvantages
take a long time
claustrophobia
expensive
need to be screened for metallic material
when to order an MRI
stoke (follow up)
chronic headache
seizure
tumor
infection
demyelinating disease
spinal lesions
normal brain MRI
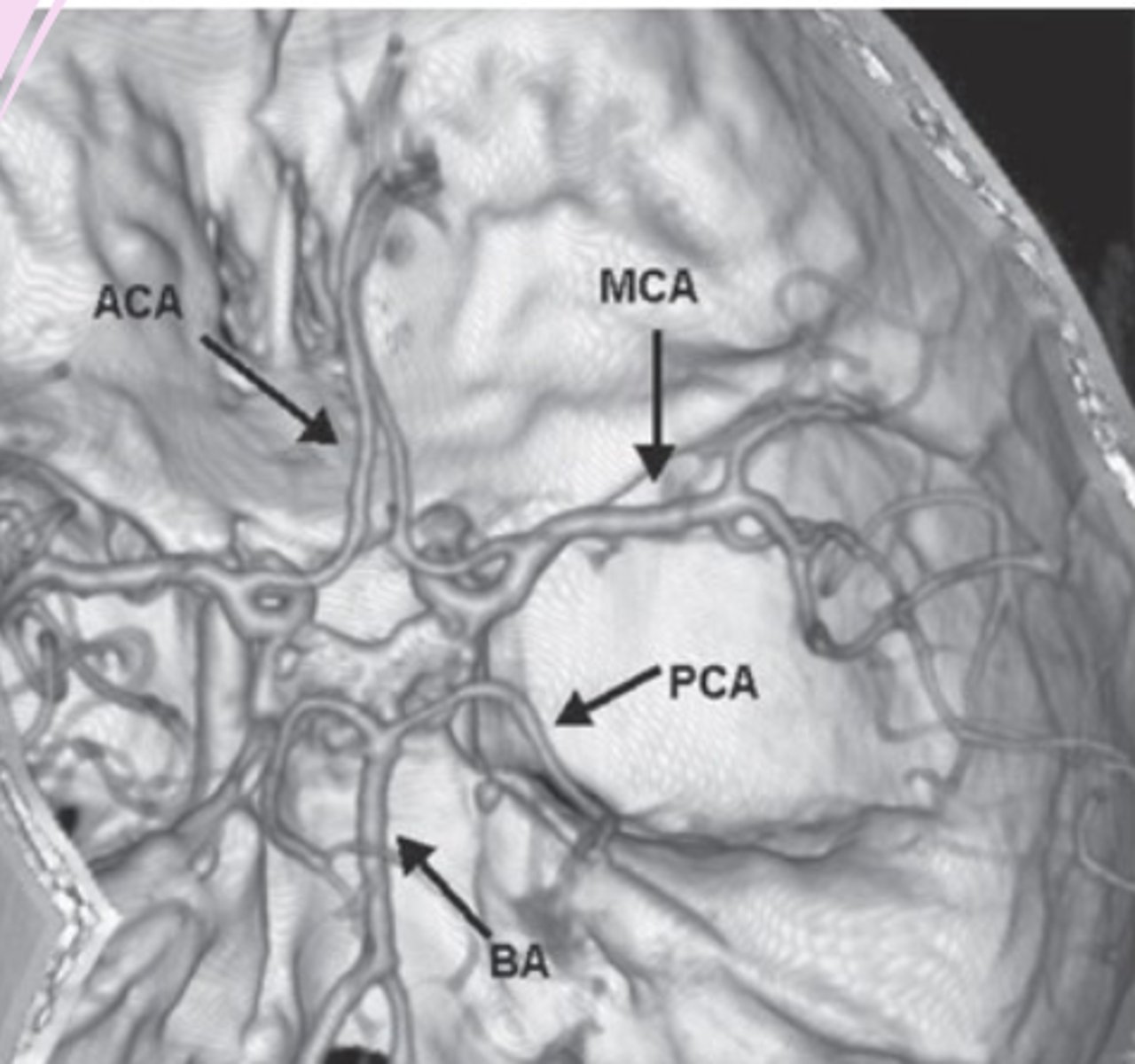
CT angiography (CTA) and MR angiography (MRA)
visualization of vasculature
look for aneurysms, stenosis, occlusion, dissection, vascular irregularities
MRA with or without contrast
CT venography (CTV) and MR venography (MRV)
visualization of veins and venous sinuses
evaluation of venous sinus thrombosis
CT angiography
-order when need to see blood vessels
3D images
safe
catheter angiography= gold standard
-can do noninvasively now
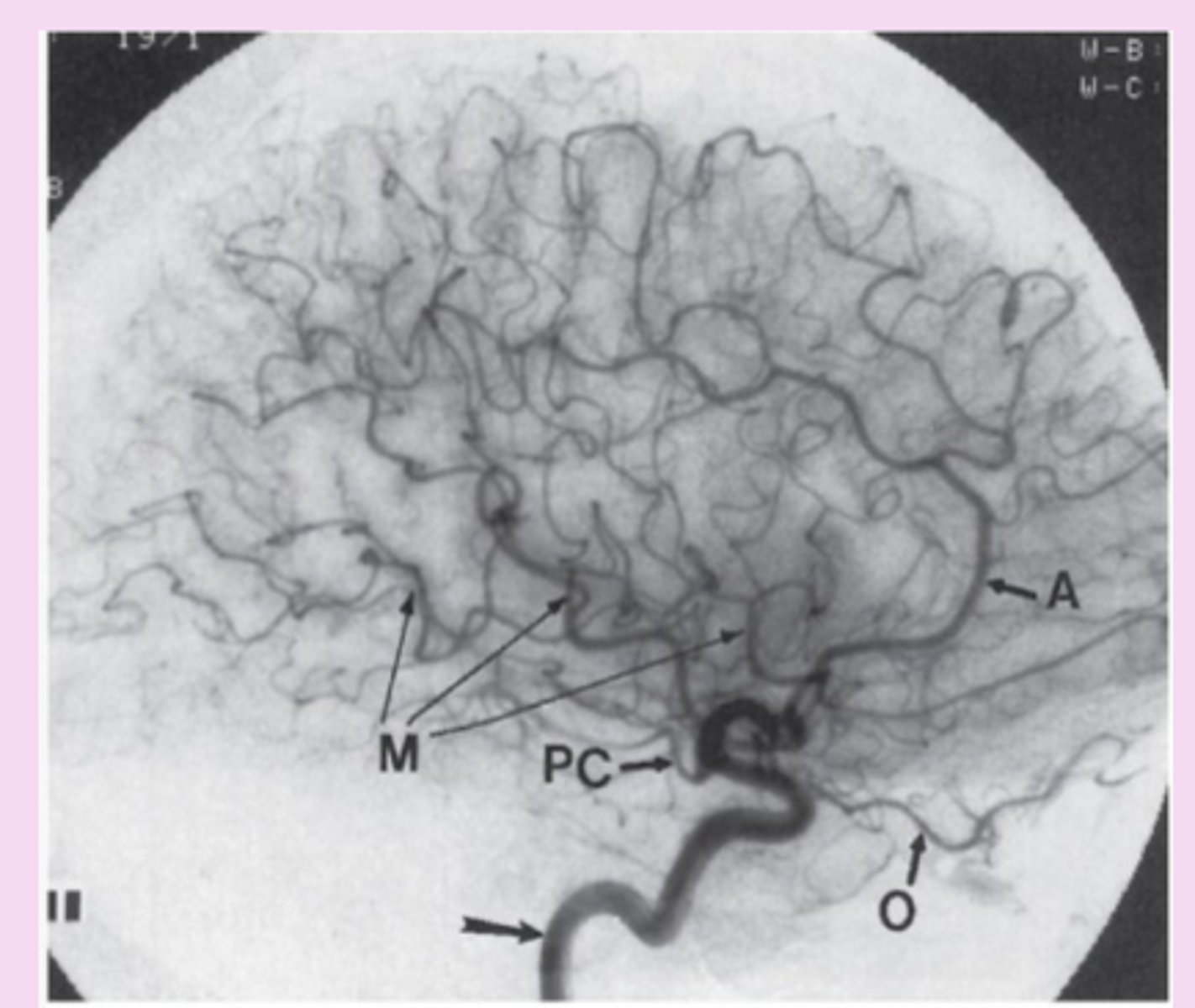
catheter-directed angiography
invasive, high risk procedure
small catheter in puncture of femoral artery > aorta > aortic arch > specific arteries > contrast material injected
gold standard= intracranial, extracranial, spinal vascular lesions
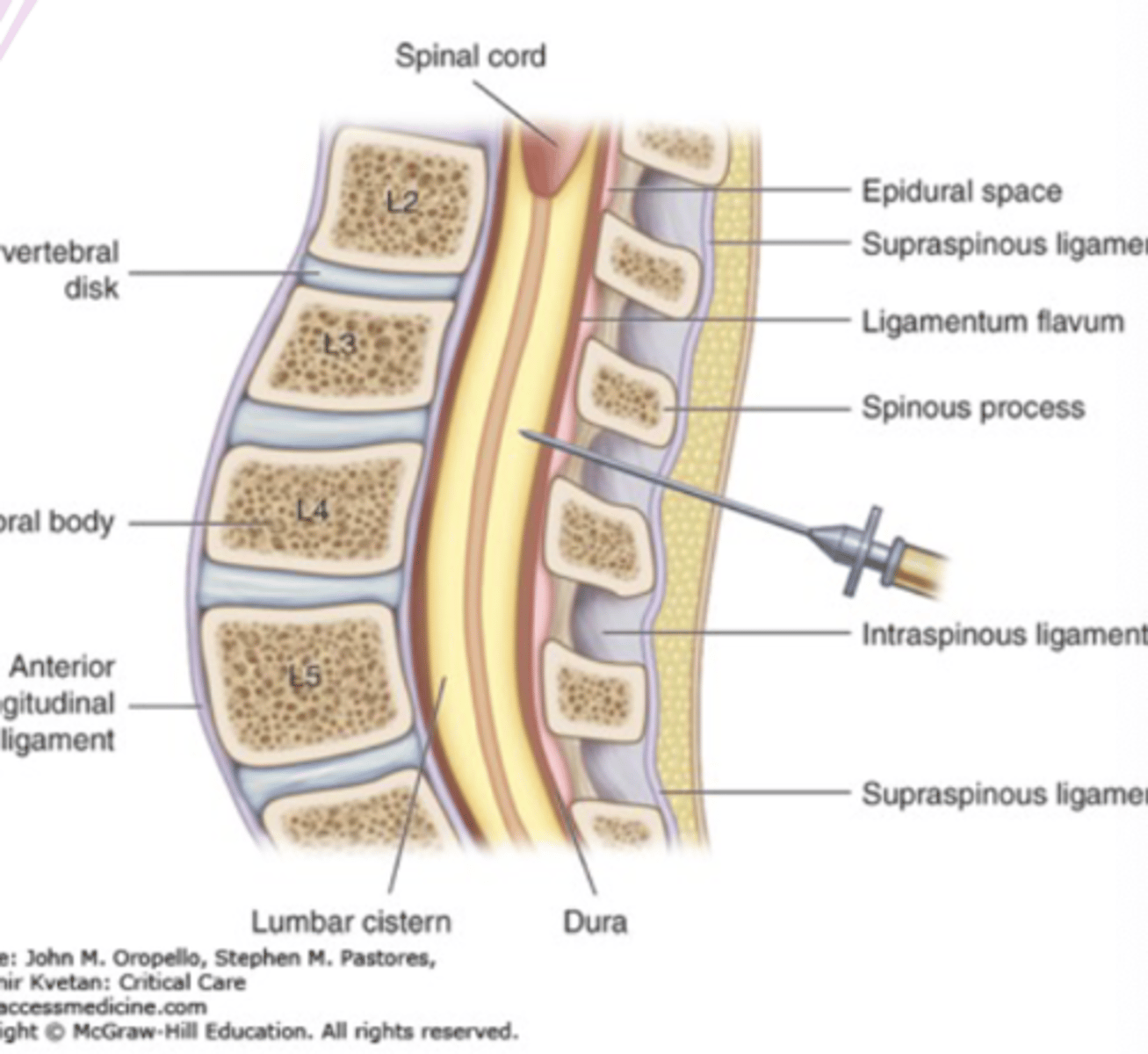
lumbar puncture
"spinal tap"
procedure of taking fluid from the spine in the lower back through a hollow needle
cerebrospinal fluid extracted
L3-L4 preferred because wider and has less soft tissue
lumbar puncture is diagnostic for
CNS infection (meningitis)
clinical concern for subarachnoid hemorrhage with a negative CT scan
lumbar puncture contraindications
infection at puncture site
acute spinal cord or head trauma
uncorrected severe coagulopathy
brain tumor
diffuse cerebral edema
lumbar puncture complication
brain herniation
headache
infection
spinal hematoma
neurologic compromise
ultrasound in lumbar puncture
reduces risk of failed or traumatic procedure, number of needle insertions
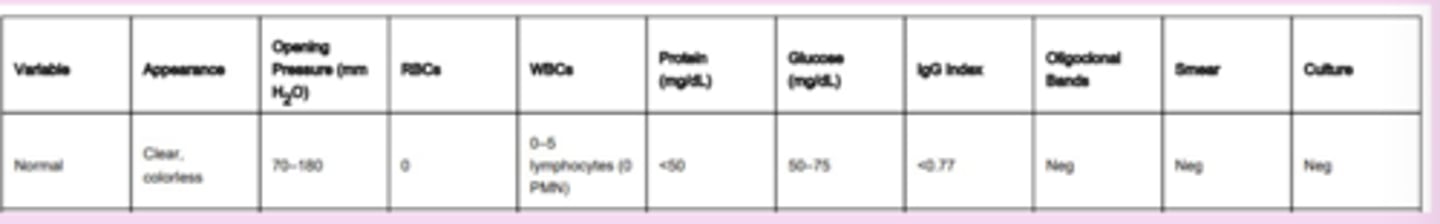
cerebrospinal fluid analysis
routine analysis: clear vs cloudy vs purulent), cell type, number of cells, glucose, total protein
gram stain and culture
can be tested by cytology
normal CSF
clear and colorless, acellular
electroencephalogram (EEG)
used for paroxysmal neurological disorders like seizures and epilepsy
uses amplification of brain electrical activity
spatial and temporal information
EEG test
electrodes on head
over 30 min period
EEG interpretation
montages: comparison of recordings from individual electrodes
interictal and ictal data are used to classify and diagnose seizures types, epilepsy disorders
EEG when to order
suspected seizure
classify seizure and epilepsy
management of epilepticus
evaluation of altered mental status
monitor things
-normal EEG does not exclude the possibility of epilepsy and seizures
Continuous EEG Monitoring
with or without simultaneous video monitoring
gold standard= concurrent video and EEG monitoring for diagnosis of seizures, epilepsy, psychogenic nonepileptic seizures
Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NSC)
motor and sensory conduction studies can be used to identify focal lesions and distinguish peripheral neuropathy from myopathy and motor neuron diseases
EMG and NSC functions
localization of symptoms
distinction between axonal and demyelinating neuropathies
distinction between disease of nerve and muscle
diagnosis of disease
NCS
nerves are electrically stimulated through the skin using electrodes
if motor nerve is stimulated: compound muscle (or motor) action potential (CMAP)
if sensory nerve is stimulated: sensory nerve action potential (SNAP)
EMG
activity of individual muscles
muscle response
small needles in the skin, electrical activity is picked up as muscle is stimulated
-measures at rest, contraction of muscles