AQA GCSE Chemistry Paper 1 Revision Combined
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Element
Substance made from one type of atom
Molecule
Fixed number of atoms covalently bonded
Compound
Two or more different elements chemically combined
Separation of sand and water
Filtration
Separation of a mixture of liquids
Fractional distillation
Separation of dyes
Chromatography
Mixture
Combination of substances in any proportion
Relative atomic mass
Average mass of an atom of an elemnt compared with one atom of C-12
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with the same protons but different neutron
Ionic bond between
metal & non-metal
Covalent bond between
non-metals
Ionic bond electrons are
Transferred from metal to non-metal
Covalent bond electrons are
shared
Conductivity of giant ionic structures
Solid = insulator Liquid/solution= conducts
State symbol solid
(s)
State symbol liquid
(l)
State symbol gas
(g)
State symbol solution
(aq)
Simple molecules low melting point
Weak intermolecular forces
Giant covalent structures melting point
Breaking many strong covalent bonds
Moles of solid
m/Mr
Linking many monomers
Polymer
Many ethene linked
Polyethene
Particles in solid
Regular arrangement, vibrating around fixed positions
Particles in liquid
Move and slide over one another
Pariticlesd in a gas
Rapid, random motion
Group 7
Halogens
Group 7 reactivity
Increases up the group
Number of atoms in 12g of C-12
Avogadro's number
Atom Economy
relative mass of useful / relative mass of reactants x100
Oxidation (electrons )
Loss of electrons
Reduction ( electrons)
Gain of electrons
Metal + Oxygen
Metal oxide
Metal + Water
Metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Metal + Steam
Metal oxide + hydrogen
Metal + Acid
Metal Salt + hydrogen
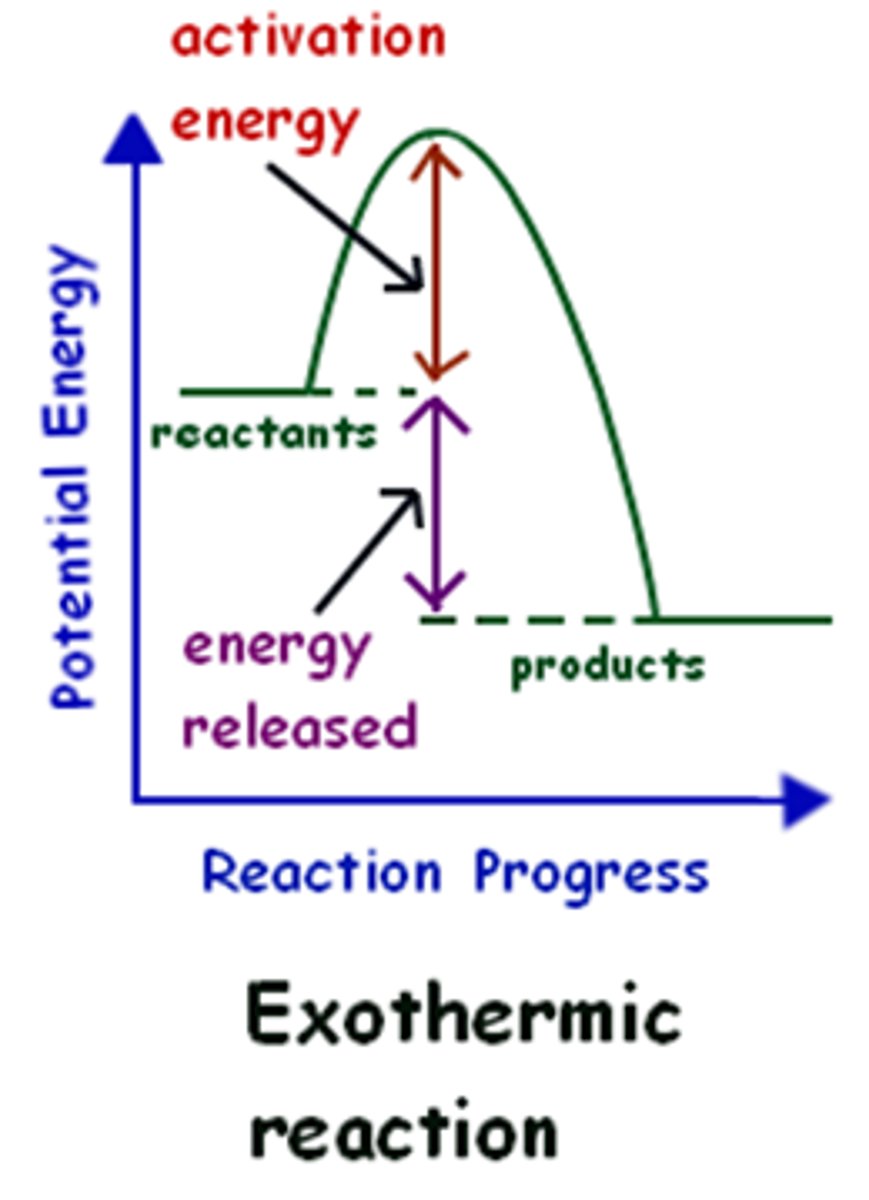
Releasing heat energy
Exothermic
Takin in heat energy
Endothermic
Curve of liquid in narrow tube
Meniscus
Phenolphthalein in acid
Colourless
Phenolphthalein in alkali
Pink
Exact reaction of acid & alkali
Titration
Moles of gas
v/24000
Copper + Hydrochloric acid
No reaction
Magnesium + Copper sulphate
Magnesium sulphate + copper
Oxidation and reduction
Redox reaction
Titration precision
Dropwise, white tile, repeat
Results within 0.1cm3
Concordant
Displacement of metals
Temperature increases
Structure that insulates as solid but conducts when melted or dissolved
Giant Ionic
Structure with a low boiling point as weak intermolecular forces
Covalent Molecular
Structure with a very high melting point due to many strong covalent bonds
Giant Covalant
Structure that conducts electricity and can react with water
Metallic
Bond made by sharing electrons
Covalent
Bond made by transferring electrons
Ionic
Bonding between positive ions ( cations ) and delocalised electrons
Metallic
Bonding between metals and non-metals
Ionic
Bonding between non-metals
Covalent
Force between simple molecules
Intermolecular
Force between oppositely charged ions
Electrostatic
Electrons which are free to move
Delocalised
Metals conduct because of
Delocalised electrons
Graphite conducts because of
Delocalised electrons
Giant ionic solids do not conduct because
Ions are not free to move
Giant ionic liquids / solutions conduct because
Ions are free to move
Giant covalent molecule that conducts electricity is
Graphite
Number of covalent bonds per carbon in diamond
4 bonds
Number of covalent bonds per carbon in graphite
3 bonds
Structure of NaCl
Giant Ionic
Structure of MgO
Giant Ionic
Structure of H2O
Simple molecular
Structure of sand, mainly SiO2
Giant covalent
Structure of iron
Metallic
1nm-100nm
Nanoparticle range
Advantage of nanoparticles
Large volume : surface area ratio
Single sheet of graphite is called
graphene
C60
Buckminsterfullerene
Democritus
Named the atom after the Greek word "atomos" which means indivisible; believed there is a limit to how many times one can break matter into smaller pieces; eventually one reaches the smallest particle.
Dalton's model of the atom
Billiard Ball model; Indivisible, indestructible, solid sphere
Thomson's model of the atom
Plum-pudding model; Positive charge spread over the sphere with negatively charged electrons inside
Gold Foil Experiment
Alpha particles that were shot at gold foil were deflected when they hit the positive center of gold atoms; the nucleus was discovered as a result of this experiment.
Rutherford's model of the atom
Nuclear model; A tiny nucleus (positive charge) around which electrons (negative) orbit
Bohr's model of the atom
Planetary model; The electrons orbit nucleus at discreet orbits which correspond to energy levels
Atom
Smallest particle of an element
Nucleus
Centre of the atom, holds the protons and the neutrons
Protons
Charge +1 Mass 1
Neutrons
Charge 0 Mass 1
Electrons
Charge -1 Mass 1/1840
Atomic Number
Equal to the number of protons
Mass Number
Equal to the number of protons + number of neutrons
Periodic Table
A chart of the elements showing the repeating pattern of their properties
Isotope
Atoms of the same element that have same number of protons but a different numbers of neutrons
Electron Configuration
the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom
Electrons in first shell
up to 2
Electrons in second shell
up to 8
Electrons in third shell
up to 8
Enthalpy change
Heat energy change
Exothermic
Releases heat energy ( gets hotter )
Endothermic
Takes in heat energy ( gets cooler )
Energy profile diagram - exothermic
Products higher in energy than reactants