15. Early Adulthood - Social + Personality Development
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Role development
____________ - Big increase in number of roles must be capable of functioning effectively in:
Associated stress
Opportunities for personal growth
Early adulthood has lots of roles needed for young adults to transfer in
Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory
_________________ - Stage: intimacy vs. isolation – individual must find a life partner or supportive friends to avoid social isolation
Intimacy
Marriage or sexual relationship not necessary for resolution
Dependent on successfully resolving the identity vs. role confusion stage
Barriers to intimacy: societal pressure to favour romantic relationships, poor sense of identity, interactions between individuals and societal beliefs
Relates to secure attachment style characteristics. Self-disclosure can be an issue in hetero relationships, where men feel satisfied in intimacy while female partner is isolated.
Intimacy
Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory
________________ - capacity to engage in (a) supportive, affectionate relationship(s) without losing one’s own sense of self
Marriage or sexual relationship not necessary for resolution
Dependent on successfully resolving the identity vs. role confusion stage
Levinson’s Life Structures
________________ - Life structures. Model of adult development AKA eras of adulthood:
Era of Early Adulthood: Transitional (17-22 years); New life structure (22-28 years); Age 30 transition (28-33 years); Settling down (33-40 years)
Era of Middle Adulthood: Transitional (40-45 years); Midlife entry structure (45-50 years); Age 50 transition (55-60 years)
Era of Late Adulthood: Transitional structure (60-65 years); Late adulthood
Each period presents new developmental tasks and conflicts; psychological responses create new life structures. Adults cycle thru periods of stability vs. instability.
Life structure
Levinson’s Life Structures
_____________ - underlying pattern or design of a person’s life at a given time, including roles, relationships, and behaviour patterns
Ex: Marriage requires a new life structure, as newlyweds do not yet know eachother in the roles of husband and wife
3 Phases of Life Structures (NMC)
Levinson’s Life Structures
______________ - Each period requiring new life structure has three phases:
Novice phase
Mid-era phase
Culmination phase
1) Novice phase
Levinson’s Life Structures → 3 phases (NMC)
______________ - period of adjustment
2) Mid-era phase
Levinson’s Life Structures → 3 phases (NMC)
______________ - increasing competence in face of new challenges through reassessment and reorganization of life structure
Adults become competent at meeting new challenges
3) Culmination phase
Levinson’s Life Structures → 3 phases (NMC)
________________ - success in life structure creation allows management of demands with more confidence and less distress
Emerging adulthood
______________ - The periods from late teens to early 20s when ppl explore options prior to committing to adult roles.
Developmentalists agree that 17-22 years is a transitional period
May not be universal, arising in cultures where individuals in late teens face many choices in adult occupational and social roles
Neuroimaging suggests it is a unique period: maturation of brain areas underlying rational decision-making, impulse control, and self-regulation
Developmental tasks across 5 domains
Developmental tasks: 5 domains
Emerging adulthood
_______________ - academic, friendship, conduct, work, romantic
Skills in academic, friendship, and conduct transfer easily from adolescence → skills you learned longer can be somewhat learned earlier
Must approach work and romantic differently due to cultural expectations and decisions about individual priorities
Marriage vs. common-law
Relationships
_________________ - Increasing acceptance of nonmarital relationships— Most young adults are not living in an intimate partnered relationship
Marriages are starting to mirror Canada’s sociodemographic diversity
Common-law
Common-law
Relationships
_________________ - legal concept that provides legal rights as a married couple even if not actually married
Theories of mate selection
____________- different ideas on romance/sex
Evolutionary theories
Parental investment theory
Social role theories
Neuroscience of human attachment
Evolutionary theories
Theories of mate selection
_______________ - focus on survival value
Males prefer physically attractive, younger females;
Females prefer males with a higher SES who offer earning potential and stability
Parental investment theory
Criticism: sexism masquerading as science → founded on patriarchal norms
Parental investment theory
Theories of mate selection → evolutionary theories
________________ - sex differences in mate preferences are explained by the different amounts of time and effort males and females must invest in child-rearing and the certainty that the child is their genetic offspring
Criticism: sexism masquerading as science → founded on patriarchal norms
Social role theories
Theories of mate selection
________________ - Men and women’s mate preferences changed as women gained economic power
The more a woman expects to earn herself, the higher her income requirements for a prospective mate → women want to be able to have children without lowering quality of life
Homogamy
Homogamy
Theories of mate selection → social role theories
______________ - members of both sexes prefer mates who are like them in SES, beliefs, religion, etc.
Neuroscience of human attachment
Theories of mate selection
________________ - Endocrine and neural processes underlie adult attachment bonds— these processes are shaped by early life experiences
Romantic-couple and parent-infant bonds have similar neural architecture and physiology
Greater socioemotional closeness, social synchrony, and neuro-imaging synchrony among couples and close friends evidenced in neuroimaging studies
Psychological aspects of marriage
Marriage
__________________ - Intention to marry decreases with age. Relationship quality prioritized across sociocultural groups in terms of what makes marriage work
Personality characteristics influence satisfaction
OCEAN influences, plus gender differences
Attitudes toward marriage affect longevity
Extraversion = higher satisfaction
Security of attachment to origin family impacts marital satisfaction
Emotional affection influences relationship quality
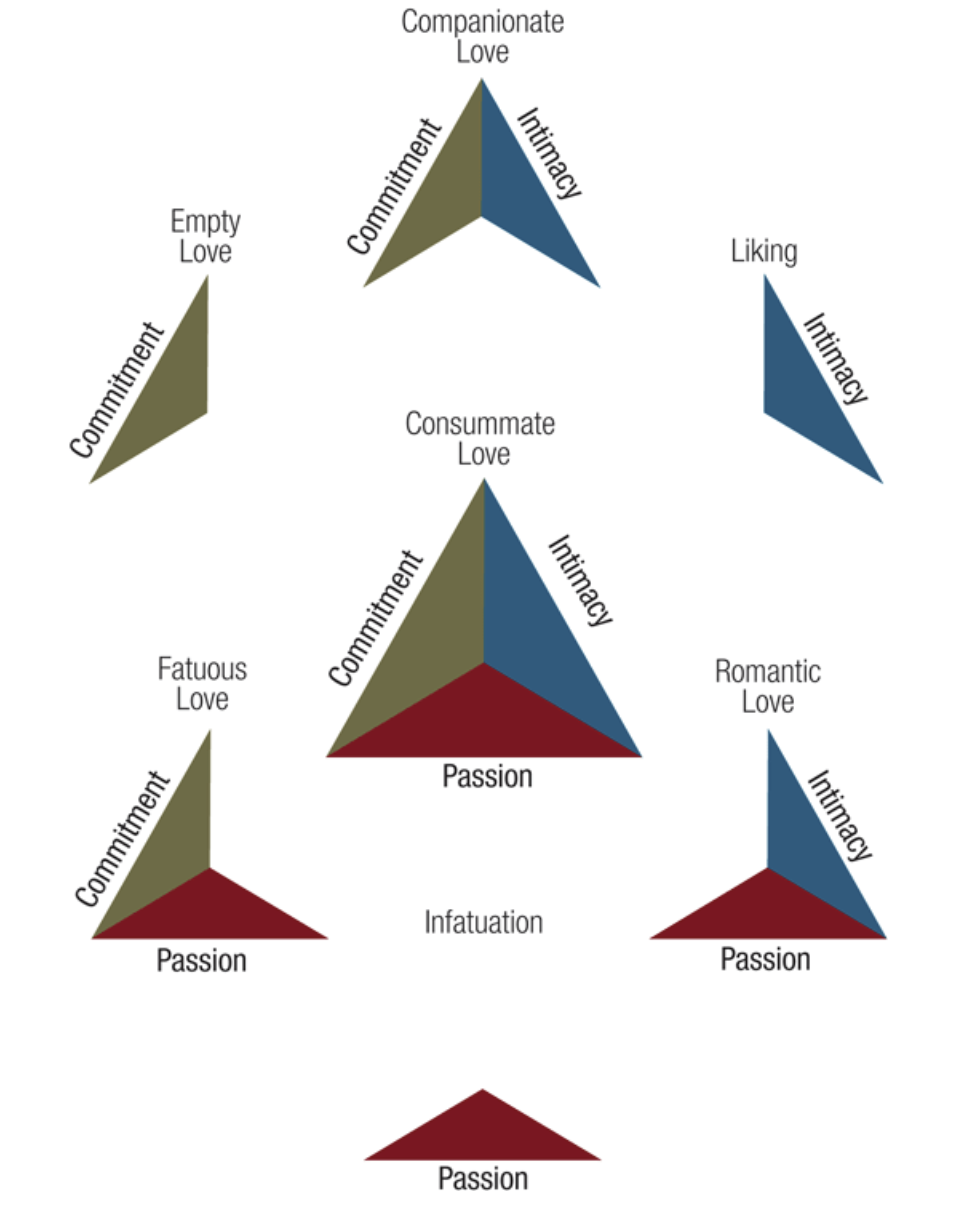
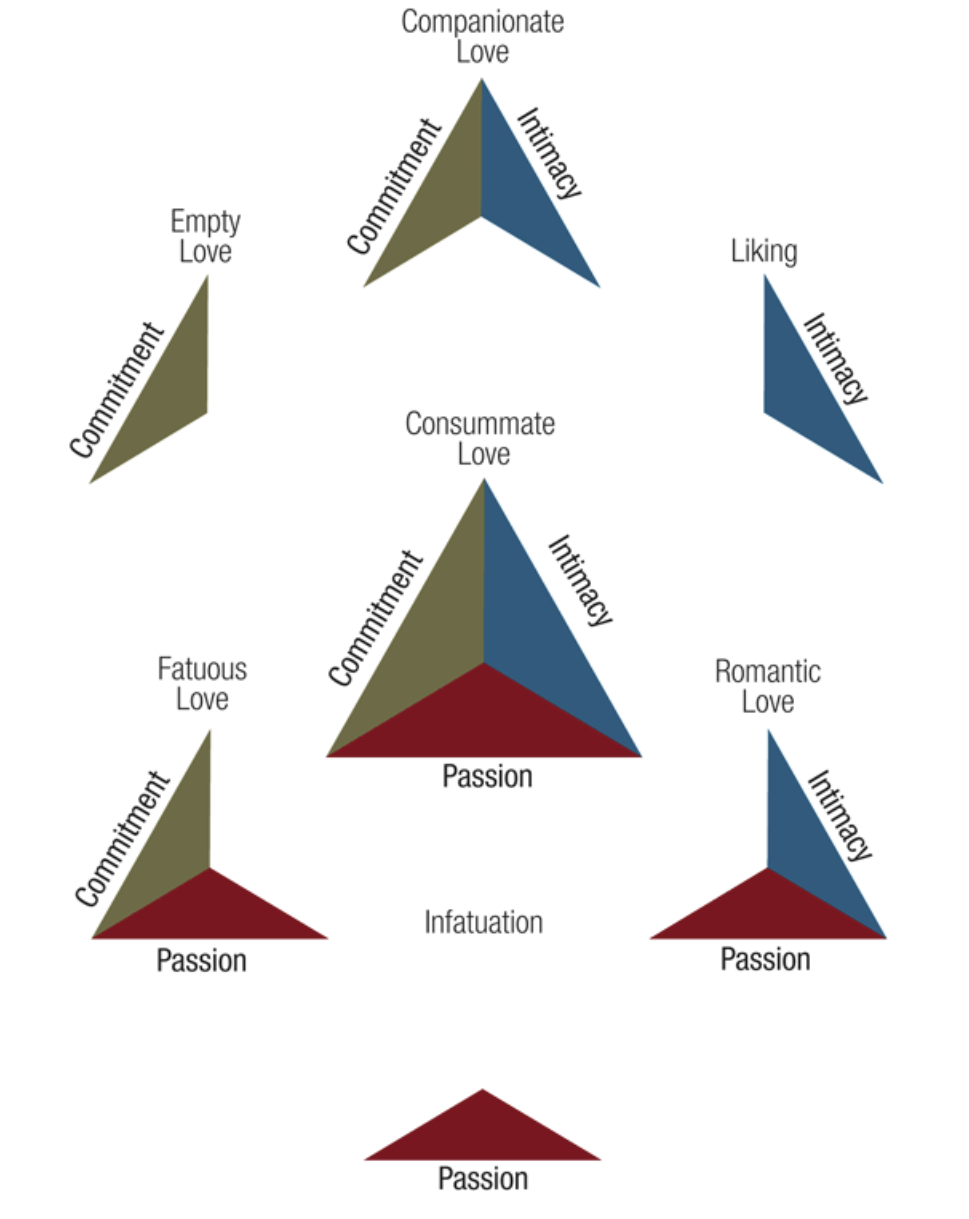
Three components of love
Conflict management
3 Components of Love (IPC)
Psychological aspects of marriage
_______________- intimacy, passion, and commitment to a particular other
5 types of couples (VV And HH)
Psychological aspects of marriage
_________________- validating, volatile, avoidant, hostile/engaged, and hostile/detached
4 Horsemen of the Apocalypse
Psychological aspects of marriage
______________ - of poor communication → criticism, contempt, defensiveness, and stonewalling
Conflict management
Psychological aspects of marriage
_______________ - also a predictor of relationship quality
Five types of couples
Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse
Criticism
Divorce
__________________ - Frequency misrepresented. Likelihood of divorce lower for a first marriage than a remarriage
50% ppl who get married divorced is misrepresented, rate of divorce over time is 38% over 30 wks
Psychological effects:
Major stressor
Associated with increased mental health problems
Economic effects…
Economic effects of divorce
Divorce
_________________ - Women have higher child-rearing responsibilities and don’t recover as easily, esp. low SES
Psychological effects often compounded by economic effects, especially for women
Divorced men’s economic position slightly improves whereas women’s significantly worsens
Women who were earning above-average pre-divorce are more likely to recover financially, even without remarrying.
For lower SES women, they never recover
Cohabitating heterosexual couples
__________________ - Variety of reasons that young adults may choose cohabitation over marriage
Adults who cohabitate before marriage are less satisfied with their subsequent marriage
The two relationships are fundamentally different, and cohabiting leads to life structure for cohabitating, not for marriage
Adults who cohabitate before marriage differ in key ways from those who marry without first cohabitating → maybe marriage causes a higher sense of commitment
Interaction effect
Housework differences
Housework w/ hetero couples
Cohabitating heterosexual couples
_________________ - Cohabitating women do 5-6 hours less of housework per week vs married women
Women do more housework when they move in with a man & vice versa
Interaction effect
Cohabitating heterosexual couples
_____________ - firm intentions to marry
Same-sex couples
_________________ - 1/3 cohabitating same-sex couples are married. High attachment security linked to happiness and satisfaction in the relationship
Higher attachment more associated with negotiation of non-monogamy than heterosexual couples
Gay men report higher levels of autonomy in their relationships than straight men; lesbian women report more autonomy, intimacy, and equality than straight women
More…
Relationship dissolution
Egalitarian; less-specific role prescription, more likely to have equal parenting and chores
Women in lesbian partnerships have significantly greater sexual satisfaction and orgasms compared to women in heterosexual partnerships
Bisexuals in relationships
______________ - Most bisexual individuals are in heterosexual relationships
More mental health challenges due to minority stigma and lack of acceptance in heterosexual and lesbian and gay spaces
Intimate partnerships w/o cohabitation
Other relationship commitments
_________________ - 1/3 Canadians aged 25-34 years live apart together: are in an intimate partnership without cohabitation
Roommate households
Other relationship commitments
_______________- fastest growing household type
Singlehood
Other relationship commitments
________________ - Impact depends on the reason for single status and attachment style
Continuous singlehood: associated with greater autonomy and capacity for personal growth
Number of years single impacts the influence of singlehood on development
Parenthood
________________ - Mixed emotional experience – fulfilling an intense desire while also bringing a number of stressful changes
Most young people expect to have at least one child though there is a decline
92% of parents believe that being a parent is the most important thing they can do; 94% enjoy being a parent most of the time
Parenting work is still primarily done by women; 10% of men are stay-at-home dads
Other aspects:
Transition to parenthood
PPD
Developmental impacts
Transitioning to parenthood
Parenthood
_______________ - Can be very stressful and contentious
Couple has less time for each other
Pre-child conflict management and communication problems can be intensified
Strong pre-existing relationship can moderate new parenting stress
Postpartum depression
Parenthood
_________________ - Affects 10-15% of new moms, can last up to a year or more
Risk factors:
PPD with previous birth;
major life stressors during pregnancy or immediately after birth;
fatigue;
difficult infant temperament;
and depression during pregnancy
Developmental impact of parenthood
Parenthood
____________________ - Sensation-seeking and risky behaviour decline. Marital satisfaction declines
Having a parenting partner is a protective factor in managing the stressful transition to parenthood
Life w/o children
_________________ - Having no children impacts marriage and employment patterns
Couples without children: marital satisfaction doesn’t fluctuate much
Having children affects earning and employment patterns
Motherhood earnings gap
Motherhood earnings gap
Life without children
________________ - the earnings of women with children are significantly below those of women without children
Earnings nearly halve in the year after birth – and don’t rebound, with a 14% loss of earnings in the five years after birth
For men, having a child is associated with an increase in earnings
Family
Social networks
______________- Spouses or partners are the most significant person in life
Most adults still feel emotionally close to parents and communicate with them regularly
Amount and kind of contact with kin is influenced by proximity
Even without physical contact, can still provide important support in times of need
Friends
Social networks
_________________ - In-person and exclusively online friends are important— Homogamy important
Cross-sex friendships more common but still the minority
Sex differences in relationship styles
Social networks
___________________ - Differences:
Women have more close friends, and friendships are more intimate
Men's friendships are more competitive, with less agreement or emotional support
Kin-keeper
Kin-keeper
Social networks → sex differences in relationship styles
_________________ - family role which includes responsibility for maintaining family and friendship relationships; usually performed by women
Women also tend to perform caretaking for parents in old age
The Role of the Worker
_________________ - Satisfying work important for good mental health and life satisfaction
Variables determining occupation selection are varied
Family influence:
Tend to choose occupations at same general social class level as their parents
Education and value systems influence
Gender:
Shifting, slowly
Slight majority of women occupy feminized labour positions
Gendered pay gap continues
Personality plays a major part
The Role of the Worker + Work preferences (RIA-SEC)
_______________ - RIA-SEC… six types of “personality types”
Realistic
Investigative
Artistic
Social
Enterprising
Conventional
1) Realistic
The Role of the Worker + Work preferences (RIA-SEC)
________________ - Aggressive, masculine, physically strong, often with low verbal or interpersonal skills
Prefer mechanical activities and tool use, choosing jobs such as mechanic, electrician, or surveyor
2) Investigative
The Role of the Worker + Work preferences (RIA-SEC)
_______________ - Oriented toward thinking (particularly abstract thinking), organizing and planning; prefer ambiguous, challenging tasks, but are low in social skills
Are often scientists or engineers
3) Artistic
The Role of the Worker + Work preferences (RIA-SEC)
______________ - Asocial; prefer unstructured, highly individual activities; are often artists
4) Social
The Role of the Worker + Work preferences (RIA-SEC)
_____________ - Extraverts; people-oriented and sociable need attention; avoids intellectual activity and dislikes highly ordered activity
Prefers to work with people and choose service jobs like nursing and education
5) Enterprising
The Role of the Worker + Work preferences (RIA-SEC)
__________________- Highly verbal and dominating; enjoys organizing and directing others; are persuasive and strong leaders, often choosing careers in sales
6) Conventional
The Role of the Worker + Work preferences (RIA-SEC)
_______________ - Prefers structured activities and subordinate roles; likes clear guidelines and see themselves as accurate and precise
May choose occupations such as bookkeeping or filing
Career development
________________ - Process of adapting to the workplace, managing career transitions, & pursuing goals through employment
Super’s Stages
Career development
________________ -
Growth stage: Developing interests, skills, and values; forming initial career ideas
Ages 4-12
Exploratory stage: Exploring different career options, setting short-term goals, and gaining experience
Ages 15-20s
Establishment stage: Establishing a career, gaining experience, and building a reputation
Ages 25-40
Maintenance stage: Focusing on career advancement, building expertise, and making long-term plans
Ages 45-60s
Job satisfaction
Career development
_____________ - lowest at mid-career, likely due to reduced job security
Alignment of career w/ personality predicts satisfaction
Work-life balance
Work-life balance
Career development → Job satisfaction
_________________ - balance between employee's work and non-work roles
Gender differences in work patterns
Career development
___________________ - Young men economically worse off than young men of previous generations; opposite for young women
Key difference: most women transition in and out of the workforce at least once to have and raise children
Intimacy vs. Isolation
Erik Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial development (textbook)
_________________ - Erikson’s early adulthood stage, in which an individual must find a life partner or supportive friends to avoid social isolation
Relationship quality and OCEAN
Psychological aspects of marriage (textbook)
High extraversion = mutual marital satisfaction
High conscientiousness = high satisfaction 4 husbands
Similar openness to experience = high satisfaction 4 husbands
Similar agreeableness = high satisfaction 4 wives
1) Intimacy
Psychological aspects of marriage → 3 Components of Love (IPC - textbook)
___________________ - includes feelings that promote closeness and connectedness
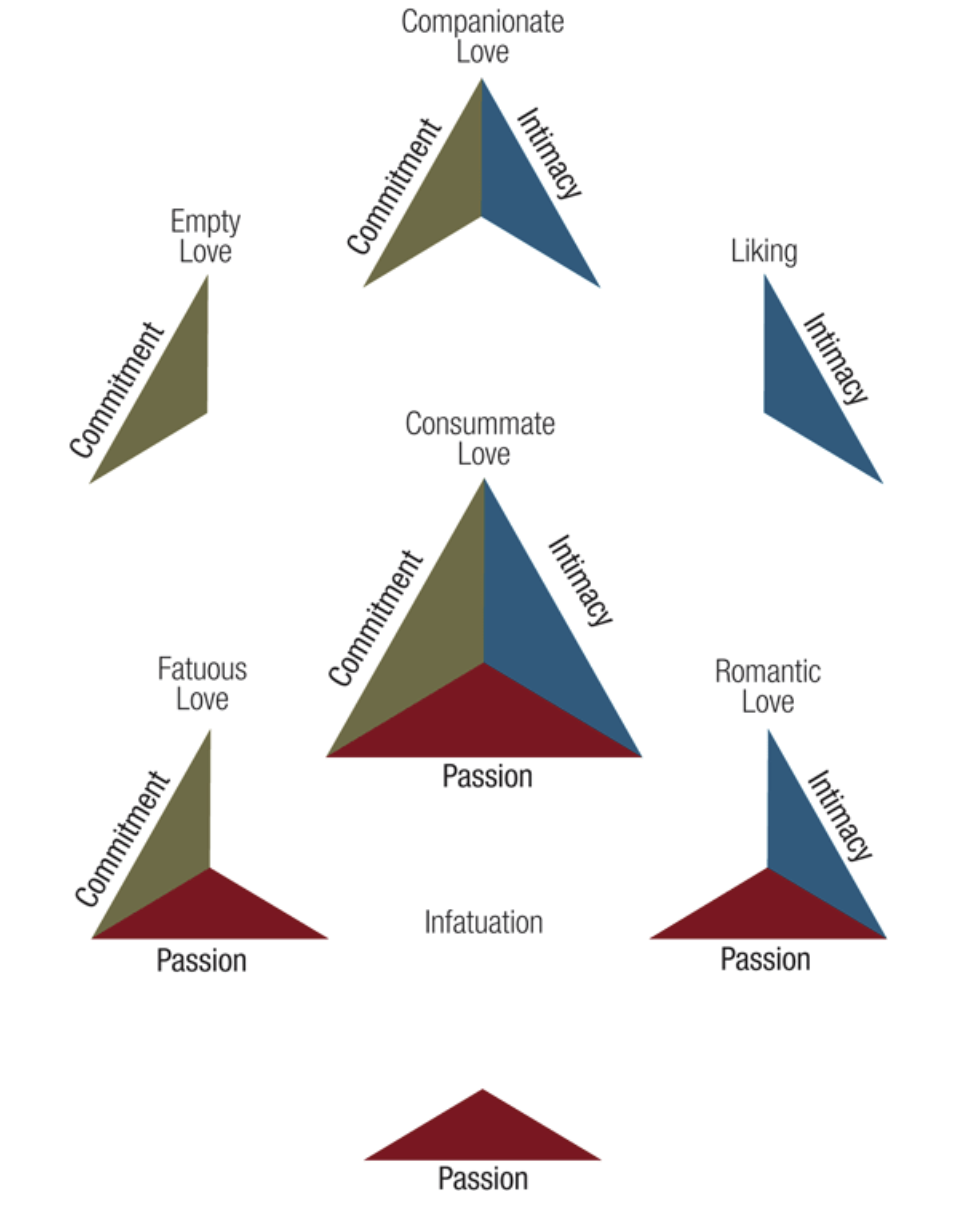
2) Passion
Psychological aspects of marriage → 3 Components of Love (IPC - textbook)
_______________ - a feeling of intense longing for union w/ the other person— including sexual union
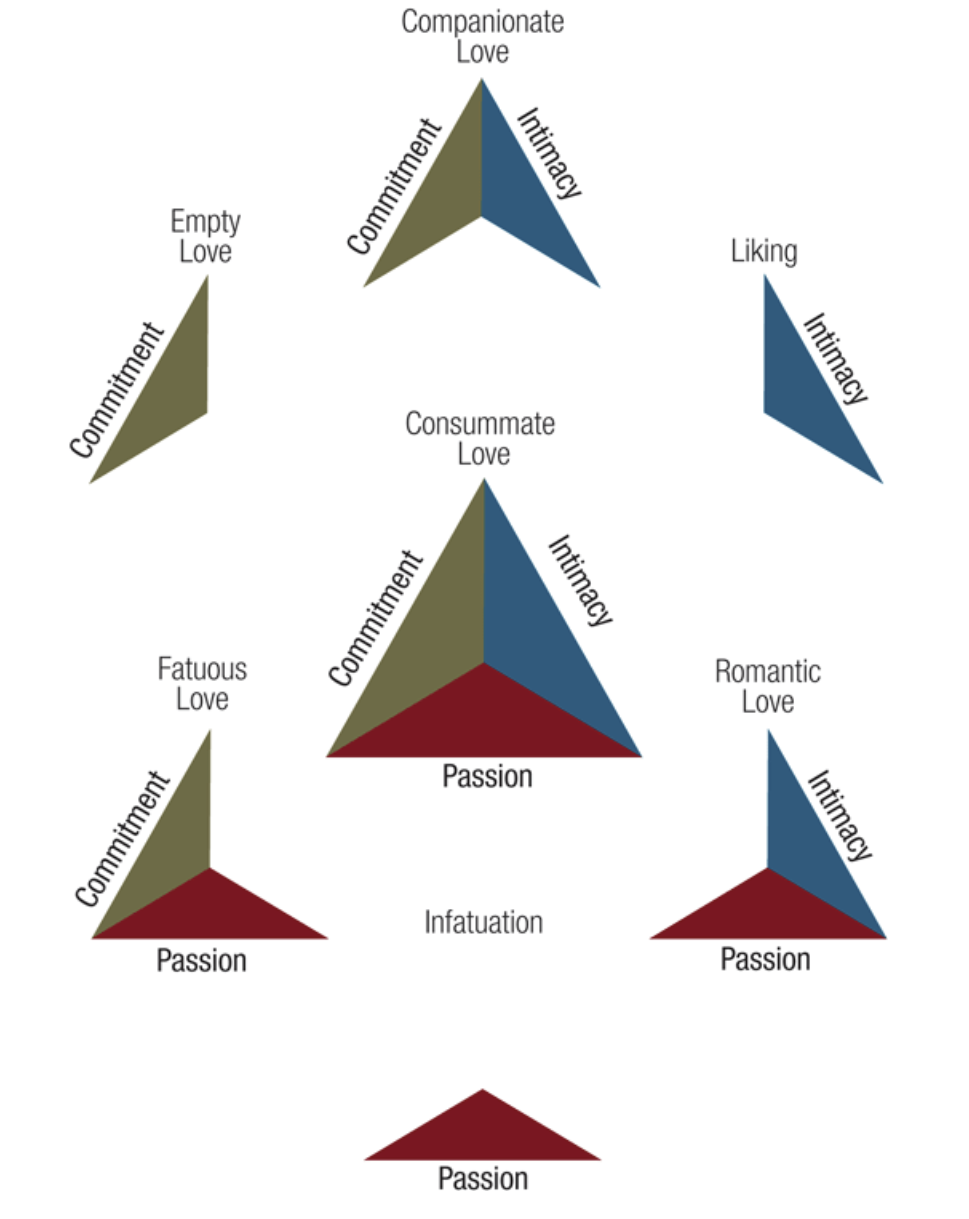
3) Commitment
Psychological aspects of marriage → 3 Components of Love (IPC - textbook)
________________ - to a particular other over a long period of time
1) Validating couples (VV)
Psychological aspects of marriage → 5 types of couples (VV And HH - Textbook)
________________ - partners who express mutual respect (even in arguments) and are good listeners
Disagreements rarely escalate— listen even in arguments
2) Volatile couples (VV)
Psychological aspects of marriage → 5 types of couples (VV And HH - Textbook)
________________ - partners who squabble a lot and don’t listen well— BUT overall have more positive interactions than neg.
Show high levels of laughter and affection still
3) Avoidant couples (And)
Psychological aspects of marriage → 5 types of couples (VV And HH - Textbook)
________________ - Partners who agree to disagree and minimize conflict by avoiding e/o
Conflict minimizers
Don’t try to persuade… AKA devitalized
4) Hostile/engaged couples (HH)
Psychological aspects of marriage → 5 types of couples (VV And HH - Textbook)
________________ - partners who have frequent heated arguments, but LACK humour and affection
Unsuccessful
Ratio of pos. to neg. interactions gets out of balance, and marriage spirals to dissolving
5) Hostile/detached couples (HH)
Psychological aspects of marriage → 5 types of couples (VV And HH - Textbook)
________________ - partners who fight regularly, rarely look at each other and lack affection + support
Unsuccessful
Ratio of pos. to neg. interactions gets out of balance, and marriage spirals to dissolving
Quality of work-life (QWL) movement
Career development → job satisfaction (textbook)
_______________ - an approach to enhancing job satisfaction by basing job and workplace design on analyses of the quality of employee experiences in an organization
Workers are more satisfied w/ their jobs when they believe supervisors share their views of work-life balance
Idea is: when ppl are happy at work, they are more productive
Telecommuting: working in their homes
Flextime: employees free to come and go, as long as they get their required amount of hours