FLUOROSCOPY Ch25
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What is conventional Fluoroscopy?
is a technique that allows still or moving image of internal structures and fluid on monitor or TV screen
When can conventional Fluoroscopy be used?
can be used in:
G.I. studies
Urology studies
Surgery
Cardiovascular exams
R/F Room
additional “features” in exam room
Fluoroscopic Imaging Chain
Monitor
Video Camera
Optical Coupling
Image Intensifier
Grid
Patient
Table
Filtration
Collimator
X-ray tube
X-ray Generator
What are the two basic components of Fluoroscopy
X-ray table
Image intensifier (conventional)
OR
FPIR used - newer technology (DR)
How are Fluoro and X-ray tube design different?
Fluoro time - smaller focal spot and operate on lower mA with longer exposure times, tube current: .5 to 5 mA
X-ray tubes - usually 1 to 3 mA (most common) - higher mA with shorter exposure time
I.I. Gride Purpose
Increase image quality
Decrease scatter radiation
Conventional Fluoroscopy → Linear grid
Lower grid ratios used
I.I. Tube Purpose
Evacuated glass envelope capable of converting x-ray photons into visible light and intensifies light (brightness)
by moving the I.I closer to the patient during fluoro, what is the result/reason:
decrease SID
decrease patient dose
improves image quality
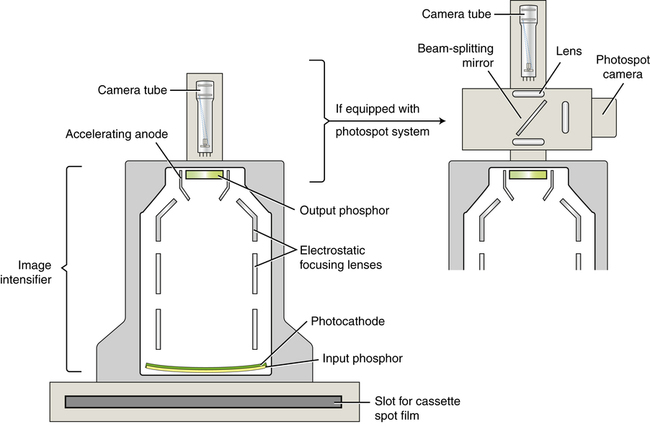
Components of the I.I. Tube
Input phosphor
Photocathode
Electrostatic Focusing Lenses
Accelerating anode
Output phosphor (screen)
What does the input phosphor do?
Absorbs x-rays and converts their energy into light (like intensifying screen)
What is the input phosphor made of?
Cesium Iodide (thin coating)
How big and what shape is the inout phosphor?
4 to 16 inches in diameter, slightly convex shape
Where is the photocathode?
attached to the input phosphor by adhesive layer
Photocathode, what are the thing layers?
Cesium Iodide and Antimony
What does the Photocathode do?
Converts light from input phosphor to electrons by photoemission
How are both Input screen and photocathode shaped? & why?
Both slightly curves so each electron travels same distance (preventing distortion)
What do Electro Static Focus lenses do?
Accelerated and focuses electrons stream onto putput phosphor
Where is the electrostatic focusing lense located?
located along length of image intensifier tube
How do electrostatic focusing lenses change modification of image?
By changing the focusing point of electrons
What is the accelerating anode?
Circular plate with a hole in the middle to allow electrons through to the output phosphor
Where do the electrons speed up?
Accelerating anode
What is the output screen phosphor?
Convert high energy Photo electrons to light photons
What is the output green phosphatase made of?
Made of zinc cadmium sulfide
How much brighter does the output phosphatase make the image?
The image from the output phosphor is over 5000 times brighter than the image at the input Phosphor
What is the image intensifier process?
output Phosphor
Accelerating anode
Electrostatic focusing lenses
Photo cathode
Input phosphor
Output phosphor
Convert photoelectrons to light photos
Accelerating anode
Speed up electrons photo electrons
Electrostatic focusing lenses
Focuses electrons
Photo cathode
Convert light protons to electrons
Input phosphatase
X-ray, converting to light photos
What is automatic brightness control ABC?
Keep brightness of image contrast at monitor
What is automatic brightness control A.k.a.
Automatic brightness stabilization ABS or automatic exposure rate control AERC
When can you adjust ABC?
Can adjust for part thickness and contrast medias
What does ABC prevent?
Prevents fluctuation and image brightness and signal to noise ratio by adjusting kVp and mA
How must the part be position for ABC?
Part must be centered properly
What happens once ABC hits maximum levels of technical factors?
The AGC kicks in and adjust the brightness by amplifying the electronic signal. It is adjusted within the viewing system and does NOT affect patient dose.
What does AGC stand for?
Automatic gain control
What is brightness Gain ?
Ability of imaging intensifier to increase brightness levels of image
What does total brightness gain equal?
Total brightness gain = minification gain x Flux gain
What is the brightness gain of most images?
The brightness gain of most image intensifiers is 5000 to 30,000 (Will decrease with tube age and use)
What is minification gain?
Occurs as a result of same number of electrons produced at large input Phosphor being compressed into area of small output Phosphor
What is the equation for minification gain?
MG = (Input screen diameter)* Squared / (output screen diameter)* Squared
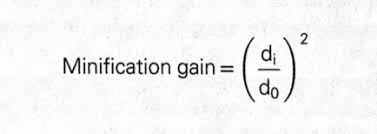
Most imaging intensifier are constructed with how big output phosphorus
1 inch
What is flux gain?
Measurement of increase in light photons due to conversion efficiency of output phosphatase
What does flex deal only with?
Deals only with the gain accomplished by the electrons to light conversion at the output Phosphor
Where does the electron energy come from?
Electron energy comes from accelerating voltage from between Photo cathode and anode
Flux gain equals?
Flex gain = Number of output light photons / Number of input x-ray photon

Two types of light receptors
Rod
Cones
What are both rod and cones responsible for?
Both are responsible for human vision
Both are found in retina and detected light
What is the function of rods?
Function in light or scotopic vision; Perceived grays (Colorblind)
Where are rods located?
On the peripheral of the retina
What is the function of cone?
Function in daylight or photopic vision; perceive color and brightness levels.
Perceive small objects better than rods
Where are the cones located?
In center of retina
What is the cornea?
Clear part of eye covering the iris and pupil, let’s light into the eye allowing site
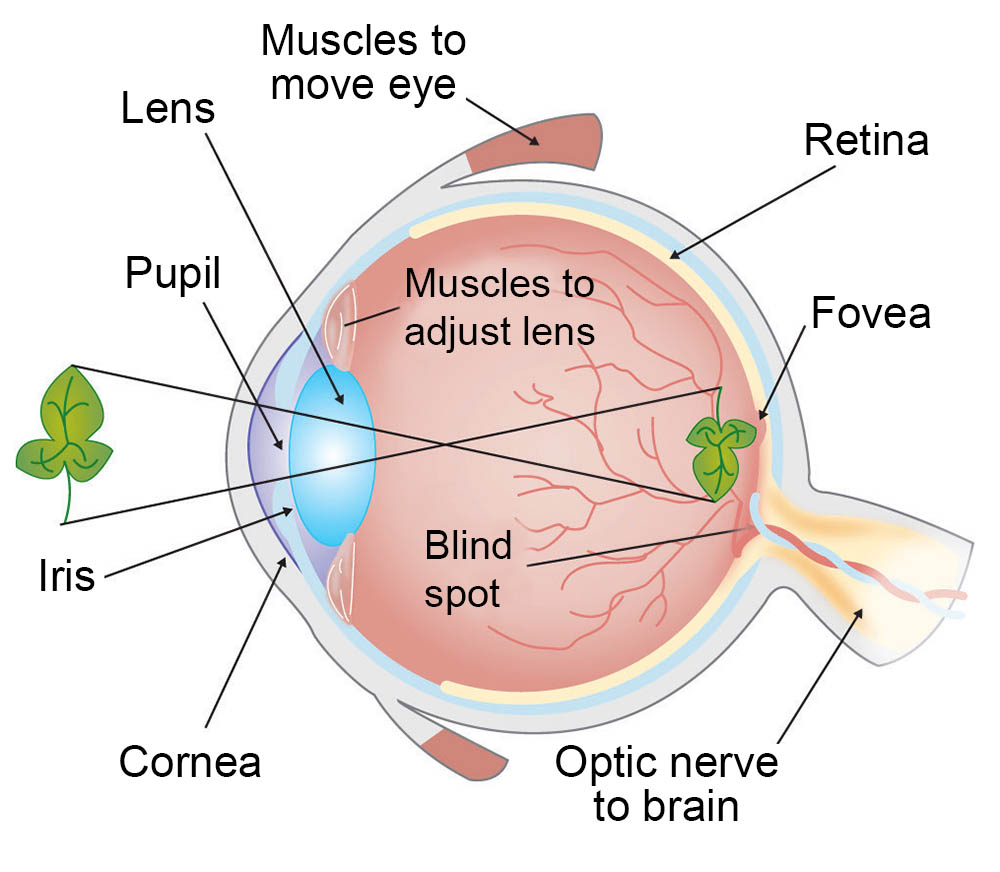
What is the pupil?
Round, dark center of eye, which opens and closes to regulate amount of light the retina receives
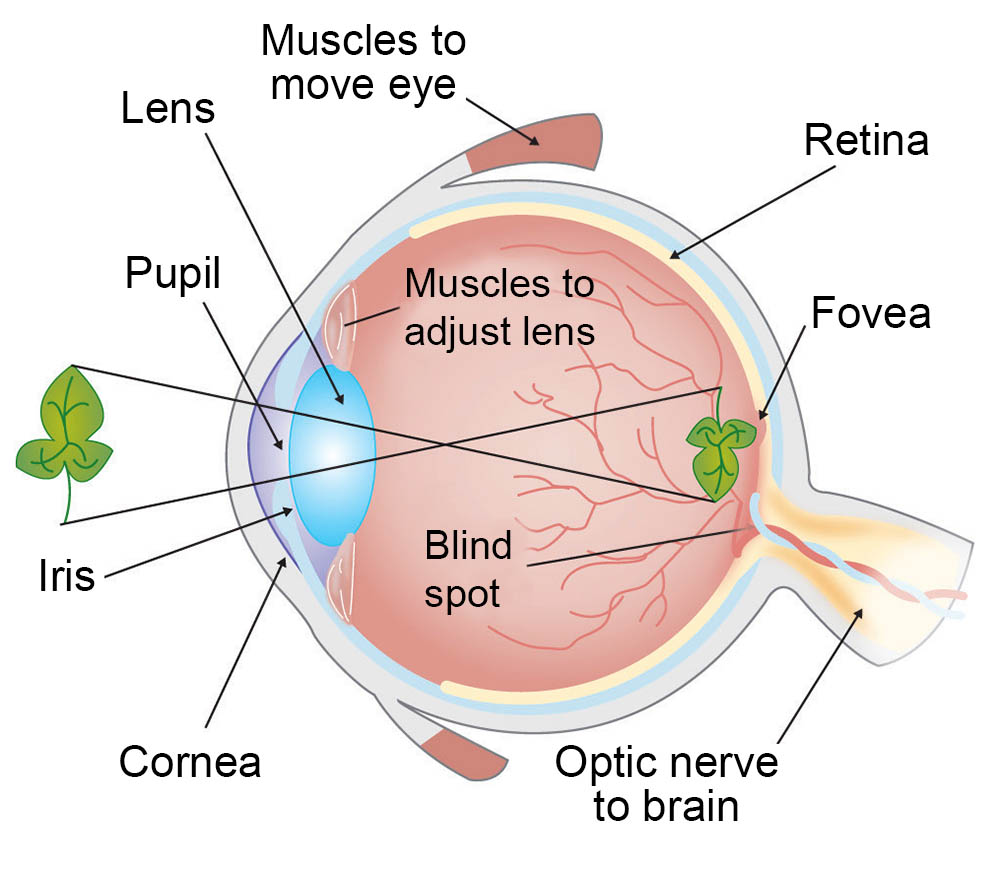
What is the iris?
Colored part of the eye surrounding the pupil. It acts like a diaphragm to widen or narrow the pupil, controlling the amount of light that enters the eye.
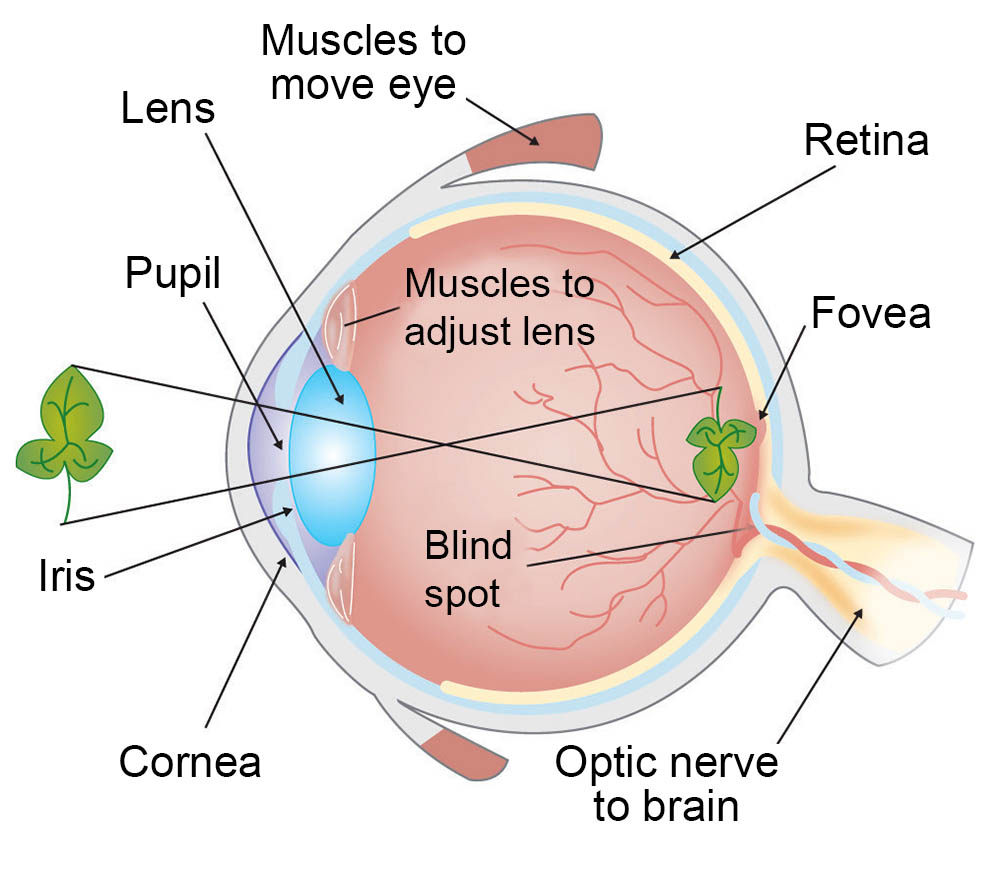
What is the retina?
Sensory membrane that line the eye; It receives image formed by the lens and converts them into signal that reaches the brain by way of optic nerve
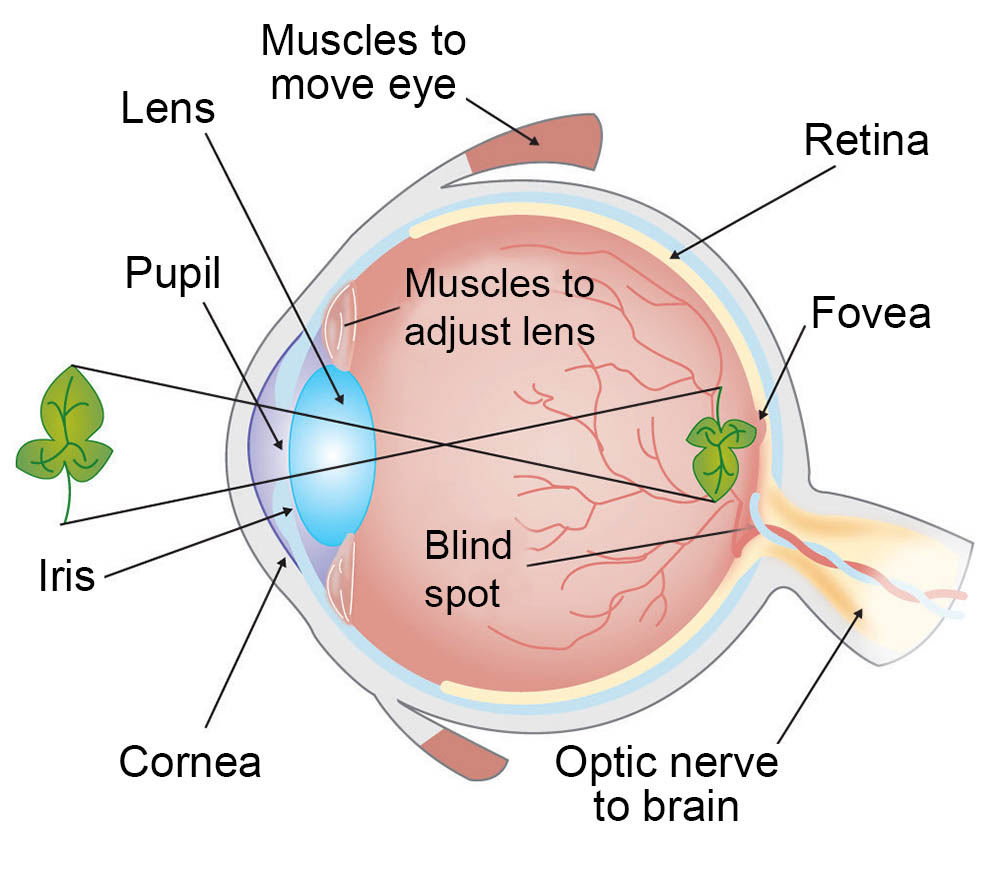
What is a lens?
Spherical body in eye located behind cornea, that focuses light raise onto retina
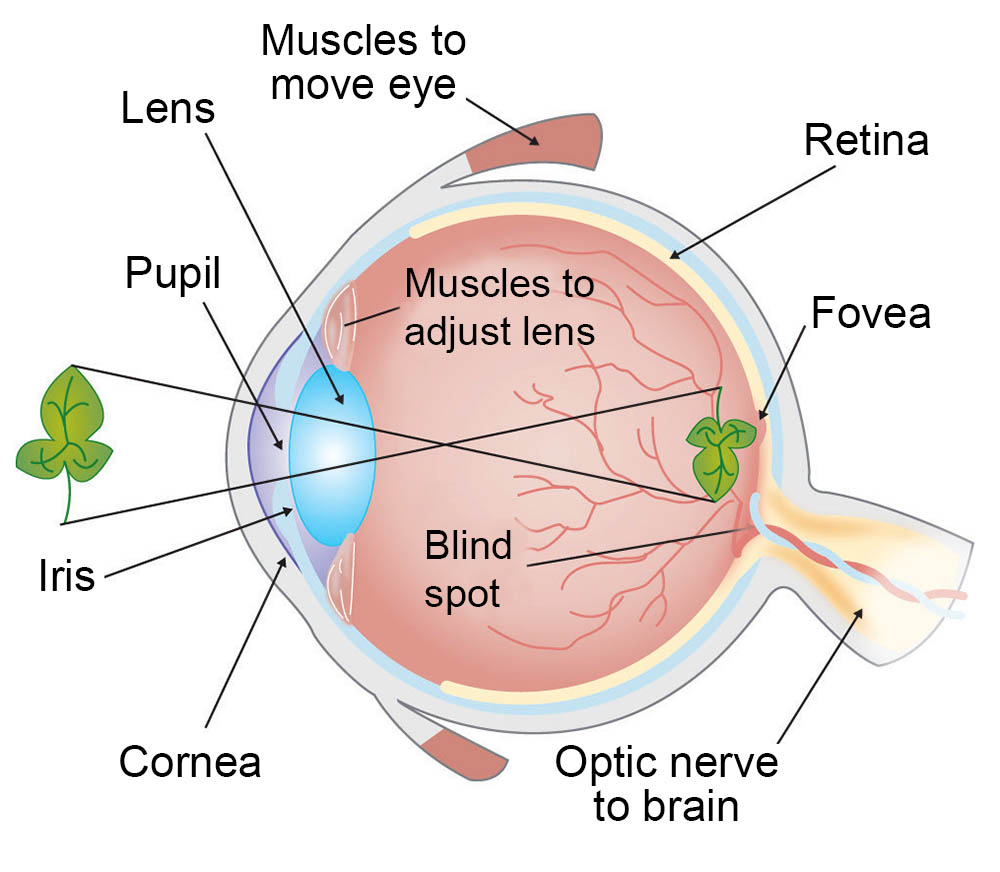
What is the vision process?
Light passes through cornea, through the lens, where light is focused on retina
Between cornea and lens is Iris (Which constricts and dilate amount of light entering the eye)
When light enters retina detected by rods and cones
Low light equals
Iris dilates (opens up) Allowing more light in
Bright light equals
Iris constricts (closes) Not allowing as much light in
What is Visual Acuity?
Ability to perceive find detail
What is the normal viewing distance of an image?
12 to 15 inches
What is the time required by the eye for recognition of an image?
Integration time is about .2 seconds
How is an image magnified?
Occurs when useful area of input phosphorus, decreased while output phosphatase remains the same
How is the image intensifier designed to magnify?
Electronically by changing voltage on electrostatic lenses
A magnified image results in =
Small diameter = Fewer photo electrons from the image = Dimmer image = Tube mA Increase to compensate or maintain brightness (ABC) = HIGHER PATIENT DOSE
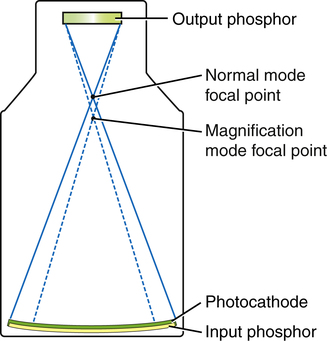
Magnification mode =
INCREASED PATIENT DOSE
Magnification Ex:
Smaller FOV = Spatial resolution is increased, and patient dose is increased
Image intensifier number refers to diameter of
Input phosphor
Normal mode equals
4 LP/MM
Mag mode =
6 LP/MM
What is resolution?
Detail; Ability of imaging system to differentiate small objects as separate images as they are position close together
Resolution relationship is
Between object, size and line pairs per millimeter is inversely related
Smaller object size =
Better resolution
How big is the resolution of cesium iodide in I.I.?
4 plus/mm
Magnification mode results in
Better spatial resolution
Better contrast resolution
Higher patient dose
What are image quality issues with imaging intensifier?
Vignetting
Pincushion effect
S shape distortion
Blooming
Vail glare
Lag
Noise
What is Vignetting?
Decrease brightness on peripheral of image; Reduces contrast and detail
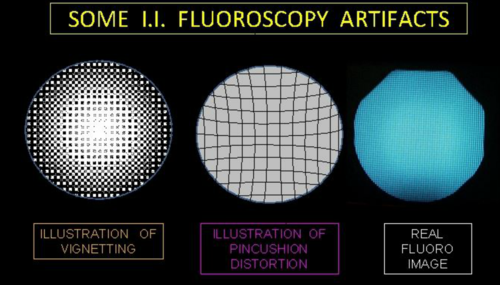
What causes Vignetting?
Curved input phosphor
Increase OID
What is pincushion effect?
Caused by curved input phosphatase to a flat output phosphor
Form of spatial distortion
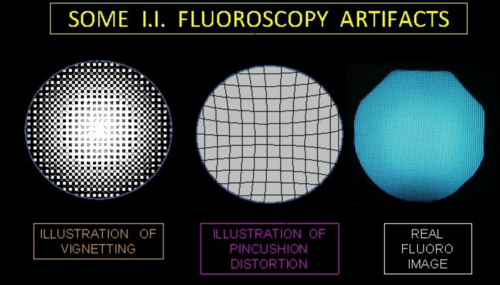
What is S shape distortion?
Same idea as pincushion effect, more of S shaped distortion
When is blooming?
High energy photons hit input Phosphor = Results in loss of acuity
Shows up on image as white streaks
What is Vail glare?
Type of blooming
Loss of visual sharpness, hazy
What is lag?
Delay in response of image intensify due to change in beam intensity
What is noise?
Quantum mottle
Not enough mAs
Impacts image clarity