Homeostatis 1
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Parts of Nervous System
Central Nervous System(Brain, spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system(all other parts)
Peripheral - somatic(concious) and autonomic(not consious)
Somatic(voluntary) - sensory(relays info to cns) and motor(initiates response)
Autonomic(involuntary) - Sympathetic and parasympathetic
Dendrite function
Receive nerve impulse from other neurons or sensory receptors and transmit them to the cell body.
Cell body function
contains nucleus and is site of metabolic processes
processes input from dendrite and sends to axon if nerve impulse is large enough
Axon function
conducts impulse away from cell body
Myelin sheath function
protects neurons and speeds up the rate of nerve impulse transmission (saltatory conduction) by insulating axon
Motor neuron
multipolar neuron
transmits info from cns to effectors(muscles, glands etc)
Sensory neuron
unipolar neuron
sensory receptors receive stimuli and form nerve impulse and transit it to cns
Interneuron
bipolar neuron
connects sensory and motor neurons
where are types of neurons found
Bipolar - retinas, inner ear, olfactory area of brain
Multipolar - brain and spinal cord
Unipolar - peripheral nervous system
Reflex arc
receptor(pain) receives stimuli
sensory neuron then sends it to interneuron in spinal cord
sent to motor neuron which sends to effector
effector initiates response
Spinal cord
carries nerve messages from receptors to brain
communication link between pns and brain
consists of grey and white matter
protected by vertebral column and cerebrospinal fluid
Central Nervous System
structural and functional centre for whole nervous system
receives info from sensory neurons, processes info, and initiates response
damage to cns can effect temperament, motor control, and homeostasis
White matter
myelinated axons which make it white
found in inner region of some parts of brain and outer area of spinal cord
Grey matter
unmyelinated neurons
grey because it consists of dendrites and cell bodies
found in outside areas of brain and h shaped cone of spinal cord
regions of brain
forebrain(thought, learning and emotion)
midbrain(processing sensory input)
hindbrain(coordination and homeostasis)
forebrain parts
olfactory lobes, cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland
highly developed
midbrain parts
4 spheres of grey matter
less developed
relay center for some eye and ear reflexes
hindbrain parts
joins with spinal cord
cerebellum, pons, medulla oblongata
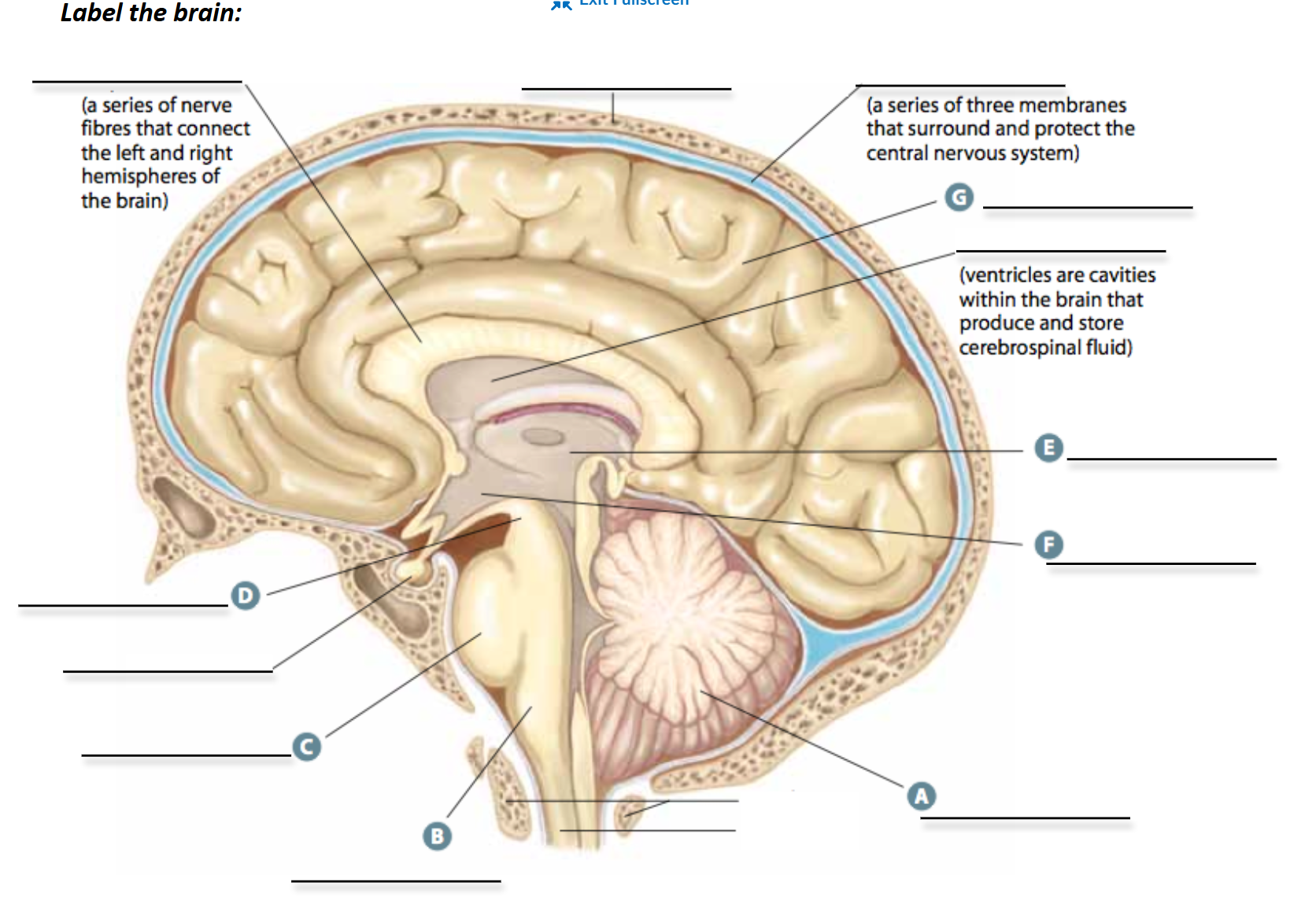
Label brain parts
What are meninges
series of 3 membranes that surround and protect the central nervous system
Blood-brain barrier
protective barrier formed by glial cells and blood vessels that seperates blood from cns
selectively controls entrance of substances into the brain from the blood
Astrocyte
type of glial cell that surrounds capillaries
cerebrospinal fluid
clear dense liquid found in ventricles of brain and central canal of spinal cord
transports hormones, wbc, and nutrients across blood-brain barrier to cells of brain and spinal cord
cushions brain by acting as shock absorber
Cerebellum function
unconsious coordination of posture, balance, body movements, reflexes, and fine, voluntary motor skills like writing, riding a bycycle
Medulla Oblongata function
connects brain with spinal cord
coordinates many reflexes and bodily functions like heart rate, rate of depth of breathing, swallowing, coughing
Pons function
serves as relay center between neurons of the right and left halves of cerebrum, cerebellum, and rest of brain
Midbrain function
process info from sensory neurons in eyes, ears, and more
relays visual and auditory info between hindbrain and forebrain
important for eye movement and control of skeletal muscles
Thalamus function
contains neurons that provide connections between parts of brain (mainly between forebrain and hindbrain, areas of sensory system, and cerebellum)
great relay station
Hypothalamus function
helps regulate internal body environment and certain aspects of behaviour
contains neurons that control bp, heart rate, body temp, and basic drives (fear, rage, pleasure)
Cerebrum function
largest part of brain
divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres
intellect, learning and memory, conciousness, and language
interprets and controls response to sensory info
Pituitary gland functions
regulates growth, metabolism, and reproduction
What is cerebral cortex?
thin outer covering of grey matter covering brain
5 mm thick and highly folded
responsible for language, memory, personality, concious thought etc
What is corpus Callosum?
bundle of white matter that connects 2 cerebral hemispheres of the cerebrum of brain
sends messages from one cerebral hemisphere to other, telling it what the other half is doing
Occipital lobe function
receive and analyze visual info
recognizes what is being seen
Temporal lobe function
also processes visual info
auditory reception
linked to understanding speech and verbal and visual memories
Parietal lobe function
receives and processes sensory info from skin
helps to process info about body’s position and orientation
Frontal lobe function
integrate info from other parts of brain and control reasoning, critical thinking, personality, and memory
contains motor areas that control various aspects of precise voluntary motor movement
function of somatic system
control voluntary movement of skeletal muscles
sensory neurons carry outside info inside
sensory neuron role in somatic system
carry info about external environment inward, from receptors in skin, tendons, and skeletal muscles
motor neuron role in somatic system
carry info to skeletal muscles
Cranial nerves
12 pairs
largely associated with functions in head, neck and face
Spinal nerves
contains sensory and motor neurons
eg. thoriac nerves control muscles of rib cage
Autonomic system function
controls involuntary glandular secretions and functions of smooth and cardiac muscle
regulates bp, heart and breathing, digestion, body temp, metabolism, urination etc
individual does not have to control body conciously
controlled by hypothalamus and medulla oblongata
nerve role in autonomic system
stimulate of inhibit glands or cardiac or smooth muscle
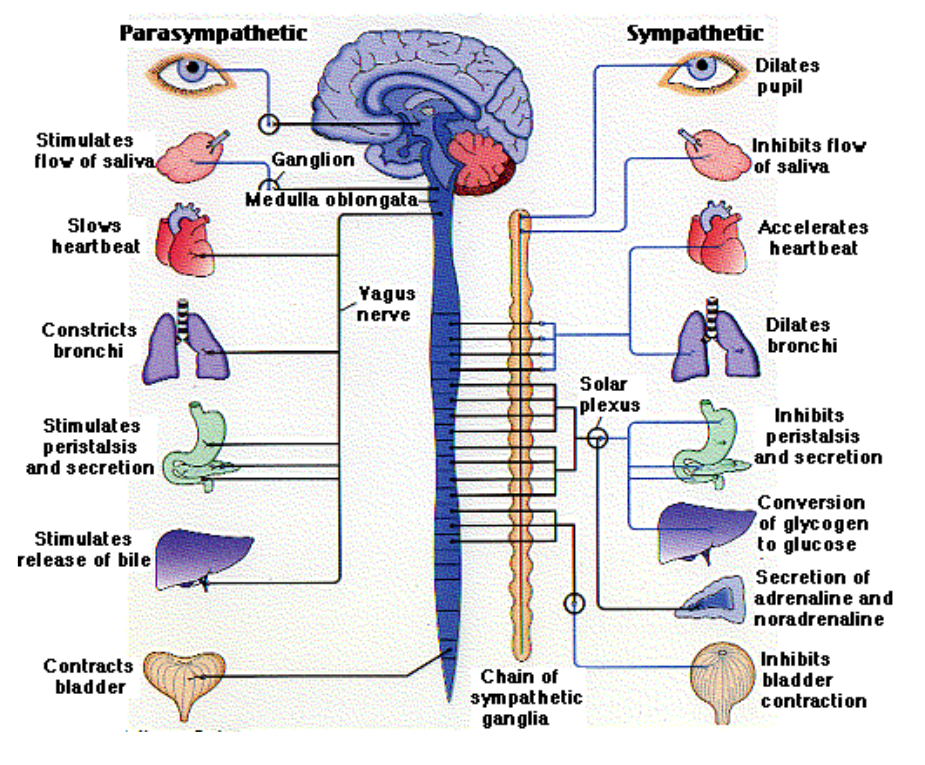
Sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight response
activated in stressful situations
regulates voluntary processes in body
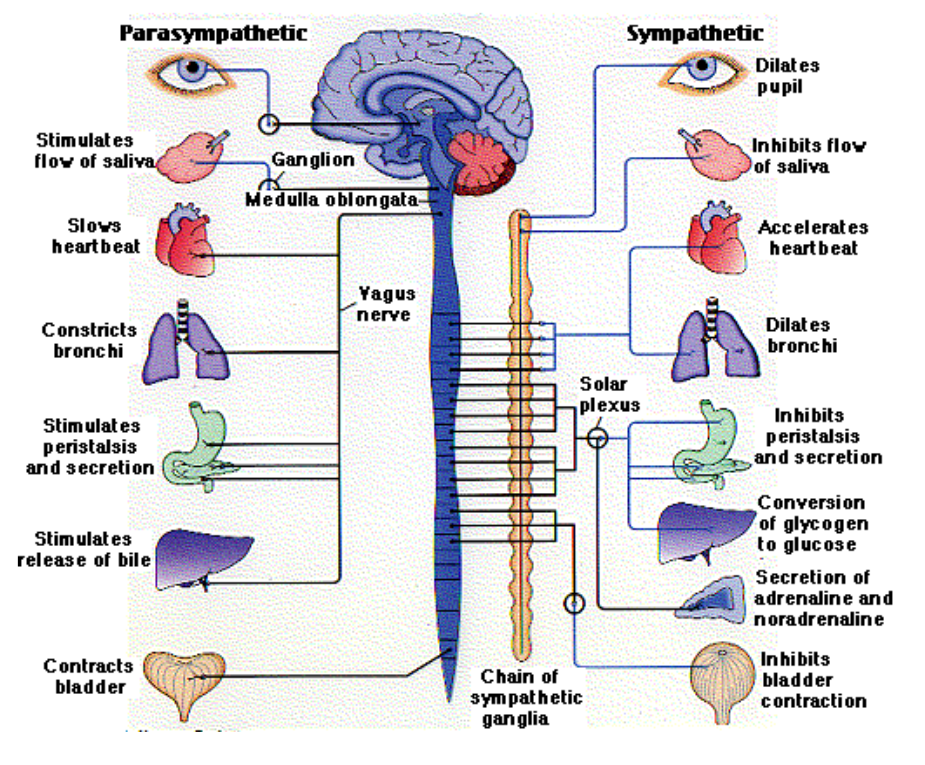
Parasymphathetic nervous system
body is calm and at rest
rest and digest response
acts to restore and conserve energy
regulates involuntary processes in body
Effector functions in symphathetic nervous system
tear ducts inhibit tears
pupils dilate
salivary glands inhibit salivation
lungs dilate air passageways
increased heart rate
liver stimulated to release glucose
inhibits activity of pancreas, stomach, and kidneys
adrenal glands stimulates adrenal secretion
decrease of intestinal activity
inhibits urination
Effector functions in parasymphathetic nervous system
stimulates tears
constricts pupils
stimulates salivation
constricts air passageways
slows heart rate
stimulates gallbladder to release bile
increased activity of stomach and pancreas
increases intestinal activity
stimulates urination
What is homeostasis/dynamic equilibrium?
process by which a constant internal environment is maintained despite fluctuating external environment
body best working functions
37 degrees
0.01 blood sugar
7.35 pH
Homeostatic Control Systems
Monitors: special sensors found in organs
Coordinating/control center: relays info from monitors to necessary regulator
Regulator: helps restore balance(initiates action)
Negative Feedback
when a system deviates from norm, internal processes help to restore balance and normal conditions
Positive Feedback
output enhances or turns up original stimulus
helps amplify conditions away from norm
eg. blood clotting
Thermoregulation
mean body temp 36.8
hypothermia <35
temp regulation stops <30
heatstroke >40
endotherm can regulate temp, ectotherms can’t
Mammalian diving reflex
heart rate slows
hypothermia
blood diverted to brain and other vital organs
Response to heat
sensors in hypothalamus detect change
nerve signal sent to sweat glands to start sweating
nerve signal also sent to blood vessels in skin to start dilating
Response to cold
sensors in hypothalamus detect change
nerve signal sent to skeletal muscles to start shivering
nerve signal sent to blood vessels in skin to start constricting
nerve signal sent to smooth muscles surrounding hair follicles to stand on end
Brown Fat Metabolism
prolonged exposure to cold causes hormonal response that increases metabolism
special adipose tissue efficient at producing heat when metabolized
important in babies
Maintaining resting potential
large negative protein molecules inside (cannot pass through membrane)
K+ channels open more at resting potential so more K+ moves out then Na+ moves in
Sodium Potassium pump transports Na+ and K+ in ratios keeping inside more negative
more Na+ out of cell than K+ in cell
creates electrochemical gradient
Sodium-Potassium Pump
most important factor in maintaining resting membrane potential
for every 3 Na+ ions pumped out, K+ pumped in
necessary because Na+ and K+ ions slowly leak across membrane (K+ diffuses faster)
All or none response
once -50 is reached, neurons fire maximally
the more intense the stimulus, the greater the frequence of impulses
intense stimuli excite more neurons (affects number of impulses reaching brain)
action potential steps
if it reaches threshold, Na+ voltage gated channels open and Na+ comes into cell, depolarizing it
Reaches 40 mV then Na+ channels are inactive and K+ voltage gated channels open
K+ leaves cell, repolarizing it and the charge drops to -90 mV, making it hyperpolarized
this is called refractory period where another action potential can’t occur
sodium-potassium pump works to bring it back to -70 mV
Synaptic Transmission steps
Action potential reaches axon end and depolarizes it
it causes Ca+ channels to open and Ca+ flows into presynaptic terminal
that causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with presynaptic membrane
neurotransmitters exit through exocytosis into synaptic cleft and diffuse across it
binds to receptors on post synaptic neuron
if inhibatory, opens K+ channels and K+ diffuses out (no action potential, nerve signal stops)
if excitatory, opens Na+ channels and Na+ diffuses in ( action potential so nerve signal continues)
Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine acts as excitatory NT, opens Na+ channels, causing depolarization
cholinesterase from post synaptic neuron destroys acetylcholine preventing constant state of depolarization
inhibitory NT’s make post synaptic membrane more permeable to K+(more channels of Na+ need to be opened for action potential)
Summation
effect produced by accumulation of NT’s from 2 or more neurons