Bio 1615 Lab Final
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Compound light microscope
When to use: slides, microscopic things
Ocular magnification: 10x
Objectives: 4x,10x, 40x,
Object orientation: inverted and upside down
Stereo microscope (dissecting)
When to use: things you can see with the naked eye
Ocular magnification: 10x
Objectives: 0.8-3.5x
Object orientation: normal does not change
Total magnification equation
Ocular (eyepiece) magnification x objective magnification
Steps of the scientific method
Recognize a problem
Search the literature
Formulate your hypothesis
Conduct and experiment
Organize your data
Accept, reject, or modify
Guess
The lowest level of certainty, no information upon which to base the guess
Estimate/ Hypothesis
An educated guess in which some research has been conducted, either supported or not supported by experimentation and evidence but are NOT PROVEN
Theory
An explanation in nature that is supported by overwhelming evidence that has yet to be refuted
Law
Similar to theory, but is explained with mathematics.
Cricket chirp experiment outcome
The lower the temperature, less crickets chirping frequency
Cricket chirp experiment DV, IV, Control
IV: temperature
DV: chirps
CONTROL: the environment and species stay the same
Monomers are building blocks that make up____
Polymers
Protein; amino acids
Carbohydrates; sugar
Lipids; fatty acids and glycerol
Hydrogen bonds
Formed between butogen based, so hydrogen hints hold the two strands of DNA together in the center
Covalent bonds
Formed between nucleotides themselves, hold down together each sugar phosphate backbone of DNA, on outside
Polymerase chain reaction
Discovered by Dr. kary Mullís, a process used to build up polymers; in this case the polymer being dna
Denaturation
Heated to break the hydrogen bonds
DNA synthesis/ Elongation
Taq polymerase adds nucleotides to the DNA strands
What is the end product of PCR
Many copies of the target DNA
Domain bacteria/ archea
Prokaryotic, unicellular or colonial, have cell walls
Kingdom Protista
Eukaryotic, unicellular or colonial, some have cell walls, animal and plant like
Kingdom Fungi
Eukaryotic, mostly multicellular, have cell walls, photosynthetic
Kingdom Anamelia
Eukaryotic, multicellular, do not have cell walls
Domain Eukarya, Kingdom Protista
Mixed green algae;
Mixed Diatoms
Llilium ovary
Mga: unicelular, colonial filaments that are green
MD: buzzard shapes and sizes
LO: contains reproductive cells called ovules, arranged in parts of three
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the process by which molecules spread from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration.
Molasses Osmometer Experiment
Due to osmosis the water went into the molasses tube increasing the volume
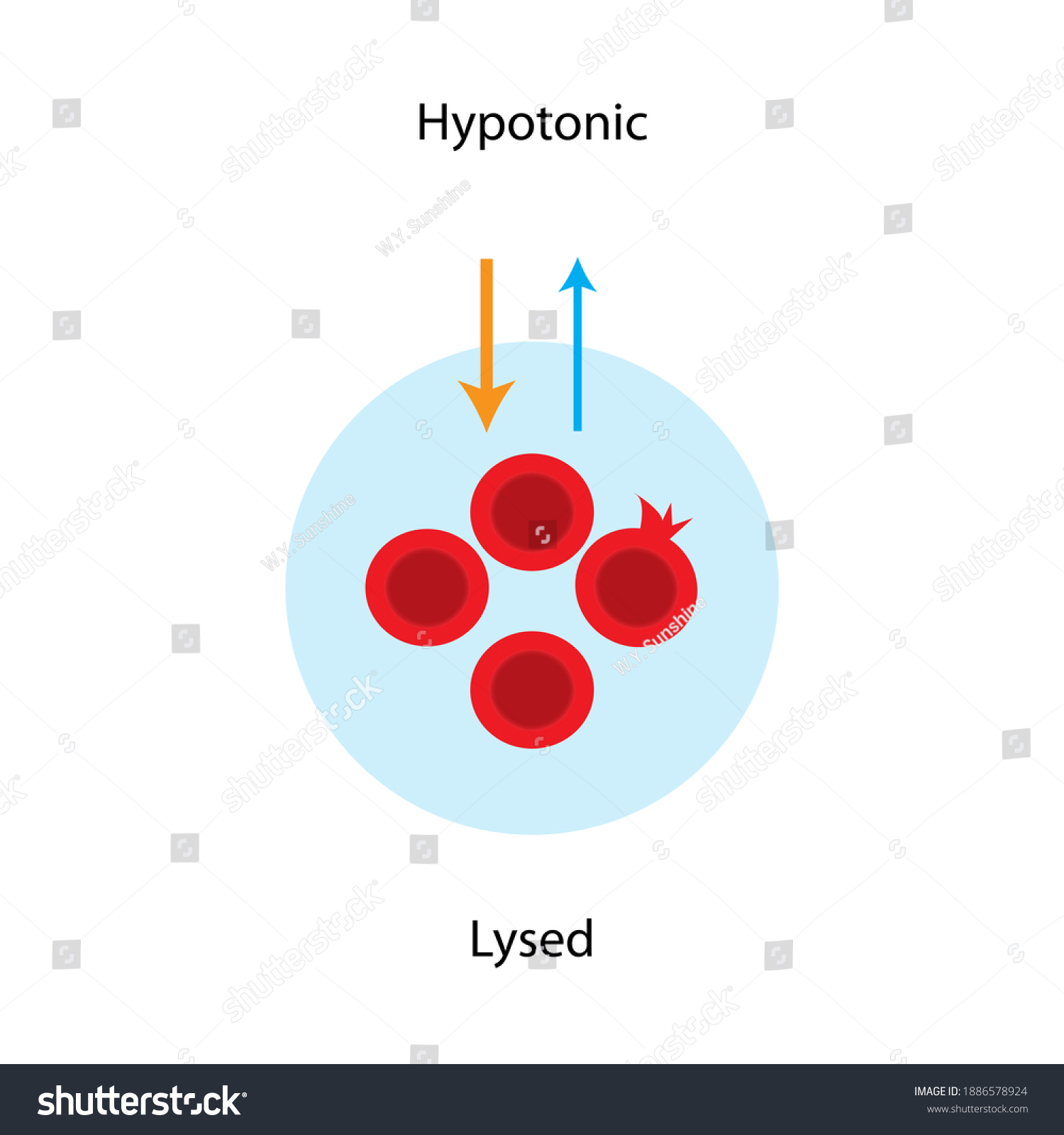
Hypotonic animal cells
Lyses and may explode
Isotonic Animal Cells
Normal
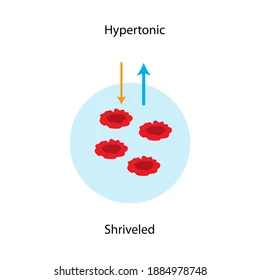
Hypertonic Animal cells
may cause an animal cell to shrivel or crenate
Factors that Affect Diffusion and Osmosis
● Solute concentration: water moves from areas of low solute concentration to
areas of high solute concentration.
● Temperature: the higher the temperature, the faster molecules move.
● Molecular weight: molecules with a higher molecular weight take longer to
diffuse.
● State of matter: molecules move fastest in a gas, slower in a liquid, and slowest
in a solid.
48
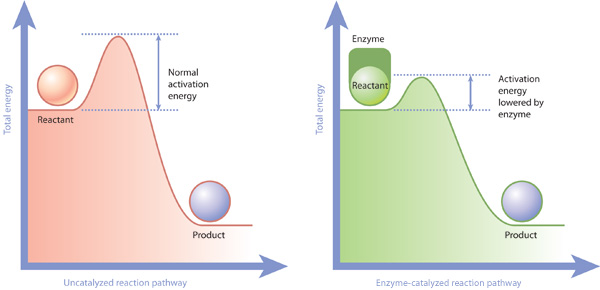
Enzyme Baiscs
Enzymes help lower the activation energy level Enzymes hold the reactants (also called
substrates) in such a way, that it takes less energy to turn those reactants into products.
Denaturation in Enzymes
Enzymes are also specific about the temperature and pH at which they are active.
Temperature and pH affect the bonds that maintain the shape of proteins. Changes in
temperature and pH may cause permanent changes to these bonds, thereby changing
the shape of the protein, a process called denaturation. The result is a non-functional
protein. Each enzyme has a different range of temperature and pH values in which it
works best.
jell-o has gelatin, what kind of macromolecule is gelatin? (look it up if needed)
Protein
If Bromelain breaks down gelatin, is it a protease, a carbohydrase or lipase?
Protease
Lab 6 Concentration of catalase
More enzyme means faster rate reaction
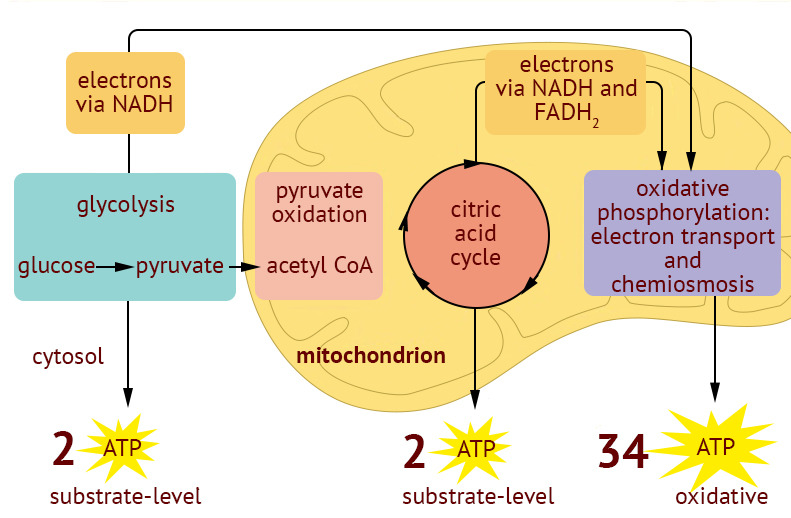
Celular respiration and ATP
Both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration harvest energy using the processes of
glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain
(oxidative phosphorylation); thereby, both aerobic and anaerobic respiration produce
about 30+ ATP respectively.
Citric acid Cycle
Glycolysis, Peruvate acid, electron transport chain
Fermentation
an anerobic process that is not part
of cellular respiration. Some microorganisms such as
bacteria, yeast and molds obtain their energy
through fermentation. This process
involves glycolysis, in which
only 2 ATP are produced, as
well as steps to regenerate the
electron carrier NAD+
Alcoholic Fermentation
the resulting pyruvate from glycolysis is converted to ethanol.
Yeast and many bacteria carry out alcohol fermentation in anaerobic conditions.
NADP+ and NADPH colors
When the dye is oxidized
(NADP+), it is blue. When reduced (NADPH), however, it turns colorless.
Light reactions
Metabolic pathway that is responsible
for absorbing light energy and
converting it into ATP and NADPH
Chloroplast
Organelle where the light reactions of
photosynthesis take place
NADPH
Produced by Photosystem I and its
associated electron transport chain
ATP
Produced by Photosystem II and its
associated electron transport chain
ATP AND NADPH
Final products of the light reactions
used during the Calvin Cycle
Why was there no photosynthetic activity in the BOILED cuvette?
It was denatured
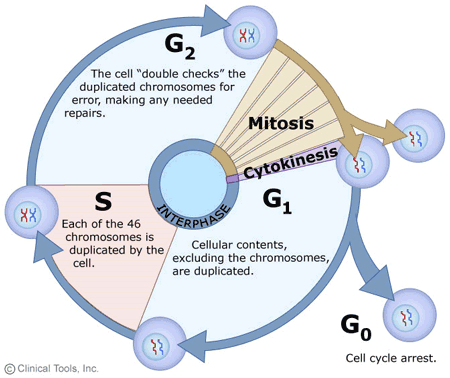
Mitosis Phases of the Cell Cycle
Mitosis: Division of the nucleus
Cytokinesis: Cytoplasm and organelles are allocated to each cell.
G1: Cellular contents excluding chromosomes are duplicated
S: Each of the 46 chromosomes are duplicated by the cell
G2: The cells checks each duplication for errors making any needed repairs
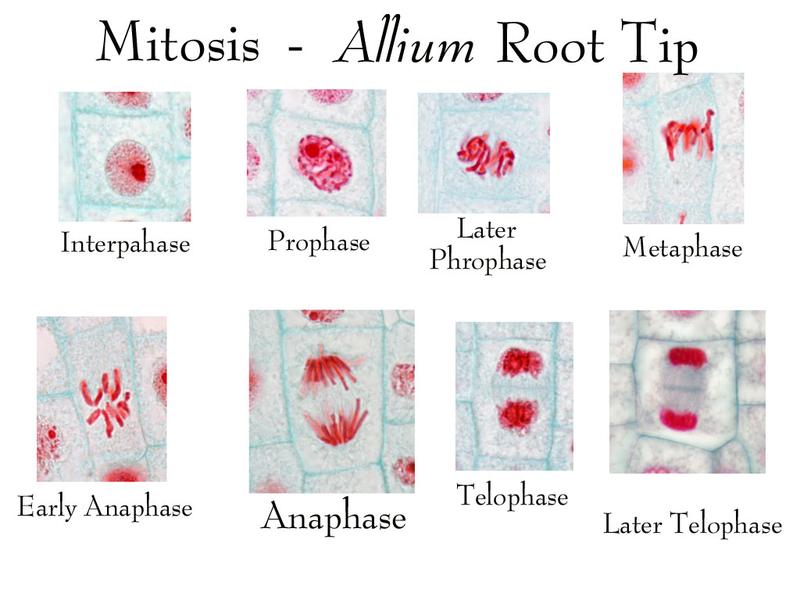
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase under a microscop
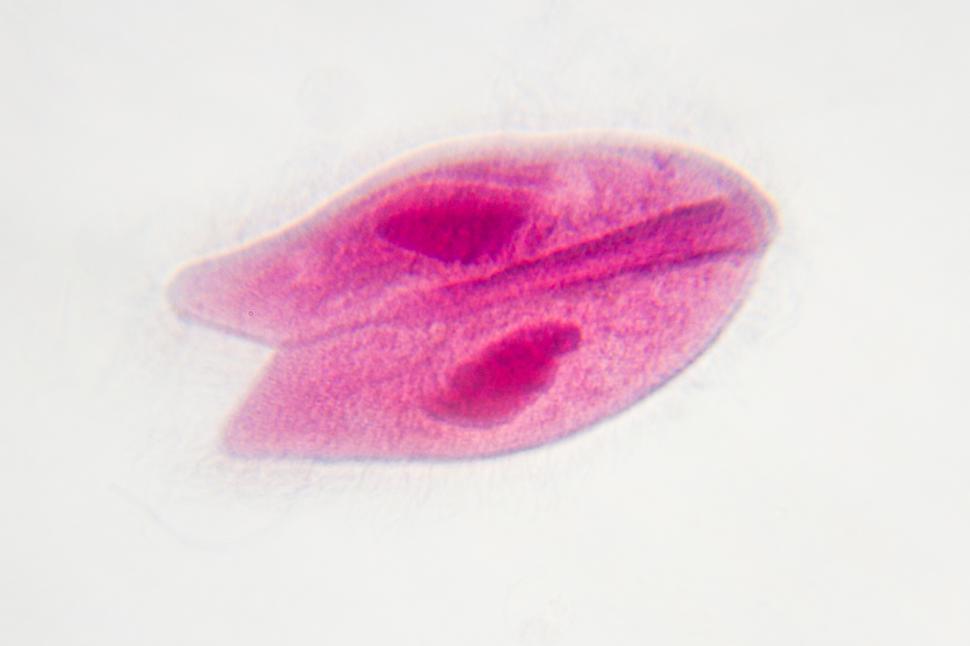
Paramecium conjugation
(Kingdom Protista)
Mitosis
Is the process asexual or sexual?
How many daughter cells produced?
Are the daughter cells haploid or diploid?
Are daughter cells genetically identical to the
parent? (Y/N)
Number of cell divisions
Involves separation of sister chromatids (Y/N)
Involves separation of homologous chromosomes
(Y/N)
Asexual
2
diploid
Yes
1
Yes
No
Meiosis
Is the process asexual or sexual?
How many daughter cells produced?
Are the daughter cells haploid or diploid?
Are daughter cells genetically identical to the
parent? (Y/N)
Number of cell divisions
Involves separation of sister chromatids (Y/N)
Involves separation of homologous chromosomes
(Y/N)
Sexual
4
Haploid
No
2
Yes
Yes
Gel electrophoresis tasters
tt: non-taster
Tt: taster
TT: taster
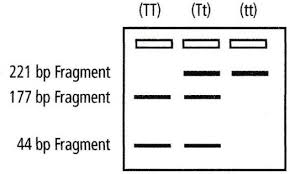
Mendels Law of Segregation/ Dominance
Mendel's Law of Segregation states that during the formation of gametes (sex cells), the alleles for a trait separate so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene.
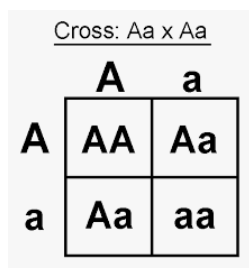
phenotypic and genotypic ratios
Phenotypic: 3 dominant, 1 recessive
Genotypic: 1:2:1
Dihybrid cross Genotypic ratios
9:3:3:1
Transcription
The specific section of
DNA that codes for that gene unzips, breaking the hydrogen bonds between the
nitrogen bases in the DNA molecule. Using the DNA bases as a template, an enzyme
called RNA polymerase builds an mRNA transcript. This mRNA transcript is similar to
the DNA strand, except it is single stranded, has ribose sugar, and has Uracil bases in
place of Thymine.
Translation
which occurs at the ribosome. The
ribosome “reads” the mRNA strand three bases
at a time (codon). A transfer RNA (tRNA) brings
the amino acid that corresponds to that codon,
using its anticodon to bind to the mRNA strand.
The amino acid is handed off, the tRNA leaves,
and the process repeats. The resulting protein
can then be used by the cell.
E-Coli and pGLO
In this experiment, your E. coli will take up a
manufactured plasmid as shown to the right,
named the pGLO plasmid. This plasmid contains a gene that codes for Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP). This protein is naturally found in the jellyfish, Aequorea victoria, giving this organism bioluminescence. A requirement for this gene to be transcribed is the sugar, arabinose, which acts as a promoter for the GFP gene. Your E. coli will only glow when arabinose is present on the bacterial plate
If there are any genetically transformed bacterial cells, on which plate(s) would
they most likely be found?
The last plate
On which plate(s) would you find bacteria most like the original non-transformed
E. coli found on the starter plates?
The first plate
Hardy Weinberg Equillibrium
1. There are no mutations in the population.
2. There is no genetic drift (the population must be large enough that a random
event will not change allele and genotype frequencies).
3. There is no gene flow between populations (no immigration and no emigration).
4. There is no natural selection (individuals survive equally well in the population).
5. Mating is completely random
p + q = 1
p = frequency of the dominant
allele (A)
q= frequency of the recessive
allele (a)
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
p2 = frequency of the homozygous
dominant genotype (AA)
2pq = frequency of the heterozygous
genotype (Aa)
q2 = frequency of the homozygous
recessive genotype (aa)
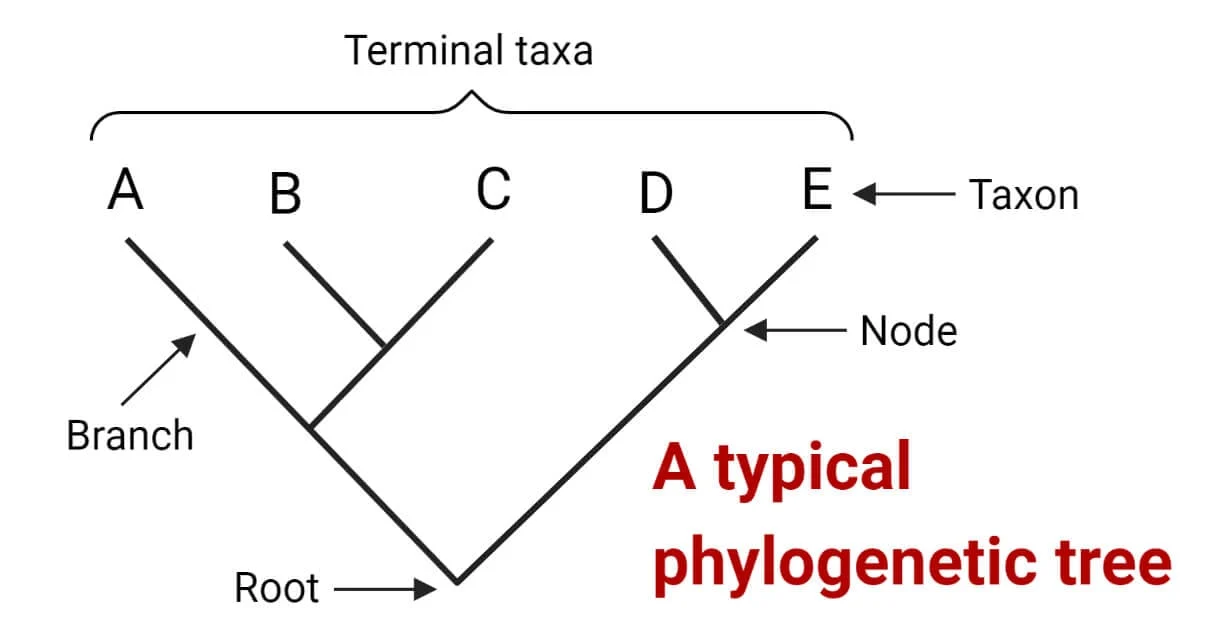
Which are the most closely related
D and E
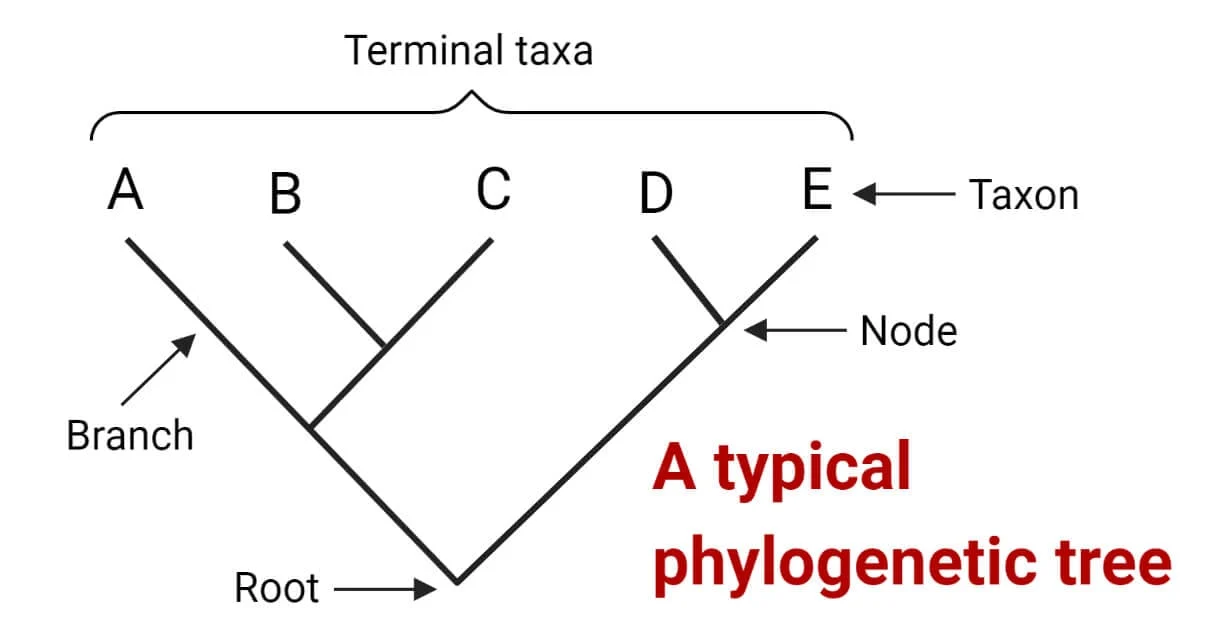
Which are least closely related
A and E
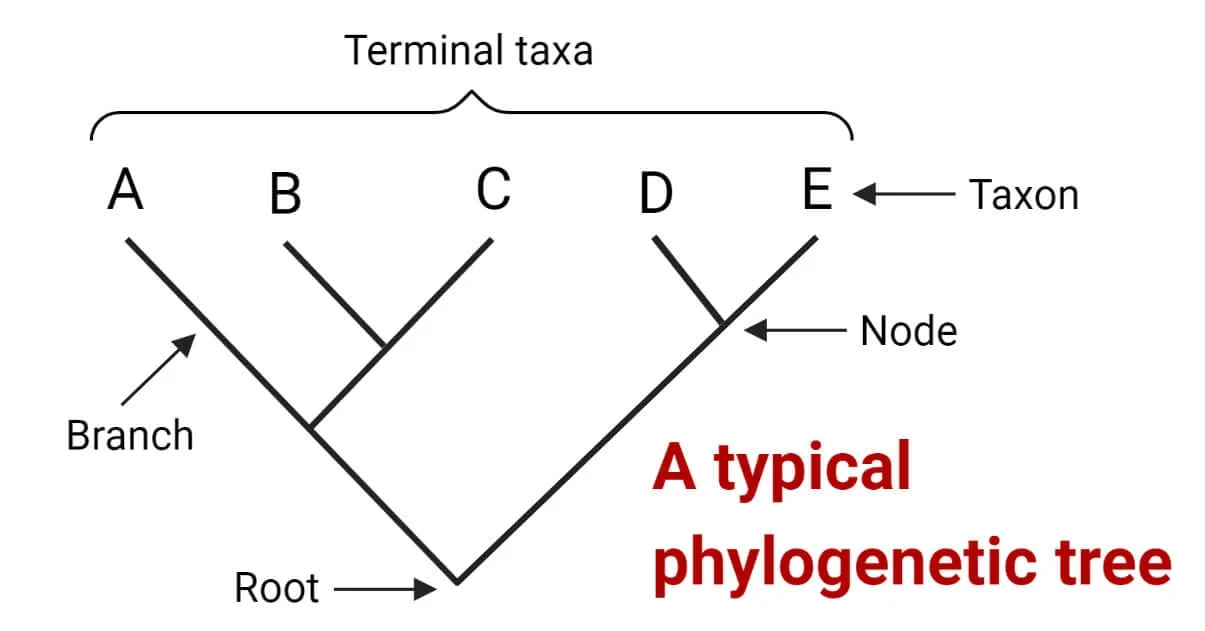
Which have most recently breaded with each other
D and E
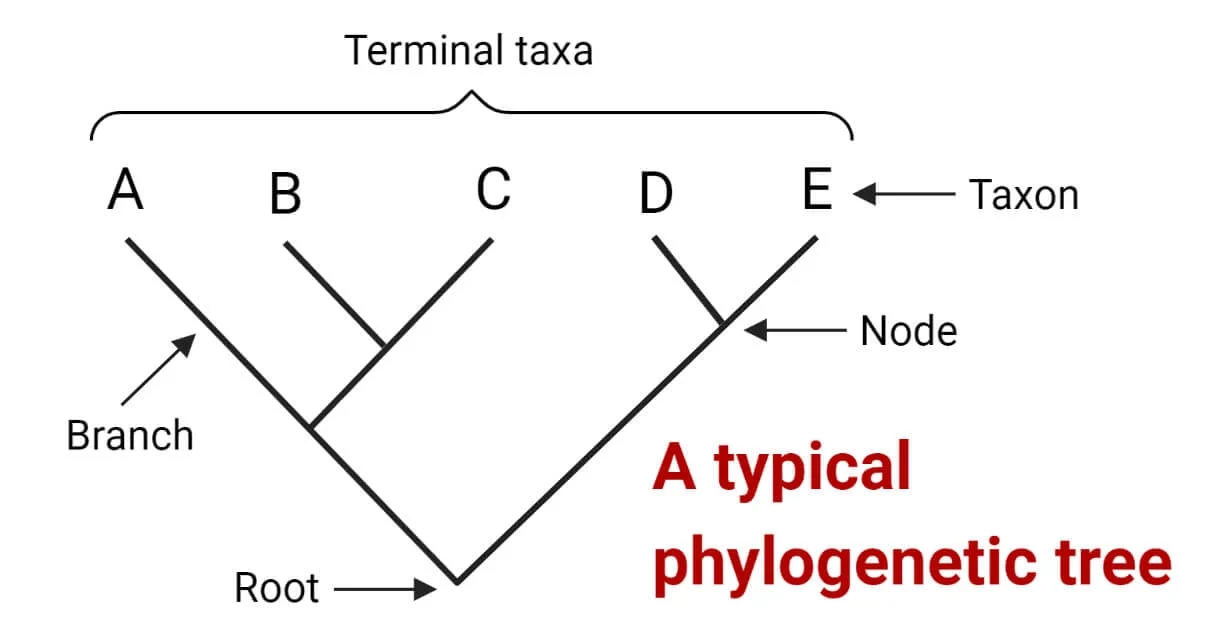
Which share the most DNA
D and E