Bio 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What should the surface area to volume ratio always be
LARGE. In order to have plenty of space to exachnage between the inside and outside of things
What are the two types of cells
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic
Light microscopes
Found in labs- used to study stained or living cells
Electron microscope
Used to study detailed structures of a cell
What is inside a prokaryotic cell
Cytoplasm
Where is DNA Found in a prokaryotic cell
Nucleoid
What surrounds a prokaryotic cell
Plasma membrane, then cell wall, followed by a thick capsule on the outside
How do prokaryotes move
With flagella
Name the parts of a prokaryotic cell
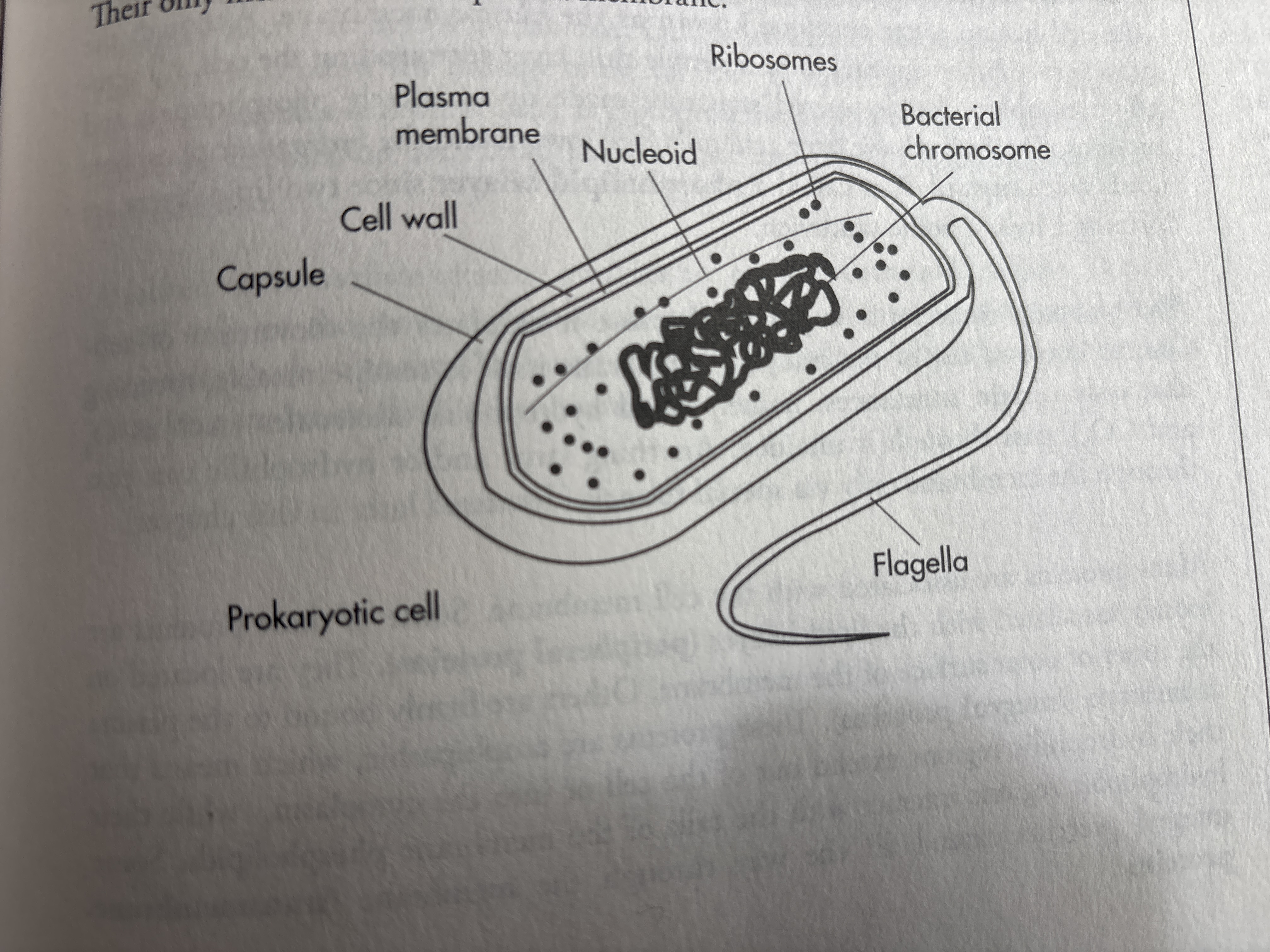
What is the only membrane in a prokaryotic cell
Plasma membrane
What is endosymbiosis
A theory that suggests that eukaryotic organelles used to be their own prokaryotic cells
What size cells have the most favorable surface area to volume ratio
Smaller cells
What is the outer envelope of the cell
Plasma membrane
What is the plasma membrane made of + which sides are hydrophobic and what direction do they face
Phospholipid bilayer (hydrophobic tails face inward and hydrophilic heads face outward)
What’s does the plasma membrane do
Regulates momvement into and out of the xell
What proteins are loosely associated with the bilayer
Peripheral proteins
What proteins are firmly bound to the plasma membrane
Integral proteins
What proteins extreme all the way through the membrane
Transmembrane proteins
What is the arrangement of the bilayer and proteins called
Fluid mosaic model
Adhesion proteins
Form junctions between adjacent ces
Receptor proteins
Docking sites for arrivals
Transport protiens
Form pumps that’s use aro to transport across the membrane
Cell surface markers
Exposed on the extrcellular surface to help identify the cell
Carbohydrate side chains
Increase membrane fluidity
What is the largest organelle in the cell
Nucleus
What is the role of the nucelus
Hold hereditary information (DNA) in the form of chromosomes + house the nucleolus
What are chromosomes and where are they found
They hold hereditary information in the nucleus
What is the nucleolus and where is it found
Makes RNA and ribosomes in the nucleus
What is the role of ribosomes
Facilitating protein synthesis and manufacturing proteins
Where are ribosomes found
Either free flowing in the cell or attached to the ER
What is the ER
Provides mechanical support and helps with transport
What is the rough er and what is it used for
Attached to the nucleus with ribosomes attached and compartmentalizes the cell. Makes Golgi bodies, lysosomes
What is the smooth er
No ribosomes, makes lipids and hormones to break down toxins
What is the role of the golgi complex
Processing of proteins, modifies sorts and packages materials to be sent out of the cell
How are packages sent across the crll
Vesicles
What are the membrane disks that the ER and golgi are made out of called
Cisternae
What is the role of the mitochondria
Converting energy from organic molecules to ones that the cell can use (ATP)
What is the most common energy molecule in the cell
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
How to recognize mitochondria
Double membrane, cristae peaks
Where is the most ATP creation done
Cristae
Role of lysosomes
Clean up crew, used to carry digestive enzymes and break down organelles and debris
How are lysosomes made
When vesicles carrying gogli fuse with vesicles made during endocytosis
What is cell death called
Apoptosis
What are centrioles
Used during cell division to make microtubules to pull chromosomes apart
Where are centrioles found
Microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs)
What are microtubules
They rip apart chromosomes during mitosis
What are vacuoles
Fluid filled sacs that hold food water etc
what are peroxisomes
detoxify various substances + produce H2O2 as a byproduct
what is the cyto skeleton and what is it made of
holds thee cell together + allows it to keep its shape and is made out of protein fibers
what types of protein fibers is the cytoskeleton made out of
microtubules and microfilaments
what are microtubules + what are they made of + where can they be found
part of cytoskeleton - made up of the protein tubulin and helps with cell division and movement - centrioles, silica, and flagella
what are microfilaments + what are they made of
made of the protein actin - assist with cytokinesis and cella movement
what are cilica and flagella
threadlike strucutres known to move by using a beating motion
cells move using….
cilica and flagella
how do plant cells differ from animal cells
they have a cell wall + central vacuole
what is a cell wall used for + what are they made out of
providing suppourt for the cells + protecting against osmotic changes. they aklso include choloroplasts
what is the cell wall made of in fungi
chitin
what do mature plants have in their vacuole
cell sap
identify if the following are found in prokaryotes, plant cells, and animal cells.
cell wall
plasma membrane
membrane-bound organelle
nucleus
centrioles
ribosomes
prokaryotes and plant cells
prokaryotes, plant cells, animal cells
animal and plant cells
plant and animal cells
plant and animal cells
prokaryotes, plant, and animal cells
was is osmoregulation
moving water across membranes to maintain homeostasis
what does the ability of molecules moving across the membrane depend on
the semipermeability of the membrane
size and charge of the particles
what will pass through the membrane easily
lipid-solubles substances (N, O, CO2)
what type of transport is necessary when the molecule is hydrophilic
facilitated transport
what does facilitated transport depend on
number of proteins that act as tunnels through the membrane
what are channels
specialized types of tunnels that only allow certain things through
what are aquaporins
channels for water
how are ions transported across the plasma membrane
membrane proteins
membranes are polar/nonpolar
polar
which was does a substance move on the concentration gradient
down
what is it called when a substance moves down a concentration gradient
diffusion
what is diffusion called when a molecule is hydrophobic
simple diffusion
what is it called when diffusion requires a channel protein
facilitated diffusion
what is facilitated diffusion
when diffusion requires a channel protein
what type of transport is diffusion
passive transport
what. ispassive transport
diffusion, no energy required, down the concentration gradient
what is osmosis
diffustion for water
where does water want to move in osmosis
from low concerntration of solute to high concentration of solute (wants to dissolve the high concentration solution)
which can change due to osmosis, cell wall or cell membrane and why
cell wall does not change, cell membrane can shrink if it loses water
isotonic
solute concentration is the same inside and outside of the cell
hypertonic
solvent concentration is lower outside than inside the cell, causing water to move out of the cell.
hypotonic
solution where the solute concentration is lower outside the cell than inside, causing the cell to swell.
what is water potential
eagerness of water to flow from high potential to low potential
what is water potential affected by
pressure potnetial and solute potential
would adding a solute increase or decrease the water potential
decrease, the water would be less likely to leave
what is transport against the gradient called
active transport
Example of active transport
sodium-potassium pump
what does activee transport depend on
atp
what is primary active transport
when atp is directly utilized to transport something
what is secondary active transport
uses energy captured from the movement of another substance flowing down a concentration gradient
3 ways that a cell can cross a cell membrane
simple diffustion, facilitated transport, active transport
what is endocytosis
the process by which a cell engulfs material from its surroundings, allowing molecules to enter the cell. this creates a vacuole or. a vesicle
3 types of endocytosis
Pinocytosis phagocytosis and receptor mediated cytosis
What is pinocytosis
When the cell injests liquid
What is it called when a cell injests liquid
Pinocytosis
what is phagocytosis
When a cell injests solids
What is it called when a cell injests solids
Phagocytosis
What is receptor mediated cytosis and what protein does it use
When it uses surface receptors - clathrin
What is bulk flow
The one way movement of fluids brought about by pressure
What is dialysis
Diffusion of solutes through a selectively permeable membrane using holes of a certain size
What is exocytosis
When a cell ejects waste products by a fusion of a vesicle with the plasma membrane (reverse endocytosis)