Microbio LAB (9.1-9.3) Parasitology 1-4
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Decontamination
destruction, removal, or reduction in the number of undesirable microbes
Sterilization
the removal or destruction of all viable microbes
disinfection
destruction of vegetative pathogens on inanimate objects
sepsis
the growth of microorganisms in the tissues
asepsis
techniques that prevent the entry of microorganism into sterile tissues
antiseptics
chemicals used on body surfaces
sanitization
cleansing technique that removes microorganisms and debris form inanimate surfaces
degermation
cleansing technique that removes microorganisms and debris from living tissue
Physical Agents Used to Kill Microbes
1) Heat
dry heat
incineration results sterilization
moist heat
steam under pressure results in sterilization (Autoclave)
boiling water results in disinfection
Pasteurization results in disinfection
2) radiation
ionizing
nonionizing
Gamma Radiation
one type of ionizing radiation
collides with molecules in the cell
creates free radicals
resulting in DNA breakages
Ultraviolet Radiation
one type of nonionzing radiation
kills by damaging DNA
triggers mutations in DNA (Thymine Dimers)
Causes direct protein damage
Limitations of Ultraviolet Radiation
cannot go through plastic or glass
mainly used for killing microbes on surfaces, air, water
damages retina of eye
ultraviolet radiation must be used when people are not present
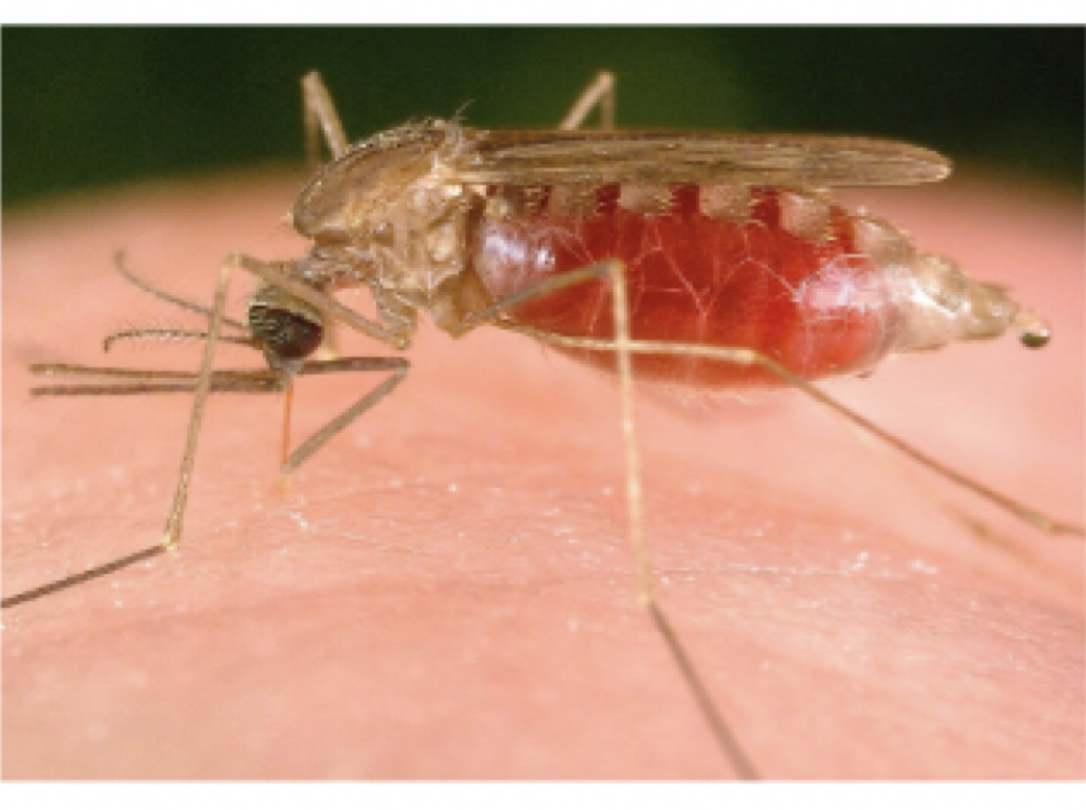
Mosquito
Representative Genus: Anopheles
Disease: Malaria
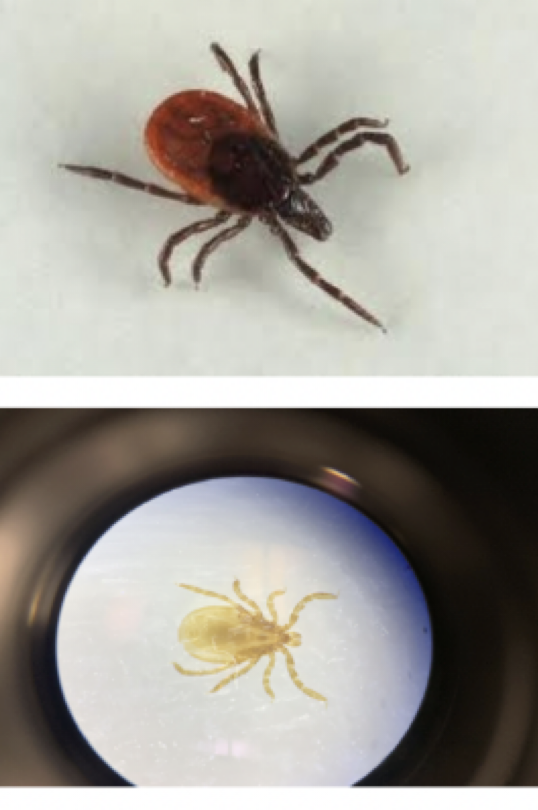
Tick
Representative Genus: Ixodes
Disease: Lyme Disease
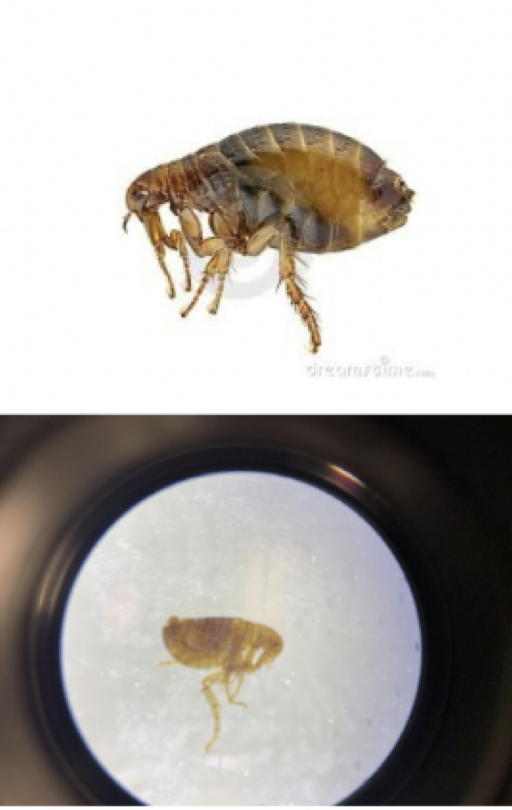
Flea
Representative Genus: Pulex
Disease: Plague
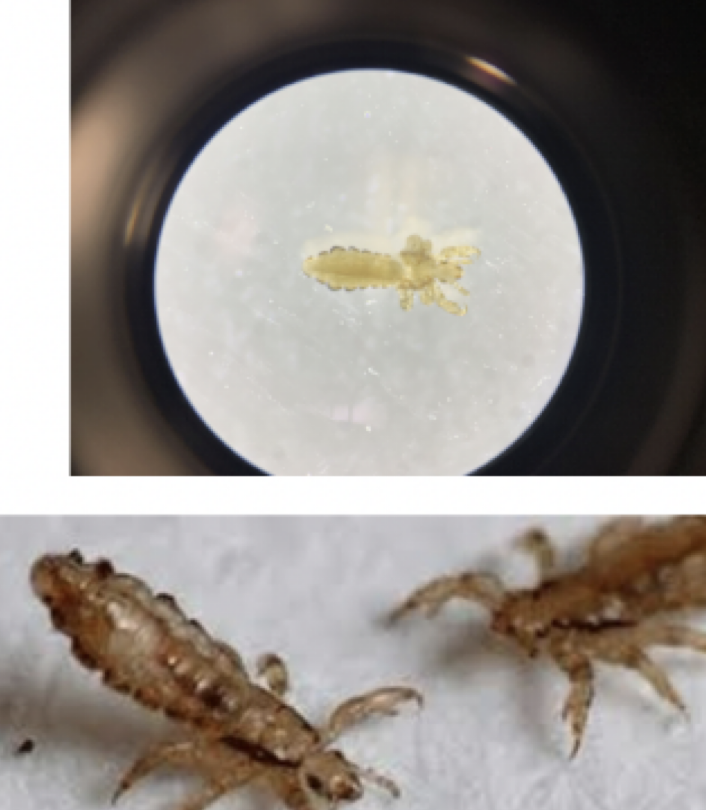
Lice
Representative Genus: pediculus
Disease: Head lice
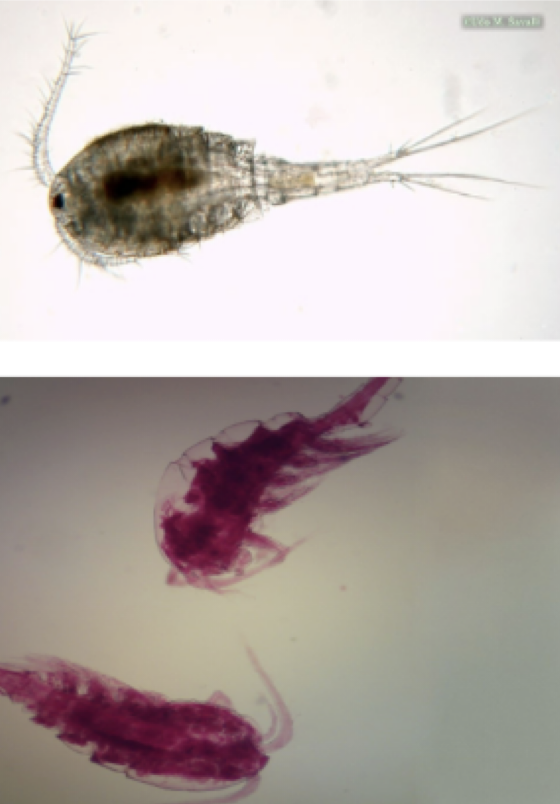
Cyclops
Representative Genus: Cyclops
Disease: Guinea Worm Disease
Anopheles
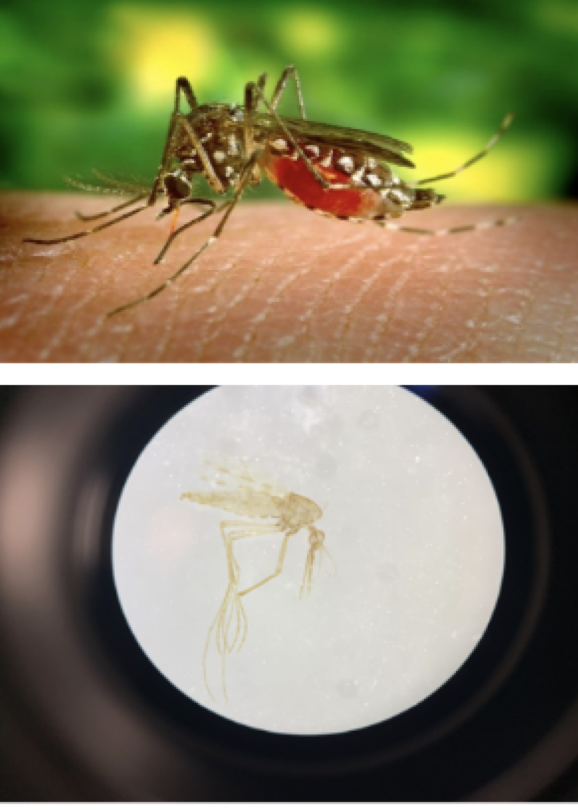
Ixodes

Pulex

Pediculus

Cyclops
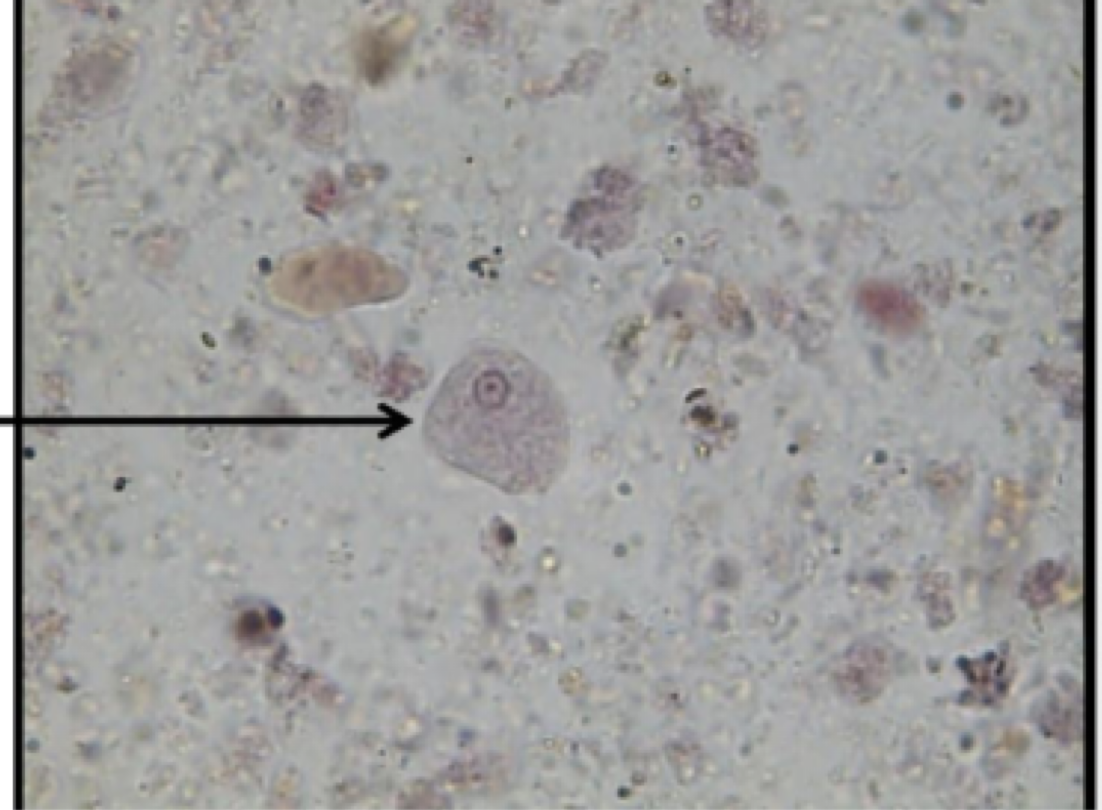
Entamoeba histolytica
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: amebiasis
parts to look for
central karyosome
bullseye nucleus
consumes red blood cells
look for RBCs inside organism
can eat through lining of GI tract and kill host
Entamoeba histolytica
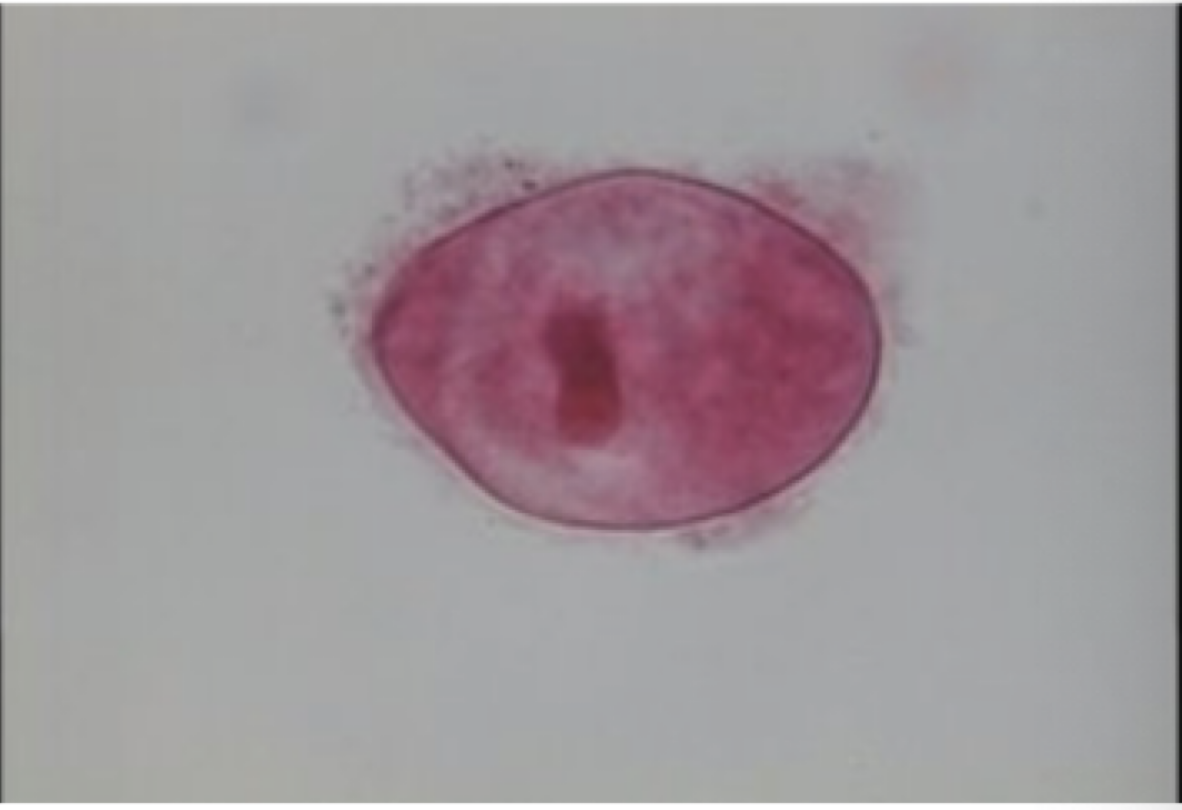
Naegleria fowleri
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: travels up the nose
water enters the nose of an organism then travels up olfactory nerve to the brain
Infective stage: trophozoite
disease: primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
parts to look for
large karyosome that take up whole nucleus
Naegleria fowleri
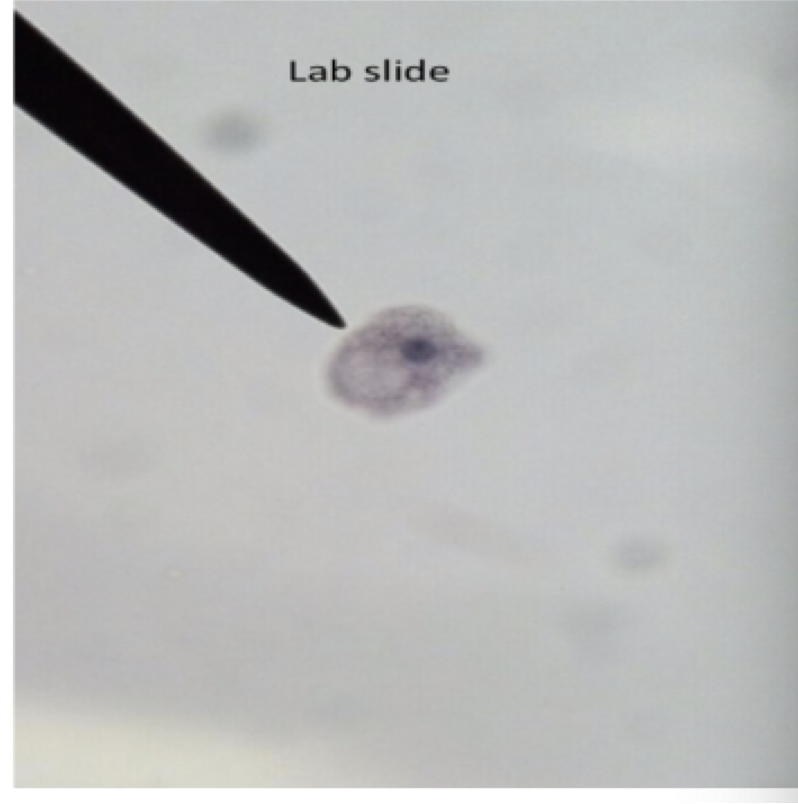
Acanthamoeba spp.
Motility: pseudopod
Mode of transmission: contaminated water or soil contact
Infective stage: trophozoite or cyst
disease: keratitis (eye), amebic encephalitis
parts to look for
karyosome takes up half of the nucleus
Acanthamoeba spp.
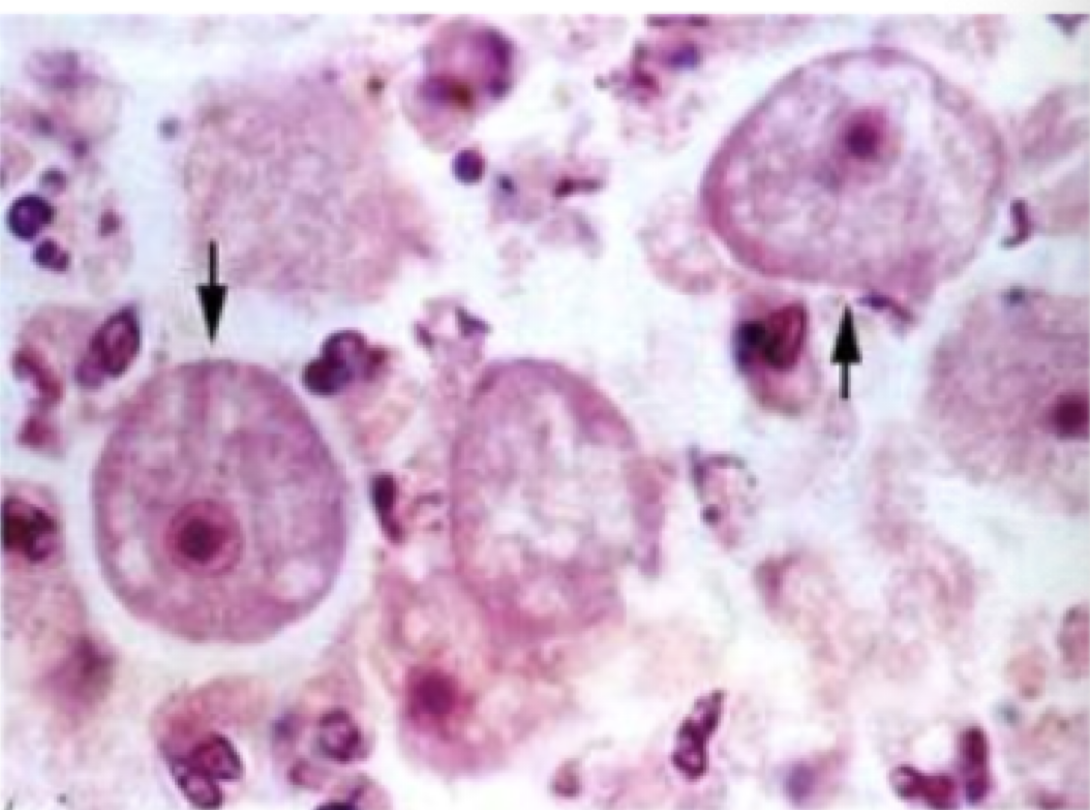
Balantidium coli
Motility: cilia
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: Balantidiasis
also, may people go asymptomatic
parts to look for
large kidney bean shaped nucleus
Balantidium coli
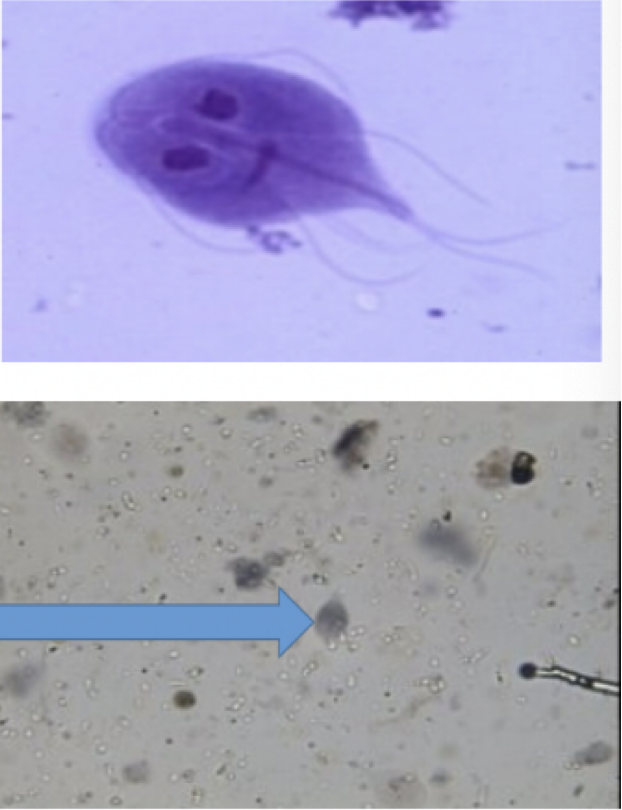
giardia lamblia
Motility: flagella
Mode of transmission: fecal-oral
Infective stage: cyst
disease: Giardiasis “Hikers’ diarrhea”
parts to look for
symmetrical heart shape
flagella
two nuclei
organelles positioned in such a way that it resembles a face
giardia lamblia
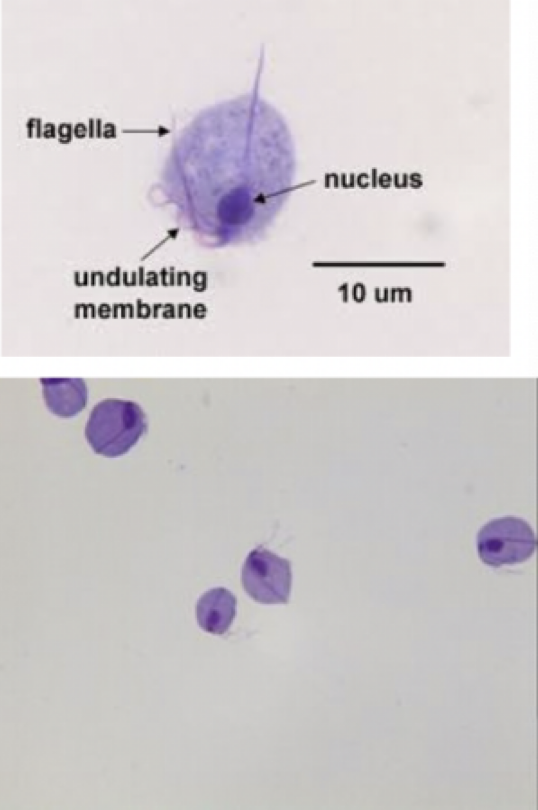
Trichomonas vaginalis
Motility: flagella
Mode of transmission: sexual intercourse
Infective stage: trophozoite
disease: Trichomoniasis
male: usually asynptomatic
female: vaginal discharge
parts to look for
pear shaped
undulating membrane
flagella
axostyle
Trichomonas vaginalis
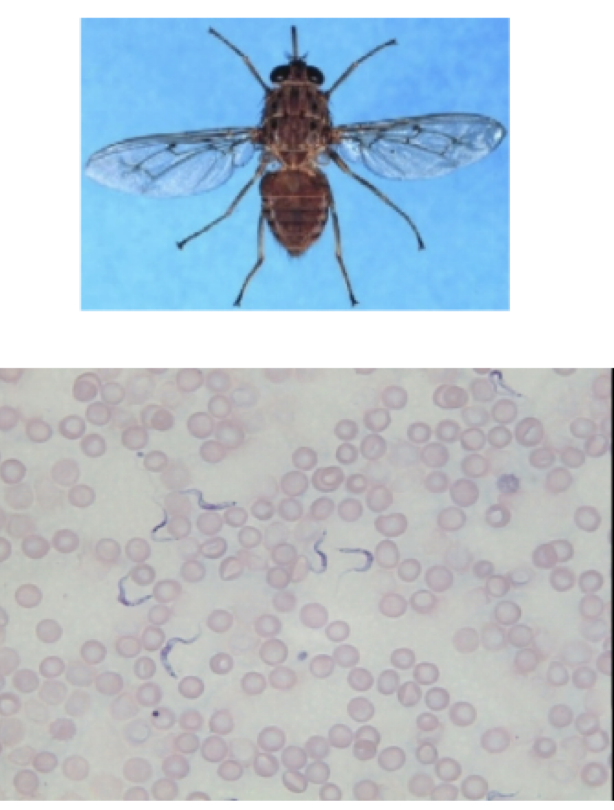
Trypanosoma brucei
motility: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from tsetse fly
infective stage: trypanomastigtoe
Host: Tsetse fly —> human
ideas; African Sleeping sickness
Trypanosoma brucei
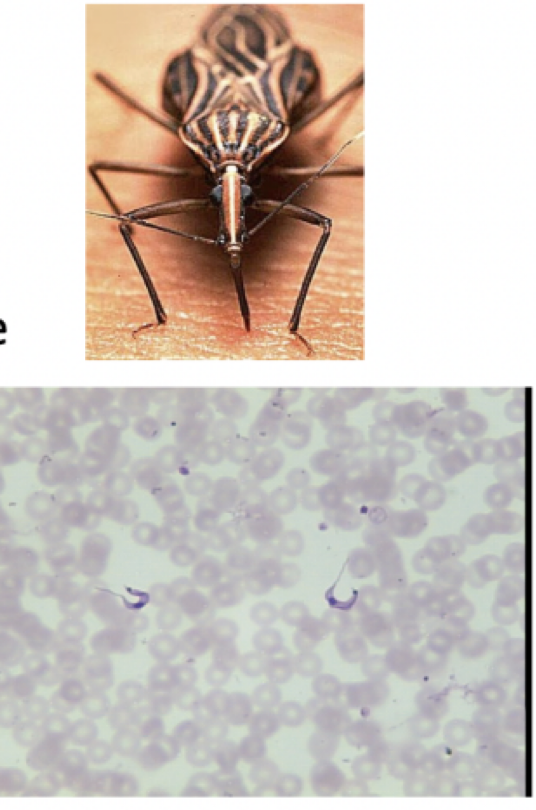
Trypanosoma cruzi
motility: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from kissing bug
infective stage: trypomastigote
Host: kissing bug —> human
Disease: Chaga’s disease
Trypanosoma cruzi
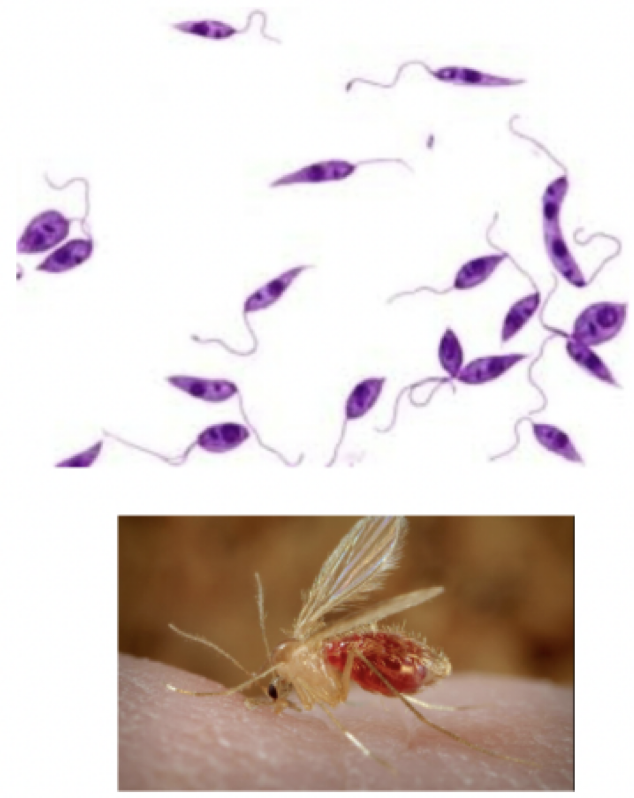
Leishmania donovani
motility: flagella
mode of transmission: bite from sand fly
infective stage: promastigote
Host: sand fly —> human
disease: Leishmaniasis
Leishmania donovani
Cryptosporidium parvum
motility: none
mode of transmission: females oral, ingestion of oocyst
infective stage: oocyst
host: humans and other animals
disease: cryptosporidiosis
Cryptosporidium parvum
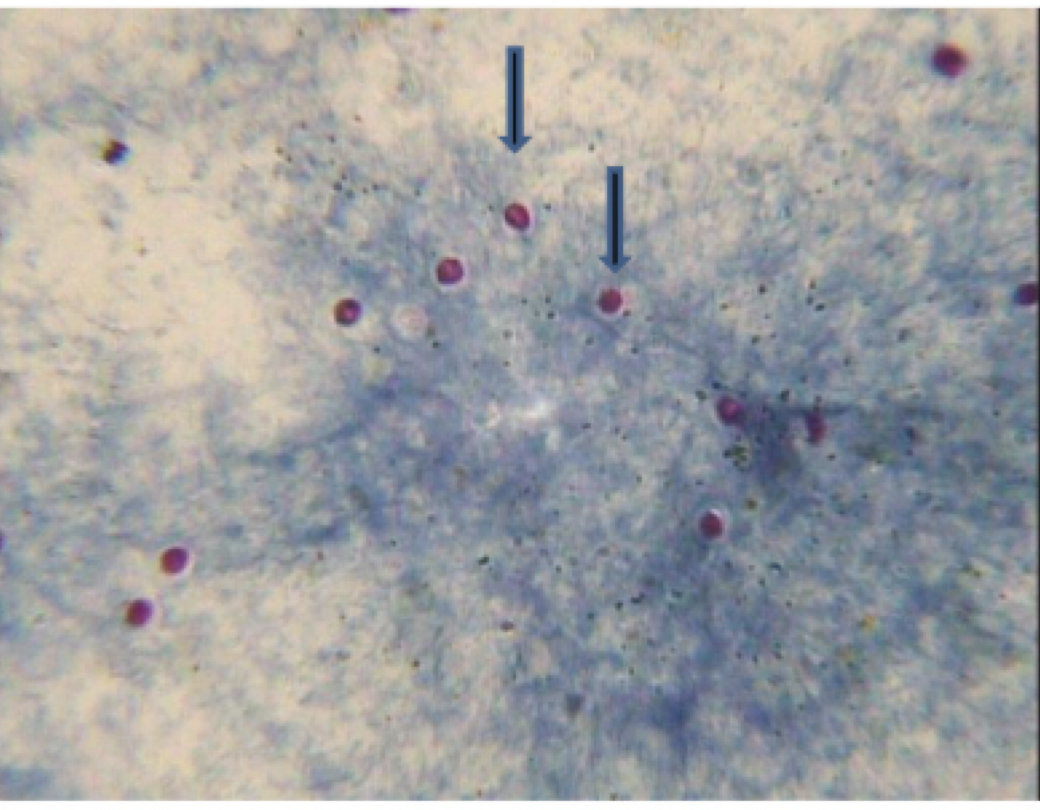
toxoplasma gondii
motility: none
mode of transmission: ingestion of oocyst
infective stage: oocyst
host: feline —> rodent, bird, human
disease: toxoplasmosis
toxoplasma gondii
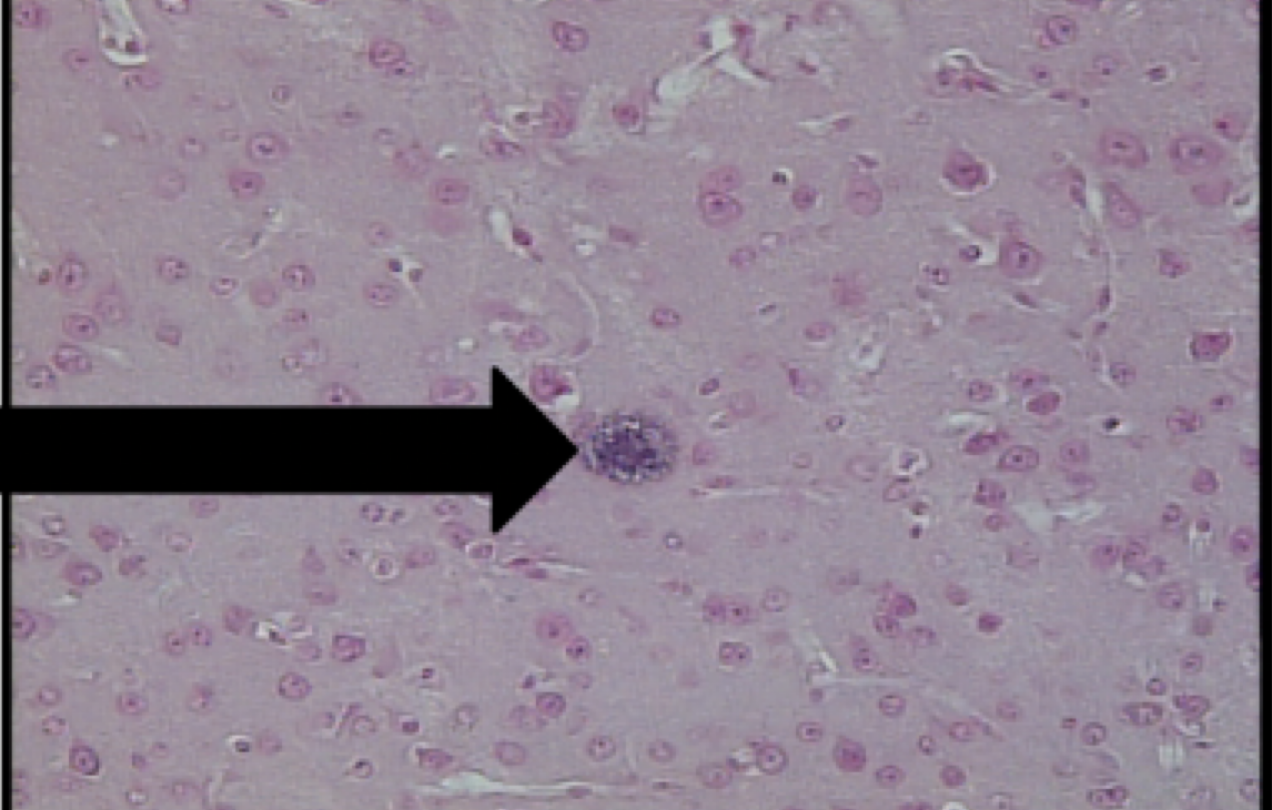
plasmodium species
motility: none
mode of transmission: bite from female anopheles mosquito
infective stage: sporozoite
host: female anopheles mojito —> human
disease: malaria
plasmodium species
Ascaris lumbricoides
Mode of transmission: ingestions of ova/ egg
infective stage: egg
host: human
Disease: Ascaris or Ascariasis
Ascaris lumbricoides
Enterobius vermicularis
Mode of transmission: ingestions of ova/ egg
infective stage: egg
host: human
Disease: Pinworm
Enterobius vermicularis
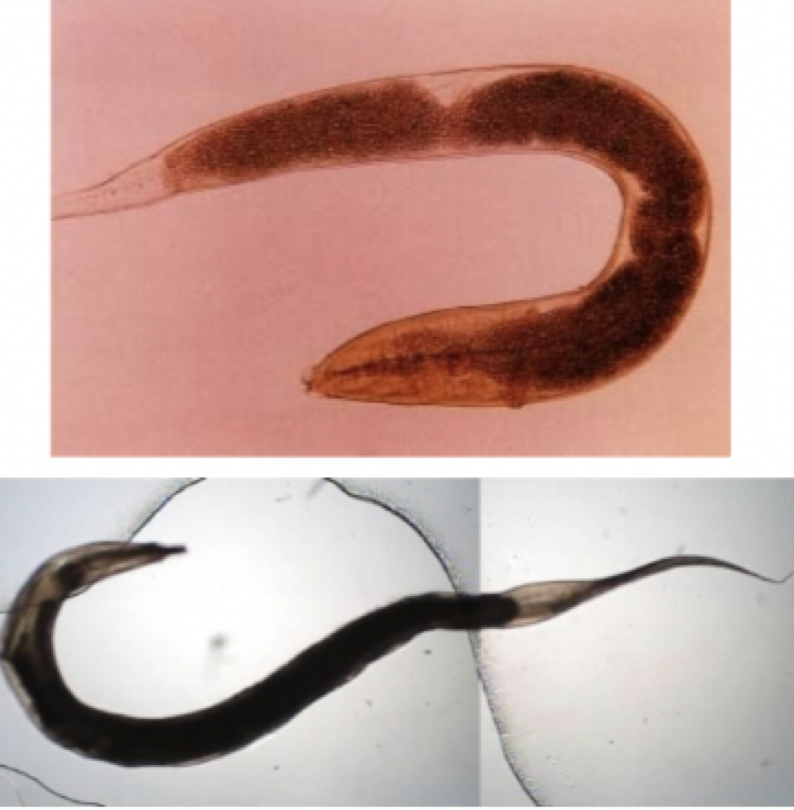
Trichuris trichiura
Mode of transmission: ingestions of ova/ egg
infective stage: egg
host: human
Disease: Whipworm
Trichuris trichiura
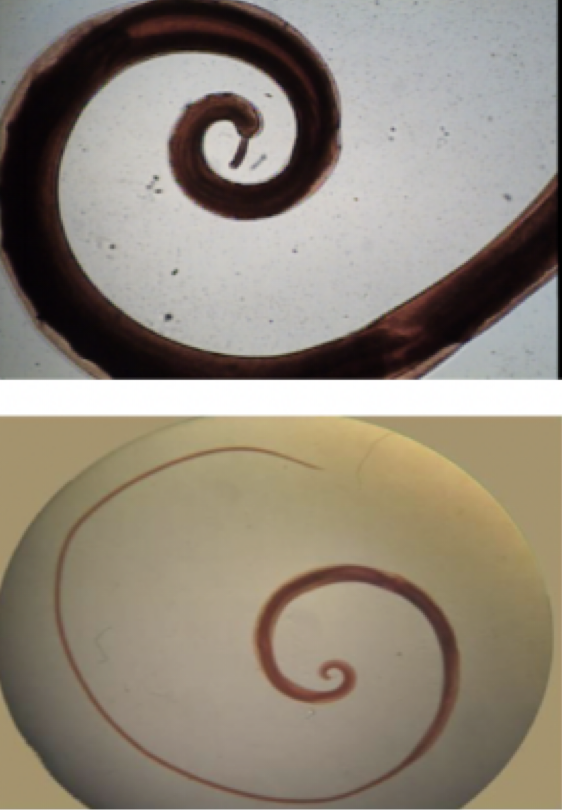

Necator americanus
Mode of transmission: larvae penetrate skin
infective stage: larvae
host: human
Disease: hookworm
Necator americanus
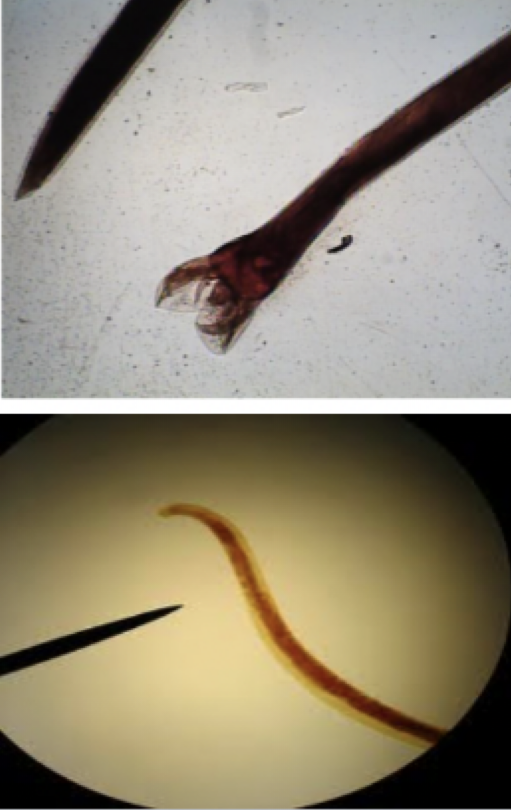

Anisakis simplex
Mode of transmission: eat uncooked infected fish
infective stage: larvae
host: marine mammal —> human, fish, squid
Disease: Anisakiasis
Anisakis simplex
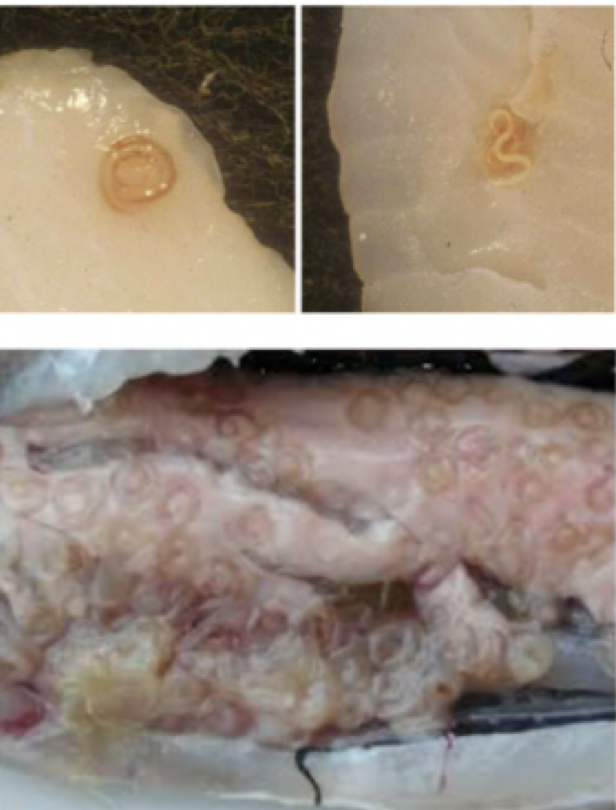
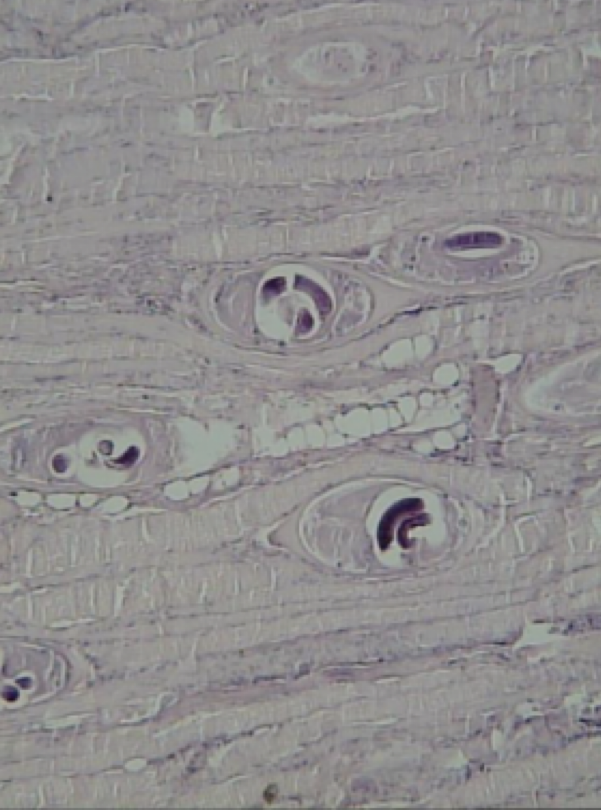
Trichinella spiralis
Mode of transmission: eat pork with encysted larvae
infective stage: encysted larvae
host: pig —> human
Disease: trichinosis
Trichinella spiralis
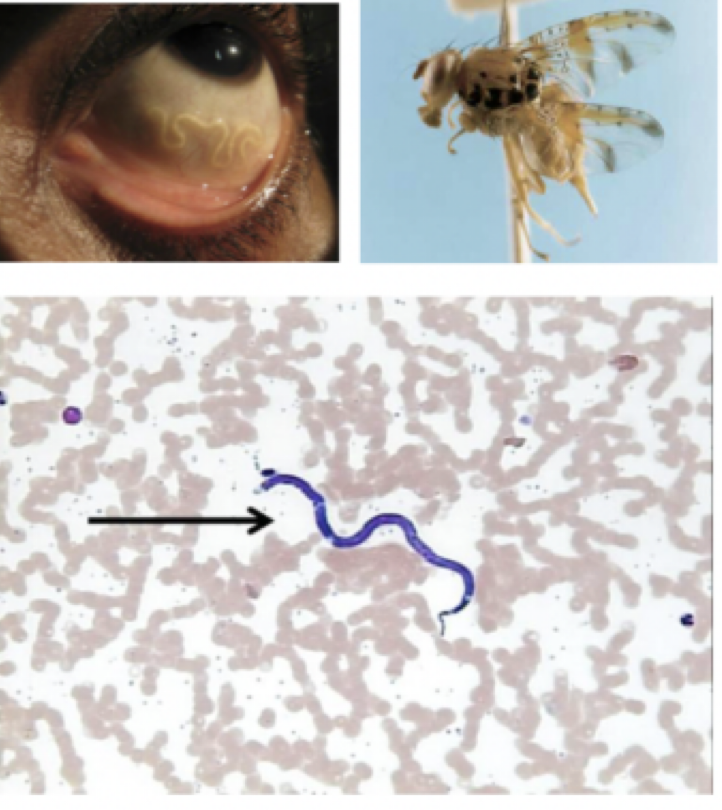
Loa loa
Mode of transmission: bite from mango fly
infective stage: microfilariae
host: mango fly —> human
vector: mango fly
Disease: African Eye worm
Loa loa
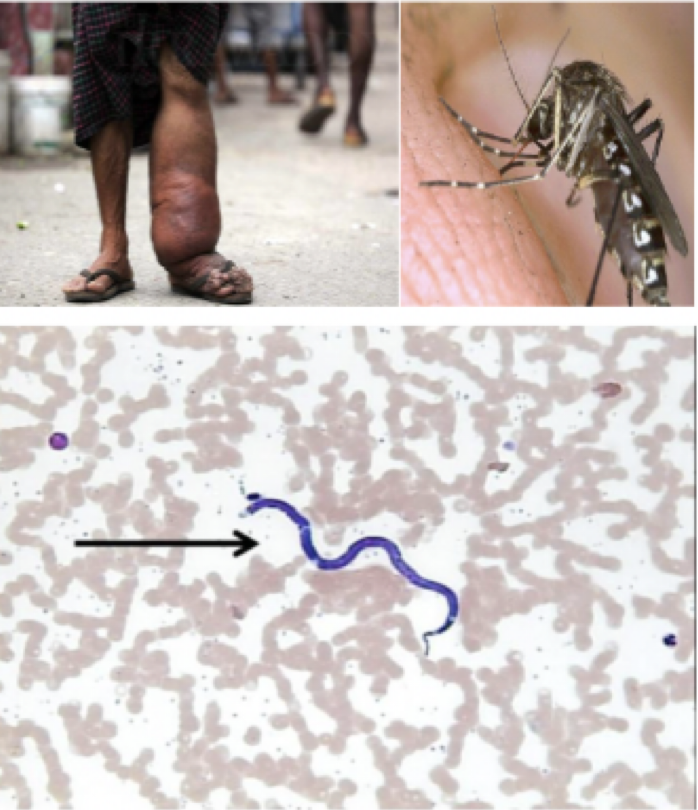
Wuchereria bancrofti
Mode of transmission: mosquito bite
infective stage: microfilariae
host: mosquito —> human
Vector: Mosquito
Disease: Elephantiasis
Wuchereria bancrofti
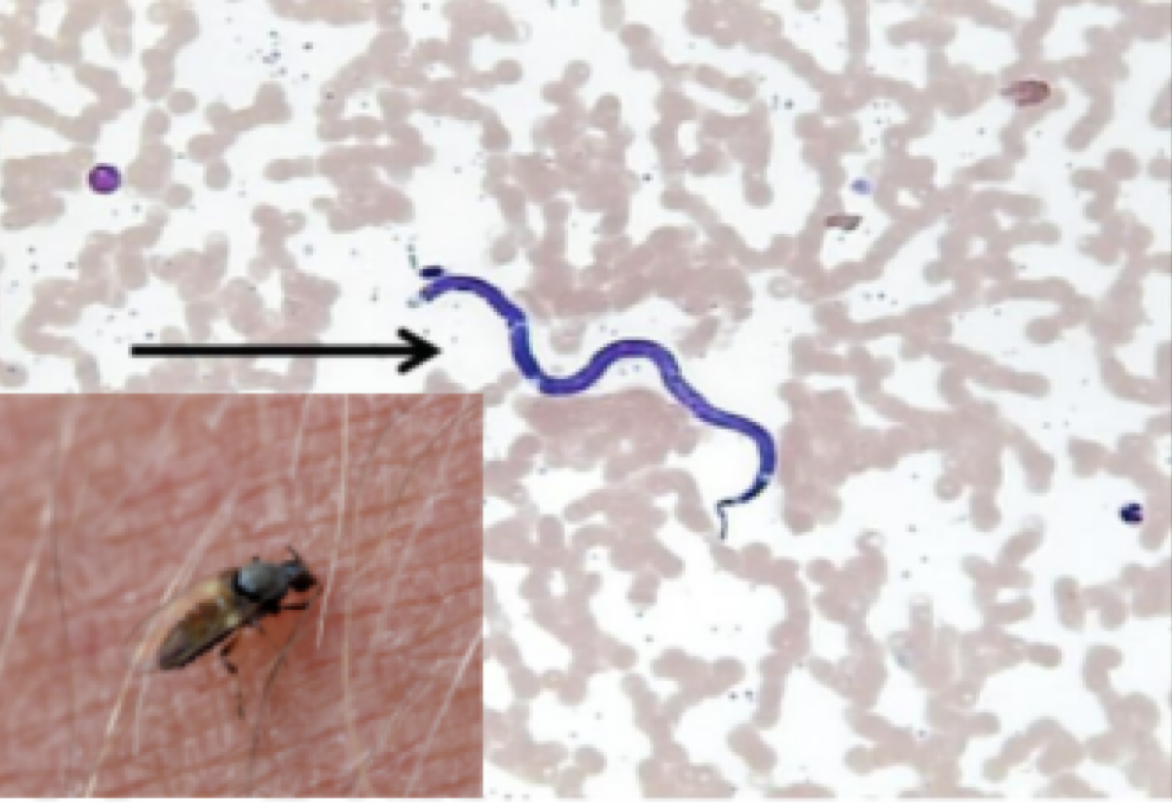
Onchocerca volvulus
Mode of transmission: bite form black fly
infective stage: microfilariae
host: black fly —> human
vector: black fly
Disease: river blindness
Onchocerca volvulus
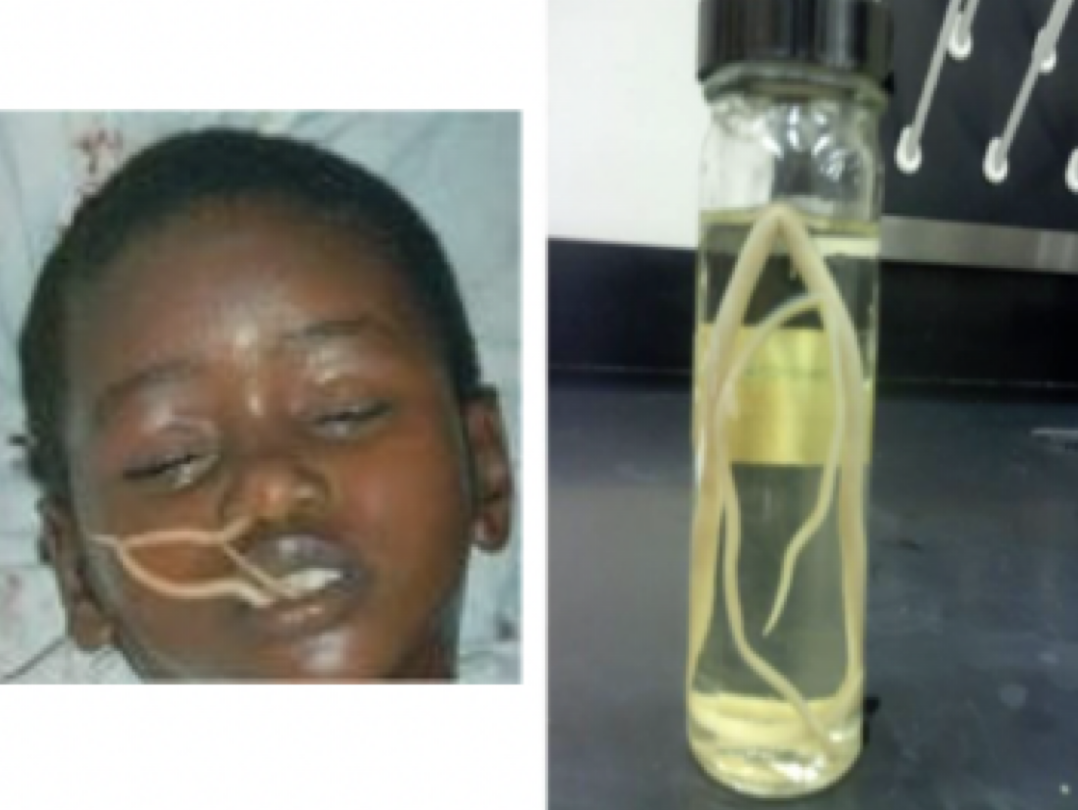
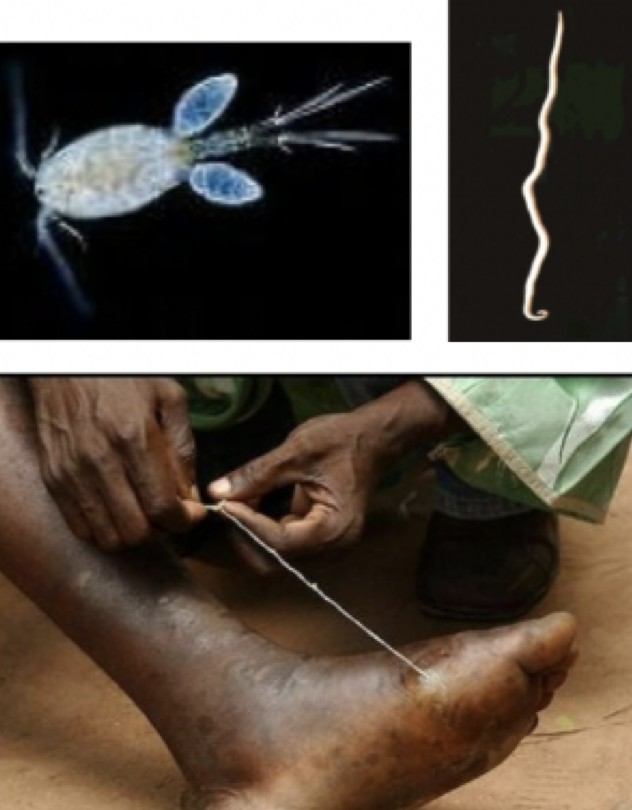
Dracunculus medinensis
Mode of transmission: drinking water with cyclops
infective stage: larvae (inside the cyclops)
host: cyclops —> human
vector: cyclops
Disease: guinea worm
Dracunculus medinensis
Round worms
cylindrical, non-segmented worms
sex organs on separate worms
no hooks or suckers to attach to host
inhabit the intestinal tract, blood, organs, tissues
flat worms
flat body shape
may be hermaphrodites
have hooks/ suckers to attach to host
inhabit intestinal tract, blood, organ tissues
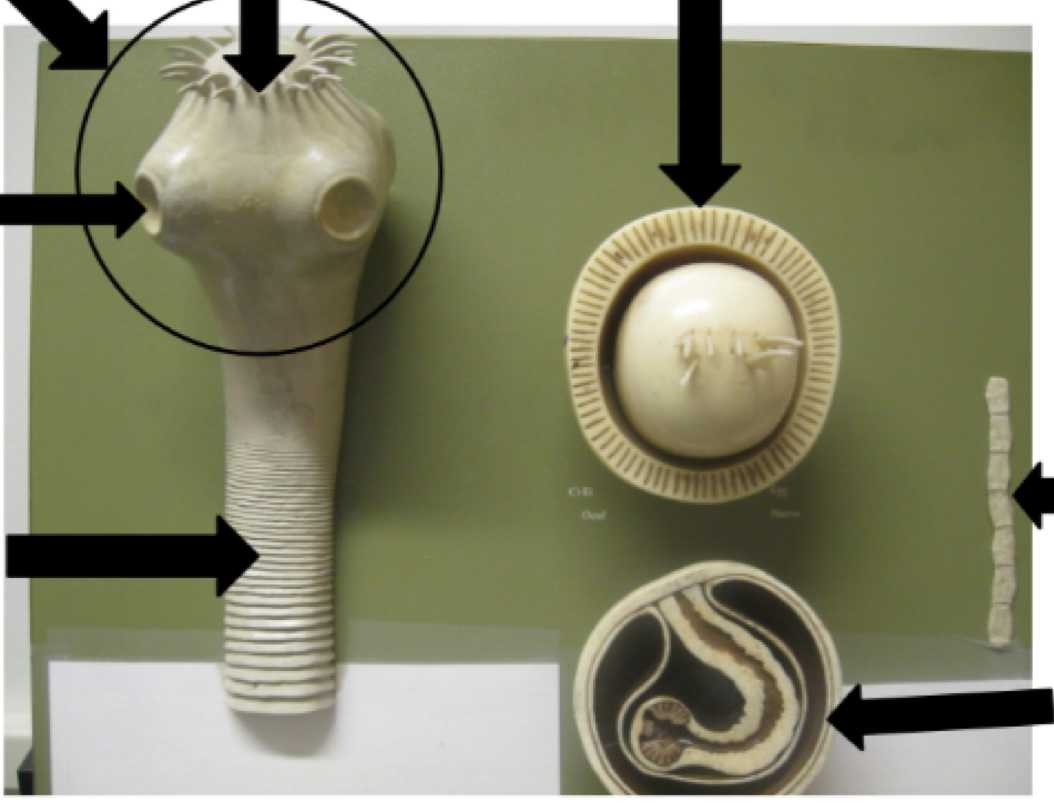
Name the parts of the tapeworm model starting in the upper right and traveling clockwise
1) ova
2) Strobilia
3) Cysticerci
4) Strobilia
5) Sucker
6) Scolex
7) Ring of hooks
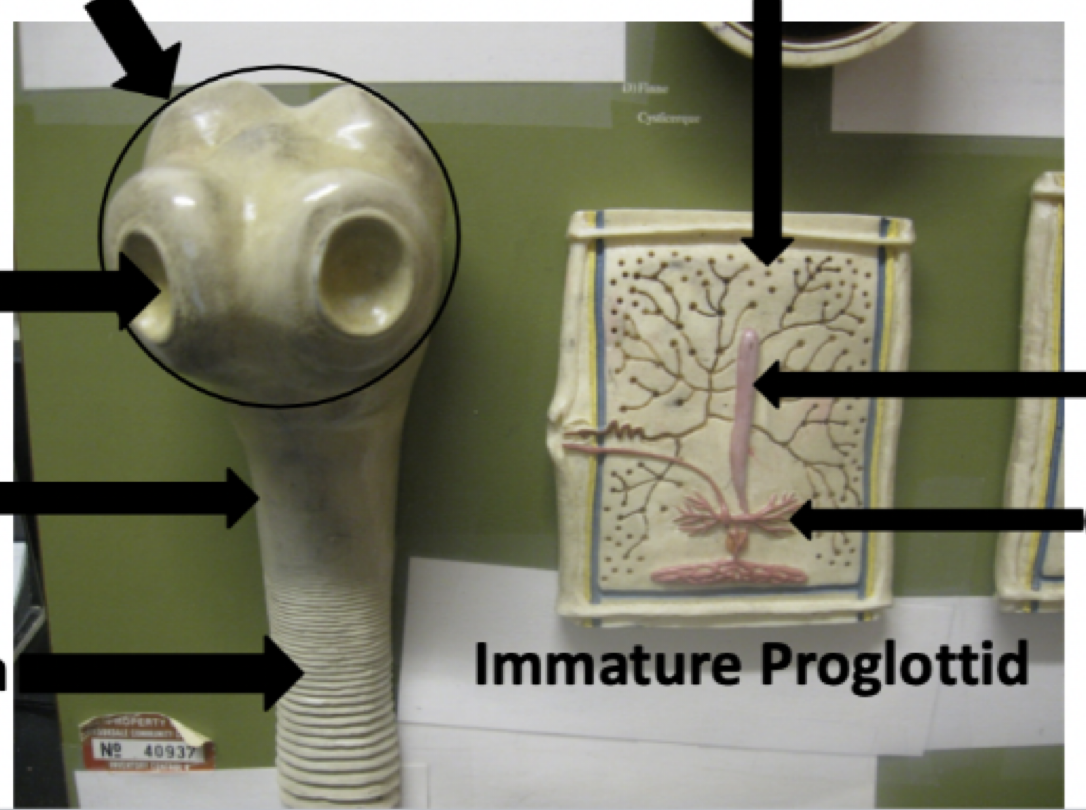
Name the parts of the tapeworm model starting in the upper right and traveling clockwise
1) Testes
2) Uterus
3) Ovaries
4) Strobilia
5) Neck
6) Sucker
7) Scolex
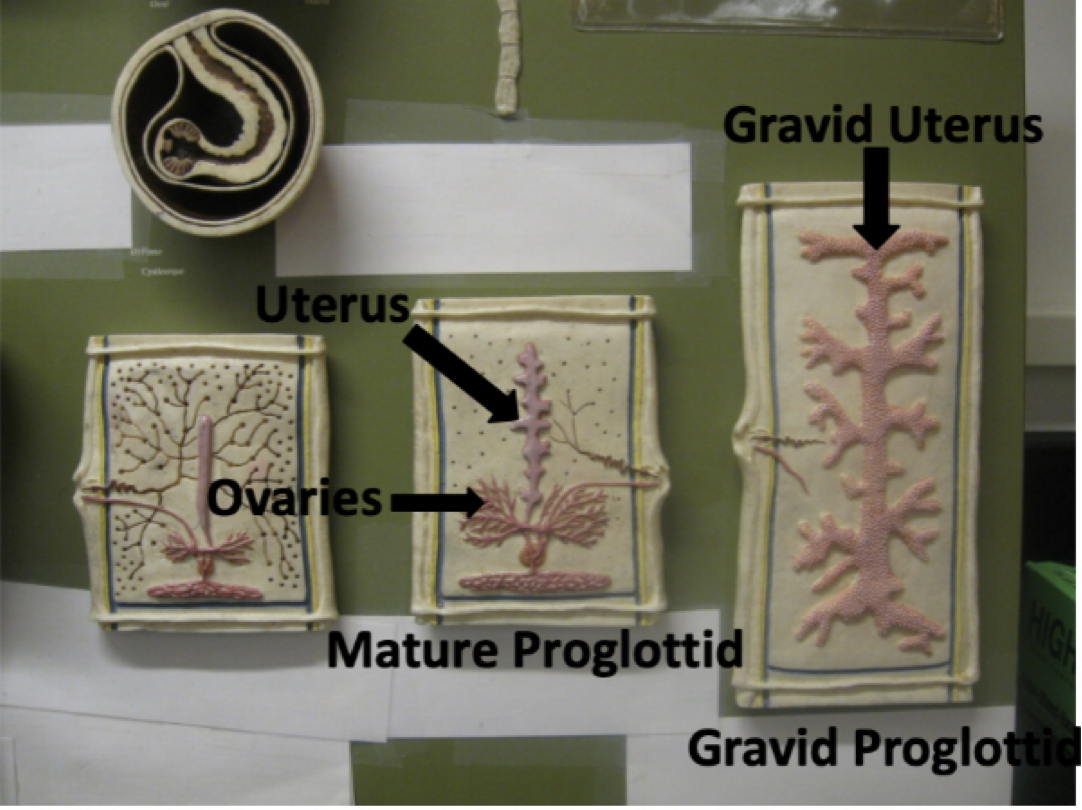
Name the parts of the tapeworm model starting in the upper right and traveling clockwise
Gravid Uterus
Gravid Proglottid
Mature Proglottid
Ovaries
Uterus
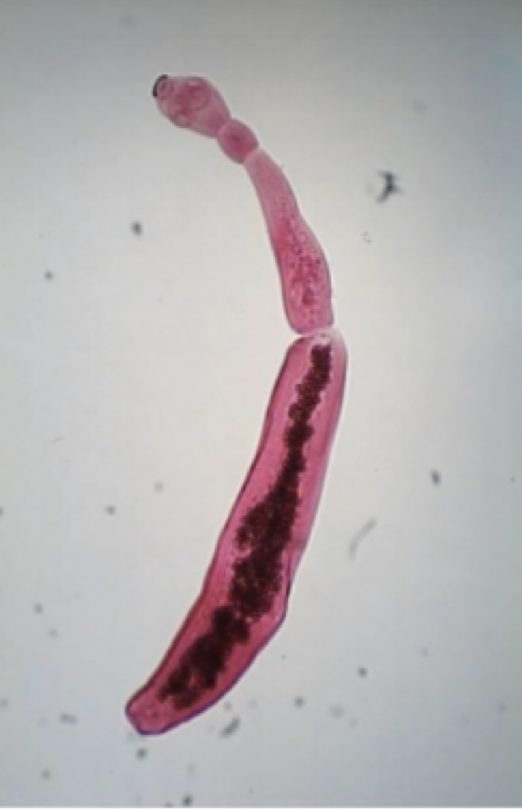
Taenia saginata
Mode of transmission: eating undercooked beef with cysticerci
Infective stage: Cysticerci
Host: D- human, I-Cattle
Disease: Taeniasis
*Large Scolex, with four oral suckers
Taenia saginata
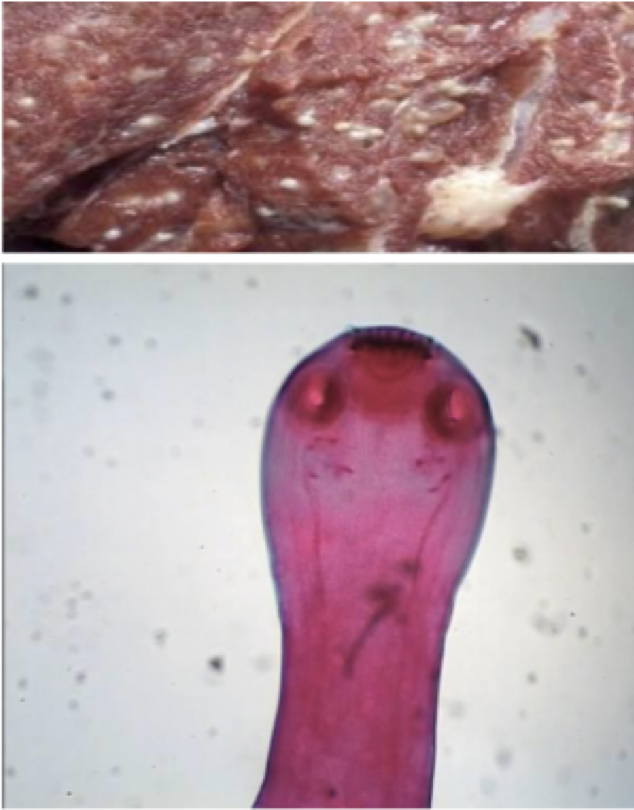
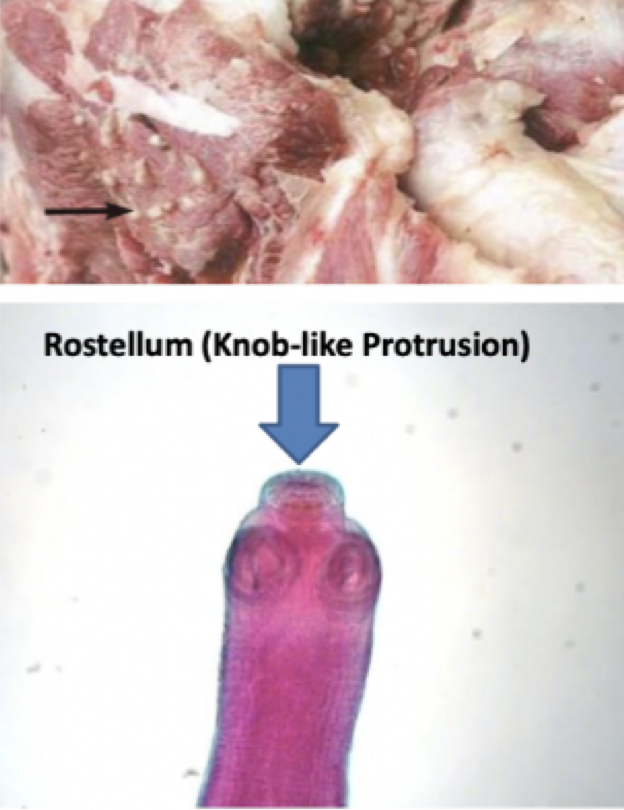
Taenia solium
Mode of transmission: eating undercooked pork with cysticerci
Infective stage: Cysticerci
Host: D- human, I-pig
Disease: Taeniasis
*smaller scolex with Rostellum
Taenia solium
Diphyllobothrium latum
Mode of transmission: eat fish with cysticerci
Infective stage: Cysticerci
Host: D- human, I-fish
*common name: fish tapeworm
Diphyllobothrium latum
Echinococcus granulosus
Mode of transmission: ingestion of egg/ ova
Infective stage: egg
Host: D- canine, I- human, sheep, cattle
*common name: sheep tapeworm
Echinococcus granulosus