Neuropsychological assessment
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the goal of neuropsychological assessments?
→ Early detection and prevention of long-term negative effects (of medical conditions)
→ Characterize cognitive strengths and weaknesses
→ Guide children towards appropriate rehabilitation, intervention or support resources
→ Monitoring outcomes (recovery or deterioration) and treatment effects
What cognitive functions exist? (8)
Intelligence
• Language (receptive and expressive) (lecture December 13th)
• Perception (visual, auditory, tactile …) (lecture December 6th)
• Memory (short term memory, working memory, long term memory)
• Attention (sustained attention, selective attention, divided attention)
• Executive functions (Inhibition, planning, flexibility, processing speed)
• Motor skills and action
• Emotion and social cognition
What is the difference between child and adult neuropsychological assessment?
In children
there’s not always available information on functioning “before” the damage
Difficult to tell when it started
• Difficult to tell what is normal/abnormal
Growing into deficit
Deficits may not directly be noticeable but
become more evident when – at later stages
of development - higher-order skills are impaired
Not always noticeable on brain scans
Natural differences
What is the psychodynamic view on child psychology?
The child exists in a context of their relationship to their caregivers
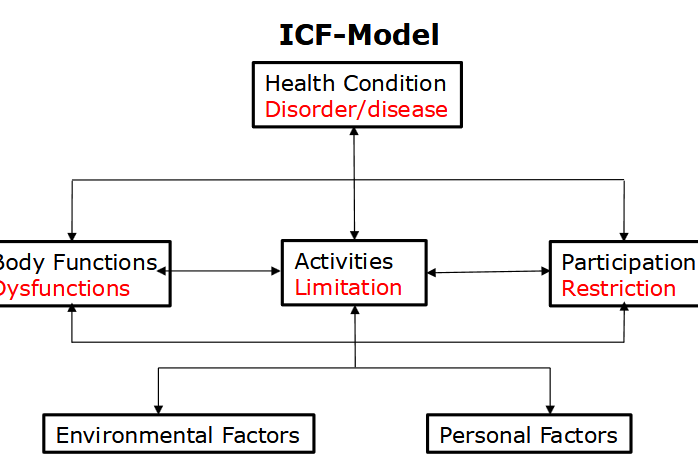
What does the ICF model do in terms of how it evaluates a child?
There is a child with a medical/brain condition
• This child has their own character/ coping style
• This child has their own environment/context
→ Both influence the dysfunctions, limitations
and restrictions, experienced by the child
Why is it important to work with the parents of young children?
They have to provide information, help the child with the training
What can a referral to a neuropsychological clinic be based on?
Based on daily life problems
• At home
• At school
Based on medical information
• Neonatal and acquired brain insult (e.g., prematurity, TBI, epilepsy, tumours)
• Congenital disorders (e.g. structural brain insult, such as spina bifida, cerebral palsy)
• Medical disorders (e.g., diabetes)
• Genetic and metabolic disorders (e.g., Down syndrome, Fragile-X syndrome)
• Neuropsychiatric (developmental) disorders (e.g. Autism, ADHD)
• But also: Sensory disorders (e.g. low vision, deafness)
What is the aim of the Bayley Scales of Infant and toddler Development (BSID): age 0.6-2
Aim: to measure development and identify infants/toddlers with developmental delay
• Five domains: Cognitive, language, motor, social-emotional and adaptive behaviour
• Not one test(instruction) with multiple items, but small tasks
• administration of structured items
• direct observation of behavior
• active participation of parents
What are the scales on the WISC-V
Verbal Comprehension Index (VCI)
Visual Spatial Index (VSI)
Fluid Reasoning Index (FRI)
Working Memory Index (WMI)
Processing Speed Index (PSI)
What does the Verbal Comprehension Index (VCI) measure?
• The VCI is a mearue of crystallized intelligence. It measures the child’s ability to access
and apply acquired word knowledge.
• The application of this knowledge involves verbal concept formation, reasoning and
expression
Tested with: Similarities, Vocabulary
What does the visualspatial index (VSI) measure?
The VSI measures the child’s ability to evaluate visual details and to understand visual
spatial relationships to construct geometric designs from a model
Tested with: Block design, visual puzzles
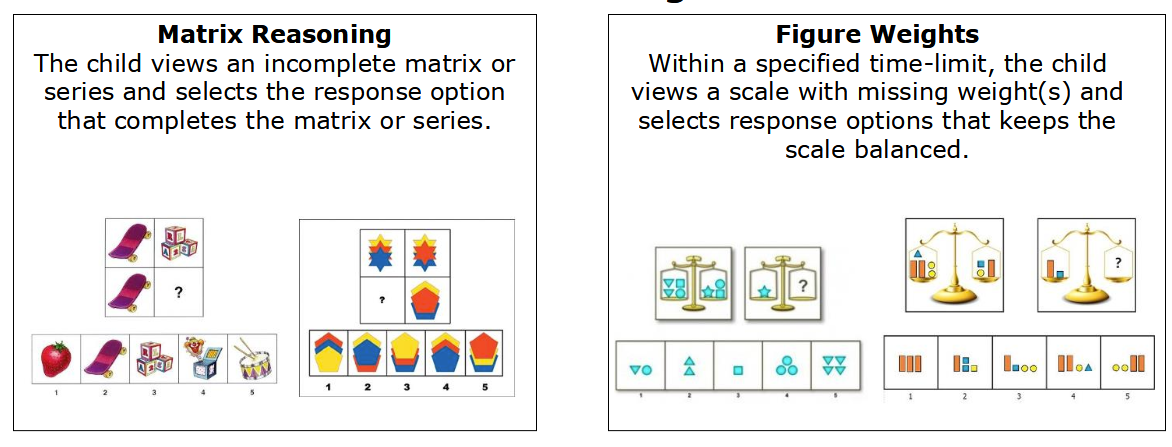
What does the Fluid Reasoning Index (FRI) measure?
The FRI measures the child’s ability to detect the underlying conceptual relationship
among visual objects and to use reasoning to identify and apply rules.
Tested with: Matrix Reasoning, Figure Weights
What does the Working Memory Index (WMI) measure?
The WMI measures the child’s ability to register, maintain, and maniplate visual and auditory information in conscious awareness.
– Registration requires attention, aduitory and visual discrimination and concentration
– Maintanance is the process by which information is kept active in conscious
awareness, using the phonological loop or visual sketchpath (Baddeley, 2012)
– Manipulation is mental resequencing of information based on the application of a
specific rule
Tested with:
Picture Span
Digit Span
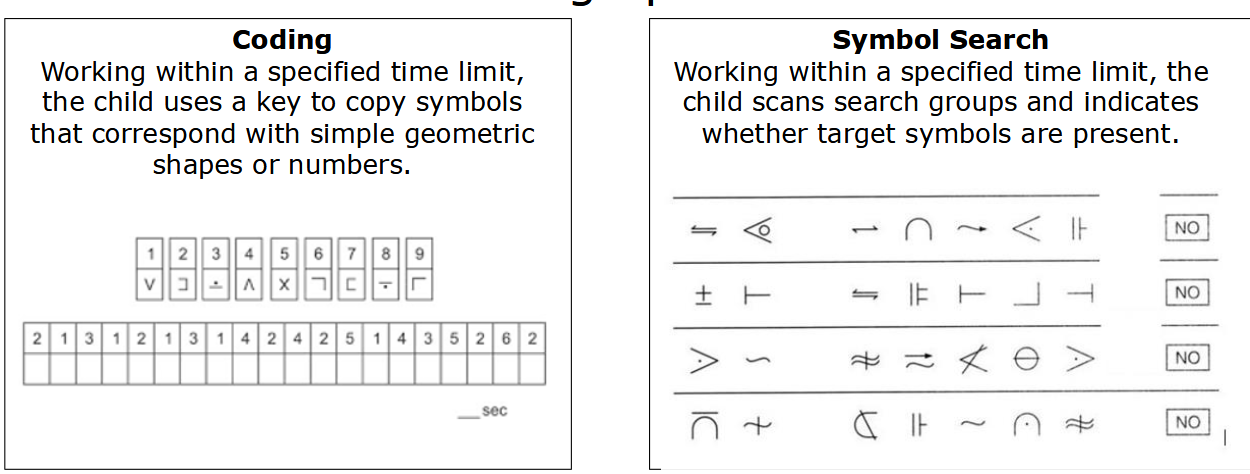
What does the Processing Speed Index (PSI) measure?
• The PSI measures the child’s speed and accuracy of visual identification, decision-making
and decision implementation.
• Processing speed involves the child quickly and correctly scanning or discriminating
between simple visual information
Tested with:
Coding
Symbol Search
What is the difference between a standardized and an eclectic battery?
Standardized battery : predetermined set of tests that are administered and scored in a
standardized manner (e.g. NEPSY-2, RAKIT-2, TEA-Ch, WISC)
– Developed for the normal population
– Discussion about the construct validity of some of the subtests
Eclectic battery: own selection of tests
– Developed for testing a specific hypothesis / specific needs of the individual
– The test battery itself is not standardized, but
– Construct validity of each of the tasks is generally good
What is the task impurity problem?
There is no task that only assesses what it aims to measure
What observations can you make about a child while they are doing a test?
Overall observations:
– Appearance
– Behaviour
– Motivation
– Alertness: tired?
• Task/Function specific observations
– Motor: Handedness, pen grip, walking the stairs
– Language: speech, comprehension of instructions
– Perception: viewing distance, squinting eyes, tripping, missing information
– Memory: Remembering instructions, second assessment
– Executive Functions: Planning, checking answers, impulsivity, processing speed
– Attention: distracted by internal or external cues?
What is important to note when interpreting cognitive function test batteries?
That a certain cognitive profile can often fit multiple neurodevelopmental disorders (e.g. impaired communication could be Developmental Language Disorder but also Autism)