Week 12 Lecture
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sedimentary minerals in metamorphic rocks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Two causes of metamorphism
Changes in mineralogy and texture (foliation, grain size)
Protolith types (parent rock)
Ultramafic - peridotites, pyroxenites
Mafic (basalt, gabbro)
Pelites (aluminum shales. Most common sediment)
Carbonates (limestone, dolostone)
Quartz rocks (chert, sandstone)
Quartzo-feldspathic rock
What do metamorphic minerals reflect?
protolith composition, and the pressure-temperature conditions of the metamorphism they went through
Paragenesis
Order of formation of minerals in a rock, and of those that were removed
Garnet
Pyralspite group (different cation), pyrope, almandine, spessartine
Ugrandite group (substituting cation Ca), uvarovite, grossular, andradite
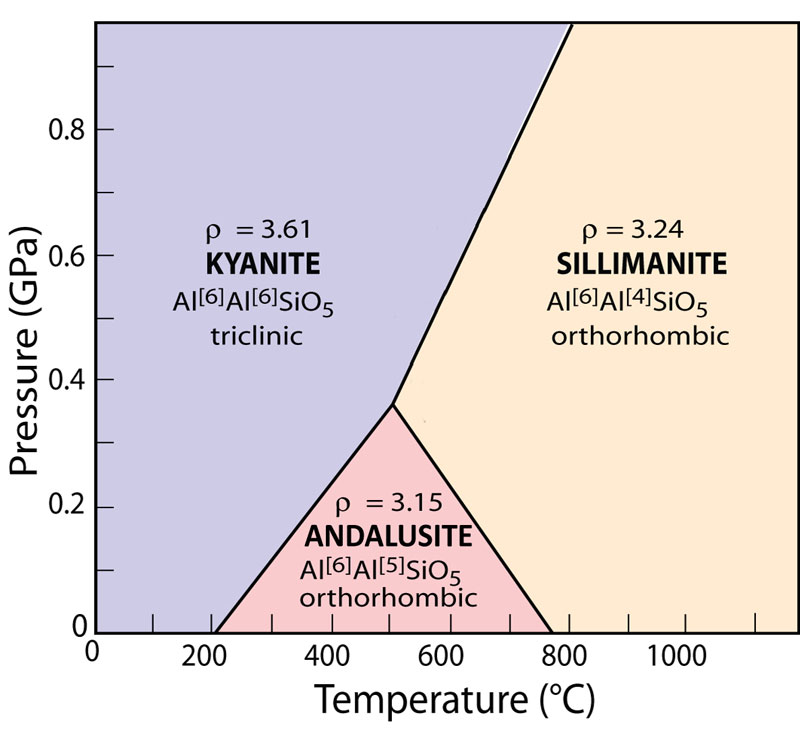
Aluminosilicate polymorphs
Al2SiO5 formula
Andalusite
Kyanite
Sillimanite
Staurolite
Fe3-4Al18Si8O48H2-4
Monoclinic (pseudo orthorhombic)
Penetration twins (cross)
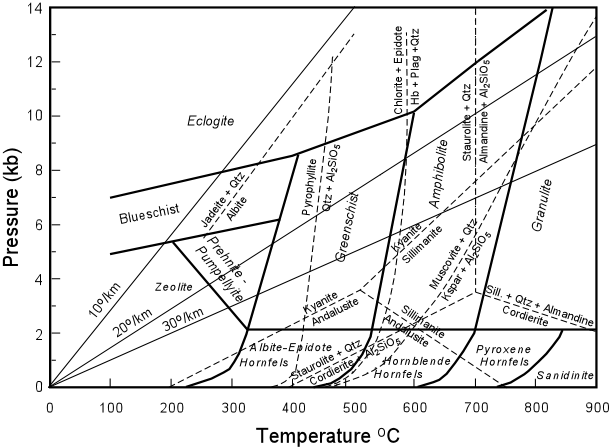
Where might high pressure, low temp conditions occur?
Subduction zones. The subducting oceanic plate creates enormous stress, but has had more time to cool and refrigerates the continental plate
Diopside
CaMgSi2O6
Single chain silicate, clinopyroxene
Produced through metamorphism of carbonates; must be impure limestone
Amphiboles
Anthophyllite (MG7Si8O22(OH)); orthorhombic, found in mg-rich ultramafic protoliths
Cummingtonite-grunerite; orthorhombic, common in Precambrian iron formations
Tremolite-actinolite; monoclinic, found in ultramafic protoliths. Aluminum poor most often, if not is hornblende
Glaucophane (blueschist); clino-amphibole, formed from basaltic protolith found in subduction zones
Wollastonite
CaSiO3
Pyroxenoid
Formed through high grade metamorphism; associated with limestones
commercial substitute for asbestos
Talc
Found in ultramafic protoliths
Low grade mineral formed from retrograde metamorphism
Sheet silicate, soapstone
Paint extender, filler, ceramic tiler
Chlorite
Sheet silicate with brucite-like sheets
Triclinic or monoclinic. One direction of cleavage
Low grade greenschist
Present in many metamorphic rocks. Found around hydrothermal veins and ore deposits
Serpentine minerals
Formed through hydrothermal alteration of ultramafic rock
Polymorphs include antigorite, lizardite, chrysotile (asbestos)
Has different structural arrangement of T-O layers
Epidote-clinozoisite
monoclinic
paired and single tetrahedra
Clinozoisite is the iron-deficient end member, while epidote is the iron-rich end member
commonly found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. They can also form as hydrothermal alteration products
Cordierite
Uncommon orthorhombic ring silicate, seen in garnet
common in pelites, favored by low pressure, high temp
May be difficult to distinguish from plagioclase feldspar in thin section. Has pleochroic haloes
Titanite
AKA sphene. independent tetrahedra, monoclinic
common accessory mineral. Can be dated due to uranium presence
Found in metamorphic and igneous rocks. Common in calc-silicates, mafic rock, and granites
Corundum
High grade metamorphic rock with barrel-shaped crystals
Hardness of 9