musculoskeletal system
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
the musculoskeletal system produces
red blood cells, stores fat and minerals, generates body heat
bone shapes
long, short, flat, irregular
bone tissue
osseous tissue - dense smooth compact structure or cancellous spongy
bone functions
support, protection, movement, mineral storage, blood cell formation
joint classification
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
fibrous joints
consists of inflexible layers of dense connective tissue, holds the bones tightly together
cartilage joints
slightly movable
synovial joints
created where two bones articulate to permit a variety of motions
Bursae
flattened fibrous sacs lined with synovial membrane and containing a thin film of synovial fluid - called tendon sheaths to protect joints
plane joint
short slipping or gliding movements; i.e. carpals
tendon
Connects muscle to bone or muscle to muscle
Ligament
Connects bone to bone
hinge joint
elbow and knee
pivot joint
rotating bone turns around an axis; i.e. connection between radius/ulna and humerus
condyloid joint
synovial joint that does everything except rotating
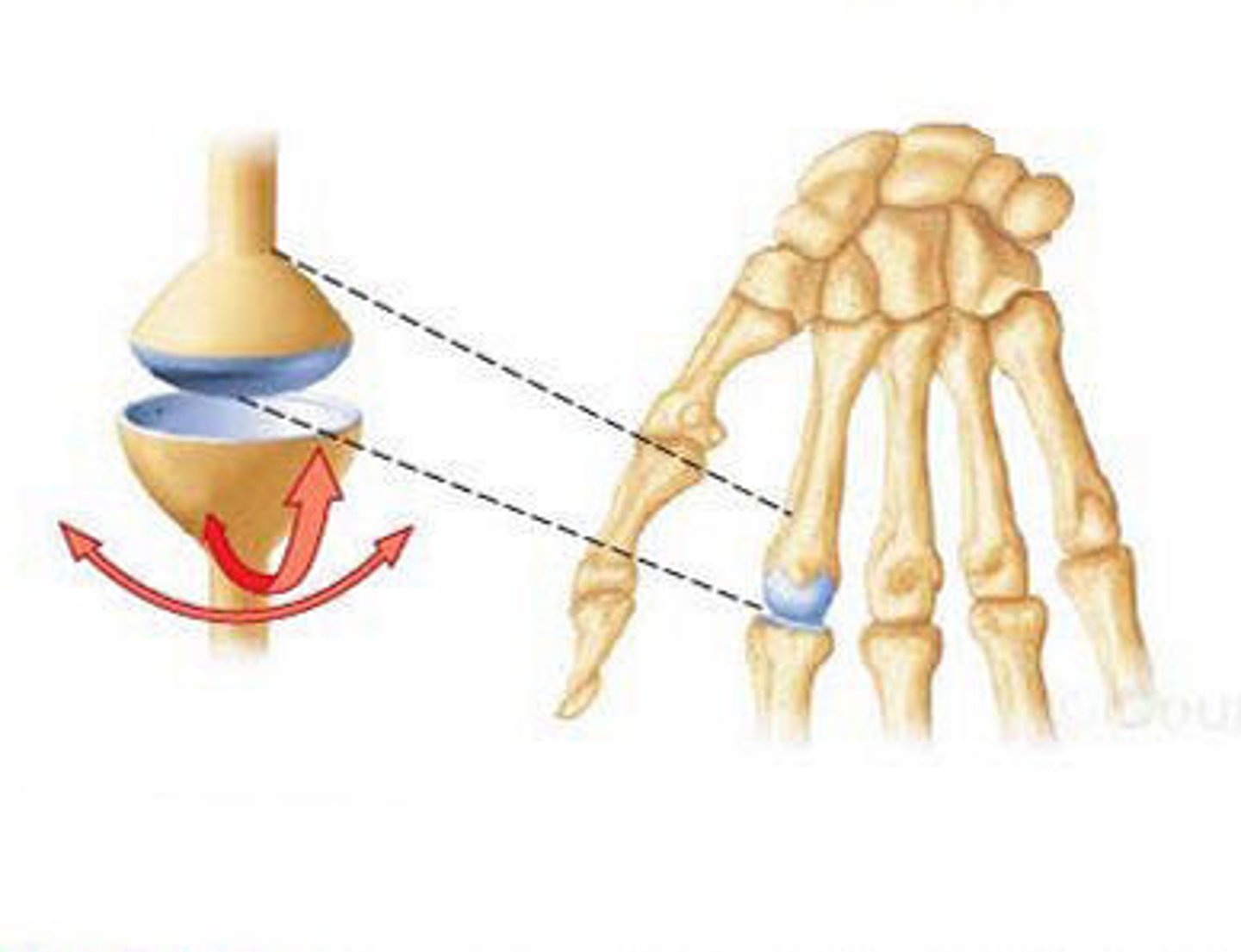
saddle joint
type of joint found at the base of each thumb; allows grasping and rotation, between carpals and metacarpals
ball and socket joint
shoulder and hip
gliding
nearly flat bone surfaces slide or glide over each other, gliding side to side movement
flexion and extension
bending and extension of a limb
Dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
plantar flexion
pointing toes
abduction and adduction
(n.) moving away from median plane (limbs); moving away from midline (fingers); moving forward (thumb)
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
rotation
rotation of a joint, head side to side
supination and pronation
palm up to palm down
inversion and eversion of foot
Inversion is moving the foot so that the sole faces medially (inward) and eversion is moving the foot so that the sole faces laterally (outward).
protraction/retraction
anterior to posterior movement of scapula or mandible
elevation/depression
up and down
opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
landmarks of the shoulder
scapula, acromion process, greater tubercle, coracoid process
subacromial bursa
helps during abduction of the arm, so the greater tubercle of the humerus moves easily under the acromion process of the scapula
Elbow landmarks
lateral and medial epicondyles, olecranon process and bursa
Ulner nerve
Nerve that runs along the little finger side of the arm and the palm of the hand, synovial membrane palpable when inflamed
scaphoid and lunate
only carpals that articulate with radius to form wrist joint
hip landmarks
iliac crest, acetabulum, greater trochanter of femur, anterior inferior iliac spine
Cruciate and collateral ligaments
Two major types ligaments that provide knee joint stability
special considerations
african ancestry has stronger bone density, women and asian and caucasians are prone to osteoporosis, asians have lower bone density, 24 vertebrae is average, poorly designed furniture can cause problems, frequent movements can cause inflammation and degeneration
joints tested in cephalocaudal pattern
shoulders, elbow, wrists and hands, knees, ankles and feet, spine
Goniometer
instrument used to measure joint angles
what force do you use to test muscle strength?
opposing force
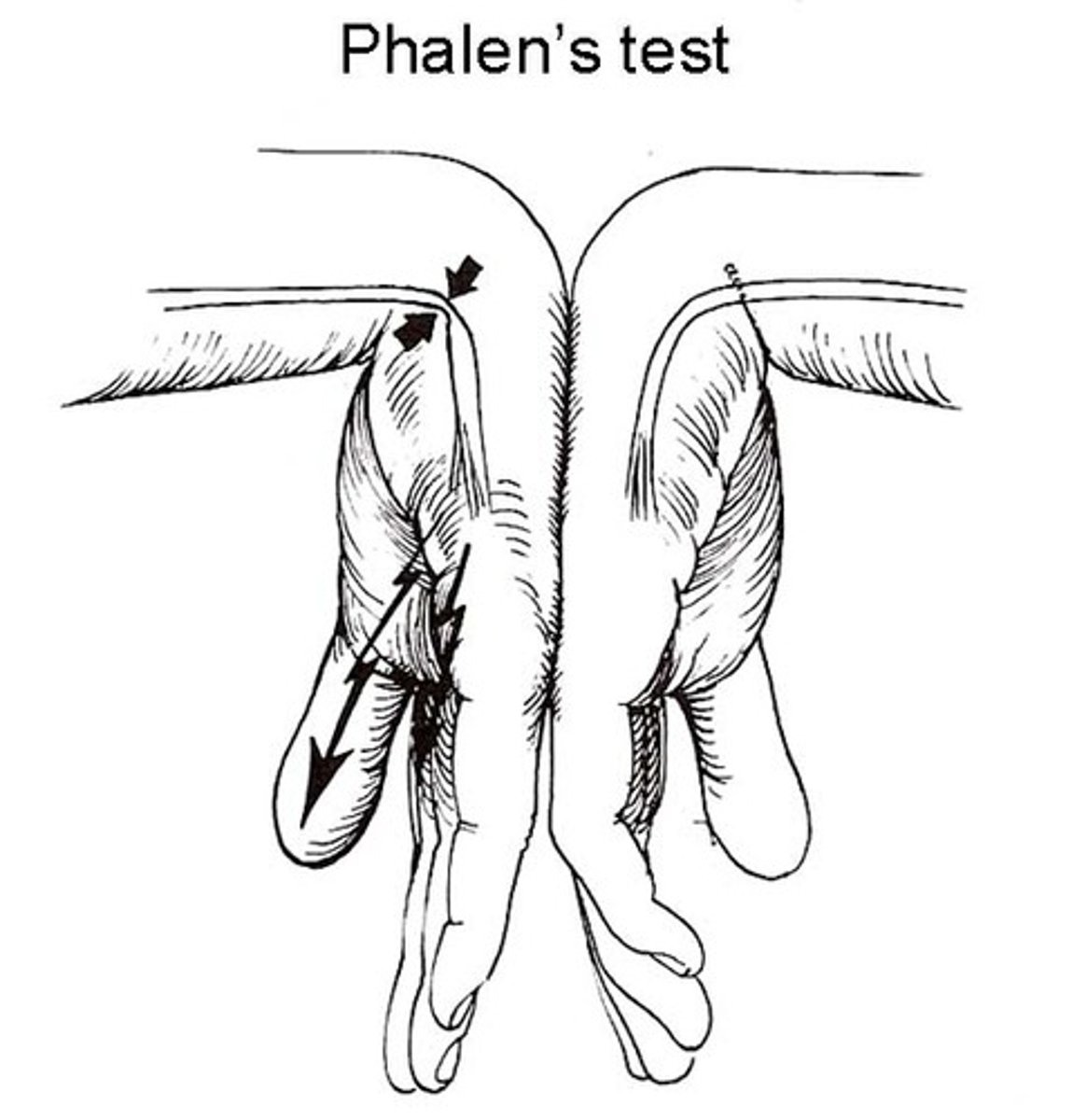
What is Phalen's test?
Hold the wrist flexed to each other
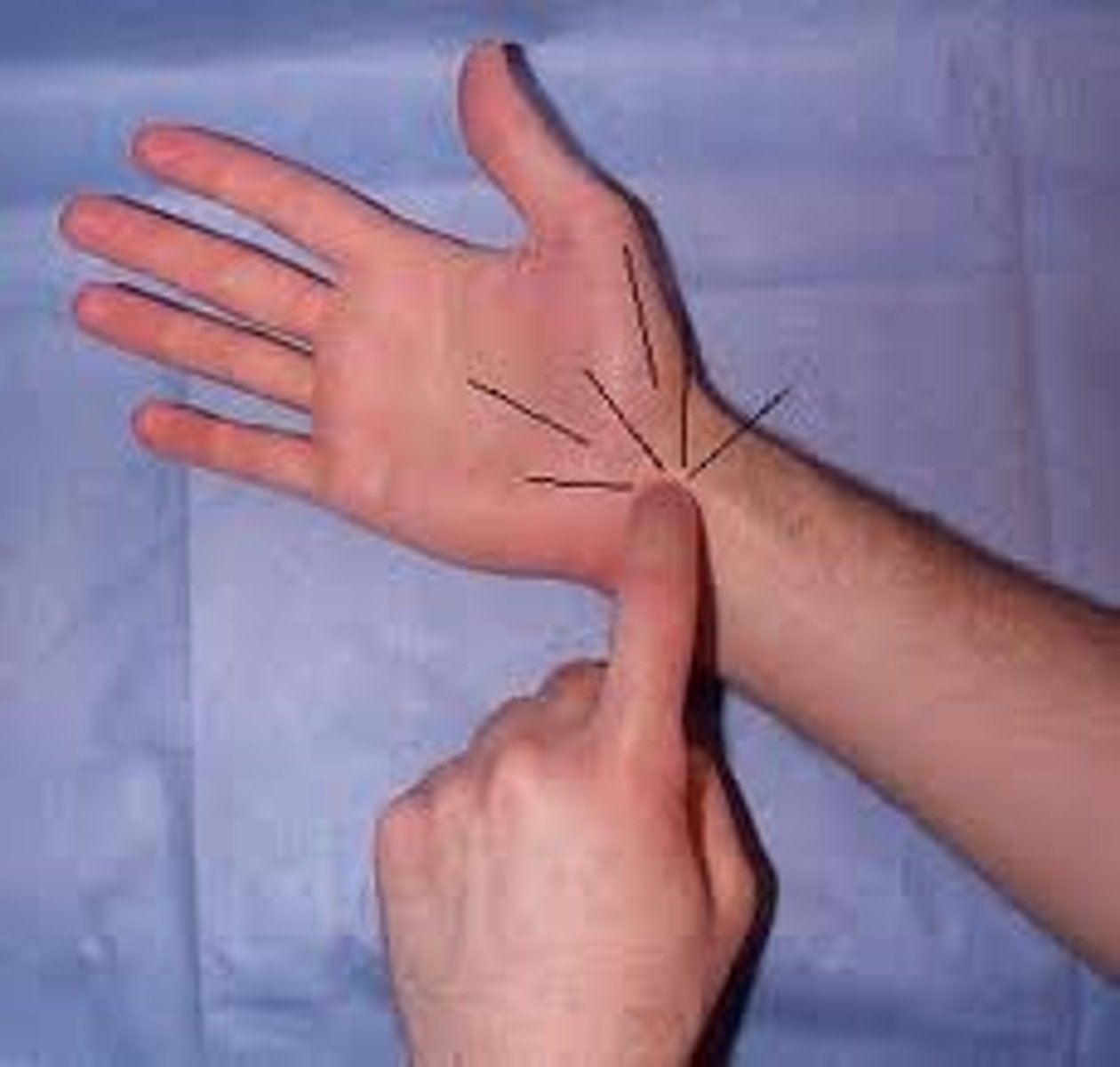
What is Tinel's sign?
tap over inner wrist, positive if tingling in thumb and first three fingers
kyphosis
hunchback
Scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
benign juvenile lordosis
large curve at lumbar
TMJ syndrome
painful jaw movement
rotator cuff tear
traumatic rip of one or more of the muscles or tendons within the rotator cuff of the shoulder
Olecranon Bursitis
inflammation of the bursa located over the olecranon process of the elbow
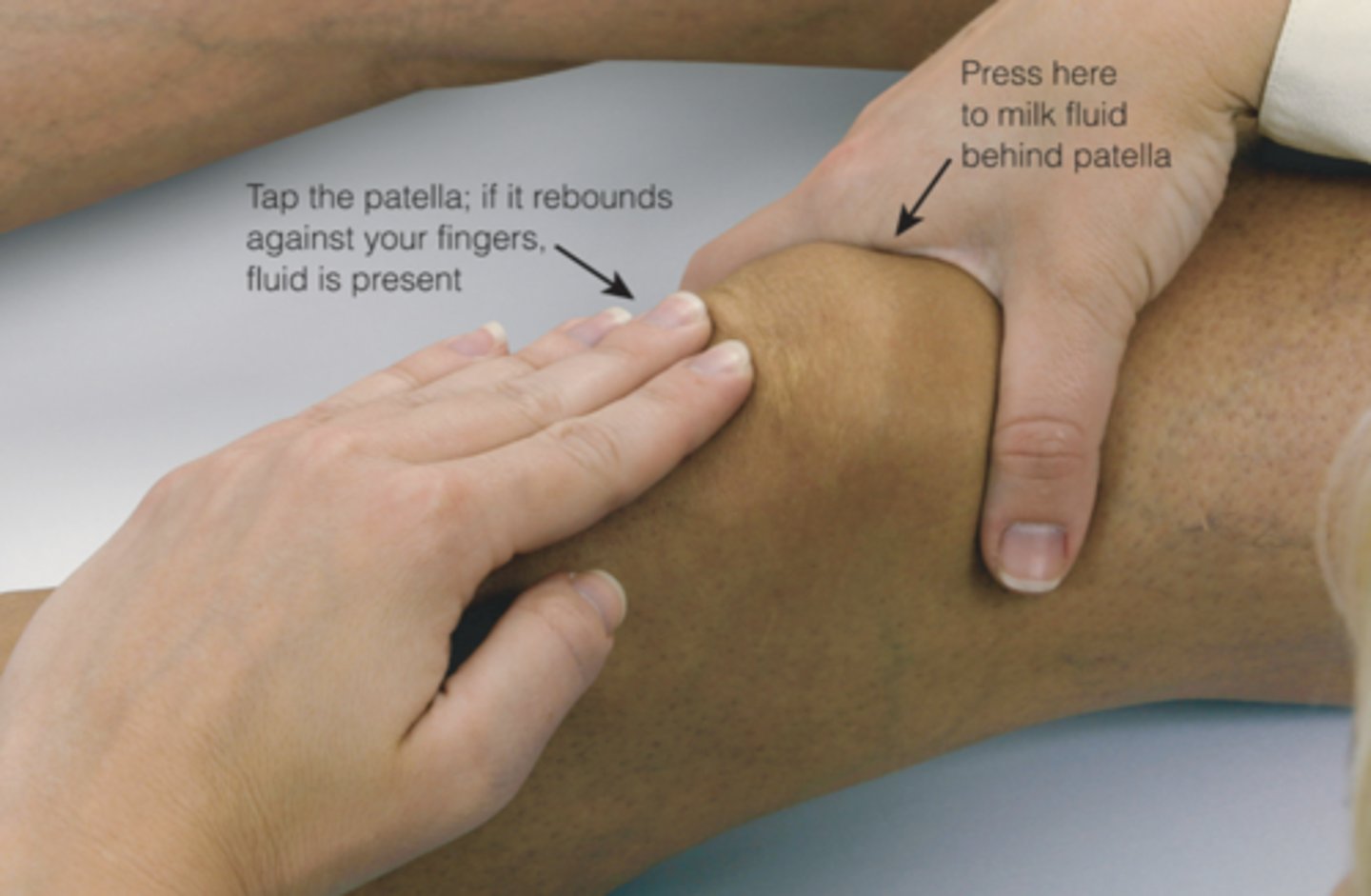
joint effusion
swelling from excess fluid in the joint capsule
Rheumatoid nodules
Firm, nontender, unattached subcutaneous nodules at pressure points (e.g., elbow, back of forearm and fingers) associated with rheumatoid arthritis
carpal tunnel syndrome
A condition caused by compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel and characterized especially by weakness, pain, and disturbances of sensation in the hand and fingers past the ring finger
Dupuytren's contracture
A gradual thickening and tightening of tissue under the skin in the hand.
swan neck and boutonniere deformity
flexion contracture resembles curve of a swan's neck; occurs with ulnar drive and chronic RA
Osteoarthritis
inflammation of the bone and joint
rheumatoid arthritis
a chronic autoimmune disorder in which the joints and some organs of other body systems are attacked - characterized by deviation of joints and deformity of fingers in late stages
synovitis
inflammation of the synovial membrane of a joint
Gout
Swollen, red, acutely painful great toe joint
hallux valgus
an abnormal enlargement of the joint at the base of the great toe (bunion)
hammertoe
condition in which the toe is bent downward at the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint
types of muscles
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
ligament
Connects bone to bone
joint
where two bones meet
review of systems for infants and children
birth trauma, anoxia or cyanotic events, premie, motor milestones
review of systems for adolescents
sports participation, warm-up routine, reports of any injury
review of systems for older adults
abilities, limitations, function and assistive devices
order of operations for assessment
inspection, palpation, ROM, strength
goniometer
instrument used to measure joint angles
strength grading

phalen's test
carpal tunnel syndrome
tinel's sign
"pins and needles" sensation felt when an injured nerve site is tapped - carpal tunnel syndrome
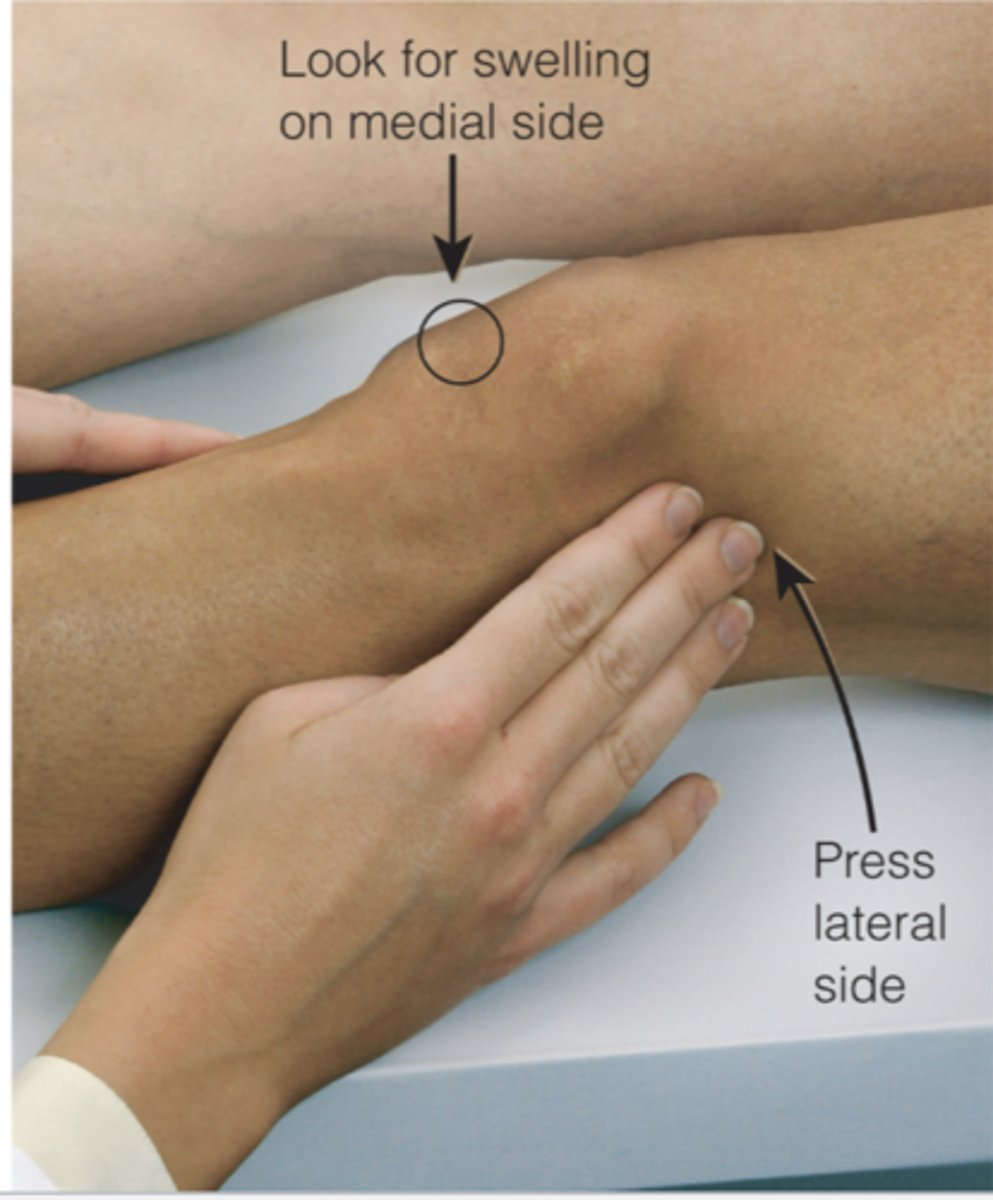
bulge sign
Effusion of fluid in the knee
ballottement
a palpation technique used in detecting or examining a floating object in the body
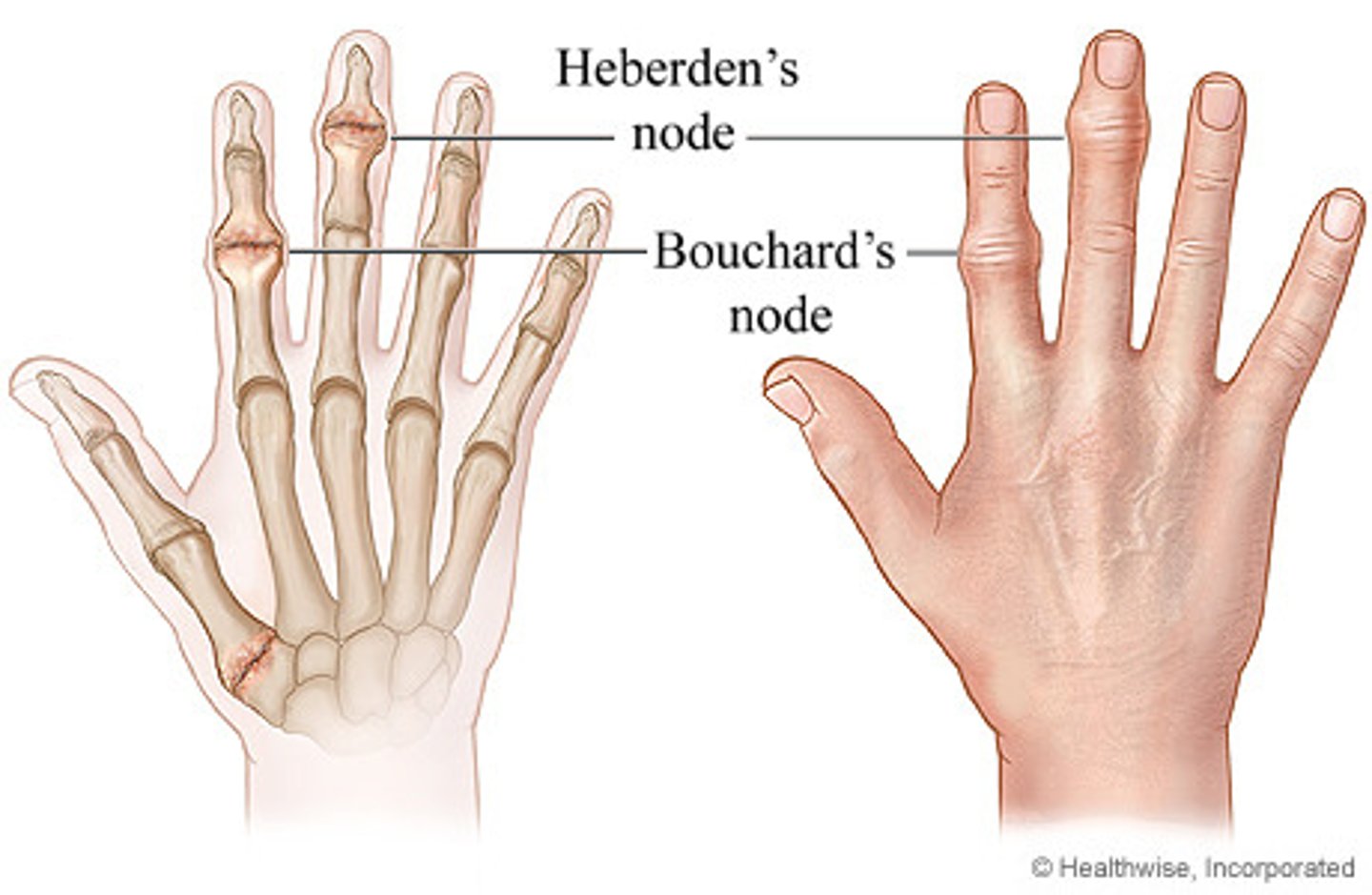
osteoarthritis
inflammation of the bone and joint; degenerative and fusiform swelling of joints, heberden's nodes
muscle tremor
rhythmic, involuntary, purposeless contraction that produces a quivering or shaking movement (like in Parkinson's)
muscle spasms
sudden, painful, involuntary muscle contractions
fasciculation
rapid continuous twitching of resting muscle without movement of limb

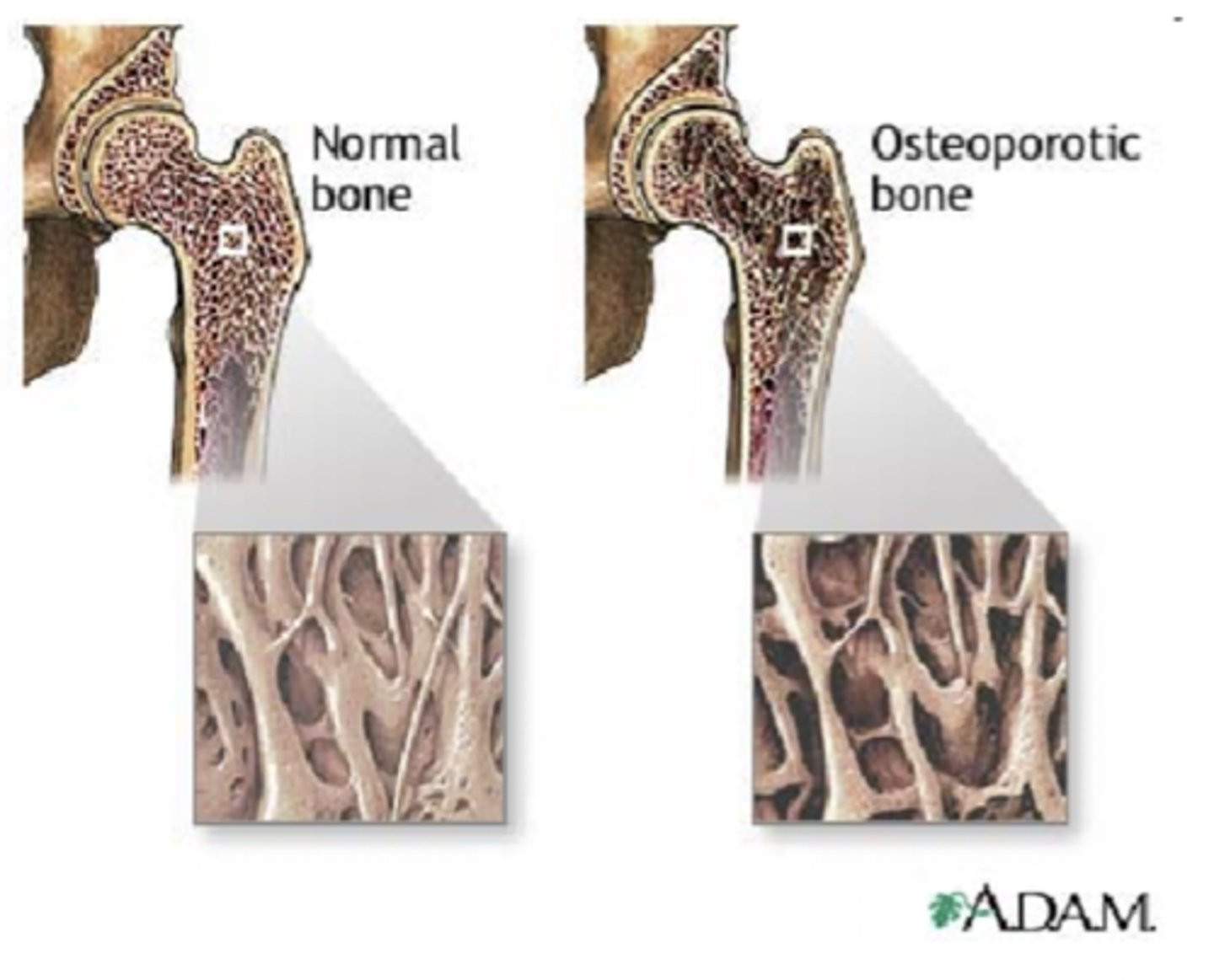
Osteoporosis
A condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily.
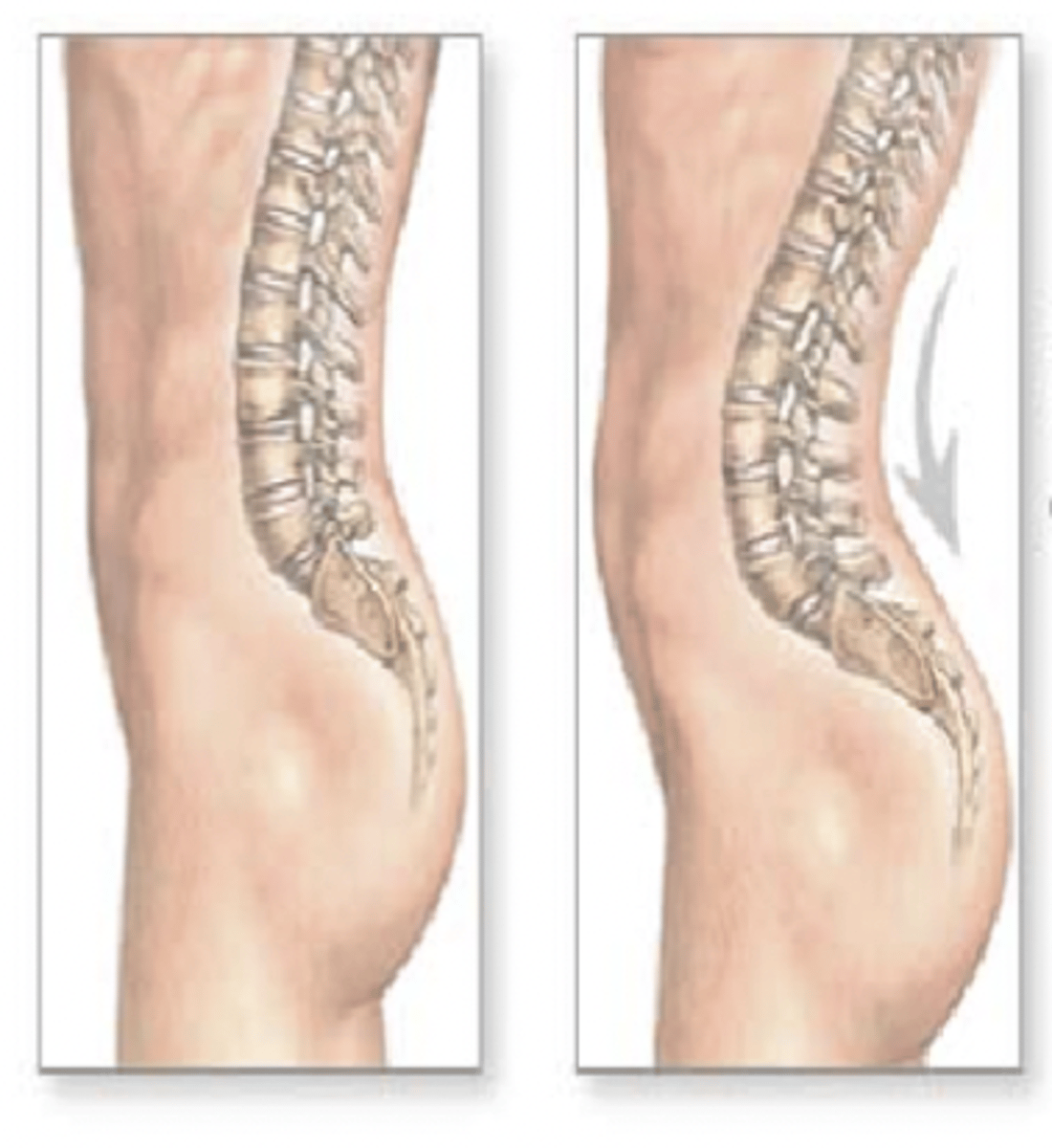
lordosis
abnormal anterior curvature of the lumbar spine (sway-back condition)
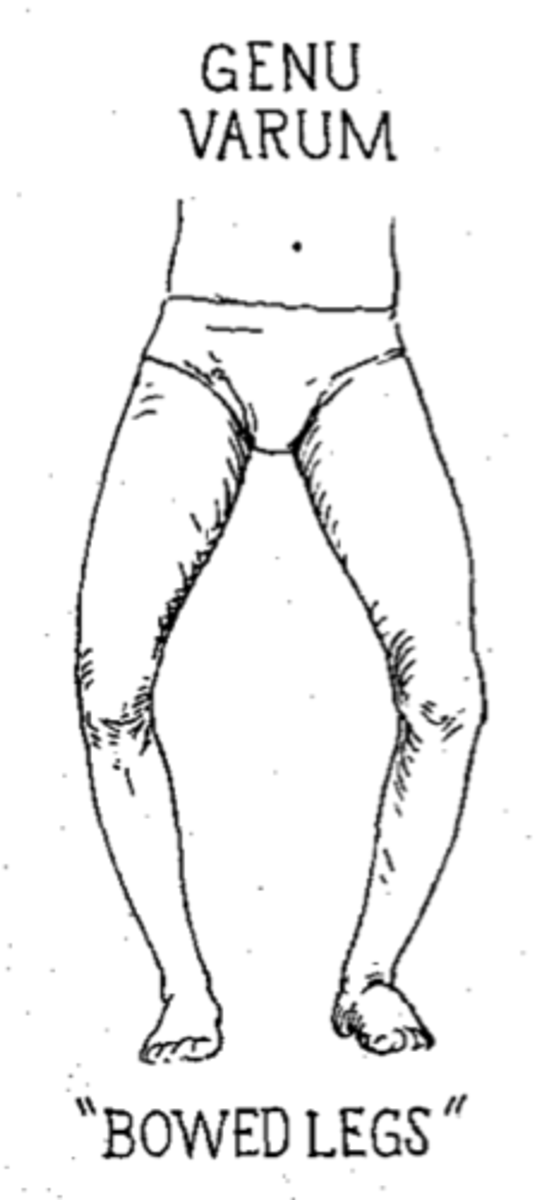
genu varum "bow leg"
legs cannot go together when standing straight, can resolve in early age but can also be permanent
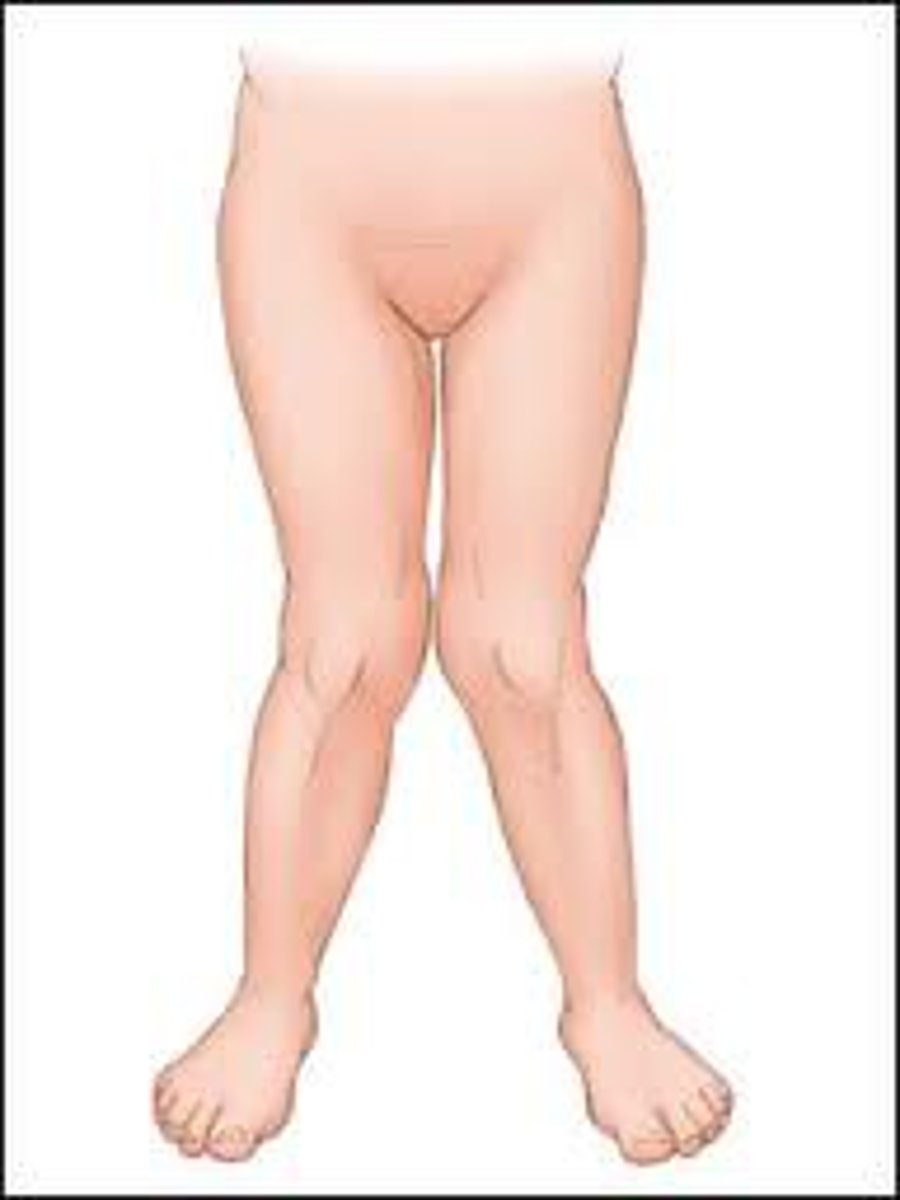
genu valgum "knock knee"
A deformity in which the knees are abnormally close together and the space between the ankles is increased due to a lateral angulation of the tibia in relation to the femur
subluxation
partial dislocation
low dislocation
dislocation that is worse than a subluxation, but is lower placed than high dislocation
high dislocation
complete dislocation - not even in socket area
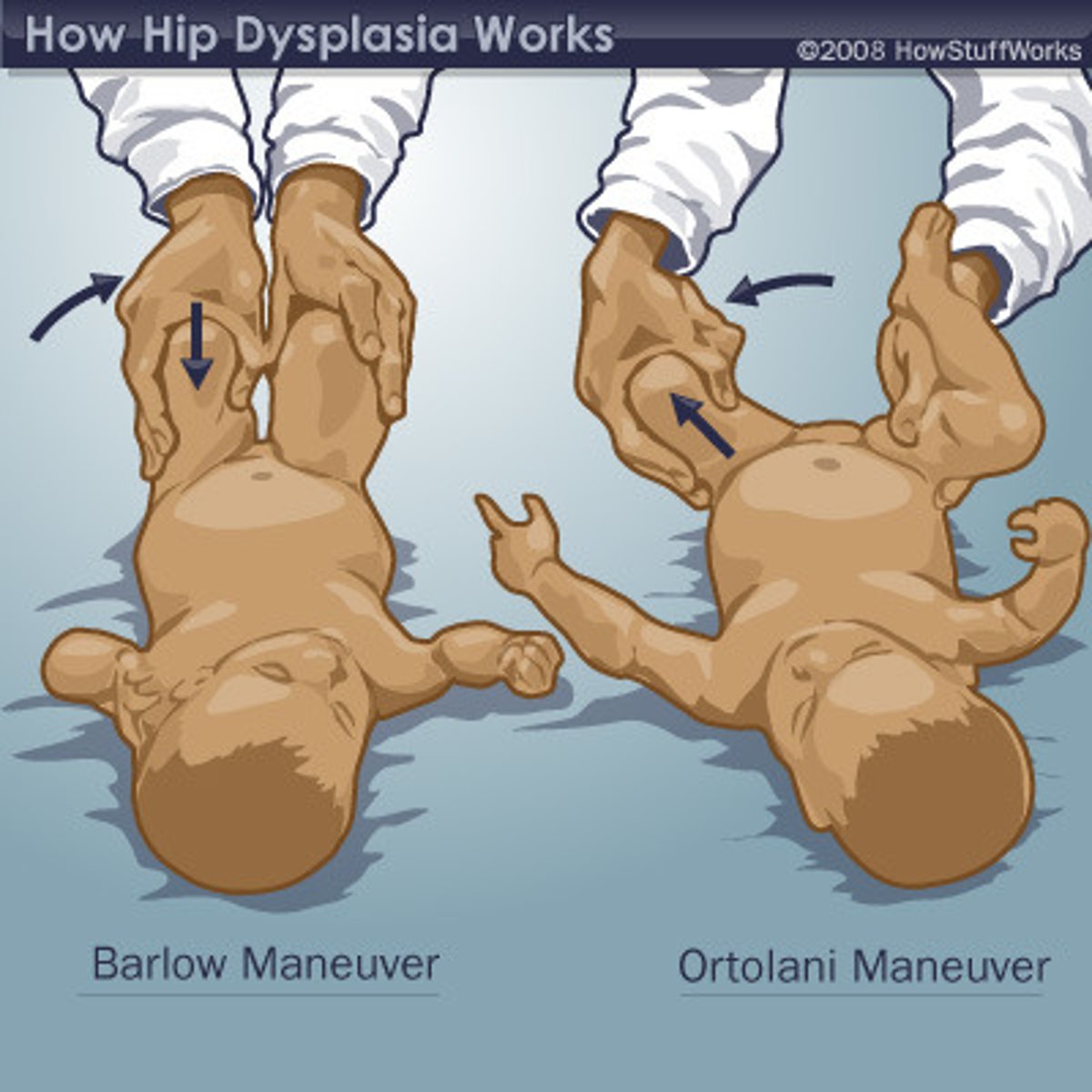
ortolani's maneuver
A manual procedure performed to rule out the possibility of developmental dysplastic hip.
simple fracture
bone is broken cleanly; the ends do not penetrate the skin
comminuted fracture
fracture in which the bone is splintered or crushed
open fracture
compound fracture; broken bone with an open wound
what are relevant lab values and testing for the musculoskeletal system?
calcium (total vs. ionized), creatinine kinase, antibody markers for disorders, X-ray, CT, MRI, bone scanning