08.B BIO Cell Growth & Division (PART B)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Why do cells divide?
DNA Overload
Exchanging Materials
Surface to Volume Ratio
DNA Overload
The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. Very large cells like muscle cells have many nuclei to control what goes on in the cell
Exchange of Materials
Cells must be the appropriate size to exchange nutrients and wastes via diffusion
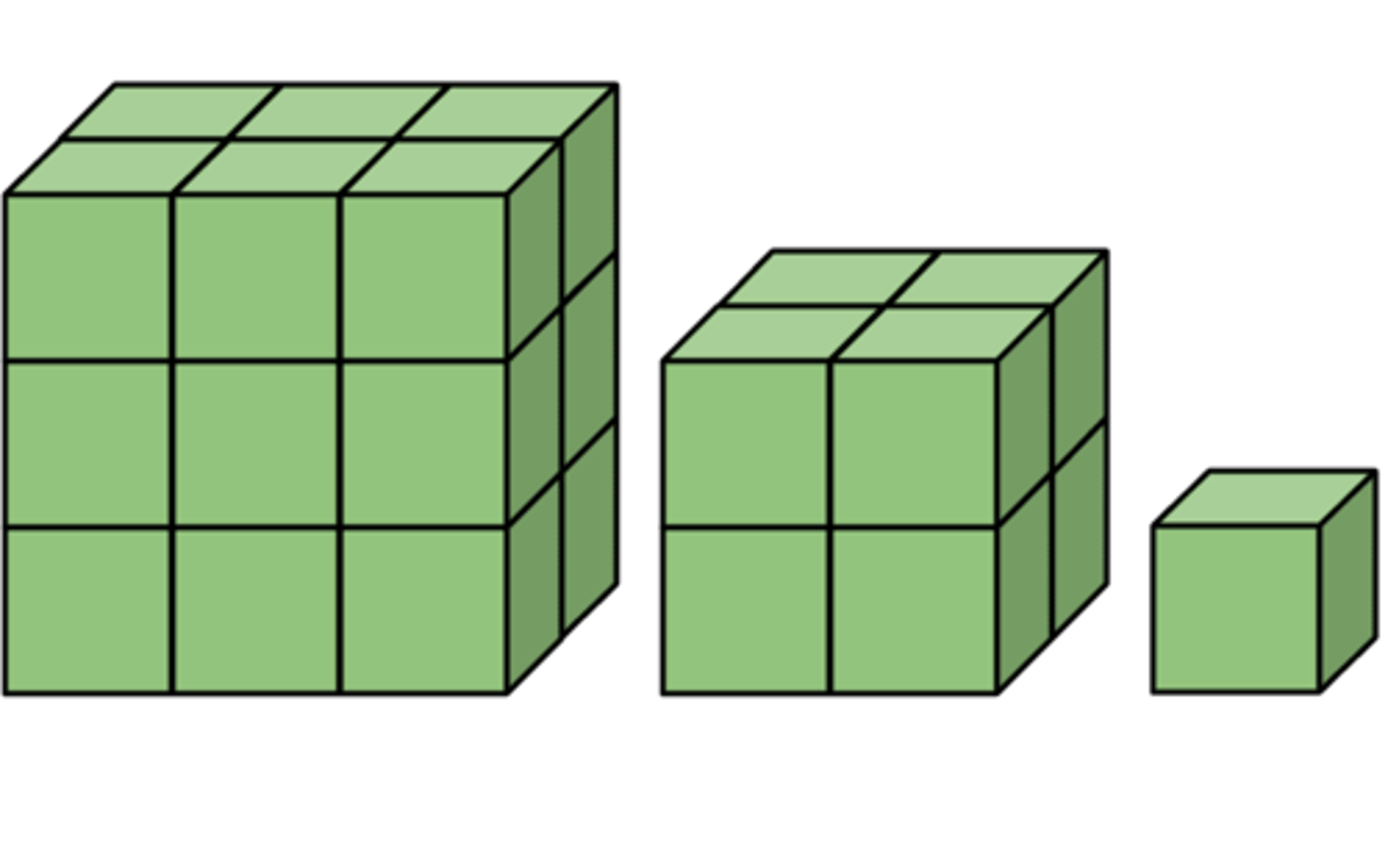
Surface to Volume Ratio
Cells must have a large surface to volume ratio so that materials can be exchanged via diffusion. The large surface area provides the area for the materials to diffuse across the membrane while the low volume ensure that the materials can travel all the way in and out the cell
Cell division
The process in reproduction and growth by which a cell divides to form daughter cells
Multinucleate
A cell with many nuclei; typical of large cells like muscle cells
Prokaryotic Cell Division (Example)
Binary fission
Eukaryotic Cell Division (Examples)
Mitosis & Meiosis
Prokaryotic Cell Division (Description)
Single circular piece of DNA replicates and is separated into the two daughter cells during binary fission
Eukaryotic Cell Division (Description)
DNA replicates and then condenses into chromosomes so the DNA is easier to separate during mitosis and meiosis
Large cells
Cells that have a small surface area to volume ratio
Small cells
Cells that have a large surface area to volume ratio