Homeostatis
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Homeostatis
the maintenence of a stable internal environment despite changes to the external environment
Why is homeostatis important?
Homeostatis is important because our body performs many functions
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
is the metabolic process by which cells make energy
GLUCOSE + OXYGEN —>
Energy (ATP) + Carbon Dioxide + Water
What does the nervous system consist of
Brain, spinal cord + interneurons!
What does the endocrine system consist of
Cranial nerves
Spinal nerves
Peripheral nerves
sensory + motor neurons!!
Photoreceptors
Light, eye
Mechanoreceptors
Sound, Cochlear in ear
Pressure, pain and temp / tongue and nose
Chemoreceptor
Chemicals, tongue nose
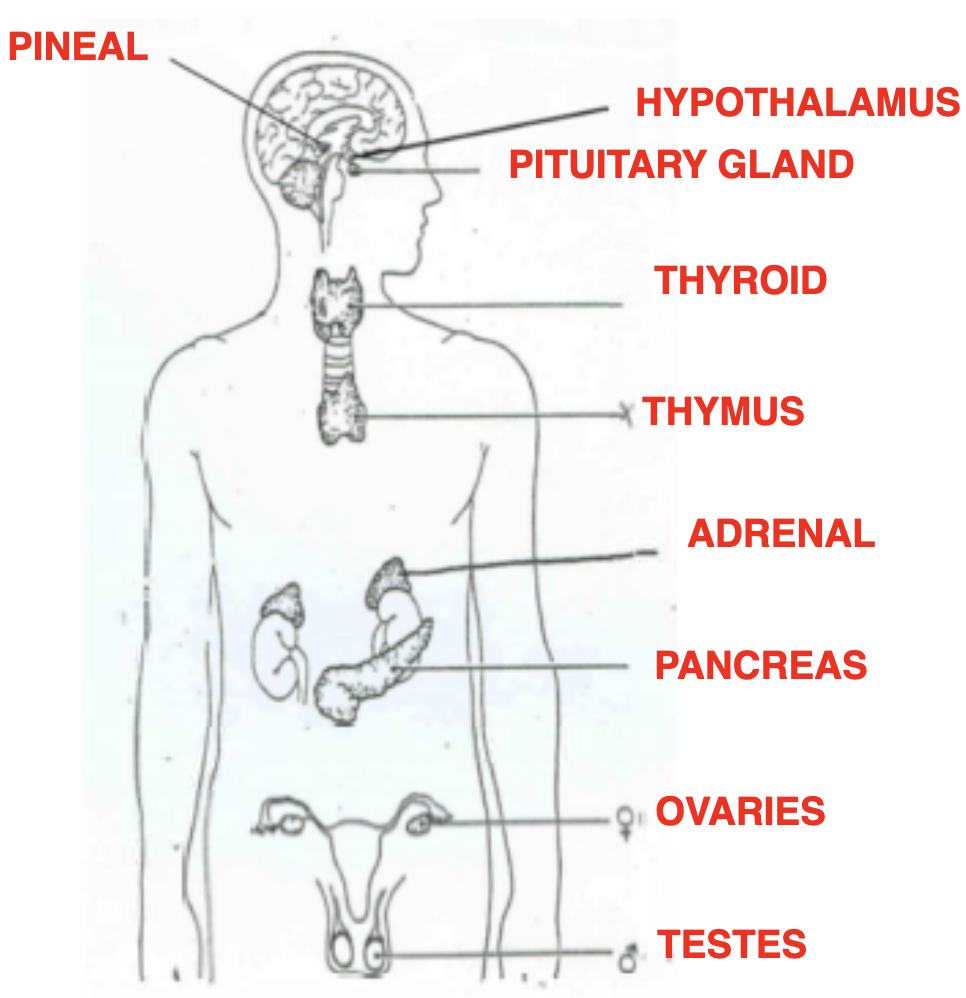
Hypothalamus
receives electrical and chemical information and is the control centre
Pituitary gland
The master gland, controls many endocrine glands, stimulating them to release their own hormones
What are hormones
They are protein molecules produced by specialised cells in different glands. Hormones are produced in very small quantities and are transported by blood
Do hormones travel slower than nervous impulses
Yes, hormones travel slower than nervous impulses, however they are longer lasting
• are delivered to all parts of the body but can also have locaI effects.
• co-ordinate longer-term processes such as growth and sexual development.
• have a unique structure and connect specifically to their targets like a "lock and key".
How do hormones know their target?
Hormones travel through the blood/circulatory system and "know" their target cells because of specific receptors on those cells. Each hormone has a unique structure that fits only with particular receptors, like a lock and key. Hormones only interact with specific target cells that have a unique receptor that allows hormone-specific binding, like a “lock & key”.Cells without the matching receptor will ignore the hormone, ensuring that each hormone affects only its intended targets.
What 4 hormones are produced by the pituitary gland
ADH (antidiuretic hormone) - water absorption by the kidneys
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) - causes follicles to mature in ovaries and produce hormones
LH (Luteinising hormone) - causes release of egg in ovaries (ovulation)
GH (growth) - Bone and muscular development
Endocrine Glands
these glands are ductless and secrete/release hormones directly into the bloodstream to target cells
Pheromones
They are chemicals that animals and humans use to communicate that work outside our body
How does the nervous and endocrine system work in homeostatis
The nervous and endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis, keeping the body’s internal environment stable. The nervous system acts quickly, using electrical signals to respond to immediate changes, such as adjusting heart rate or body temperature. The endocrine system works more slowly, releasing hormones that adjust longer-term processes like metabolism, growth, and blood sugar levels.
In homeostasis, the nervous system first detects changes through sensory receptors, and if a rapid response is needed, it sends signals to organs or muscles. Meanwhile, the endocrine system releases hormones to fine-tune the response or maintain long-term balance. For example, when blood sugar rises, the pancreas (an endocrine gland) releases insulin to lower it, while the nervous system can signal hunger or fullness to help regulate food intake. Both systems work together to achieve a balanced internal state.
Why do you feel warm after exercise?
To exercise, you need energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), which is produced through aerobic cellular respiration. As your muscles work harder during exercise, they increase ATP production to meet the energy demand. This process releases heat as a by-product, which raises your body temperature.
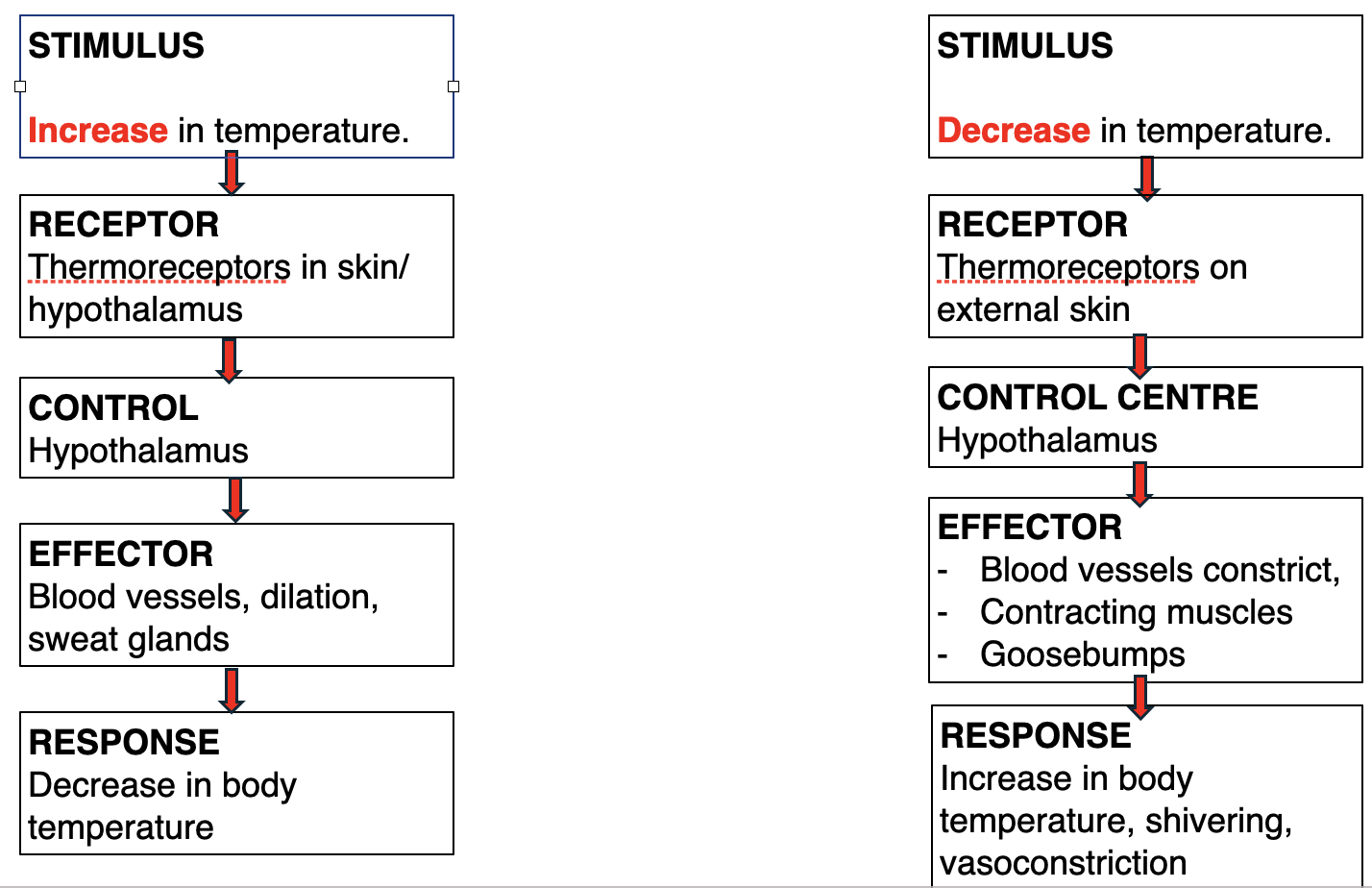
Ways that your body might respond to changes in temperature…..
Sweating, vasodilation, feeling of thirst, taking off clothes
Body responses to decreased temperature:
Shivering, Goosebumps, Vasoconstriction, Putting on more clothes
What is Vasodilation
blood vessels in your body widen or dilate, allowing more blood to flow and heat to be lost to the environment. Vasodilation helps to remove excess heat
What is Vasoconstriction
Vasoconstriction is the narrowing of blood vessels, particularly small arteries and arterioles. During this process, the muscular walls of these vessels tighten, reducing blood flow to the skin and extremities. This helps conserve heat by keeping blood closer to the body's core, which is particularly useful in cold environments or when the body needs to preserve warmth. Vasoconstriction is part of the body’s homeostasis mechanisms and is controlled by the nervous system and certain hormones to help regulate blood pressure and body temperature.
Stimulus-Response Model

what does Negative feedback do
Feedback helps our body to keep its internal conditions stable so that you can function effectively.
In a negative feedback loop, feedback serves to reduce an excessive response and keep a variable within the normal range.
what does Positive Feedback do
increases or amplifies the stimulus
How does the Nervous System control temperature?
the hypothalamus in the brain, which is the control centre of the nervous system acts an internal themometer as it receives messages from the skin and from internal
receptors, then decisions can be made based on the temperature of the body.
involuntary nervous system
how does the endocrine system control temperature
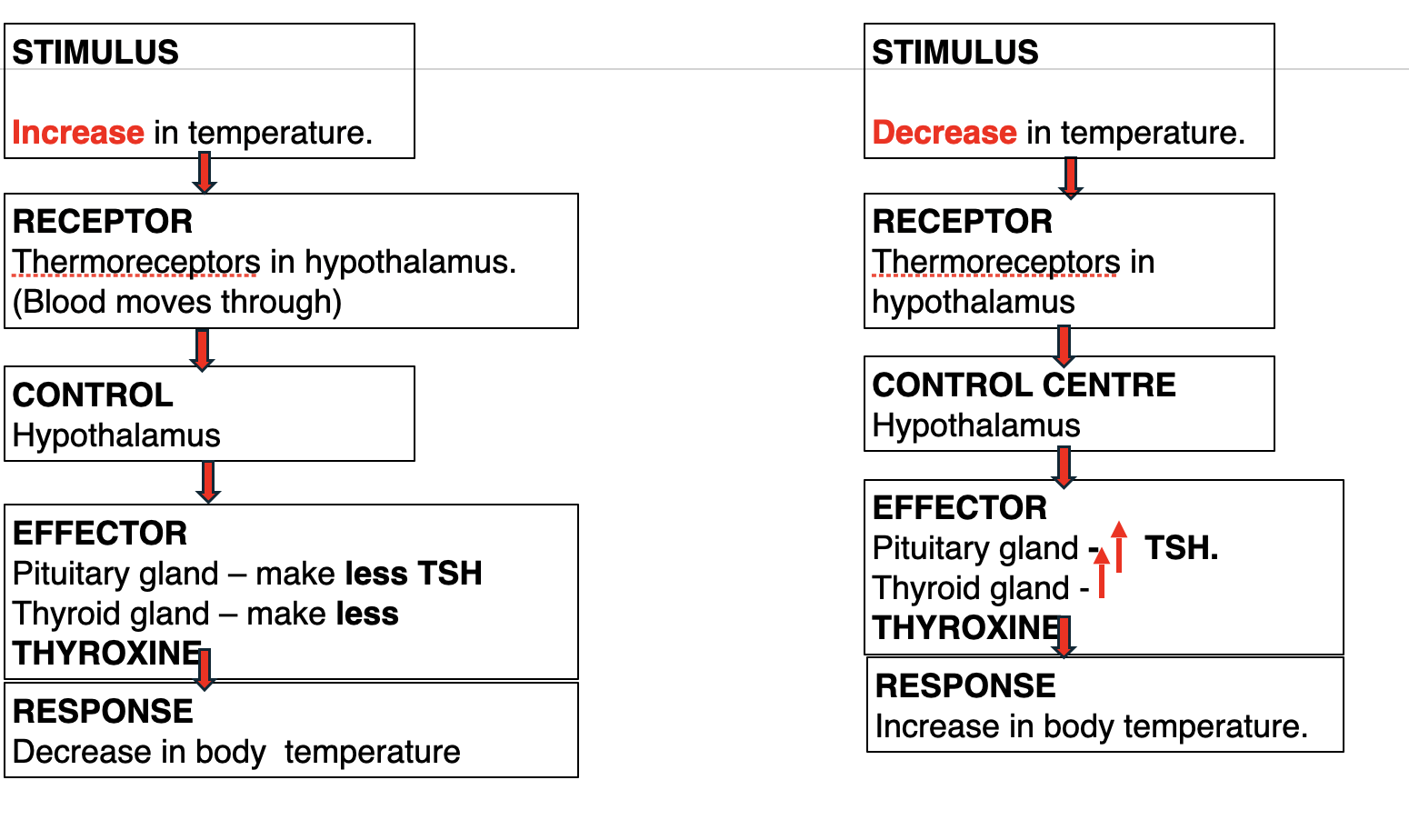
Where is glucose stored if there is excess
Stored in our liver and our muscles as GLYCOGEN using insulin as the key. Insulin instructs body cells to take in extra glucose from the blood stream.
TYPE 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the pancreas’s β cells, which produce insulin. Without these cells, the body can’t produce insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
– AUTOIMMUNE CONDITION
– β cells make insulin.
– thirst, urination, weight loss, blurred vision
TYPE 2 Diabetes
– insulin does not interact with receptors properly.
– caused by an over stimulation of increased insulin
levels.
How does the endocrine system control blood glucose
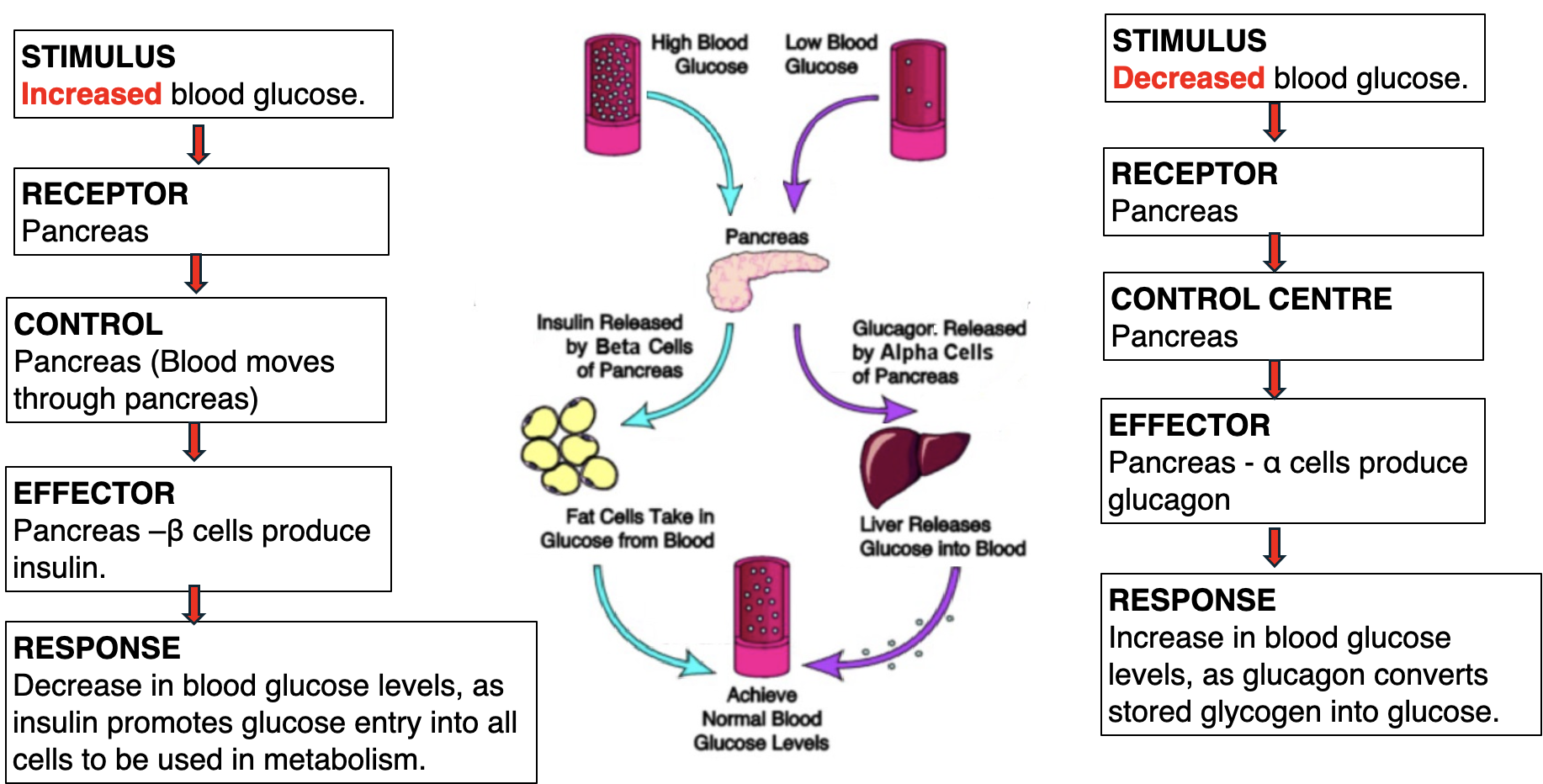
Glucagon
Hormone produced by α (alpha) cells in the pancreas. Tells liver & muscles to release glucose into bloodstream.
Insulin
Hormone produce by the β cells in the pancreas. Tells body cells to take in glucose from the blood stream & use in metabolism.
Osmolarity
is the total concentration of solutes dissolved in 1 litre of water
What is a solute
A solute is a substance dissolved in another substance called a solvent.
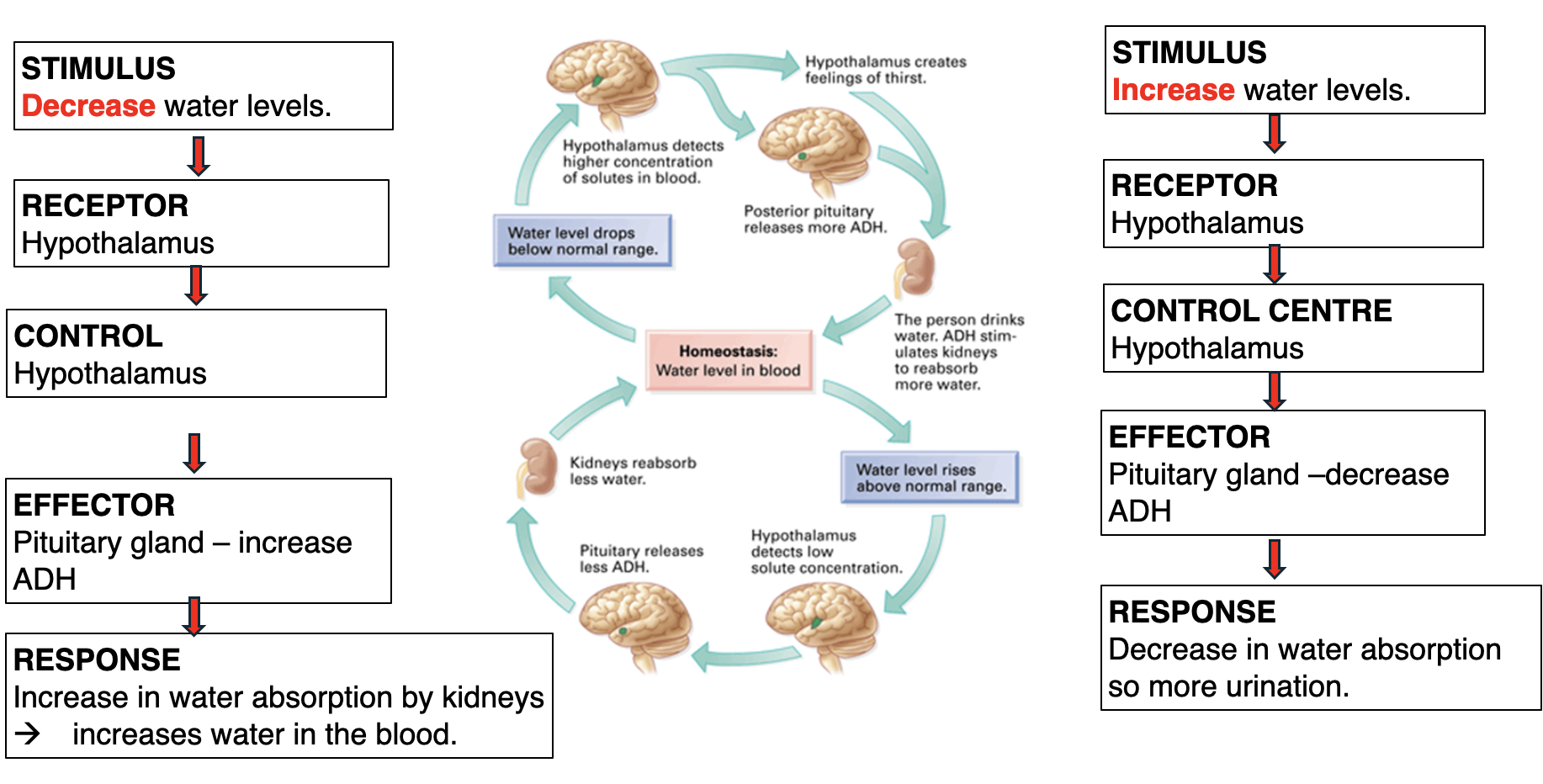
what hormone is used to regulate water balance
Anti Diuretic hormone, which is part of the endocrine system
If we produce ADH, what would you expect to happen to
d. The volume of urine? _____________________________
e. Concentration of our urine? _________________________
f. Concentration of the salt in the body? _________________
d. The volume of urine? DOWN
e. Concentration of our urine? UP
f. Concentration of the salt in the body? DOWN
If we stop producing ADH, what would you expect to happen to
g. The volume of urine? _____________________________
h. Concentration of our urine? _________________________
i. Concentration of the salt in the body? _________________
g. The volume of urine? UP
h. Concentration of our urine? DOWN
i. Concentration of the salt in the body? INCREASE as there is less water in the body
You have been to the café and indulged in an iced coffee.
Coffee is a known inhibitor of ADH.
Will you produce more ADH or less ADH? What will happen to your urine output?
You will produce less ADH.
Therefore, your urine output will increase.
Endocrine water balance.