Muscular System KIN202-M1
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
3 types of muscle
cardiac muscle
skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
musculotendinous unit
muscles attach to bones by tendons
type of tissue connected to the musculotendinous unit
tough fibrous connective tissue
bone to tissue in order
bone → tendon → muscle → tendon → tissue
3 other connective tissue
epimysium
endomysium
perimysium
function of connective tissue
stabilizes and supports many organizational levels of muscle
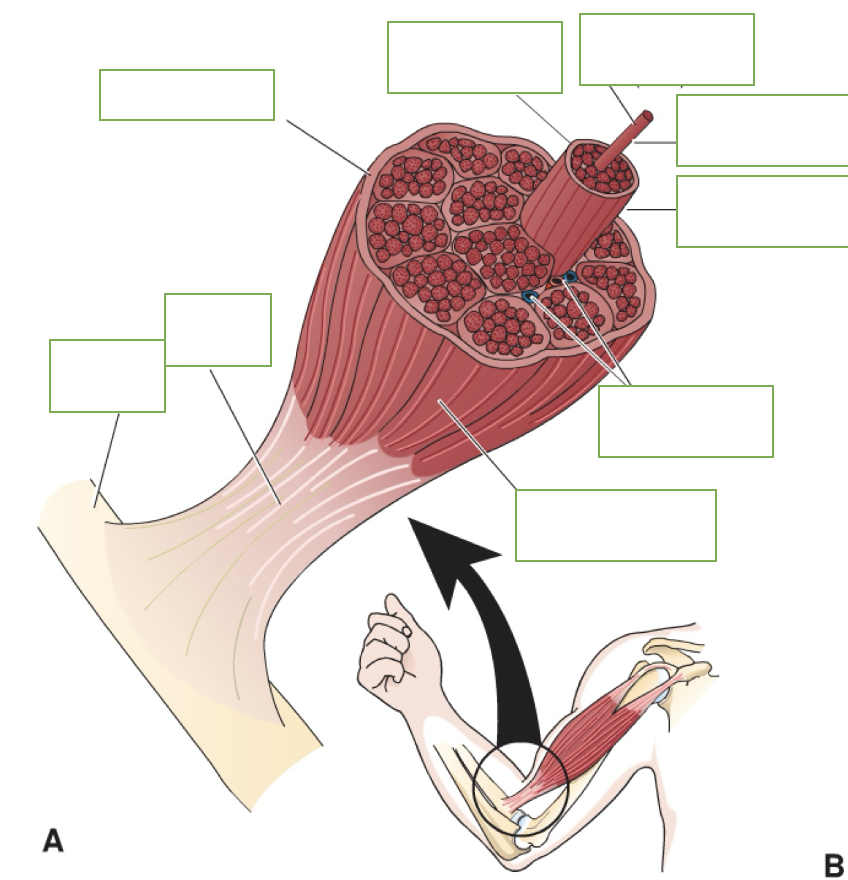
label: bone, tendon, epimysium, muscle fascicle, muscle fiber (cell), endomysium, permysium, blood vessels, body of muscle
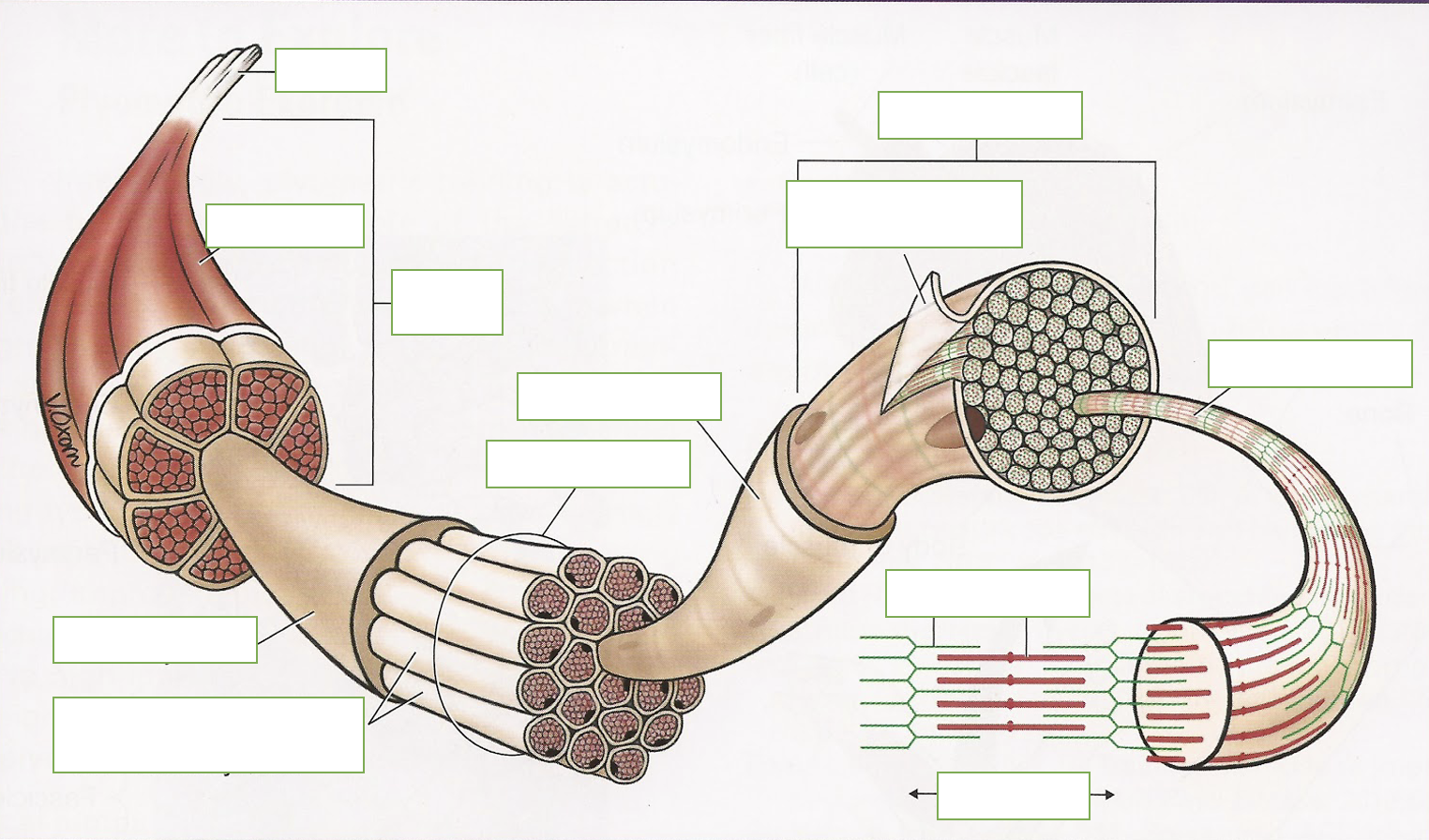
label: tendon, epimysium, perimysium, skeletal muscle, endomysium, muscle fiber, endomysium, sarcolemma membrane, microfiber, actin myosin, sarcomere, fasciculus, muscle fibers covered with endomysium
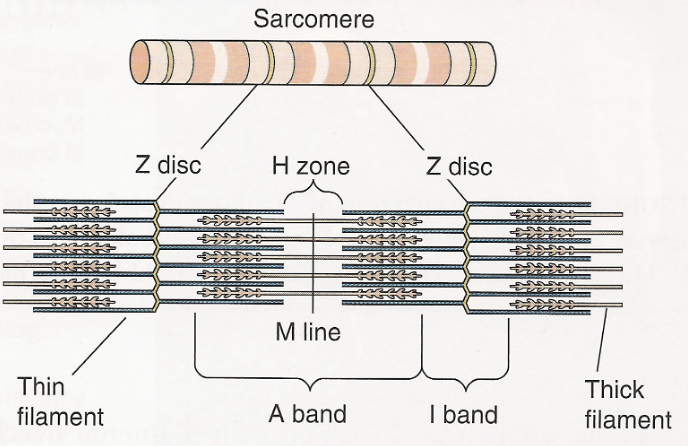
sarcomere function
smallest most basic contractile unit of skeletal muscle that produces force and shortening
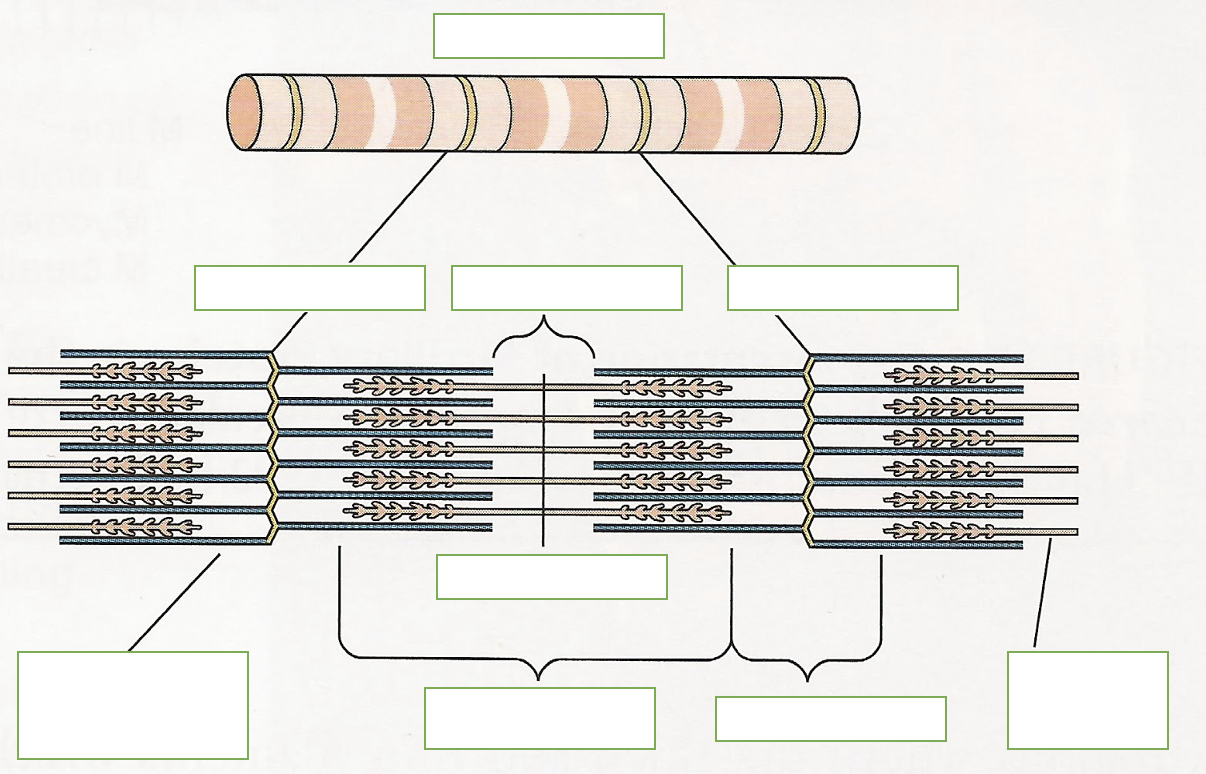
label: sarcomere, z disc, thin filament, thick filament, m line, H zone, A band, I band
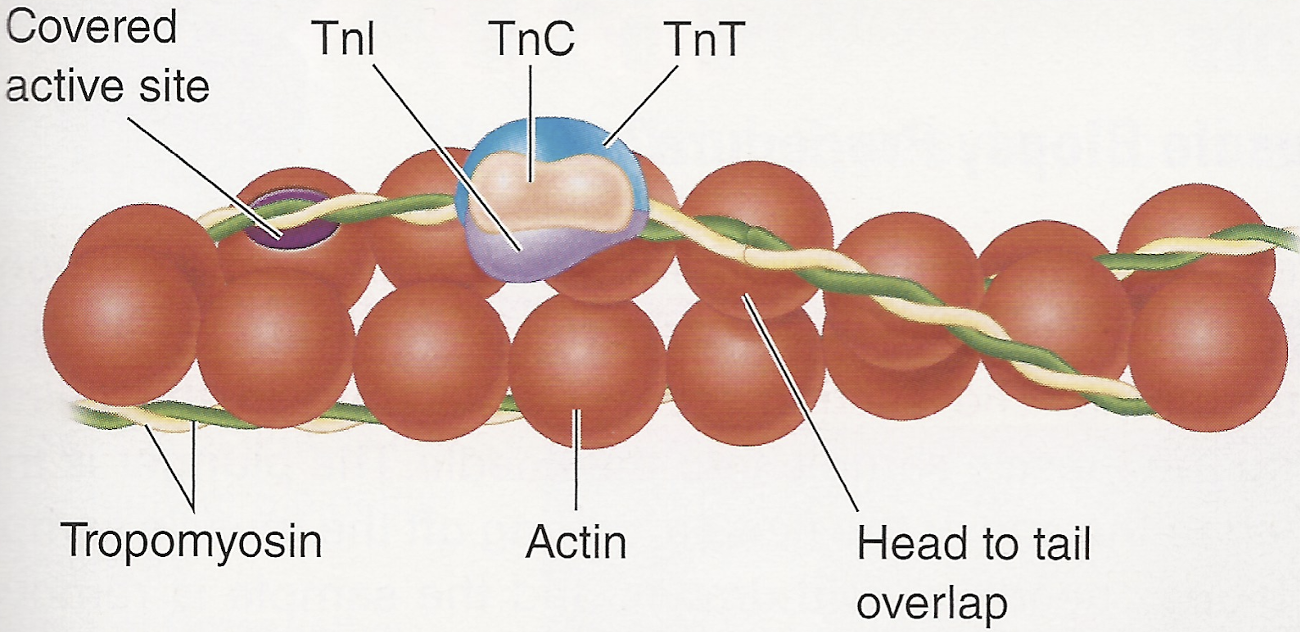
triposmysin
tube shaped protein molecule wrapped around actin
troponin
3 regulatory proteins located along tropomyosin molecule
the 3 troponin molecule
troponin I (Tnl)
troponin T (TnT)
troponin C (TnC)
Troponin I function
holds tropomyosin - troponin to actin
troponin T function
holds troponin to tropomysin
troponin C function
affinity for calcium. KEY for muscle activation
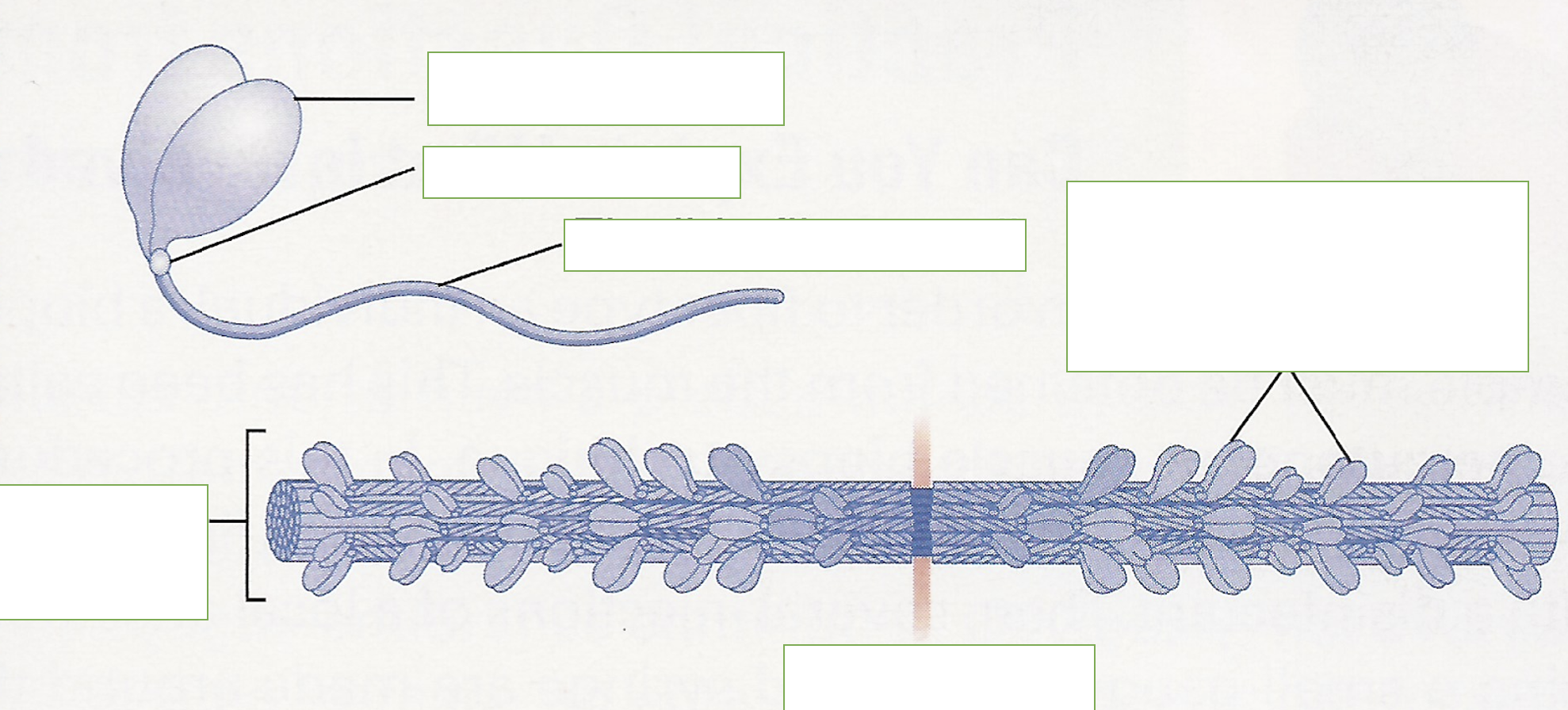
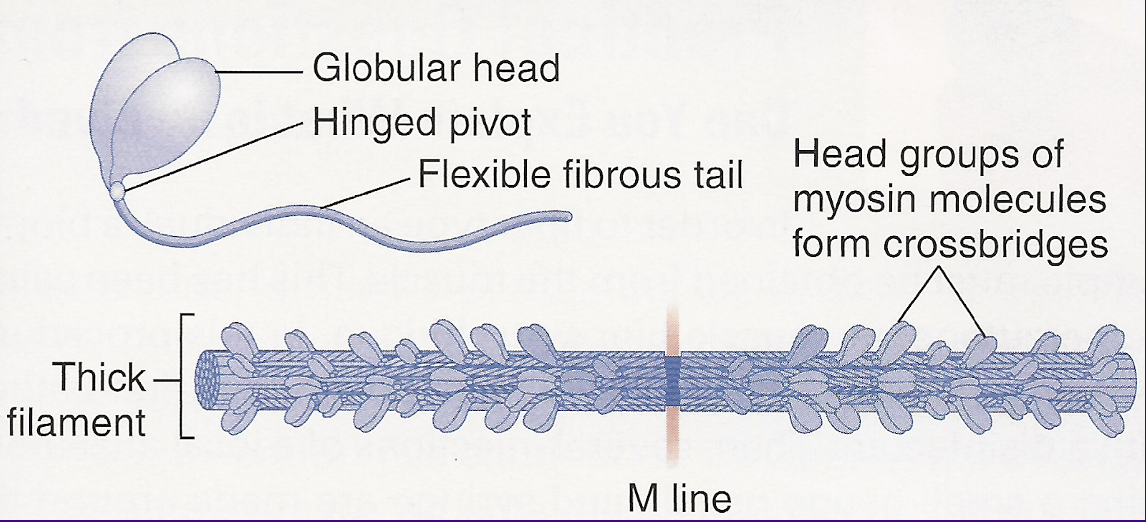
label: globular head, hinged pivot, flexible fibrous tail, thick filament, M one, head groups of myosin molecules form cross bridge
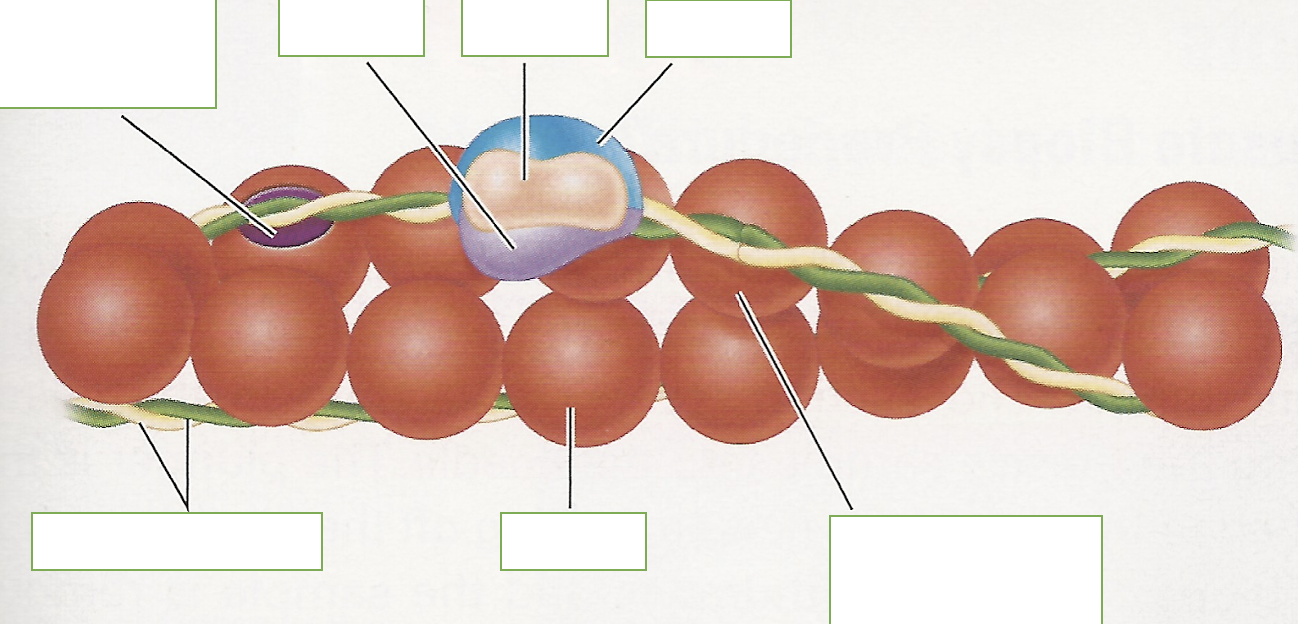
label: covered active site, Tnl, TnC, TnT, tropomyosin, actin, head to tail overlap
The ____ ____ of the muscles (contraction) is preceded by ____ ____ that are dependent on an ____ ____
mechanical response, chemical changes, electrical stimulus
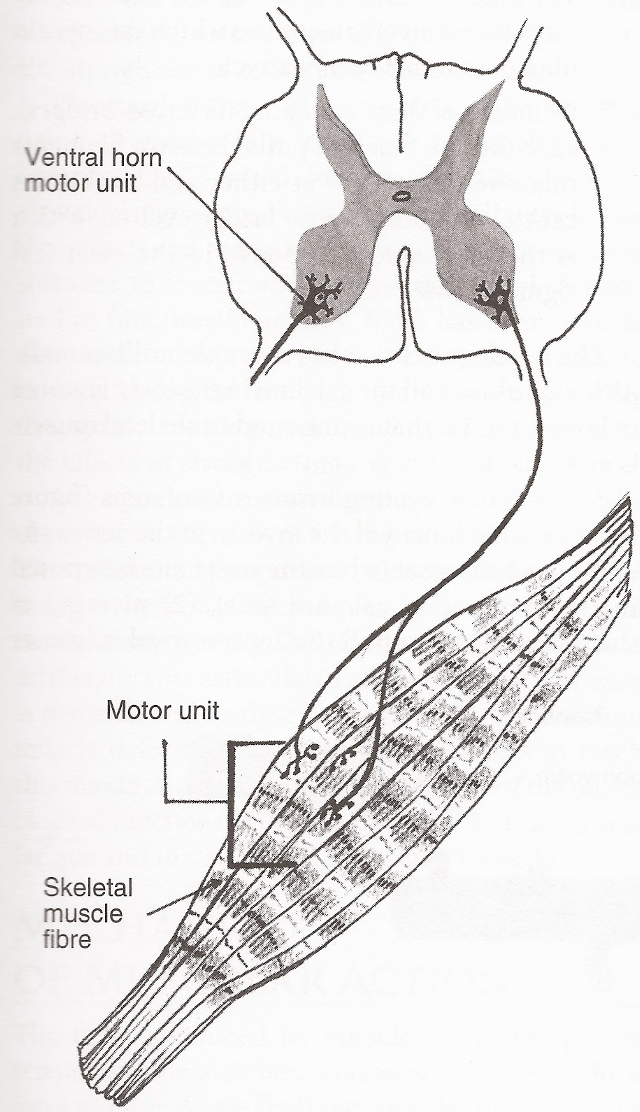
The electrical stimulus is provided via the ___ ___
motor unit
The motor unit is what kind of nerve?
single motor nerve
single motor nerve originates in what 3 locations?
brain
brainstem
spinal cord
the motor unit has all of what that does what?
all the muscle fibers that a single motor nerve innervates
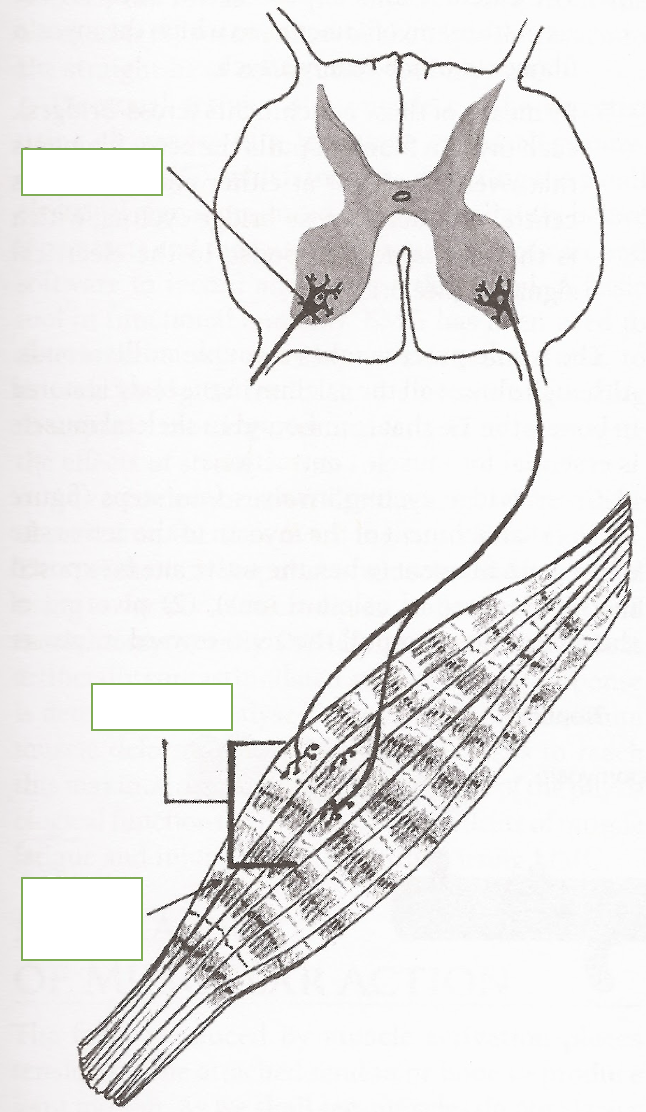
label: ventral horn motor unit, motor unit, skeletal muscle fiber
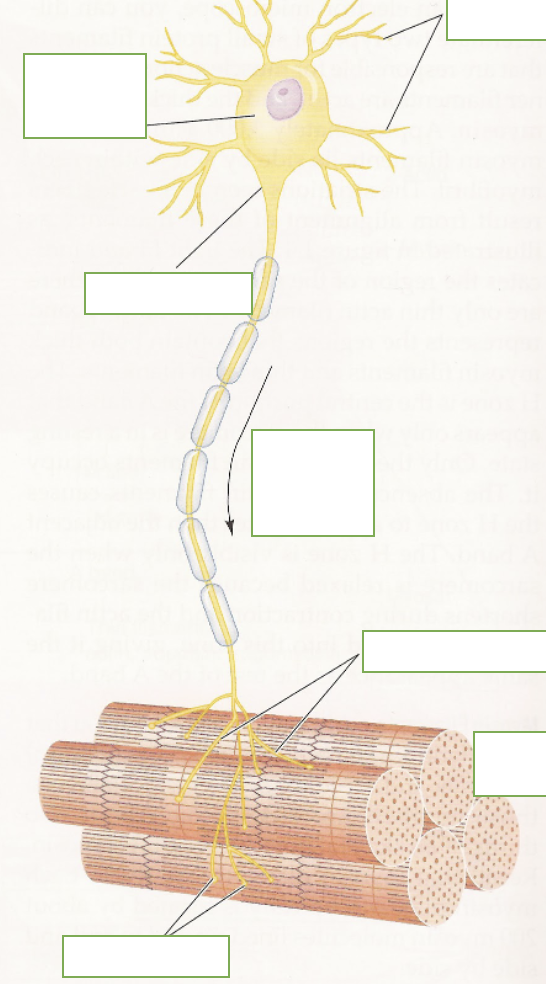
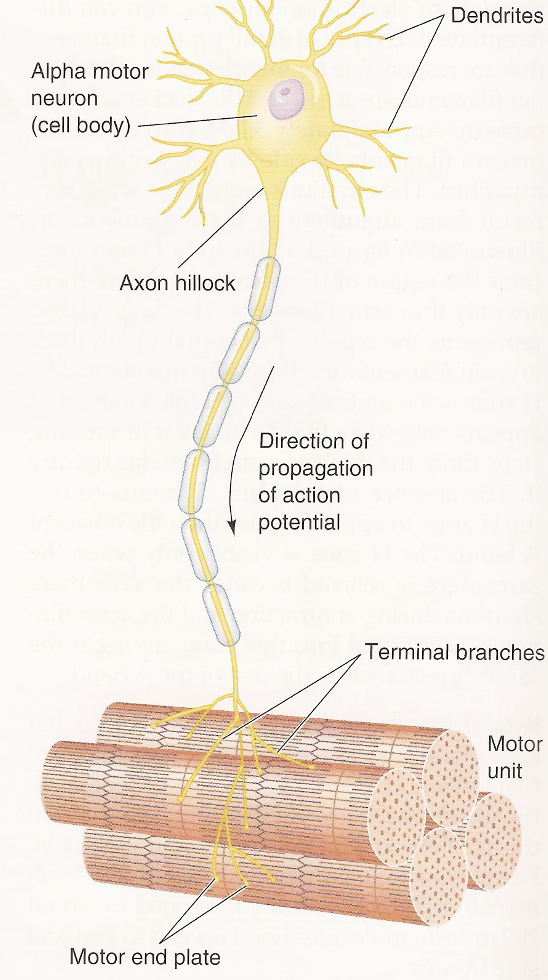
label: alpha motor neuron (cell body), axon hillock, dendrites, direction of propagation of action potential, terminal branches, motor unit, motor end plate
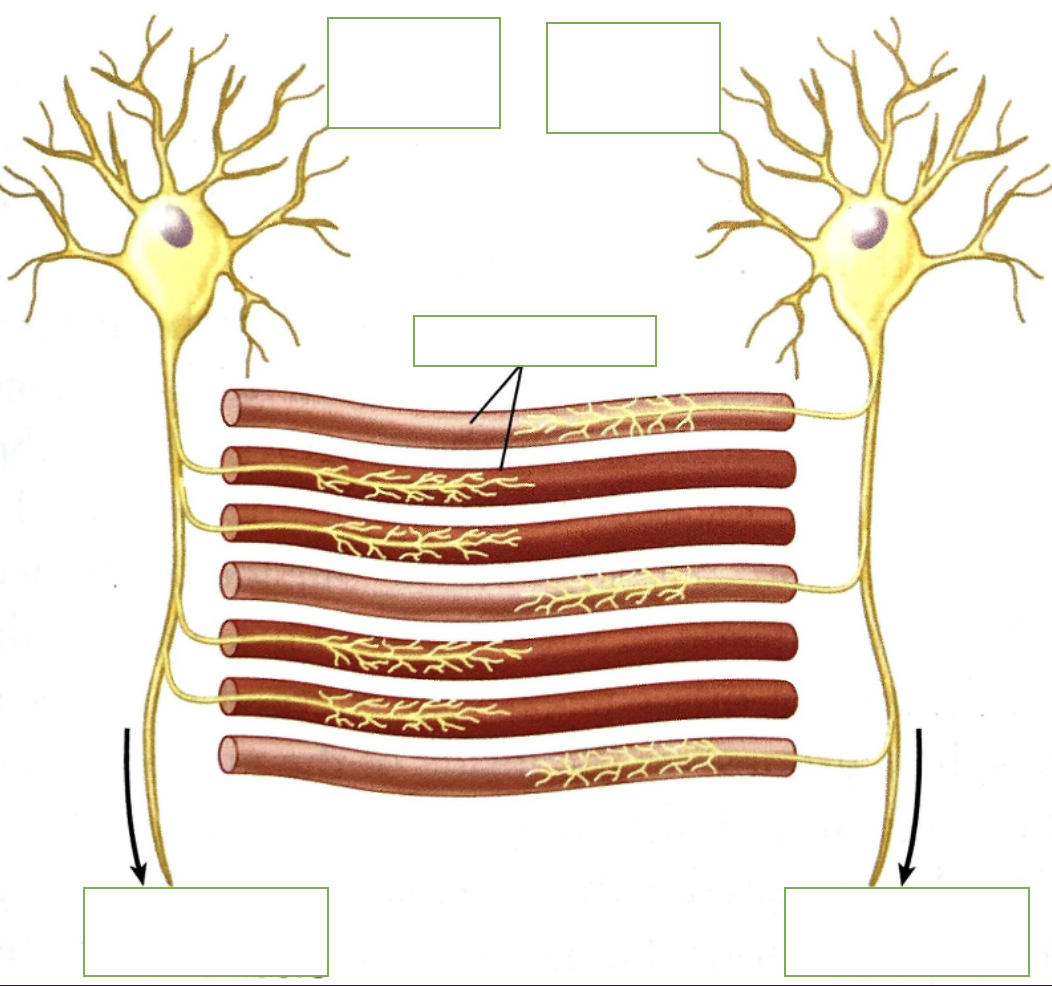
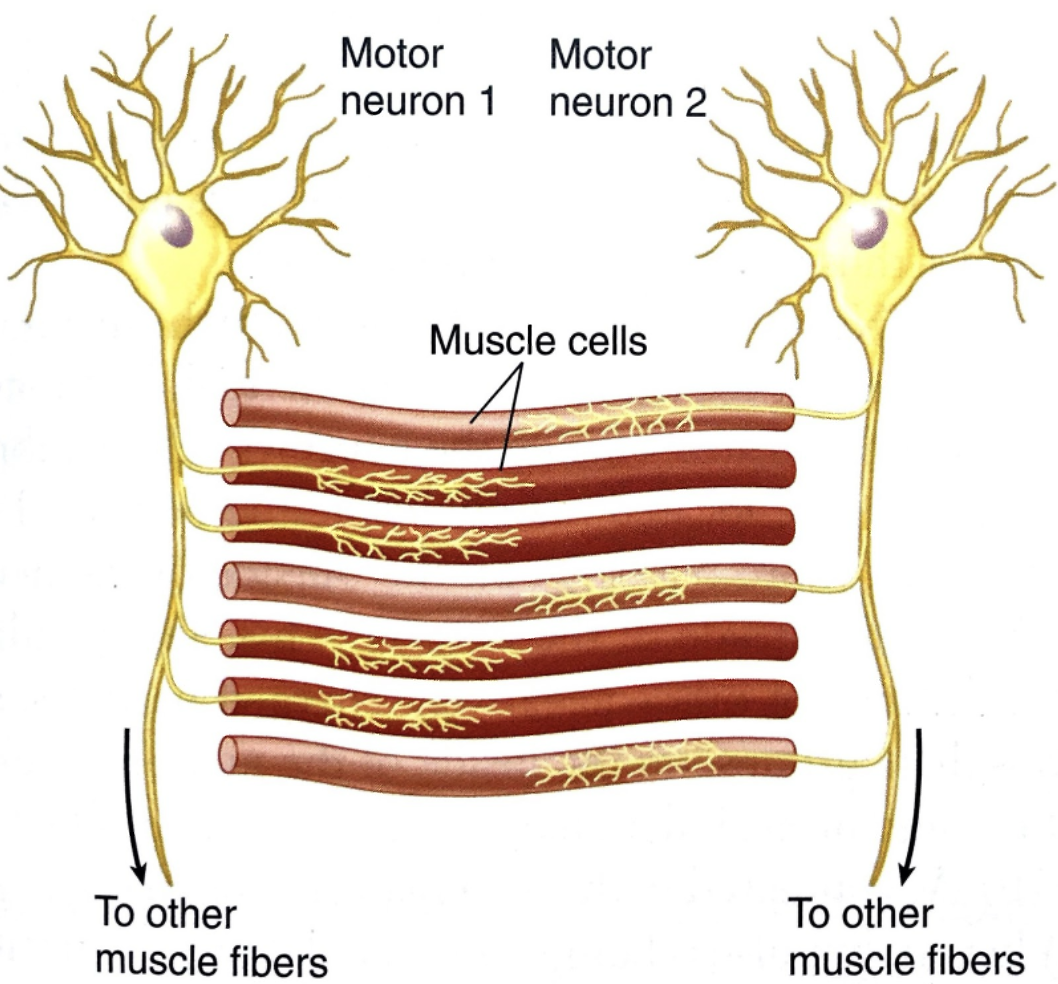
label: motor neuron (2), muscle cells, to other muscle fibers (2) and function
allows for uniform activation as well as graduations in force production
What does an electromyography do (EMG)?
detects the electrical activity or motor unit/muscle
easier than detecting the mechanical activity
T Tubules
spread electrical impulse from motor unit
sarcoplasmic reticulum
storage of Ca²+
what percent of calcium in the body is unbound from bones?
1%
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
the energy molecule that is produced from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi) and when broken down to ADP and Pi energy is released
energy needed to bound ADP and Pi obtained from (2)
aerobic metabolism and anaerobic metabolism
the 5 steps of muscle contraction
resting muscle
activated muscle
movement of the muscle
tightly bound
detachment
What happens during the first step of muscle contraction
active sites are covered, ADP and Pi are on the myosin head
What happens during the second step of muscle contraction
neural activities cause a release of Ca++ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ca++ bind to troponin, altering its shape and causing tropomyosin to shift, exposing the active sites. Myosin filaments can now attach to actin
What happens during the third step of muscle contraction
the release of Pi results in high affinity binding of x-bridge head with the actin binding site
What happens during the fourth step of muscle contraction
the release of ADP occurs during the power stroke
What happens during the last step of muscle contraction
ATP binds to myosin head causing detachment from actin active site. ATPase breaks down ATP to ADP+Pi which repositions myosin head at 90 degrees position like in the first step. step1-5 are then repeated to produce further shortening
the type of contraction depends on the ___ ___ relative to the force produced by the ___
external force, muscle
concentric
occur during dynamic tasks where the muscles shorten (like bringing your arm up while doing bicep curls)
Isometric
occur in static situations, no movement
eccentric
occurs during dynamic tasks, muscle lengthening (like when you’re moving your arm down during bicep curls)
lengthening velocity and force are high
eccentric
shortening velocity is high and force is low
concentric
force is 0 and neither at lengthening or shortening velocity
isometric
to exert a high force you need a ___ ___
high load
muscle fiber typing
biopsy to obtain muscle samples
sectioned cross-sectionally
pointed on glass slide
stained for various enzymes to discriminate among fiber types
Henneman’s “size principle”
most force is generated by ST fibers at low intensity exercise, but as force needs increase, FT fibers begin to be recruited (stronger neural signal). at maximal effort, all types of fibers are utilized, but even at maximal effort 100% of muscle fibers are not activated to prevent injury and muscles or tendons won’t tear
smaller and lower threshold motor units are recruited before larger and higher threshold units. the force required determines the number of active motor units