Joints of the Vertebral column and Ligaments
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Z joints are located where?
between adjacent vertebral arches
What type of joints are Z joints?
synovial joints surrounded by capsular ligaments with joint cavity
Hyaline cartilage
Covers articular surface in Z joints
Planes for Z joints
Cervical: transverse
Thoracic: coronal
Lumbar: sagittal
Cervical Plane
transverse for flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation
Thoracic plane
coronal for lateral flexion, rotation, limited flexion and extension
Lumbar Plane
sagittal for flexion and extension, limited rotation
Where are symphyses joints?
Between adjacent vertebral bodies
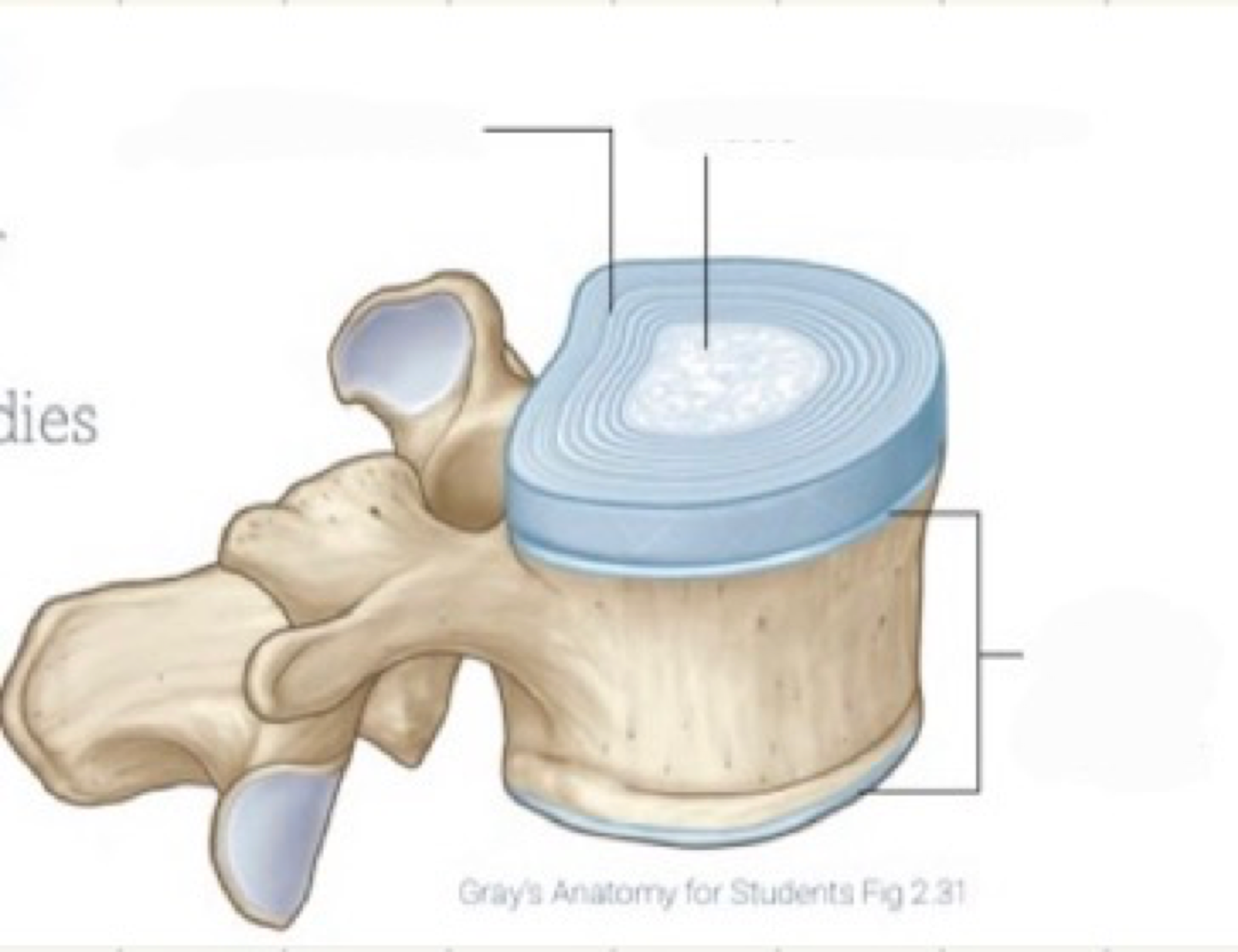
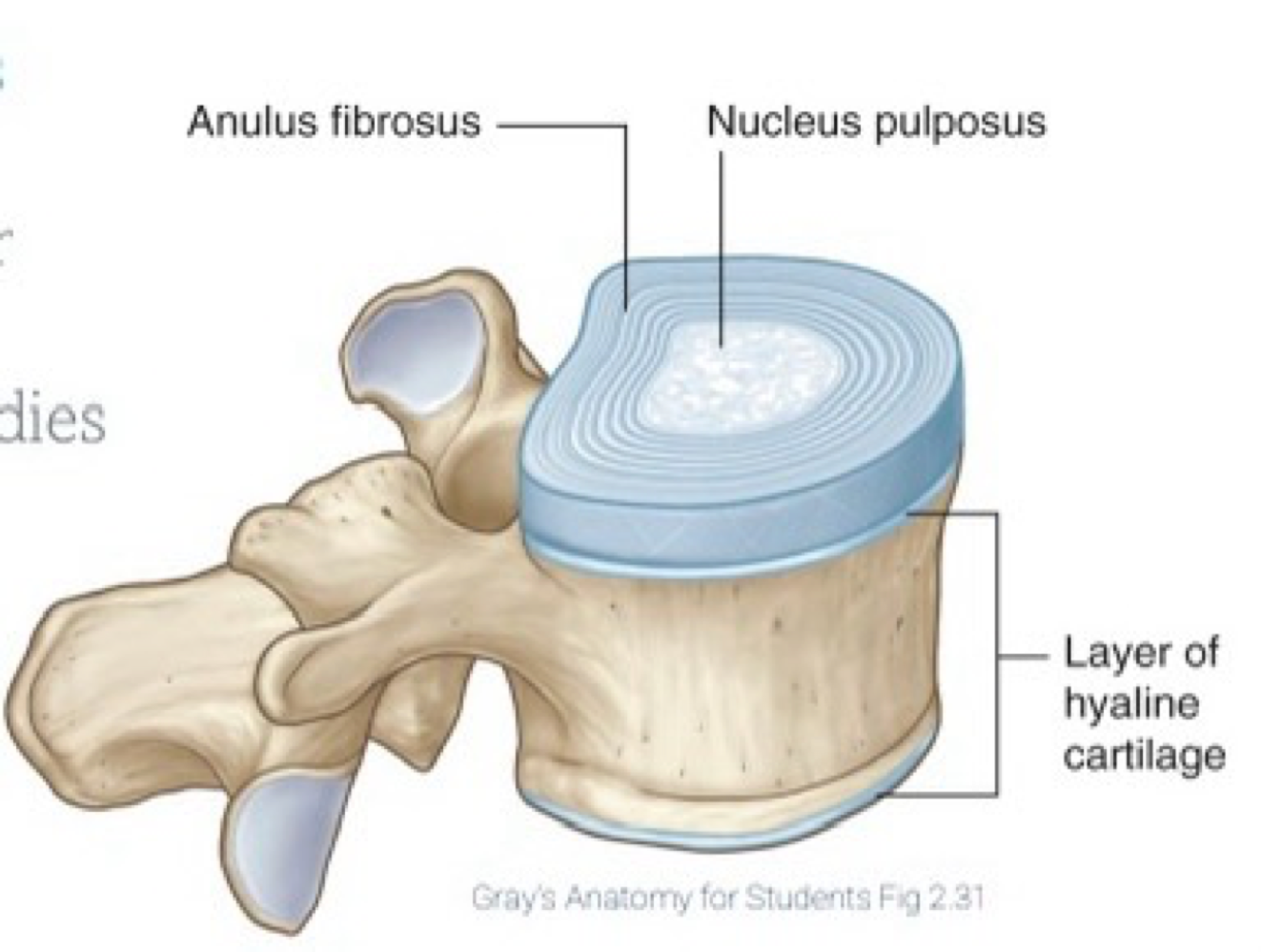
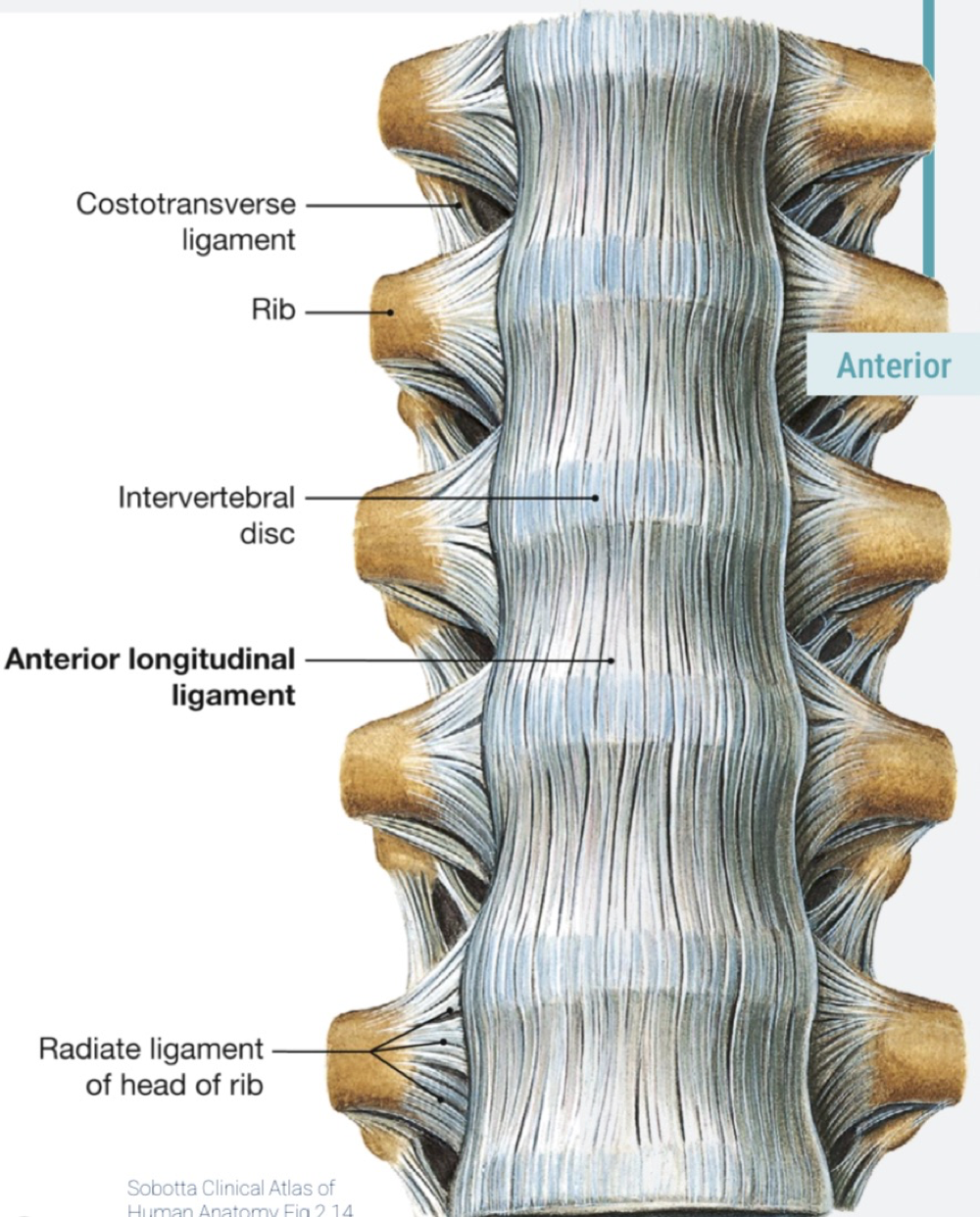
What do intervertebral discs do?
separate bodies of vertebrae from each other
Anulus fibrosus
outer portion consisted of concentric bundles of collagen fibers and fibrocartilage
Nucleus pulposus
inner portion, gelatinous with high water content
What part of the vertebral column does not have intervertebral discs?
between CV1 and CV2
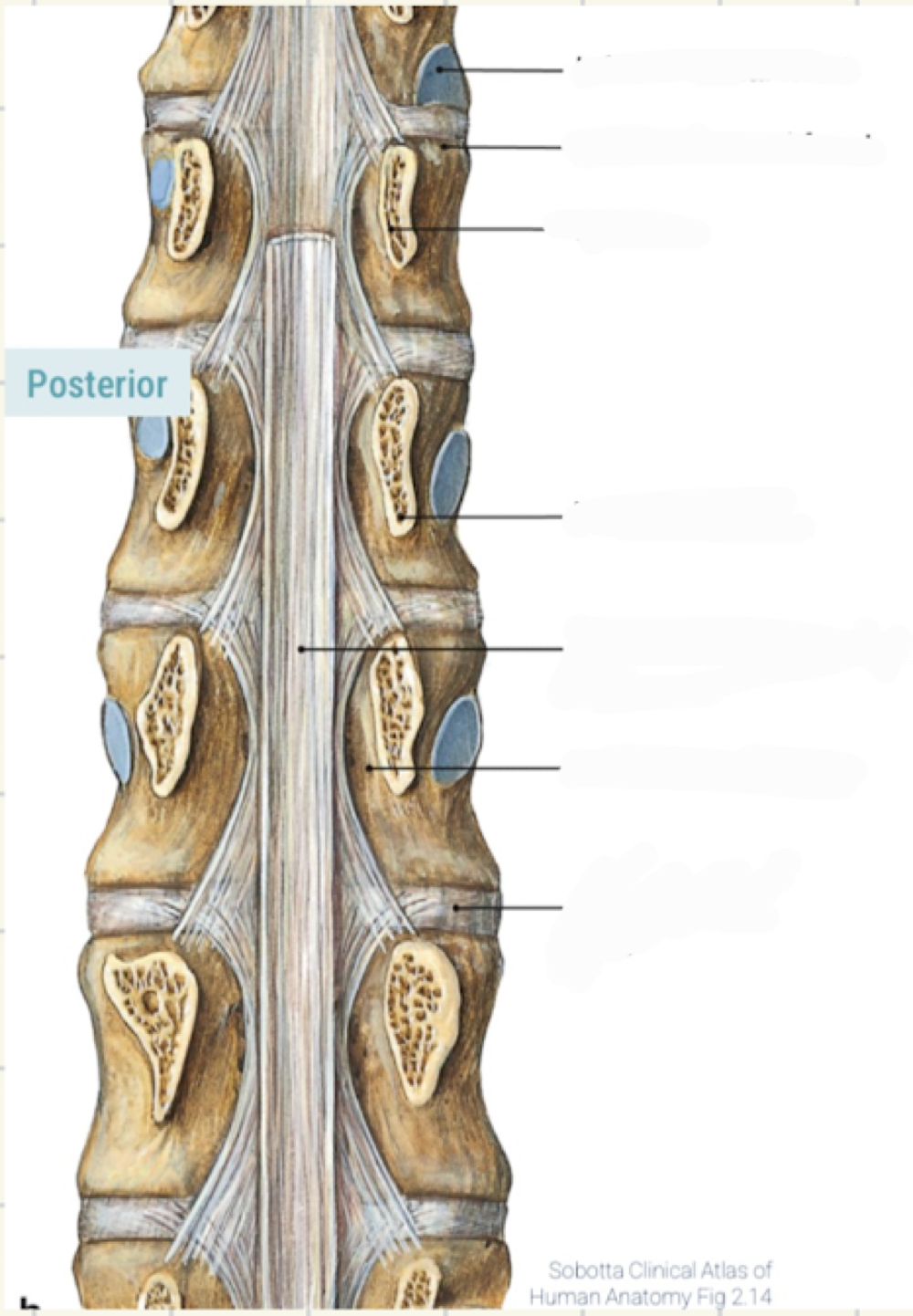
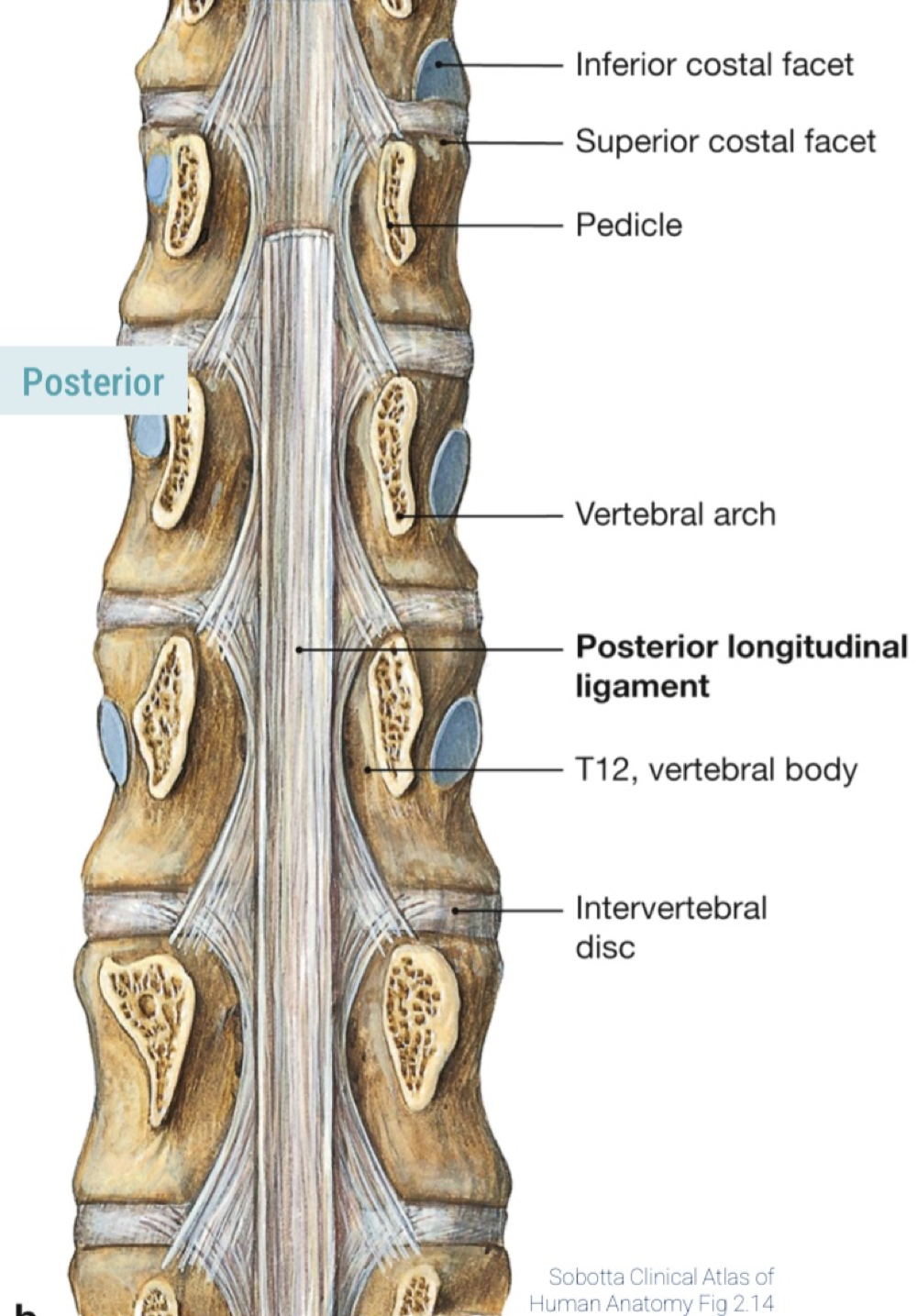
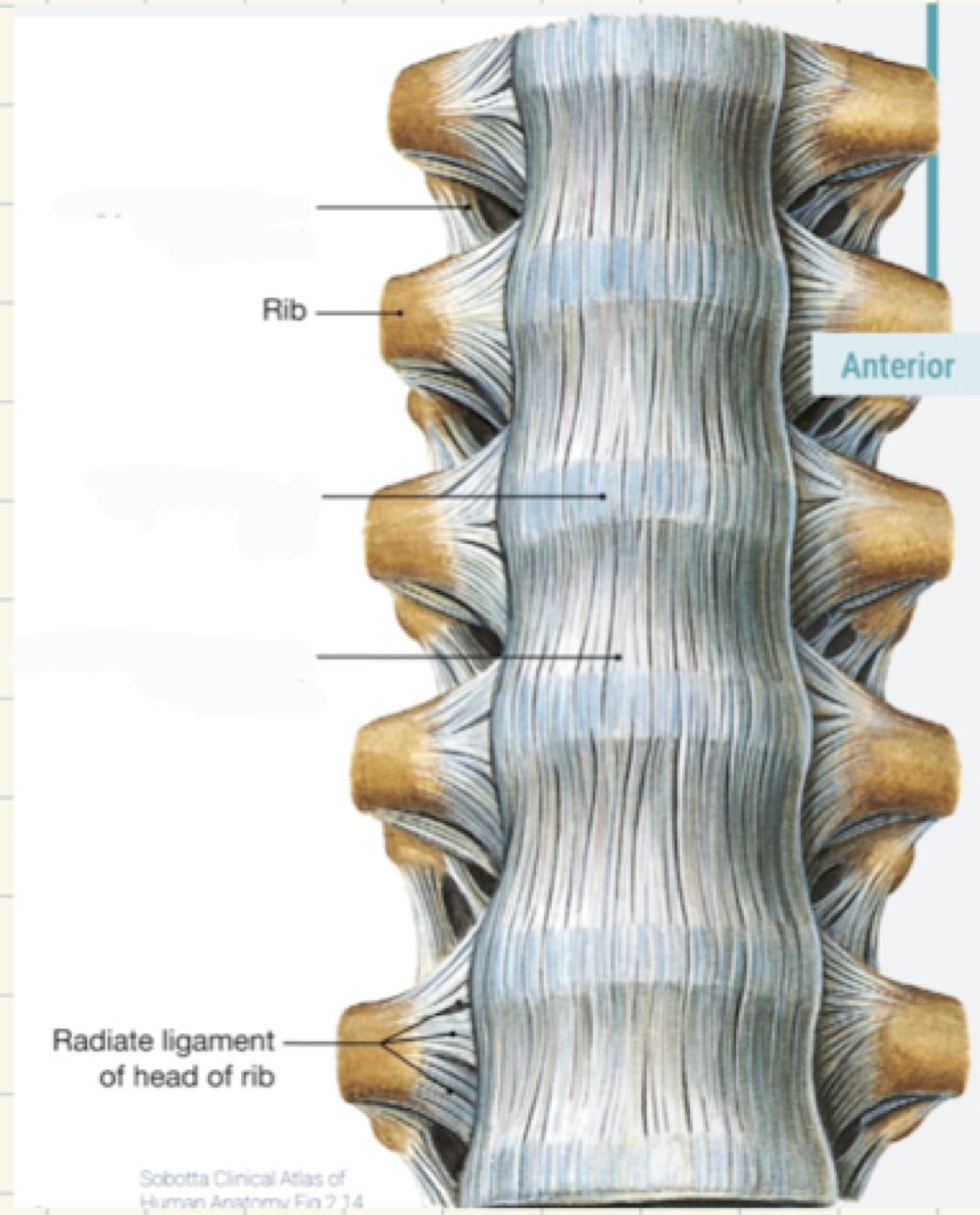
3 types of ligaments
Longitudinal ligaments, anterior longitudinal ligament (ALL), posterior longitudinal ligaments (PLL)
longitudinal ligaments
length of vertebral column to strengthen vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs
Anterior longitudinal ligaments location
anterior surface of vertebral bodies from occipital bone to sacrum
what does the anterior longitudinal ligament do?
limits excessive extension of vertebral column, reinforces annulus fibrosus anterioly
where is the posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL)
posterior side of vertebral bodies from axis CV2 to sacrum
PLL description
within vertebral canal, broadens over intervertebral discs, narrows over vertebral bodies, limits flexion, reinforces annulus fibrosus
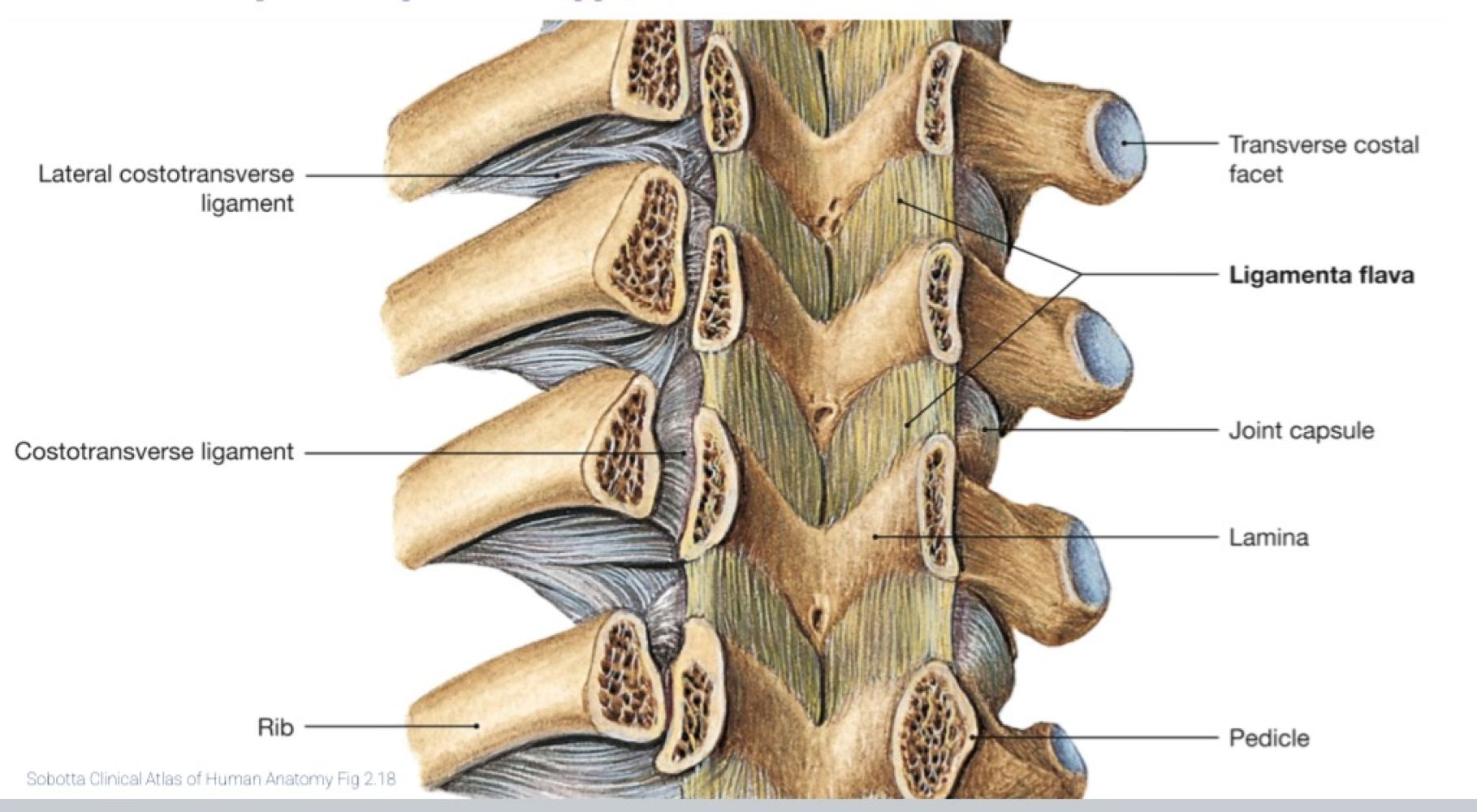
ligamentum flauvm
yellow, strong, bit elastic, attaches from lamina to lamina
What does the ligamentum flavum do?
limits flexion, provides postural support of vertebral column
Supraspinous ligament
strong fibrous cord, connects spinous processes from CV7 to sacrum, limits flexion
Capsular ligaments
surround synovial z joints
interspinous ligaments
connect adjacent spinous processes, limits flexion
intertransverse ligaments
connects adjacent transverse processes, limits contralateral flexion
Atlantooccipital joints (CV1 and occiput)
Between superior articular surface/facet of lateral mass of CV1and occipital condyles
What type of joints are atlantooccipital joints?
Synovial joints
Anterior and posterior atlantooccipital membranes
connect margins of foramen magnum of the skull and the anterior and posterior arches of CV1
Atlantoaxial joints (CV1 and CV2)
2 lateral and 1 median joints
2 lateral joints in atlantoaxial joints are where?
between inferior articular surface of lateral masses of CV1 and superior fact for CV2
where are median joints?
between CV2 dens and CV1 anterior arch
Rotation movement
skull and CV1 rotate on CV2 as unit
What type of joint is a pivot joint?
median joint
tectorial membrane
covers posterior surface of odontoid process, apical, alar, cruciate ligaments
cruciform ligament
cross shaped ligament that consists of transverse and vertical part
transverse part in cruciform ligament
transverse ligament of atlas holds CV2 dens against CV1 anterior arch
vertical part in cruciform ligament
posterior surface of body of axis to anterior margin of foramen magnum
apical ligament
connects apex of odontoid process to anterior margin of foramen magnum
alar ligaments
extend from side of dens to occipital condyles, check side to side head movements