Fungal Diversity
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology 1010
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
adaptation
adjustment of organisms to their environment over time
reproduction
biological process to produce offspring
homeostatsis
maintenance of stable internal conditions
cellular organization
living organisms are composed of cells
energy processing
conversion of energy for biological functions
response to stimuli
[reaction of organisms to environmental changes
molecular transport
movement of molecules across membranes
sexual reproduction
involves fusion of gametes from two parents.
asexual reproduction
offspring produced without gamete fusion
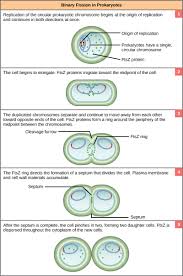
binary fission
asexual reproduction in bacteria; cell division.
genetic variation
differences in DNA among individuals
natural selection
survival of the fittest; evolutionary process
mutation
change in DNA sequence; source of variation
gene flow
transfer of genes between populations
genetic drift
random changes in allele frequencies
alteration of generations
life cycle involving both sexual and asexual phases
hermaphroditism
organism with both male and female reproductive systems
internal fertilization
sperm fertilizes egg inside the female
external fertilization
sperm fertilizes egg outside the female
positive feedback
amplifies physiological responses for specific outcomes
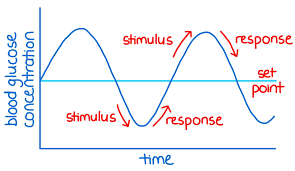
negative feedback
stabilizes physiological systems around a set point
ovulation
release of an egg from the ovary
fertilization
fusion of sperm and egg to form zygote
oviparous
eggs laid outside; young hatch later.
ovoviviparous
eggs hatch inside female; live birth
viviparous
young develop inside the mother; live birth
hormones
signaling molecules regulation physiological processes
testosterone
male hormone produced by leydig cells
estrogen
female hormone regulating reproductive functions
progresterone
hormone involved in menstrual cycle and pregnancy
LH
luteinizing hormone; triggers ovulation
FSH
follicle-stimulating hormone; stimulates egg production
GnRH
gonadotropin-releasing hormone; regulates reproductive hormones
corpus luteum
remnant of follicle; secretes hormones post-ovulation
endometrium
uterine lining; thickens for potential implantation
blastocyst
early stage of embryo; implants in uterus
hCG
hormone maintaining corpus luteum during pregnancy
oxytocin
hormone involved in childbirth and lactation
sertoli cells
support and nourish developing sperm
leydig cells
produce testosterone in male reproductive system
protandry
males change to females in some species
protogyny
females change to males in some species
parthenogenesis
development of egg without fertilization
fragmentation
regeneration from broken parts of an organism
budding
new individual grows from parent organism
fission
division of an organism into two or more parts
temperature-dependent sex determination
sex determined by incubation temperature of eggs
zygote
fertilized egg; first cell of a new organism
gametes
reproductive cells; sperm and eggs
heterosporous
plants producing male and female spores
angiosperms
flowering plants; reproduce via seeds
gymnosperms
non-flowering seed plants; include conifers