Sci Circuits
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Stored energy due to the position or arrangement of electric charges relative to each other. The amount of work you need to separate the charges.
An imbalance of unbalanced charge within or on the surface of a material.
Energy stored in an object due to its position or condition.
A complete path through which electric current flows. Must be closed
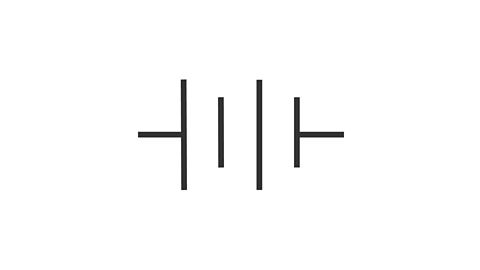
A device that creates a potential difference by separating electrons from their atoms using a chemical reaction. They move electrons to one side and positive ions on the other.
Longer line = positive end, short line = negative end
The number of Es dlowing through a circuit at a particular point per second.
Use Amperes (Amps) bc 1 Amp is 6.25 quintillion Es
The potential difference between two points in a circuit.
Depends on difference between postive and negative ends or circuit made by the battery.
Friction blocking electrons from flowing through.
Short Circuit
Circuit that has only powersupply + conductor.
Need resistance bc electrons gain energy each time they cross battery + no place to lose energy (no resistors)
Irl, loads have nonzero resistance
Load
Take all excess energy from Es + slow them down.
Can be lightbuls, alarms, carmeras (anything that requires electrical energy to work)
Ammeters
A tool used to measure current in an electrical circuit.
Called placing the ammeter ‘in series’ to the light bulb.
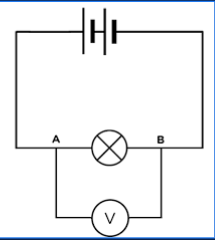
Voletemeter
Measure Voltage.
Need connection to 2 separate areas of circuit.
Called the volteemeter is positioned ‘in parallel’ to the lightbulb.
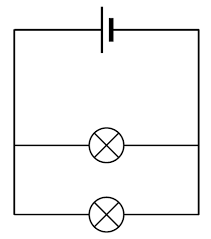
In a circuit in parallel
What happens to brightness of globes when 3rd globe is added? Y?
Brightness of globes stayed the same.
Bc all loads still receive the same amount of energy regardless of no. of bulbs (upto a certain amount)
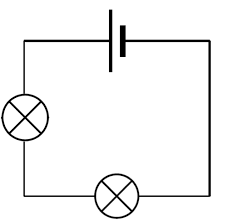
In a circuit in series
What happens to brightness of globes when 3rd globe is added? Y?
Brightness of globes all decrease.
Bc electrons have to evenly distribute same amount of energy w more loads
Conductor
A material that allows electrons to flow through it. Tpyically copper + aluminium
Delocalised Electrons
Electrons that are not associated with a single atom or ion, these electrons are free to move throughout.
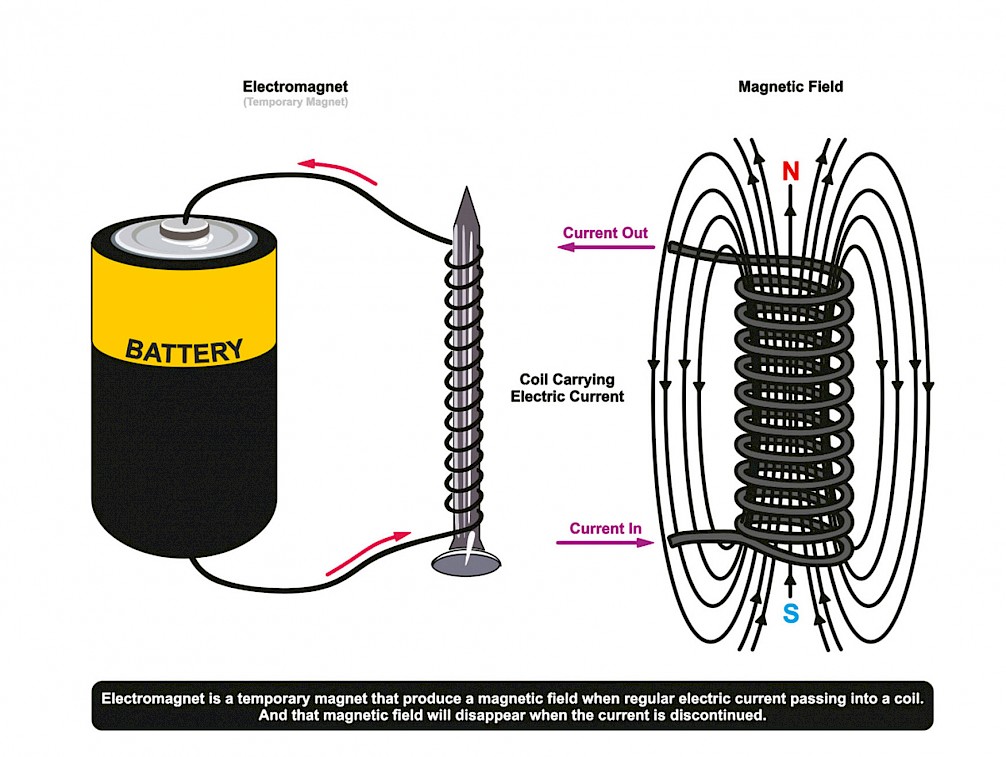
Electromagnet
A magnet where the magnetic field is produced by an electrical current.
insulator
A material that does allow electric current to move freely.