#4 - Chapter 2: What are the parts of the nervous system?
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
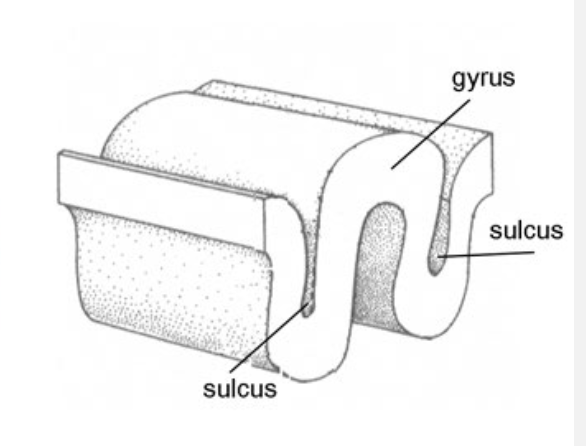
sulcus
a groove in the cerebral cortex
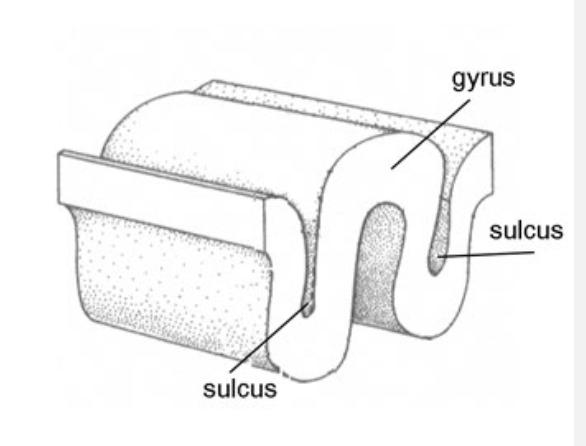
gyrus
matter between 2 grooves/wrinkles
gray matter
contains cell bodies and dendrites, which lack myelin
white matter
consists of axons white myelin sheath
axon tracts
when lots of myelinated axons travel together, they appear white
what is a tract
when multiple axons form together
which regions communicate with one another on the axon tracts?
cortical and subcortical
corpus collosum
axon tract that joins the two hemispheres
what are the lobes of the cerebral cortex?
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, occipital lobe
how are the cortical regions divided?
sensory, associative, motor processing areas
what are the three parts of the sensory?
primary sensory cortex, visual cortex, and auditory cortex
what is sensory?
involved in processing sensory input; receive strong input from sensory organs
what is motor?
involved in driving movements or generating motor responses; makes strong connections to the spinal chord
what is the motor related to?
primary motor cortex
what is associative?
involved in cognitive operations that are intermediate between sensing stimuli and acting upon them
what are the parts of associative?
parietal lobe, temporal lobe, prefrontal cortex
primary motor cortex
in front of the central sulcus
primary sensory cortex
is behind the central sulcus
what is the cerebral cortex made up of?
different sub-regions that have different but similar structure
what is another name for different sub-regions that have different but similar structure?
cytoarchitecture
how are cortical regions defined by?
what they are connected by and their sub-regional cellular architecture
how many layers does cortical regions have?
pyramidal cells
pyramidal cells
cell bodies of pyramidal neurons reside
what are the major output layers?
#5 & #6
which layer does the apical and basal dendrites receive from?
layer 4
what type of dendrites receive information from layer 4?
apical (top) and basal (bottom)
pyramidal neurons
projection cells - project information to other cortical and subcortical areas
thalamus
major relay station for sensory information into cerebral cortex
hypothalamus and the pituitary gland
neurohormone center, biological rhythms, hunger/thirst, body temperature, sexual drive
caudate
habit formation
substantia nigra
consists of cell bodies that produce a neurotransmitter dopamine involved in movement continuation
cingulate gyrus
attention
amygdala
fear processing, appetitive behavior, emotion “center”
stria terminalis
sex and threat responses; integration of hormonal signals'; basal part of the stria terminalis is involved in appetitive behavior and emotion regulation
what is in the brainstem parts?
midbrain, pons medulla
where are the axons from the brainstem going through?
coming and going between spinal cord and brain
what does the brainstem control?
head, eyes, gaze
what type of functions do the brain stem control?
autonomic/automatic functions
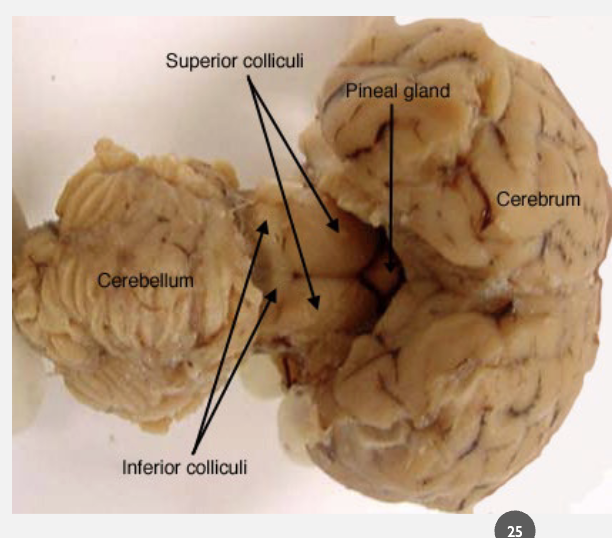
super colliculus
visual information processing specifically gaze information
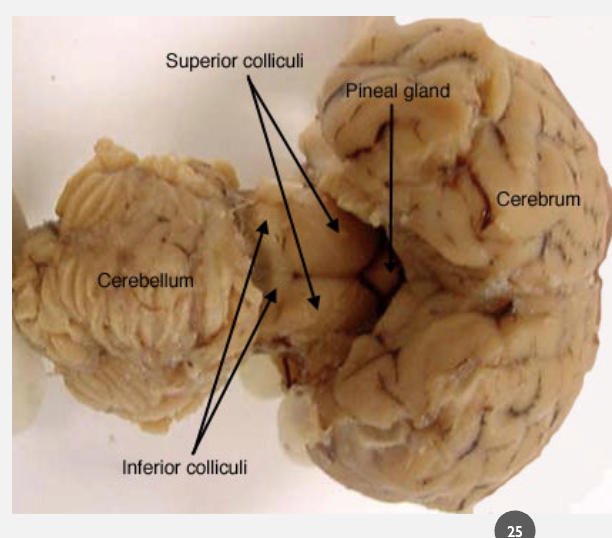
inferior colliculus
auditory information processing
where is the pons located?
attached to the cerebellum
what does the pons do?
contains motor control and sensory nuclei, gives rise to cranial nerves
what does the medulla contain?
cranial nerve nuclei and marks transition from brain to spinal chord
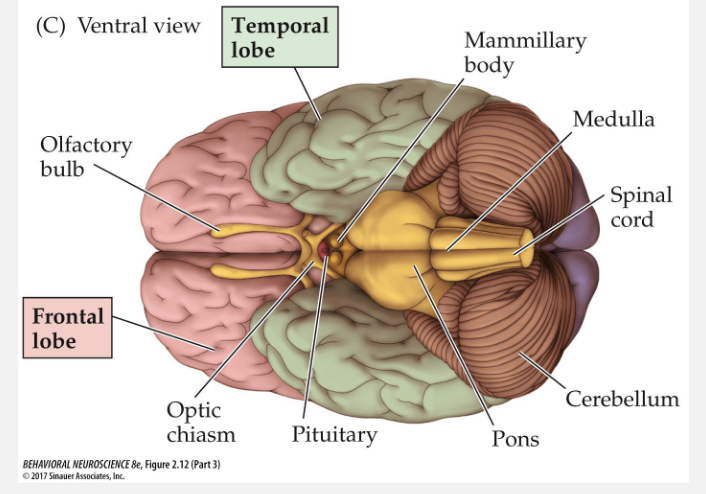
what is the function of the medulla?
breathing and heart rate regulation
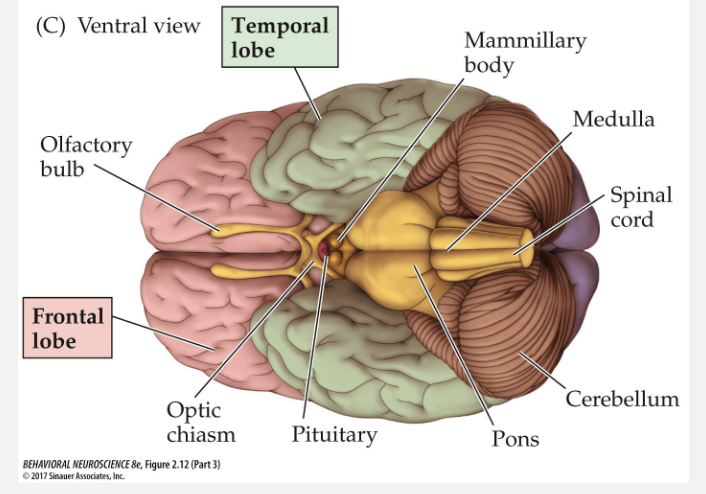
what are the cranial nerves?
bundle of axons
what do the cranial nerves control?
within a nerve, different axons control sensory and motor processing
the cerebellum controls
fine motor control, gait, balance, and muscle coordination