B2.3 Cell specialisation
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is fertilization?
When a sperm and an egg fuse to form a zygote. This occurs in sexually reproducing organisms that produce gametes
What are stem cells?
undifferentiated cell that can divide to create more stem cells, or differentiate to become a specialized cell type
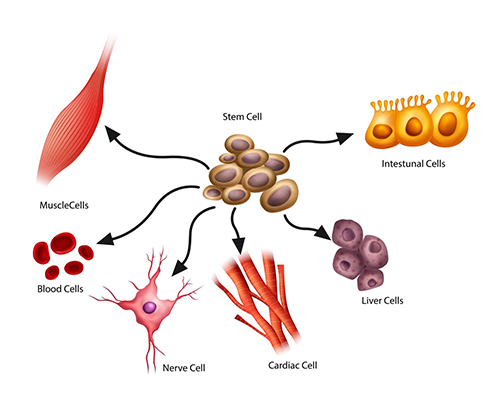
Give an example of stem cells.
A zygote and embryo
Why does cell specialization occur?
It helps cells to perform functions with increased efficiency and they can develop into specific shapes to carry out specific processes
What is differentiation?
It is the development of specialized structures, which mainly happens during embryonic development. They take on individual characteristics. Once a cell has become differentiated, it only expresses the genes that produce the protein characteristics for that cell
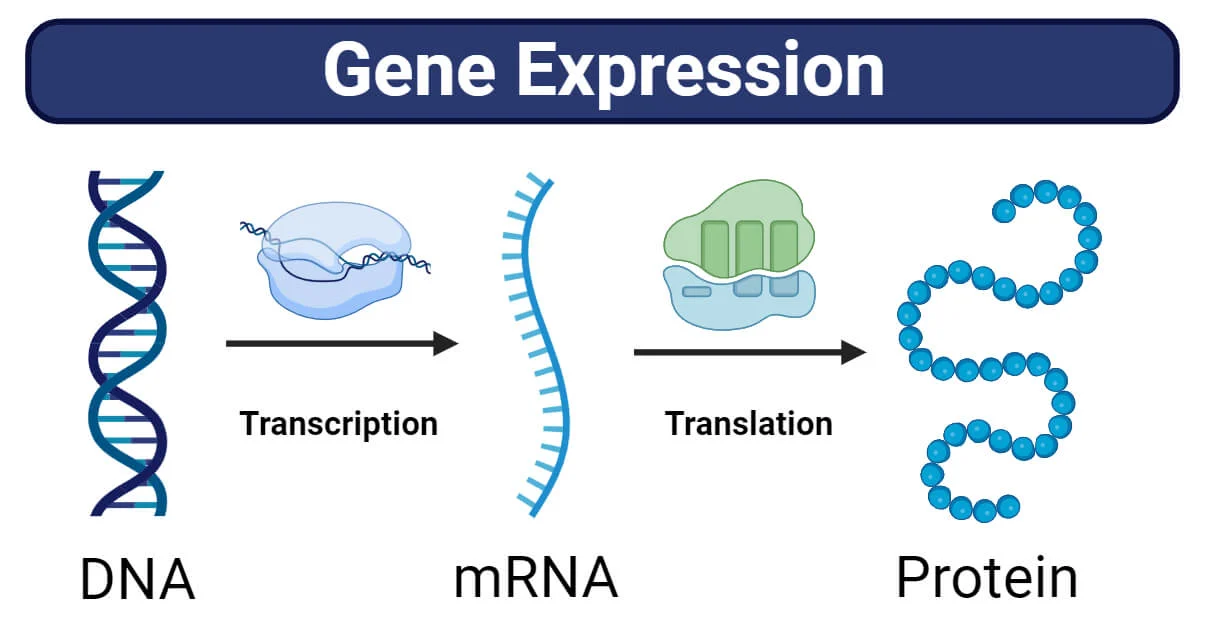
What is gene expression?
the process where information encoded in a gene is turned into a function, such as a protein. First, the process of DNA transcription into RNA occurs. The RNA travels out of the nucleus and to the ribosomes, where translation occurs, and an amino acid chain forms. This then folds into a protein
Gene expression determines cell specialization
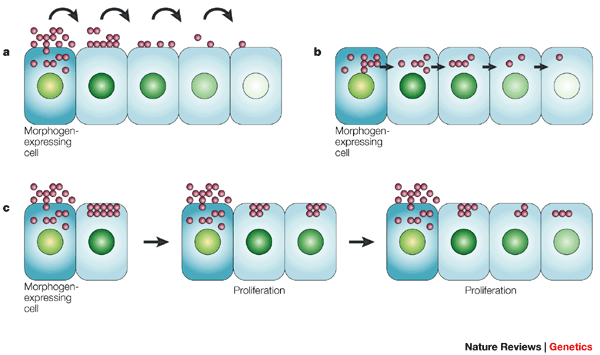
How does the position of a cell within an embryo determine how it differentiates?
Some cells secrete morphogens, which are signaling chemicals that impact gene expression and differentiation of a cell, and depending on how far away surrounding cells are from the morphogens, they differentiate into a certain type. This means that the concentration gradient of morphogens has an impact on cell specialization
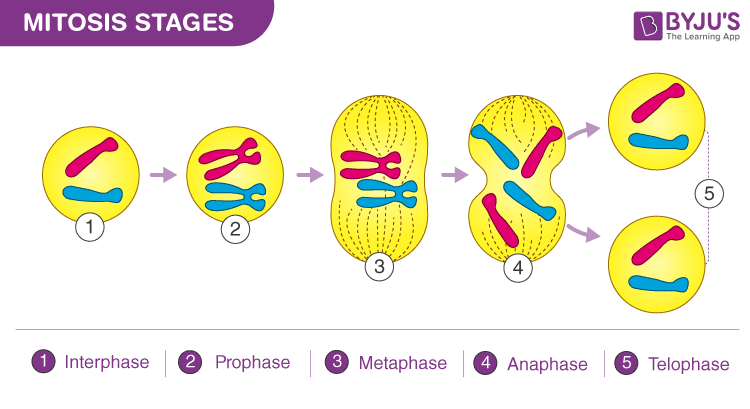
How do stem cells divide?
By mitosis
What are adult stem cells?
They are undifferentiated cells that are found in many tissues in the body, in places called stem cell niches.
What are stem cell niches for?
They are locations within the tissues where stem cells can differentiate when they are needed, for example in the case of an injury
Give an example of a cell niche?
Bone Marrow stem cell niche:
Blood cells differentiate from adult stem cells, which are found in the bone marrow, where protection is provided
What are the categorizations for cells on how much potential for differentiation they have?
Totipotent → total potential
Pluripotent → many potentials
Multipotent → multiple potentials
Unipotent → fully differentiated, but can self-renew
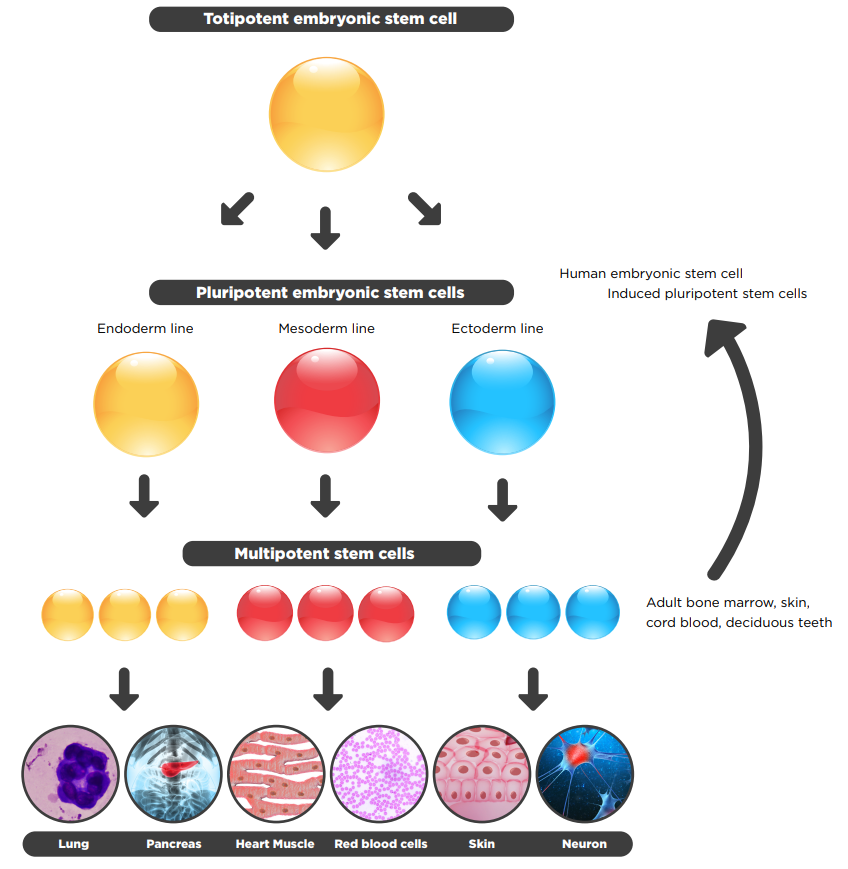
Give examples of these categories in animals
Totipotent → zygote
Pluripotent → embryo
Multipotent → adult stem cells
Unipotent → muscle fibre cell
Example: How is the human sperm cell specialized?
The function of the human sperm cell is to fertilize the egg during sexual reproduction.
The flagellum (tail) helps the sperm cell to swim
The acrosome releases digestive enzymes which help it to bury through the egg layers
It is long and narrow
It has lots of mitochondria for energy
Example: How is the Human egg cell specialized?
It’s function is to store materials needed for the development of the embryo → it’s nucleus merges with that of the sperm during sexual reproduction
It stores nutritional materials, and is large so that it can carry reserves and nourish the embryo during development
Example: How is the red blood cell specialized?
It’s function is to transport oxygen in the blood
It has haemoglobin which carries oxygen
It has a biconcave shape to maximize surface area
It is small and flexible so that it can fit through narrow capillary vessles
It doesn’t have a nucleus in order to maximize volume uptake of oxygen
Example: How is a motor neuron cell specialized?
It’s function is to carry information from the central nervous system to muscles and glands to evoke a response
They have long axons for a quick transmission of electrical impulses
The large body has many organelles which allow for the synthesis of proteins needed to transmit electrical impulses
Coated by myelin which acts as an insulator
Example: How are Muscle cell fibers specialized?
Their function is to generate force or contract in order to cause movement
They have long, narrow cells, which allows for a greater length of contraction
What is more efficient in regards to volume and surface area in cells?
The greater the ratio between surface area and volume, so the larger the surface area is in regards to the volume, the more efficient the cell
This is because the diffusion pathways are shorter
More nutrients can diffuse through the membrane and more waste products can leave