SPONGES
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What Phylum are Sponges in?
Porifera “pore-bearing”
What are Homoscleromorpha?
Skeleton absent or of siliceous spicules without an axial filament
What are Calcarea?
Calcium carbonate spicules
What are Demospongiae?
Spicules not with 6 rays, spongin network often present
What are Hexactinellida?
Spicules with 6 rays, syncytial trabecular reticulum
Characteristics of Sponges
Sessile, benthic, suspension feeders
Primarily consume bacteria inside specialized cells
No true tissues (independent but work together)
Cells are not connected
Cells are totipotent (can change form and function)
Intracellular digestion
No nerves or muscles
Skeleton is made of spongin and spicules
What is spongin?
Tough flexible protein fibers
What is spicules?
Hard calcium carbonate (corals) or silicon dioxide (quartz/glass)
What are the parts of a sponge called?
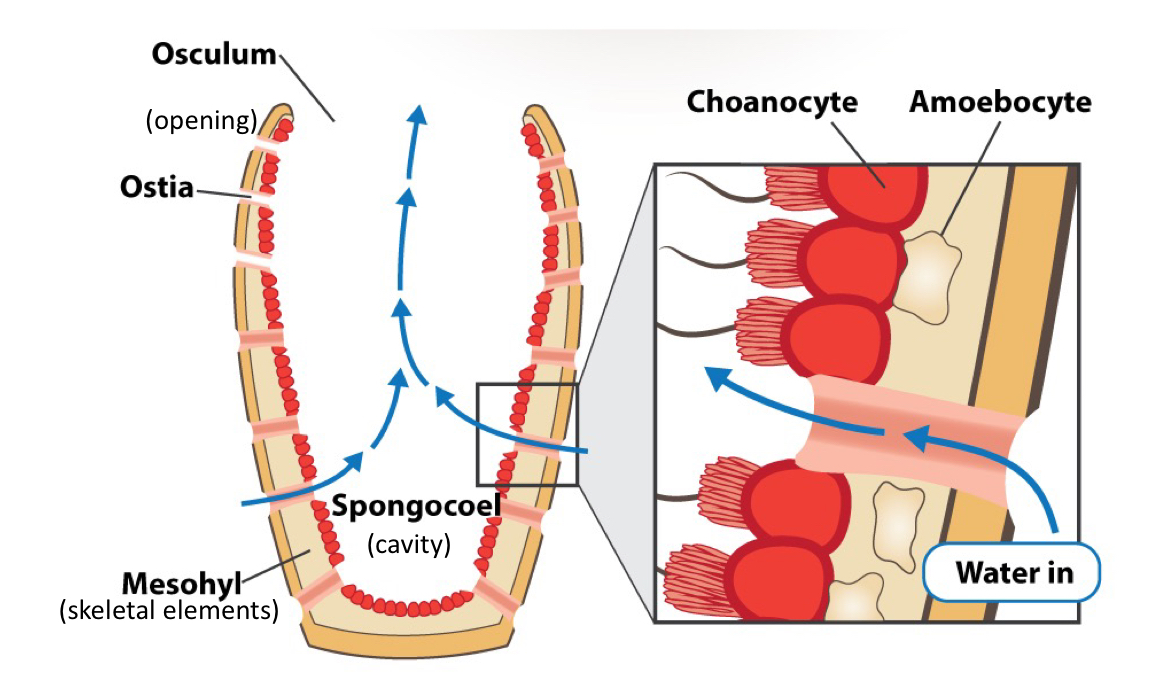
What is the function of choanocytes?
“Collar cell”
Responsible for food uptake
Flagellum draws water into the collar to trap food in mucus
Capture sperm for fertilization
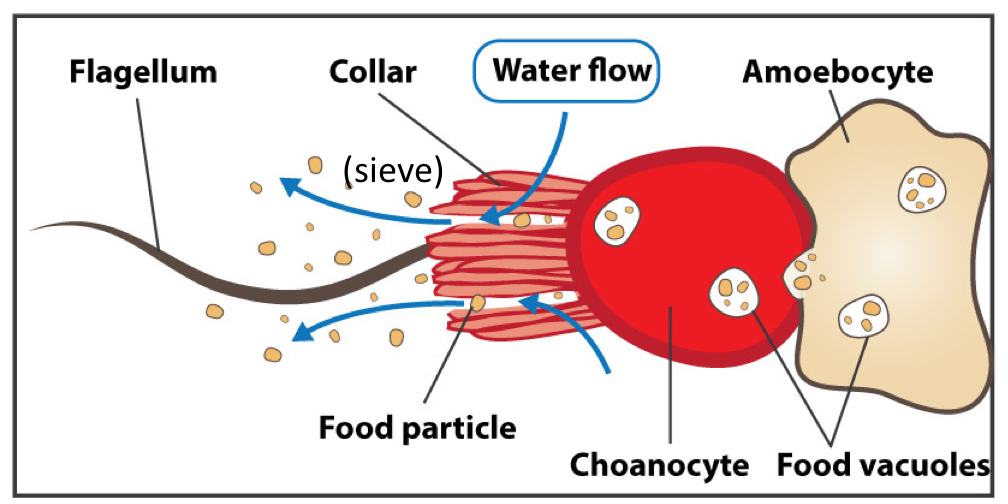
What is the function of amoebocytes?
Motile cell—can transfer food
Totipotent
Involved in feeding, reproduction, and clearing debris
What are the two ways food can enter cells?
Phagocytosis (particles) or pinocytosis (dissolved organic materials)
What are porocytes?
Pore cells
Line the pores (ostia) and channel to spongocoel
What are pinacocytes?
Tablet cells
Form outer epithelium
What is the mesohyl?
Middle layer of sponge
Acellular matrix (gelatinous, nonliving, acellular)
Contains amoebocytes, spicules, and spongin
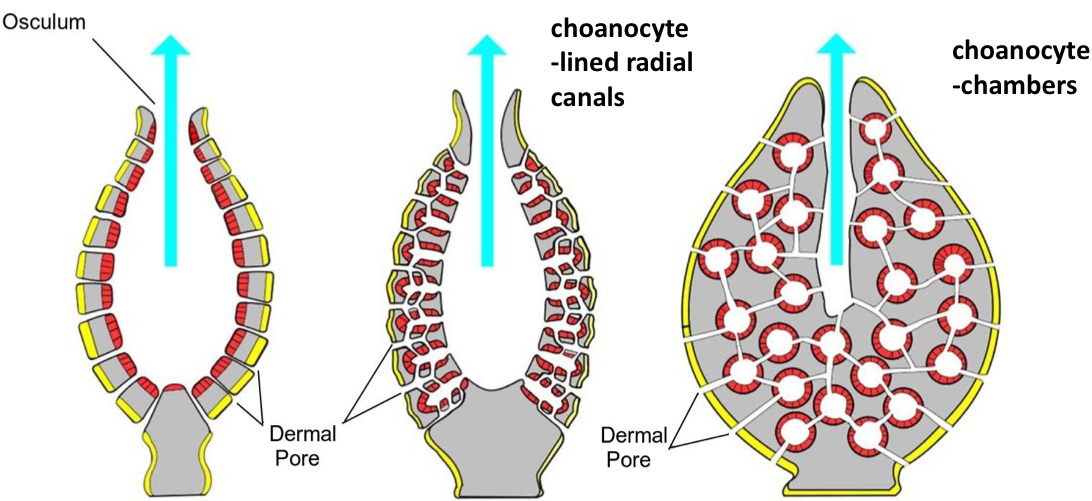
What are the different body plans of sponges?
Asconoid
Syconoid
Leuconoid
Ecological roles of sponges
Refuge inside sponge (grow much faster than coral)
Many cyanobacteria inside sponge (food)
Filter vast quantities of seawater (maintain water clarity and quality)
Potential use as drugs
Calcareous and siliceous sponges
Bioeroders
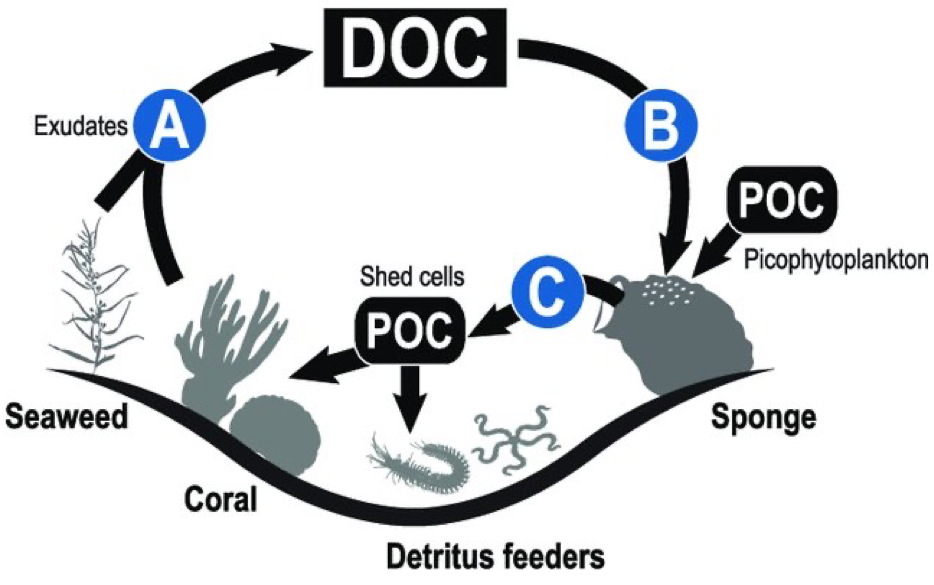
What is the difference between DOC and POC?
DOC is 0.45 µm and below
POC is anything above 0.45 µm
What is the sponge loop?
Alternative pathway for transferring DOM to higher trophic levels on coral reefs
Plays a major role in organic matter cycling
What are characteristics of sponge-dominated reefs?
Lower structural complexity
How has the top-down control on sponges in Caribbean reefs changed over time?
Before: more predators —> sponges in refuge habitat
Now: less predators —> more sponges with palatable sponges dominating, sponges are growing larger
What is an effect of overfishing on sponges?
Less sponge-eating fish —> sponges overgrow reef-building corals
What are secondary metabolites?
Responsible for chemical defenses
Important for human health (diabetes, cancer, HIV, antibacterial)
What are palatable species?
Faster rates of growth or reproduction (invest more energy to growth than defense)
What are defended species?
Make metabolically expensive chemical defenses (secondary metabolites)
What is the relationship between palatability and healing rate?
Positive correlation
How would a sponge reef function?
Greater abundance of spongivorous fish
Greater flux between benthos and water column and higher bacterial abundance
Habitat complexity is reduced, primary production increases, bioerosion increase, decrease in accretion
How sponge convert DOC into POC?
DOC uptake by sponge cells
DOC is metabolized into microbial biomass or used as an energy source and converted into bacterial cells (living biomass)
Sponges shed dead cells, mucus, and symbiotic microbes (POC)
How does higher microbial biomass affect morphology?
Smaller choanocytes
Increased ability to process more DOC
Bacterial symbionts are larger and more abundant
How do sponges reproduce?
Asexually —> budding (newly grown piece)and fragmentation (pieces break off and form a new sponge)
Sexually —> release of sperm and eggs for larval development
How do sponges regenerate lost body parts?
Mitotic cell division (asexual)
What is totipotency?
Cells can become any other cells
Can self-assemble into a sponge
What are colonial organisms?
A separated sponge will re-associate to form another sponge
What are survival pods?
Gemmules (specialized buds)
Contain food, amoebocytes, and a protective covering of spicules
Released when a sponge dies
Resist desiccation
Become adult sponge when conditions become favorable