UNIT 3 AOS1 - Revolutions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Social & Economic conditions of Imperial Russia
middle class
represented 1.5% of population
had a good living standard
more opportunities for social advancement
where the reformist & revolutionary groups emerged
working class
4% of population
concentrated in major cities
could influence authority
bad working conditions - long hours, no pay, dangerous working conditions
no trade unions cause they were illegal - couldn’t bargain for better conditions
peasants
82% of population
commercial farms owned by nobility - produced grain (wheat & rye), decided by mir (village command council)
basic farming techniques - harvested using sickle and people pulled ploughs (no livestock)
land distributed according to family size
serfdom
the state of being owned
‘serfs’ worked for landowners who could buy and sell them
similar to slavery
empire
group of states/countries ruled over by a single monarch, oligarchy or sovereign state
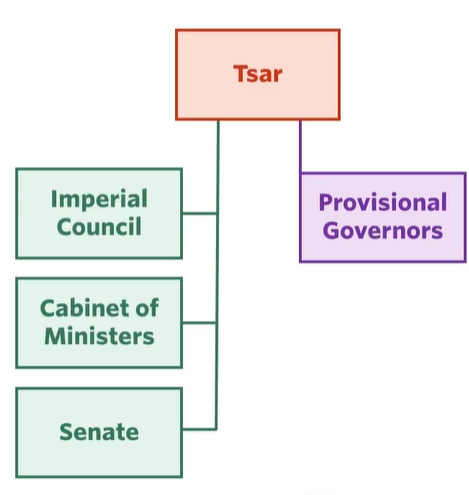
Government is Russia
Romanov Dynasty reigned in Russia from 1613 - 1917
Imperial council: personal advisors
Cabinet of ministers: managing individual portfolios
Senate: Transforms the will of the tsar into law
Provisional governors: in charge of the 96 provinces
given some autonomy over regions
inconsistencies in education, health, police because of distribution in resources throughout the empire
answered to Nicholas directly
a connection between the Tsar and his people
key gov policies allowed to be implemented and interpreted by each governor
Bureaucracy
System of gov where most important decisions are made by state officials
Role of Russian Orthodox church
promoted tsarism
held traditional views that were aligned to Nicholas II’s traditionalist autocracy
Tsar could elect individual of the highest position in the church - maintained connection & influence
tsar was unable to make judgements based on faith - connection to church upheld pillars of his reign
Orthodox
following traditionally accepted beliefs
Role of Okhrana
unlawfulness was NOT tolerated - classes as terrorism
okhrana was the Tsar’s secret police
they monitored counter revolutionaries, censorship, imprisoning, executing/exiling potential criminals
separate to the police force - used to maintain public order
60 stations internally & externally by 1911
symbolizes suppressive nature of Romanov autocracy
patrimonial
inherited or inheritable by established rules (legal) of descent
reactionary
opposing social progress & reform
zemstous
local self-government
russification
assimilating non-Russian ethnic minorities into Russian culture, language & identity through state-led programs
difference between communism and socialism
communism: most property & economic resources are owned and controlled by the state
socialism: all citizens share equally in resources allocated by a democratically elected government
marxism
theories of Karl Marx & Fredrich Engels
formed the basis of communism
method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development
main philosophy uses historical materialism to understand class relations and social conflict
uses a dialectical perspective to view social transformation
historical materialism: theory that human history is the result of material conditions
dialectical: logical discussion of ideas and opinions
geographical weakness of Russia
size and diversity of Russia = difficult for unification and rule
spans 2 continents, 11 time zones & 5 vegetation zones
major cities (Moscow and St Petersburg) were in the European side of Russia
national policy & infrastructure controlled by central gov - only ones capable of funding and directing major projects
distance to travel made communication difficult
industrialization
pushed as a key gov policy from 1870’s onwards
people moved to major city to work in factories
Russian PM Sergei Witte headed industrialization campaign by securing financial and advisory support
imposed tariffs to support Russian industry
increased production & output of iron, steel, coal, cotton
facilitated poor living conditions in overcrowded facilities + influx of ppl moving to cities = overcrowding
proletariat
collective of working class people
bourgeoise
capitalist class who owns most of societies health & means of production
aka the middle class
imperialism
extending a power & influence through colonization, use of military force or other means
decree
an official order that has the force of law
censorship
suppression or removal of writing, artistic work that’s considered obscene, politically unacceptable or a threat to security
garrison
a group of troops stationed in a fortress or town to defend it
‘little father’
the tsar, seen as people who were marching
militant
favoring confrontational or violent methods in support of a political cause
soberign
a person or entity with supreme power such as a monarch or a self governing state