Philosophy final
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
p value or significance level
the probability of getting results at least as good as the results actually obtained (smaller values are more significant)
p value for a result to be significant
0.05 , if the result is smaller than 0.05 then it is significant
null hypothesis
the hypothesis that the test hypothesis is false
statistically significant result
some evidence in favour of being a genuine effect but not attributable to mere chance (less than 0.05)
replication
repeating a trial if a group gets a positive result in a trial
false positive
result can still be due to chance
what does knowing the false positive and false negative rate tell us
not enough information to tell us anything about a case that tests positive, u need to look at the base rate
conditional probability

standard statistical testing
tells u when a result gives some evidence in favour of a given hypothesis
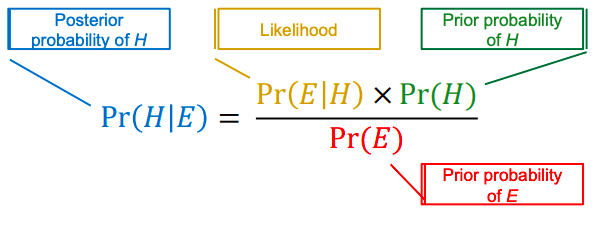
bayes theorem
follows from definition of conditional probability & used to compare the impact of evidence on two hypothesis
Pr(H|E)
posterior probability of H
Pr(H)
prior probability of H
Pr(E|H)
likelihood
Pr(E)
prior probability of the evidence
the climate change campaign
fossil fuel industry ran a campaign to discredit the growing body of evidence that anthropogenic greenhouse gases were having an effect on the planet
CRU email hack (“climategate”)
emails were stolen from University of East Anglia from researchers at Climate Research Unit and made public, comments were made that suggest climate researchers are engaged in fraud and deception
stochastic terrorism
mass mediated process where hostile violence occurs repeatedly (random acts)
tobacco strategy
forming apparently independent organizations to make it appear that the message sent was the result of independent research (eg. the council for tobacco research)
refined tobacco strategy
philip morris formed TASSC to fight concerns about global warming, nuclear waste disposal, biotechnology
The advancement of Sound science coalition
sought funding from Exxon to fight concerns about global warming, nuclear waste disposal, biotechnology. employed steven milloy as director
cultural cognition
people form beliefs about climate change, not on evidence but in line with their political orientation
Old denial
global warming is not happening, human generated greenhouse gasses are not causing global warming
new denial
the impacts of global warming are beneficial or harmless, climate solutions won’t work, climate science and climate movement are unreliable
model based attribution
computer simulations of the earths climate system
reproduce observed warming (anthropogenic greenhouse gases r included)
can be run again without anthropogenic greenhouse cases
ensemble
none of the models used by clmate scientists are perfectly accurate
IPCC
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changed
formed by UN in 1985
evaluate & report on the scientific literature and prepare summary reports on climate science
NOT a research organization
aimed at policy makers and other non specialists
IPCC statements
summaries of the scientific literature, shoe a pattern of getting increasingly stronger as the evidence for human induced climate change got stronger
claimed purpose of the tobacco industry
to find out whether smoking was dangerous and if so how to eliminate the danger from tobacco
actual practice of the tobacco industry
discrediting research on the dangers of tobacco
milankovitch cycles
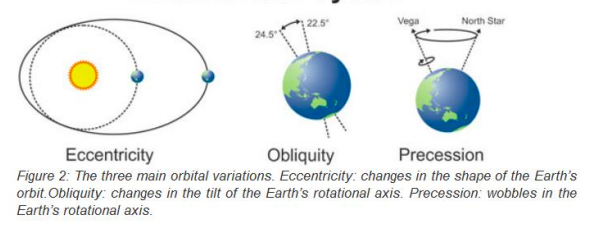
eccentricity = changes in shape of earths orbit
obliquity = changes in tilt of earths rotational axis
precession = wobbles in the earths rotational axis
detection vs attribution
knowing that the climate is changing (detection)
knowing what is causing the change (attribution)
attribution studies
studies aimed at understanding the causes of some observed phenomenon
evidence of anthropogenic climate change
nights warming faster than days
winters warming faster than summers
lower atmosphere warming; upper atmosphere cooling
greenhouse gases
carbon dioxide
methane (nonfossil and fossil)
nitrous oxide
nitrogen trifluoride
sulfur hexafluoride
bayesian approach to statistics
goal = give us what we want: an assessment of how likely we should take a hypothesis to be in light of all the evidence
subjective probability
how sure you are about somehting is indicated by the odds you’d accept for a bet on it.
degrees of belief in various hypothesis based on subjective assesment of how likely these are
bayesian approaches estimate these by numerical subjective probabilities
bayes theoreom diagram
H is hypothesis and E is evidence
test results
target is present: positive result = true positive, negative result = false negative
target is absent: positive result = false positive, negative result = true negative
we want low false positive rate and a low false negative rate
base rate & base rate fallacy
base rate = how frequent are positive cases
ignoring the base rate is called the base rate fallacy
reproducibility crisis
attention has been drawn to the fact that most studies that show a statistically significant effect are not reproducible
pre trial registration
online databases in which researchers can register trials before they are carried out
'p-hacking’
improper procedures (scientific misconduct)
change # of trials after collecting data
change hypothesis your testing
change what your counting as an indicator of an effect
change the pvalue for counting something statistically significant
cause for the greenhouse effect
what happens to the solar light
greenhouse effect
greenhouse gases trap some of Earth’s outgoing heat, keeping the planet warm, but too much trapping causes climate change
what happened to the global mean temperature
gone up as greenhouse gas concentrations have gone up
climate communication
a number of climate scientists engage in public outrech through books, interviews, talks, videos and social media
Merchants of doubt
number of issues:
nuclear winter
acid rain
ozone depletion and regulation of cfcs
philip morris
formed the advancement of sound science coalition to fight concerns like global warming, nuclear waste disposal, biotechnology
temperature anomaly
interested in how much the climate is changing
observed phenonmenon: increase of global temperature
Multiple models
intentionally created to have different simplifying assumptions and use different methods of modelling
differ in their estimates of past and future climates
global climate coalition
created in 1989 disbanded in 2002
funded by Amoco, american forest and paper association, texaco (many more)
1994-2001 spent more than $63 million
total lobbying by all environmental groups in the US: $4.7 million
global science team
created by exxonmobil (1998)
raises questions about who chart the future US course on global climate change
measurement of the publics perspective on climate science is taken before the plan is launched
victory achieved when:
citizens & media understand uncertainities in climate science
media coverage reflects balance on climate science of the validity of viewpoints that challenge the current conventional wisdom
technique of the media campaign
online harassment of climate scientists
balance as bias
press’s adherence to balance leads to biased coverage of both anthropogenic contributions to global warming and resultant action
climate of fear editorial
climate science is sound but scientists face political attacks and mistrust
science judged by power not evidence
media creates confusion
truth needs social trust to survive
anthropogenic
human impact on the environment
Publication bias
Failure to publish the results of a study on the basis of the direction or strength of the study findings
(if researchers do a study and dont get a statistically significant result they dont usually publish it)
brown and williamson memo
“doubt is our product”
brown & williamson is a large tobacco company
companies created doubt about scientific evidence to confuse the public and delay action instead of proving their product was safe