Chemistry Unit 3: Bonding Vocab
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Atom
The smallest unit of matter
Element
A specific atom
Molecule
Two or more elements bonded together (can be the same or different)
Compound
Two or more DIFFERENT elements bonded together
Pure Substance
All molecules/atoms are the same within a sample
Mixture
Molecules/atoms are different within a sample
Covalent solids have very ______ (strong/weak) intramolecular covalent bonds & ______ (strong/weak) intermolecular forces
Strong, Weak
Intramolecular Bonds
Bonds between atoms within a molecule
Intermolecular Forces
Forces/attraction that exist between molecules
Ionic Bond
Complete transfer of valence electrons(s) between atoms. Generates two oppositely charged ions. Has an electronegativity difference greater than 1.7.
Covalent Bond
Sharing electrons to reach the octet rule and become more stable. Formed between atoms with similar electronegativities and has an electronegativity difference of less than 1.7.
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
Difference in electronegativity between bonded atoms is less than 0.5 (very similar electronegativities)
Polar Covalent Bond
Difference in electronegativity between bonded atoms is between 0.5 and 1.9 (slightly different electronegatvities)
The types of intermolecular forces (in order from strongest → weakest) are:
Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, & Induced Dipole
Hydrogen Bonding
Occurs when a H atom is bonded to either an O, N, or F atom. δ+ end of hydrogen is attracted to the δ- end of the O, N, or F of another molecule. This is the strongest force of intermolecular attraction, making it have high BPs and MPs.
Dipole-Dipole
Forces occur when the δ+ charged part (pole) of a molecule interacts with the δ- charged part (pole). Out of the intermolecular forces, this is in the middle regarding strength.
Induced Dipole
Forces between essentially non-polar molecules. “Temporary dipoles” are formed by the shifting of the electron clouds within molecules. These temporary dipoles attract or repel the electron clouds of nearby non-polar molecules. This is the weakest kind of attraction.
Order of the type of bonds from weakest → strongest attraction
Induced Dipole, Dipole-Dipole, Hydrogen Bonding, Ionic Bonds
Ionic Compounds Properties
Crystalline solid at room temperature, high melting points, conducts electricity as a liquid, soluble in water, conducts electricity when dissolved in water.
Covalent Compounds Properties
Liquid, gas, & solid at room temperature, low melting points, doesn’t conduct electricity, not soluable in water
Odd-Electron Molecules
A violation of the octet rule
Some stable compounds have an odd number of electrons in their valence shells
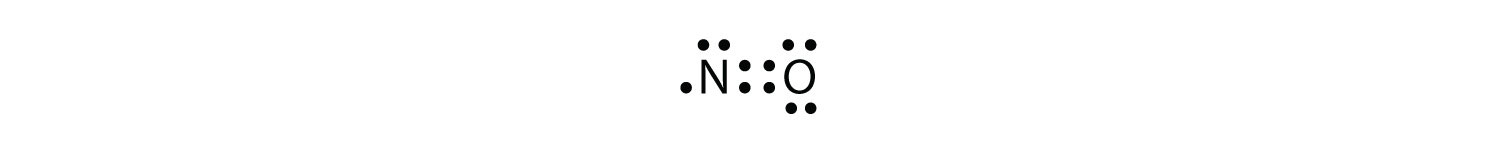
Electron-Deficient Molecules
A violation of the octet rule
Occurs when stable compounds have less than eight electrons around the central atom

Expanded Valence Shells Molecules
A violation of the octet rule
Occurs when more than 8 electrons are assigned to the valence shell. Formed only by central atoms in the third row of the periodic table or beyond because they have empty d orbitals in their valence shells.
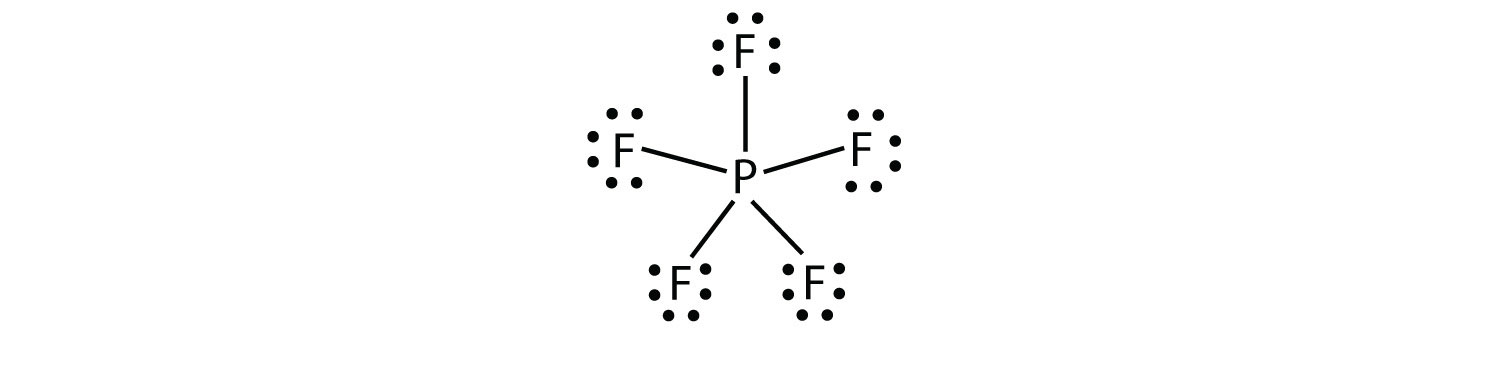
Formal Charge
A way to determine which structure is the most valid and would exist in real life. Molecules are the most stable when the formal charge is minimized.
Formal Charge Formula
The # of valence electrons it should have (period number) - actual amount of valence electrons it has
OR
Valence electrons - nonbinding valence electrons - # of bonds
Electronegative elements are more likely to gain a ______ charge.
Negative