Biology Exam 2 chapter questions - chapters 3, 4, 6, 7, 8
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
The cell theory states
A. all organisms are composed of only one cell.
B. organelles are the basic living unit of structure and function of organisms.
C. all cells come only from other cells.
D. all organisms are composed of only one cell AND organelles are the basic living unit of structure and function of organisms.
c
According to cell theory
A. all organisms are composed of tissues.
B. the smallest unit of life is a nucleus.
C. a multicellular organism is composed of many cells.
D. new cells arise only from preexisting cells.
D.
Proteins are processed and modified in the interior of the
A. mitochondria.
B. nucleus.
C. chloroplasts.
D. rough endoplasmic reticulum.
D
Which cellular structure is responsible for packaging materials with the cell?
A. mitochondria
B. chloroplasts
C. Golgi apparatus
D.lysosomes
C
In order to digest materials within a cell, the material to be digested must fuse with
A. a lysosome.
B. the Golgi apparatus.
C. a secretory vesicle.
D. smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
A
This organelle absorbs and converts oxygen while releasing CO2 and water?
A. lysosomes
B. Golgi apparatus
C. mitochondria
D. chloroplasts
E.endoplasmic reticulum
C
Cellular respiration is best associated with the
A. Golgi apparatus.
B. ribosome.
C. mitochondrion.
D. chloroplast.
E. microtubule.
C
Which of the following is NOT evidence supporting the endosymbiotic theory?
A. the vacuoles can "come and go" across the plasma membrane.
B. mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA.
C. mitochondria and chloroplasts are nearly identical to some free-living prokaryotes.
D. mitochondria and chloroplasts divide by splitting.
A
This is a multiple-answer question. Choose all that are correct. Choosing incorrect questions will subtract from the grade on this question. However, you cannot receive a negative grade on the question. The nucleus
A. is found in eukaryotes.
B. has a single-layered membrane.
C. stores genetic material.
D. is the only organelle containing DNA.
E. contains chromatin.
F. can live independently of a cell.
A, C, E
This is a multiple-answer question. Choose all that are correct. Choosing incorrect questions will subtract from the grade on this question. However, you cannot receive a negative grade on the question. The nucleus
A. is found in bacteria.
B. has a double membrane.
C. stores genetic material.
D. is the only organelle containing DNA.
E. contains chromatin.
F. can live independently of a cell.
B, C, E
This is a multiple-answer question. Choose all that are correct. Choosing incorrect questions will subtract from the grade on this question. However, you cannot receive a negative grade on the question.
This structure has hereditary material inside it.
A. mitochondrion
B. nucleus
C. chloroplast
D. ribosome
E. flagellum/cilium
F. lysosome
A, B, C
This is a multiple-answer question. Choose all that are correct. Choosing incorrect questions will subtract from the grade on this question. However, you cannot receive a negative grade on the question.
Which of the following would be found as part of all cells.?
A. DNA
B. plasma membrane
C. ribosomes
D. mitochondria
E. chloroplasts
F. fimbriae
A, B, C
A flagellum is able to bend due to being made of ______________ that can bend by sliding past one another under the influence of the motor protein _____________.
A. microtubules/dynein
B. actin filaments/myosin
C. phospholipids/thylakoids
D. intermediate filaments/keratin
A
The innermost membrane of the chloroplast is referred to as the
A. thylakoid membrane.
B. inner membrane.
C. cristae.
D. stroma.
A
IImagine starting in the innermost space of the chloroplast and moving outward until leaving the chloroplast and entering the cytoplasm. What is the starting points an proper order of things you would move through?
A. thylakoid space - thylakoid membrane - stroma - inner membrane - outer membrane
B. stroma - inner membrane - thylakoid space - thylakoid membrane - outer membrane
C. stroma - inner membrane - thylakoid membrane - thylakoid space - outer membrane
D. matrix - inner membrane - intermemebrane space - outer membrane
A
Which of the following is NOT a function of the cell membrane?
A. It provides mechanical strength to the cell.
B. It gives shape to the cell.
C. It regulates passage of molecules into and out of the cell.
D. It is largely responsible for cellular homeostasis.
E. It serves as a site for protein synthesis
E
According to the fluid-mosaic model of membrane structure,
A. proteins make up the bulk of the membrane.
B. only lipids are found in the membrane.
C. cholesterol is the main constituent of the membrane.
D. proteins float inside or within the phospholipid bilayer.
D
**The plasma membrane is composed of
A. proteins and microtubules.
B. phospholipids and actin filaments.
C. phospholipids and microtubules.
D. phospholipids and proteins.
E. proteins and actin filaments.
D
Proteins do NOT pass through cell membranes because
A. the membrane is made of protein.
B. they contain nitrogen.
C. they are very large molecules.
D. they cause digestion of the cell
C
Permeability refers to
A. the movement of molecules from an area of greater concentration to an area of lesser concentration.
B. the extent to which a membrane allows a substance to pass through.
C. the amount of solute in a solution.
D. the ability to establish a permanent solute level in a solution.
B
Which statement is FALSE concerning movement of molecules across the cell membrane?
A. Small uncharged molecules pass through easily.
B. Large molecules do not pass through easily.
C. Charged molecules do not pass through easily.
D. Lipid molecules do not pass through easily
D
If 0.9% NaCl were isotonic to a cell, then
A. 0.9% would also be hypotonic.
B. 0.9% would also be hypertonic.
C. 1.0% would be hypertonic.
D. 1.0% would be hypotonic.
E. 0.1% would be hypertonic.
C
If you have a 10% sugar solution and a 35% sugar solution, how does the 10% solution compare to the 35% solution?
A. isotonic
B. sweeter
C. osmotic
D. hypotonic
E. hypertonic
D
The term hypertonic means
A. to lose water.
B. to gain water.
C. a higher solute concentration.
D. a lower solute concentration.
E. an equal solute concentration.
C
An isotonic solution means that the solute concentration outside the cell
A. is greater than inside the cell.
B. is less than inside the cell.
C. is the same as inside the cell.
D. has no effect on the cell.
E. is greater than outside the cell.
C
Which is true of facilitated transport by carrier proteins?
A. Facilitated transport only applies to small and lipid soluble molecules.
B. It is represented by the glucose carrier that can transport hundreds of molecules a second.
C. After a carrier has transported a molecule, it is unable to transport any more.
D. Facilitated transport requires expenditure of chemical energy and is therefore active transport.
E. One carrier protein can carry a variety of different molecules.
B
Carrier molecules are required for
A. osmosis.
B. both osmosis AND diffusion.
C. facilitated diffusion.
D. active transport.
E. both facilitated diffusion AND active transport
E
When a substance moves from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration while using energy, the process is termed
A. diffusion.
B. osmosis.
C. facilitated diffusion.
D. active transport.
D
If a cell lacks ATP, which of the following processes would cease to operate immediately?
A. diffusion
B. sodium/potassium pump
C. facilitated diffusion
D. osmosis
B
When an intestinal cell ingests substances inside very small vesicles that can only be seen with an electron microscope, this is
A. pinocytosis.
B. phagocytosis.
C. exocytosis.
D. diffusion.
A
Receptor-mediated endocytosis involves all of the following EXCEPT
A. receptor proteins to bind to specific molecules.
B. a coated pit due to a layer of fibrous protein on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane.
C. the mechanism for regulating exchange between a mother and fetus.
D. secretion of materials from a cell.
D
Which of the following refers to materials only leaving the cell?
A. diffusion
B. exocytosis
C. endocytosis
D. phagocytosis
B
Which condition must be met for diffusion to occur?
A. a differentially permeable membrane
B. a true solution
C. a concentration difference
D. a non-permeable membrane
C
Match the type membrane protein with its proper function
1. channel protein
2. carrier protein
3. cell recognition protein
4. receptor protein
5. enzymatic protein
A. allows molecules to move through a membrane through space provided by the protein
B. interacts and binds to a molecule to help it move across a membrane, usually requiring a change in protein shape
C. glycoproteins that allow cells of the immune systems determine if a cell belongs in the body or is an invader
D. catalyze specific reactions at the cell membrane
E. binds to a specific extracellular molecule to bring about a change within the cell
A, B, C, E, D
This is a multiple answer question.
Following is a list of examples of the forms of movement of molecules across a membrane. Choose only those that require energy input from the cell whose membrane is directly involved.
A. Insulin starts out in a vesicle inside a beta cell of the pancreas. When blood sugar level rises the vesicle moves to the cell membrane and fuses with the cell membrane.
B. Glucose levels outside a cell are high and enter the cell though a carrier protein by facilitated diffusion.
C. Ldl cholesterol receptors fill up in a coated pit and the pit is pulled into the cell and made into a vesicle.
D. A person eats a salty snack and the salt concentration outside the cell rises. Water rushes out through aquaporins.
E. The cell uses a sodium-potassium pump to create a high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell.
A, C, E
Glucose levels go up in the bloodstream after a meal. Beta cells of the pancreas detect the elevated glucose levels. This causes them to secrete insulin protein into the bloodstream. How is this secretion accomplished?
A. Motor proteins drag insulin-containing vesicles to the cell membrane along microtubules.
B. Insulin-containing vesicles diffuse to the cell membrane.
C. Insulin is exported from the cytoplasm by receptor mediated endocytosis.
D. Insulin is exported from the cytoplasm by facilitated diffusion with a carrier protein.
A
The GLUT protein
A. moves glucose across a membrane by simple diffusion.
B. moves glucose across a membrane by facilitated diffusion.
C. moves glucose across a membrane by active transport.
D. moves glucose across a membrane by receptor mediated endycytosis
B
Which statement most accurately describes the second law of thermodynamics?
A. Energy cannot be changed from one form to another without a loss of usable energy.
B. One usable form of energy can be completely converted into another usable form.
C. Energy cannot be created nor destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another.
D. Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
A
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the first law of thermodynamics?
A. One usable form of energy cannot be completely converted into another usable form.
B. One usable form of energy can be completely converted into another usable form.
C. Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
D. Energy can be neither created nor destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another.
D
Which of the following is NOT a correct statement about the second law of thermodynamics and entropy?
A. The amount of disorder in the universe is always increasing.
B. To maintain organization of a cell, a continual input of energy is required.
C. Living cells without energy would become less organized.
D. Carbon dioxide and water form glucose without the input of energy.
D
Occasionally someone claims to have built a machine that can run forever, producing as much energy as it consumes. This has always been disproved because it violates
A. the first law of thermodynamics.
B. the second law of thermodynamics.
C. laws preventing any conversion between types of energy.
D. coupled reaction equations.
B
This image demonstrates the second law of thermodynamics in that
A. the plants convert light energy from the sun to chemical energy.
B. the plants create chemical energy.
C. the animal is able to convert chemical energy from the plant into mechanical energy.
D. the animal loses some energy to heat when chemical energy is converted to mechanical energy.
D
The high energy bond in ATP that is used by cells is found in or between
A. the adenine base.
B. the adenine and the ribose.
C. the adenine and the phosphates.
D. the phosphate groups
D
ATP contains
A. an adenine base and two phosphate groups.
B. an adenine base and three phosphate groups.
C. an adenine base, a ribose sugar, and two phosphate groups.
D. an adenine base, a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups.
D
The main reason that ATP is considered the energy currency in cells is because it
A. carries a positive charge.
B. contains accessible energy in phosphate bonds.
C. contains an adenine base.
D. contains a sugar ring.
B
During an enzymatic reaction, what happens to the enzyme?
A. It becomes the product.
B. It becomes the substrate.
C. It is used up.
D. The enzyme and the substrate form a temporary complex.
D
Enzymes are specific. This means that they
A. have a preferred pH.
B. have a preferred temperature.
C. have a particular substrate.
D. are only in certain cells.
C
Which of the following statements is true about enzymes?
A. Their 3D shape can vary and still be active.
B. Boiling temperatures do not affect their activity.
C. They catalyze only one specific type of reaction.
D. They can associate with a wide variety of substrates.
E. They are unaffected by changes in pH.
C
Which is true about energy of activation?
A. Energy of activation is measured as the energy that is released after a reaction occurs.
B. Adding the correct enzyme can lower the energy of activation.
C. Energy of activation is the difference between the energy of the reactant and the energy of the product.
D. The energy of activation is always lower than the energy of the reactant.
B
Each enzyme has a particular substrate because enzymes
A. increase the energy of activation.
B. decrease the productivity of the cell.
C. have active sites complementary in shape to their substrates.
D. are named for their substrate.
C
The function of an enzyme is to
A. provide the energy for metabolic reactions.
B. increase the rate of a metabolic reaction.
C. change the direction of metabolic reactions.
D. raise the energy of activation for a reaction.
B
Which of the following statements is not true concerning enzymatic activity?
A. Each enzyme has a preferred pH at which the enzyme reaction rate is highest.
B. Above a certain temperature, an enzyme will become denatured.
C. As the temperature increases, most enzymatic reactions will still proceed at the same rate.
D. Enzyme activity increases as substrate concentration increases until the maximum rate is achieved.
C
If you wished to increase enzyme activity, you would do all of the following except
A. increase the temperature moderately.
B. increase the concentration of substrate.
C. change to optimum pH for the reaction.
D. decrease the temperature.
D
If an enzymatic reaction was controlled by feedback inhibition, we would expect it to stop
A. only if the substrate was exhausted.
B. when the cofactors are exhausted.
C. when the product changed the pH.
D. as soon as a critical level of end product builds up.
D
In feedback inhibition of a metabolic pathway, where does the inhibitor bind?
A. to the substrate of the first reaction
B. to the product of the first reaction
C. to the enzyme of the first reaction
D. to a substrate or the product of the last reaction
C
The location in which the enzyme and substrate complexes is called the
A. active site.
B. inhibitor site.
C. receptor site.
D. enzyme-substrate complex
A
If A -> B -> C -> D -> E represents a metabolic pathway, then letter E would be
A. a substrate.
B. a product.
C. energy.
D. an enzyme.
E. an enzyme-substrate complex.
B
This is a multiple answer question.
In which of the following ways is the enzyme inhibitor warfarin used?
A. rat poison
B. anticoagulant medicine
C. recreational drug
D. cancer drug
A, B
Which of the following can act a an enzyme cofactor?
A. iron
B. vitamines
C. NAD+
*D. All of the above.
D
Some metabolic reactions require that one molecule undergoes a reaction that causes it to lose energy and that energy is then transfered to a new chemical bond on another molecule. This describes
A. a coupled reaction.
B. an anabolic reaction.
C. the activation energy of a reaction.
D. feedback inhibition
A
If you give a child a surgary snack you might notice that they become hyperactive right afterward. Much of the sugar in the blood can be quickly absorbed by the neuronal cells of the brain where the glucose is quickly broken down to create ATP. This is an example of which factor affecting rates of enzymatic reactions?
A. Substrate Concetration
B. Temperature
C. pH
D. Enzyme Inhibition
A
While paddling your canoe down a river you notice many turtles laying on logs in the sun. This is an example of which factor affecting rates of enzymatic reactions?
A. Substrate Concetration
B. Temperature
C. pH
D. Enzyme Inhibition
B
Which is NOT a correct attribute of a metabolic pathway?
A. A constant supply of new enzymes must be produced to keep the metabolic pathway active.
B. The product of one reaction can become the reactant for the next.
C. Reactants act as substrates for specific enzymes.
D. Reactants are the input molecules.
A
We often say that we need food for energy. In a biological sense, is this correct?
A. Yes, because the food we eat has potential energy in its structure and this chemical energy can be converted into mechanical energy.
B. Yes, because the smallest units inside the atoms that make up the food are simply pure energy.
C. Yes, because the food must move through the digestive system, and motion is kinetic energy.
D. No, because food consists of matter and cannot be transformed into energy.
E. No, since all food matter stays matter, and energy remains energy
A
Put the following reactions of cellular respiration in the correct order:
1. preparatory reaction
2. glycolysis
3. electron transport chain
4. citric acid cycle
2, 1, 4, 3
Cellular respiration does NOT include which of the following events?
A. glycolysis
B. citric acid cycle
C. light reactions
D. electron transport chain
E. preparatory reaction (prep)
C
Which molecules are the reactants or substrates for aerobic respiration?
A. glucose and carbon dioxide
B. carbon dioxide and water
C. oxygen and glucose
D. glucose and water
C
Which molecules are the products of aerobic respiration?
A. glucose and water
B. glucose and oxygen
C. lactate and carbon dioxide
D. carbon dioxide and water
D
Which of the following is a substrate of cellular respiration?
A. carbon dioxide
B. water
C. glucose
D. energy
C
Which of the following does not describe the role of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
A. It accepts two electrons.
B. It is a coenzyme.
C. It is necessary for glycolysis.
D. It is broken down to CO2 and water.
D
What role does NAD+ play in cellular respiration?
A. It is a coenzyme.
B. It is an enzyme.
C. It provides the oxygen.
D. It provides the energy.
A
What are the input requirements of glycolysis?
A. NAD+, FAD, acetylCoA, and ADP,
B. ATP, NAD+, glucose, and ADP
C. pyruvates, NADH, and ADP
D. glucose and oxygen
B
The final products of glycolysis are
A. pyruvate, ATP, and NADH + H+.
B. pyruvate and ATP
C. pyruvate and NADH + H+.
D. ATP and NADH + H+.
E. pyruvate.
A
Where does glycolysis take place within the cell?
A. endoplasmic reticulum
B. mitochondrial matrix
C. mitochondrial membrane
D. cytoplasm
D
Choose the one correct statement?
A. Glycolysis results in the release of carbon dioxide.
B. Glycolysis is a cyclical reaction.
C. Glycolysis is a reduction reaction where only glucose is reduced.
D. Glycolysis occurs twice per glucose molecule.
E. Glycolysis breaks glucose down to two pyruvate molecules.
E
Muscles undergo fermentation when
A. no oxygen is available.
B. no carbon dioxide is available.
C. no ATP is available.
D. no pyruvate is available
A
Pyruvate can be converted to lactate instead of going to the preparatory reaction. Why does this occur?
A. The cells need lactate to produce ATP.
B. The cells doing the reaction are prokaryotes
C. Oxygen is not available.
D. There is a shortage of glucose.
C
Why do organisms without oxygen need to convert pyruvate to lactate?
A. in order to regenerate NAD+
B. because lactate is needed to produce ATP
C. because pyruvate is toxic to the cells
D. in order to use lactate in the citric acid cycle
A
What phase(s) of cellular respiration produce(s) NADH?
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. glycolysis and preparatory reaction
E. glycolysis, preparatory reaction, and citric acid cycle
E
Which stage(s) will produce carbon dioxide in cellular respiration?
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. both glycolysis and the electron transport chain
E. both the preparatory reaction and the citric acid cycle
E
The largest number of ATP molecules is produced in which phase of cellular respiration?
A. glycolysis
B. preparation reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain
D
Pyruvate is converted to a two-carbon acetyl group attached to coenzyme A (CoA), and CO2 is given off. This phase is called
A. substrate-level ATP synthesis.
B. the preparatory reaction.
C. the citric acid cycle.
D. fermentation
B
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A. The end product of glycolysis is pyruvate.
B. The citric acid cycle begins and ends with pyruvate.
C. NADH2 will eventually produce three ATP molecules.
D. Aerobic respiration uses oxygen and releases carbon dioxide
B
Which pathway in cellular respiration will produce ATP, NADH, and carbon dioxide?
A. glycolysis
B. preparatory reaction
C. citric acid cycle
D. electron transport chain
C
The production of ATP as a result of an electrochemical gradient is called
A. substrate-level phosphorylation.
B. chemiosmosis.
C. deamination.
D. substrate level phosphorylation.
B
Why does chemiosmosis require a membrane?
A. to anchor proteins within the mitochondria
B. because the phospholipids are involved in the electron transport chain
*C. to separate two compartments of the cell to allow for gradient formation
D. to generate H+ from water
C
What is the final electron acceptor at the end of the electron transport chain in respiration?
A. Oxygen
B. Water
C. NADH
D. ADP
A
Which molecules donate electrons to the electron transport chain of respiration?
A. NADH and FAD
B. ATP and ADP
C. Water and Oxygen
D. Carbon Dioxide and Water
A
Where is NAD+ converted to NADH?
A. Cytoplasm and Matrix of the Mitochondrion
B. Cytoplasm Only
C. Matrix of the Mitochondrion Only
D. Intermembrane Space of the Mitochondrion Only
A
ATP and ADP have a strong negative charge. How could that get into and out of the mitochondrion?
A. Through a membrane transport protein.
B. By diffusion throught the phospholipid bilayer.
C. Diffusion through the mitochondrial membranes since those membranes are not made of phospholipids.
D. By endocytosis and exocyctosis of the mitochondrial membranes.
A
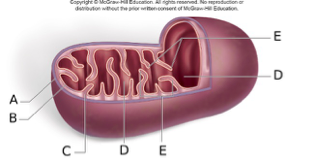
Match the letter in the above diagram to the part of the mitochondrion indicated.
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
5. E
A. Cristae
B. Outer Membrane
C. Inner Membrane
D. Matrix
E. Intermembrane Space
B, C, E, D, A
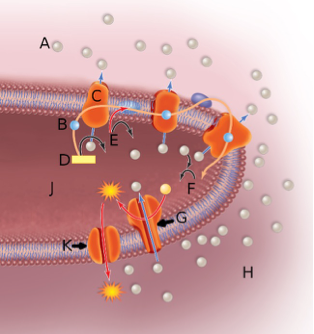
In the above image, the sphere next to the letter A represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. an electron.
C. the matrix.
D. oxygen.
A
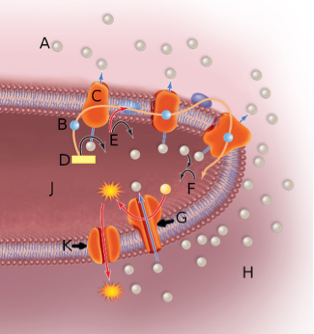
In the above image, the sphere next to the letter B represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. an electron.
C. the matrix.
D. oxygen.
B
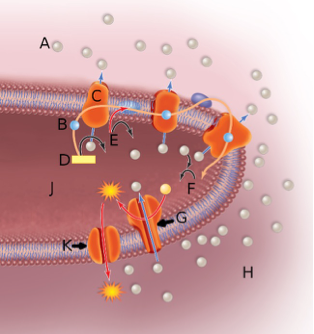
In the above image, the orange globule embedded in the membrane labeled by the letter C represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. a proton pump.
C. the ATP synthase complex.
D. NADH
B
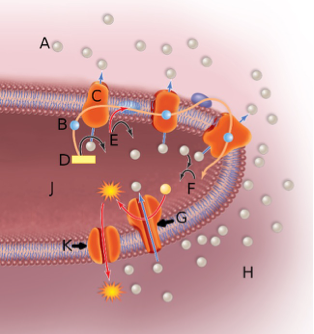
In the above image, the orange globule embedded in the membrane labeled by the letter G represents
A. a proton or hydrogen ion.
B. a proton pump.
C. the ATP synthase complex.
D. NADH
C
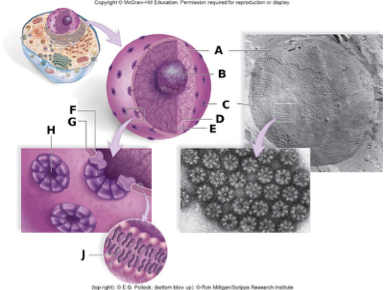
In the above diagram, the label B represents
A. the nuclear envelope.
B. the nucleolus.
C. a nuclear pore.
D. the inner membrane.
E. nucleoplasm.
B
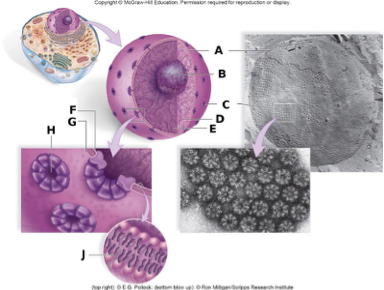
In the above diagram, the label A represents
A. the nuclear envelope.
B. the nucleolus.
C. a nuclear pore.
D. cytoplasm.
E. nucleoplasm.
A
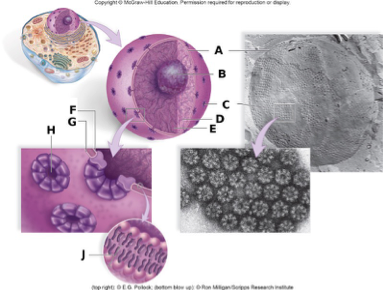
In the above diagram, the label J represents
A. the nuclear envelope.
B. a phospholipid.
C. a nuclear pore.
D. the inner membrane.
E. nucleoplasm.
B
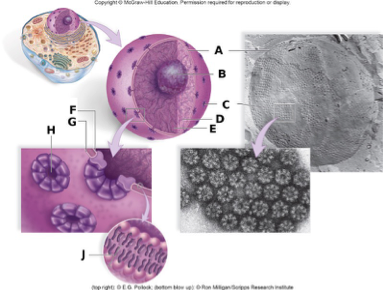
In the above diagram, the labels C and H represents
A. the nuclear envelope.
B. the nucleolus.
C. a nuclear pore.
D. the inner membrane.
E. nucleoplasm.
C
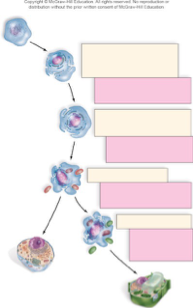
Place the stages of the endosymbiotic theory in the proper order. The above image represents the process.
1. A prokaryotic cell evolves the ability to fold in, invaginate, its cell plasma membrane.
2. The DNA is isolated from the rest of the cell becoming a nucleus.
3. The eukarytic cell envelopes an aerobic bacterium that evolves into a the mitochondria.
4. The eukaryotic cell that has mitochondria envelopes a green photosynthetic bacterium, a cyanobacterium, that evolves into chloroplasts.
1. A prokaryotic cell evolves the ability to fold in, invaginate, its cell plasma membrane.
2. The DNA is isolated from the rest of the cell becoming a nucleus.
3. The eukarytic cell envelopes an aerobic bacterium that evolves into a the mitochondria.
4. The eukaryotic cell that has mitochondria envelopes a green photosynthetic bacterium, a cyanobacterium, that evolves into chloroplasts.