MOS - Chp 11 (Dividends, Stock, Repurchases and Payout Policy)
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Types of Dividends
Regular Cash Dividend
cash dividend paid on a quarterly basis
Extra Dividend
often paid at the same time as regular cash dividiends
ensures that a minimum portion of earnings is distributed to shareholders each year
Special Dividend
one-time payment to shareholder in large amounts of cash
Liquidating Dividend
Paid to stockholders when a firm is liquidated (last priority)
money from the sale of asset to creditors, stockholders etc.
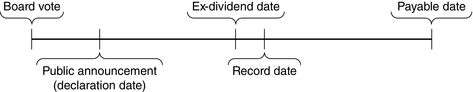
Dividend Payment Process
Board Vote — The firm’s board votes to issue a dividend, specifying the amount and key dates of the issue.
Public Announcement Date — The firm releases the information regarding the dividend payment. Often the stock price will move on the dividend announcement date because investors use this dividend information as a signal regarding the future prospects of the firm.
Declaration Date - announces the value that stockholders received per share (subject to change), dividend payment dates
Ex-Dividend Date - set by stock exchange, shares traded without the right to receive the dividend
Record Date - an investor must be a stockholder or record to receive dividend, typically 2 days after ex-dividend date
Stock Repurchases
when a company repurchases shares (which reduces the number of shares held by investors)
taxed on the profit of the total value
added to liability side of balance sheet
How are Stock Repurchases Purchased?
Open Market Repurchases
limited purchasing power due to government limited number of shares purchased daily
Tender Offer
Open offer by a company to purchase shares
Fixed-Price: the company offers a fixed price to
investors who agree to sell their sharesDutch Auction: the company seeks bids for the number of shares investors would sell at a series of prices. The company may then choose the price in the series that will result in the desired number of shares being
repurchased.
Targeted Stock Repurchases
used to buy blocks of shares from large stockholders
Dividends Benefits and Costs
Benefits of Dividends | Costs of Dividends |
|
|
Dividend vs Stock Repurchase
| Dividend | Stock Repurchase |
Who is impacted? | All shareholders receive a dividend when declared | Shareholders if they want to sell shares |
Shares Outstanding | No change in the number of shares outstanding | Number of shares that exist decreases when a company repurchases shares |
Tax Treatment | Treated as dividend income
| Treated as a capital gain
|
Balance Sheet |
|
|
*stock repurchase a slightly unethical given managers have inside knowledge and can be used to their advantage
Stock Dividends vs Stock Splits
Stock Dividends | Stock Split |
Shareholders receive shares | Division of each share into more shares
|
Usually indicated as a % | Does not provide cash |
Factors that managers consider WHEN setting dividend payouts
Excess Value in the form of…
expected profitability
future investment requirements
financial reserves and flexibility
firm’s ability to raise capital quickly