Abdominal Pain
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Visceral Pain
Fibers located in the walls and capsules that are “activated” by elicited by distention, inflammation, or ischemia or by sensory nerves - results in pain that is slow in onset, dull, poorly localized, and protracted (deep-seated and felt in the midline)
Parietal Pain
What type of pain is characterized by an acute onset that is sharp and better localized pain sensation that results from direct irritation of the parietal peritoneum - occurs in 1 of the 4 quadrants
Vitals, GCS (if not 15 quantify), Distress (peritonitis = still, obstructive = restless), point to MAX point, divide into 4 quadrants, Lungs, Pelvic, back, rectal (above and below)
Problem Focused Physical Exam for Abdominal pain
distended abdomen with surgical scar (adhesions, SBO), Scaphoid contracted abdomen (perf ulcer), visible peristalsis (advanced bowel obstruction), Soft doughy fullness (early paralytic ileus, mesenteric thrombosis), everted umbilicus (increased intra-abdominal pressure)
Things to look for on abdominal inspection
Peristalsis, Absence of bowel sounds (ileus), hyperactive/hypoactive (normal), high-pitched (mechanical bowel obstruction)
Things to look for on Auscultation
Tympany (bowel obstruction, hollow viscus perf, free air), Lower tones (solid organs, fluid), Tenderness on percussion (peritonitis - do a heel tap), observe for discomfort
Things to look for with percussion
Guarding voluntary vs. involuntary, Tenderness (diffuse/rebound/localized), Palpate the painful part last, try to distract (put stethoscope in the same area), Specific signs (Rovsings, murphy, psoas, obturator), Pain out of proportion in older CAD (bowel ischemia (mesenteric))
Things to look for on palpation (most informative aspect)
Grey-turner’s sign, Rhonchi, Diminished breath sounds, tactile fremitus (99), CVA tenderness
Red flags on chest exam
Adenopathy, masses, discoloration, edema, crepitus; check the rings (hernia), pelvic exam, discharge, symmetry
Red flags on GU exam
CBC, CMP, UA, serum beta HCG, Coags, lipase (pancreatitis)
Lab work up for Abdominal Pain
Elderly patients, Hx of cardiomyopathy, dysrhythmia, ischemic heart disease
Who gets an EKG?
U/S (gallstones, female GU stuff), Helical CT (most efficient), Plain chest (all cases of acute abdomen, pre-op, subdiaphragmatic air), Pain abdominal
Imaging studies for Abdominal Pain
Adequacy, bones, calcifications, deformity/density (organomegaly), extraluminal/peritoneal air, foreign bodies/fracture
ABCDEF for a plain abdominal X-ray
Air in the stomach, small bowel, rectosigmoid; psoas muscle (not great), enlarged liver (displacement of bowel), soft-tissue eval is limited
Landmarks of abdominal x-rays (KUB)
3 way abdomen - flat, upright + CXR that looks for hemo/pneumoperitoneum and identifies the need for NG tubes
KUB (kidneys, ureter, bladder) - used in trauma every once in a while
Displaced stomach, spleen projects 12th posterior rib
Signs of splenomegaly on X-ray
Stomach (rugae and the mucosal layer), Plicae circulares/valvulae conniventes (Small intestine - abnormal), Haustra (Colon - sacculated gross)
Spots for intraluminal air
ileus or obstruction
Diffuse air is a sign for
acute obstipation (nothing is moving), abdominal pain, distention, N/V
Symptoms of obstruction
Mechanical (ileus is diffuse, mild, and occurs with other intra-abdominal pathology)
Which type of obstruction has more localized and severe pain?
abdominal operations (should respond spontaneously BUT we might have to throw in an NG tube or alvimopan)
Ileus is most common after
Closed-loop obstruction
A mechanical obstruction in which a segment of a bowel obstructed proximally and distally (like an internal hernia)
adhesions from previous surgery, hernia, tumor
Most common causes of SBO
Cancer, diverticular strictures, volvulus
Most common causes of LBO
Entire bowel has air and is dilated, long air fluid level, gas in the rectum/sigmoid, no transition point on CT
Imaging findings of Ileus
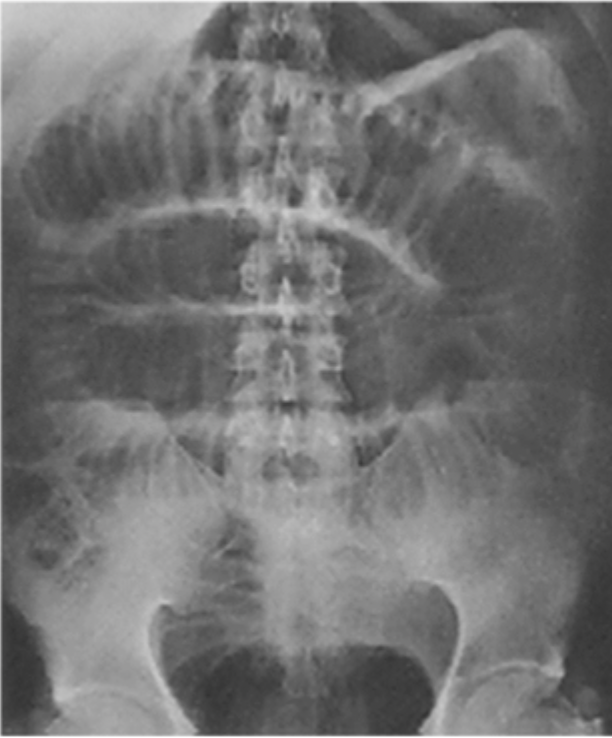
multiple dilated loops (2.5 cm+) of small bowel, multiple air fluid levels
Imaging findings of a mechanical SBO
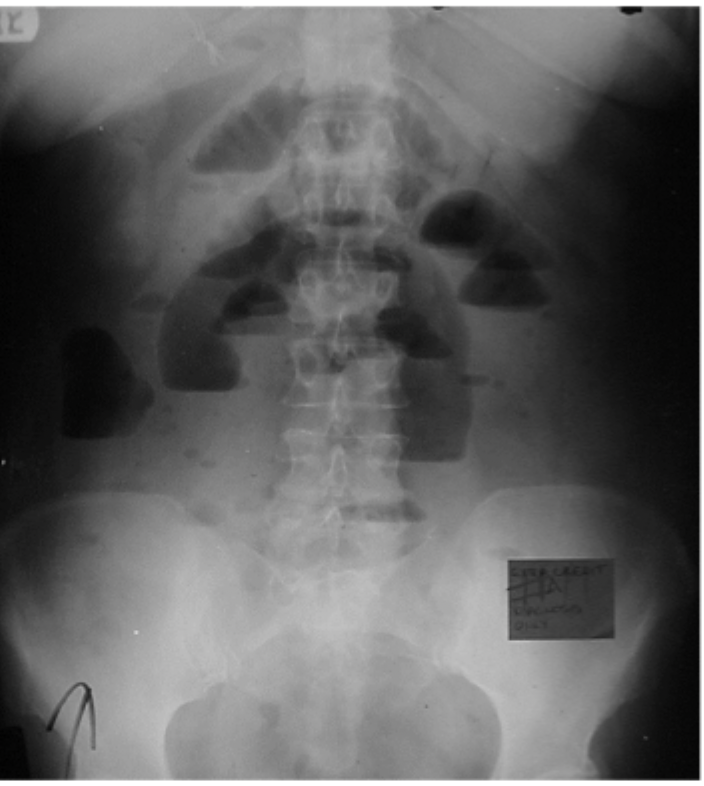
12+ cm, 6+ days dilated
Risk of Ischemia and perforation increases with the degree and duration of colon distention
Upright CXR
What is most sensitive for free intraperitoneal air?
Air under right diaphragm, rigler’s sign (air on both sides of the abdomen)
Signs of Pneumoperitoneum
Upright xrays
When it comes to air fluid levels, what do you need to order?
tubular structures (vessels), Aortic aneurysms (lateral projections), Intra-abdominal organs, Phleboliths (small rounded calcifications with a lucent center)
Calcifications to look for on KUB
Lamellar (laminar)
What type of calcification forms around a nidus inside a hollow lumen and calcifies in concentric layers?
Popcorn calcification (amorphous)
What type of calcification is formed inside of a solid organ or tumor?
Well hydrated (contrast is nephrotoxic), Metformin are at an increased (hold 24 hours before and 2 days after)
IV contrast education measures?
Barium Swallow (UGI), Barium Enema (lower GI), Cystogram, retrograde urethrogram
GI/GU contrast studies
Fever, N/V, intractable pain (not sent home if narcs are needed)
Strict return protocols if a patient is discharge
Do or DIE - blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, rupture aneurysm, aortic transection
Who needs emergent surgery?
Appendicitis, ectopic, incarcerated hernia, Anyone with guarding/rigidity, increased/severe localized tenderness, tense/progressive distention, tender abdominal/rectal mass with high fever, rectal bleeding with shock/acidosis, SIRs, pneumoperitoneum, bowel distention, free extravasation of contrast
Who needs urgent surgery (within 24 hr)