M3: The Logic Gates
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Logic Gate
It is a basic electronic building block used in digital circuits.
It performs a logical operation on one or more binary inputs (0 or 1) to produce a single binary output (0 or 1)
They're physical devices that perform Boolean algebra, a branch of mathematics dealing with logical operations on binary variables.
Low state, represents a 0 volts in its application
High state, represents a 5 volts in TTL and 3.3 in some mid-generation CMOS
A logic gate works in the binary system, so it only has two states:
Logic families
__________ are groups (families) of electronic logic gates that are built using the same type of electronic components and have similar electrical characteristics (like speed, power consumption, and voltage levels).
In other words, it’s a technology used to build logic gates in digital circuits.
Diode Logic (DL)
Resistor–Transistor Logic (RTL)
Diode Transistor Logic (DTL)
Transistor–Transistor Logic (TTL)
Emitter-Coupled Logic (ECL)
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
BiCMOS (Bipolar Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
Types of Logic Families:
Diode Logic (DL)
• oldest and simplest
• uses only diodes and resistors
• cannot provide amplification (weak signal)
• rarely used now
Resistor–Transistor Logic (RTL)
• uses resistors and bipolar transistors
• faster than diode logic
• higher power consumption
• mostly obsolete now
Diode Transistor Logic (DTL)
• uses diodes for logic and transistors for amplification
• improved over RTL
• used before TTL became common
Transistor–Transistor Logic (TTL)
• uses bipolar junction transistors (BJTs)
• very popular in older computers and digital circuits
• faster than DTL, moderate power
Emitter-Coupled Logic (ECL)
• uses BJTs in differential amplifier configuration
• very high speed
• high power consumption
• used in high-speed applications
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
• uses complementary MOSFET transistors (NMOS + PMOS)
• very low power consumption
• high noise immunity
• very widely used today (in microprocessors, memory chips, etc.)
BiCMOS (Bipolar Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor)
• Combines BJT (bipolar) and CMOS
• High speed like TTL + low power like CMOS
• Used in advanced, high-performance circuits
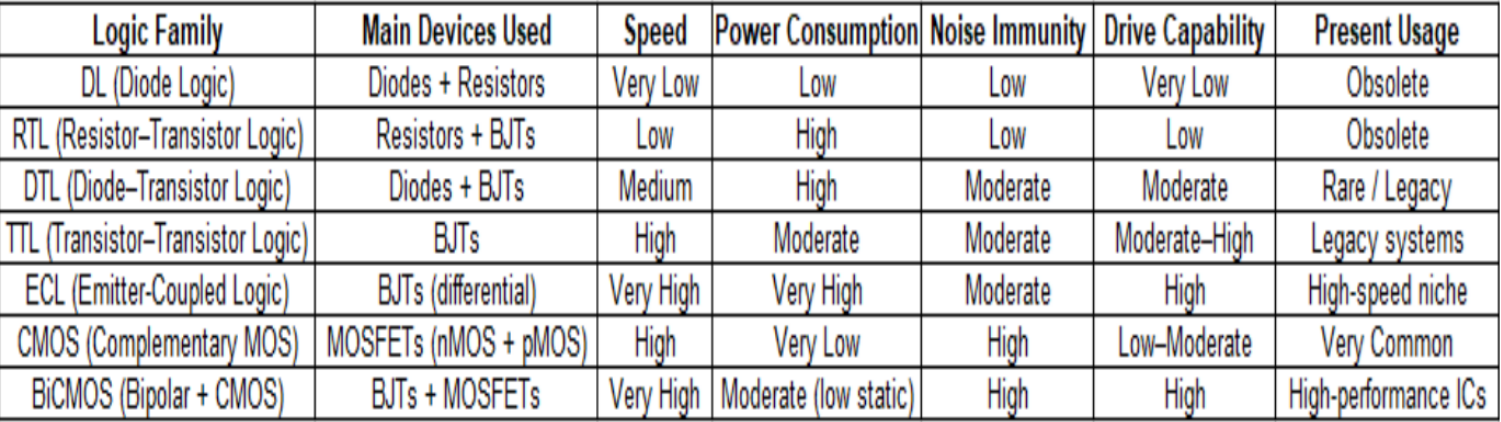
Memorize it!!
Integrated Circuit (IC)
It is a tiny electronic circuit built on a small flat piece (chip) of semiconductor material, usually silicon, that can contain millions or even billions of microscopic components like: Transistors, Diodes, Resistors, Capacitors
Complete electronic circuit built into a single small chip that makes modern electronic devices smaller, faster, cheaper, and more reliable.
Legacy Gates (Fundamental Gates)
NOT Gate
OR Gate
AND Gate
YES Gate (Buffer)
Universal Gates
NOR Gate
NAND Gate
Derived Gates
XOR Gate (Exclusive OR Gate)
XNOR Gate (Exclusive NOR Gate)
Types of Logic Gates:
NOT Gate
• also known as Inverter
• the output is the complement of the input
OR Gate
• follows the principle of addition
• any input of “high” will results to a “high output”
AND Gate
• follows the principle of multiplication
• any input of “low” will results to a “low output”
YES Gate (Buffer)
• also considered as a legacy gate
• the output follows whatever the input
NOR Gate
• an OR gate followed by an inverter
• Any input of “high” will results to a “low output”
NAND Gate
• an AND gate followed by an inverter
• any input of “low” will results to a “high output”
XOR Gate (Exclusive OR Gate)
• sometimes called Inequality detector, because it outputs 1 when the inputs are different (unequal)
• sometimes called Modulo-2 adder, because it performs binary addition without carry
XNOR Gate (Exclusive NOR Gate)
• Sometimes called Equivalence gate or Equality detector because it outputs 1 when the inputs are the same
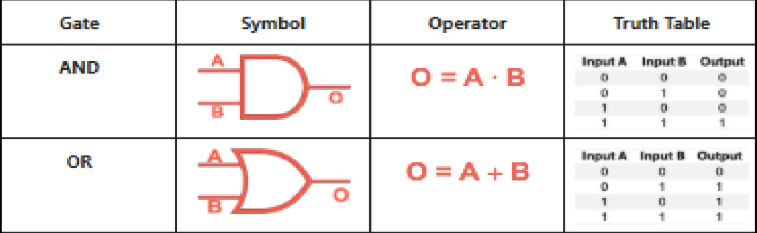
Logic Gate Symbols of AND and OR:
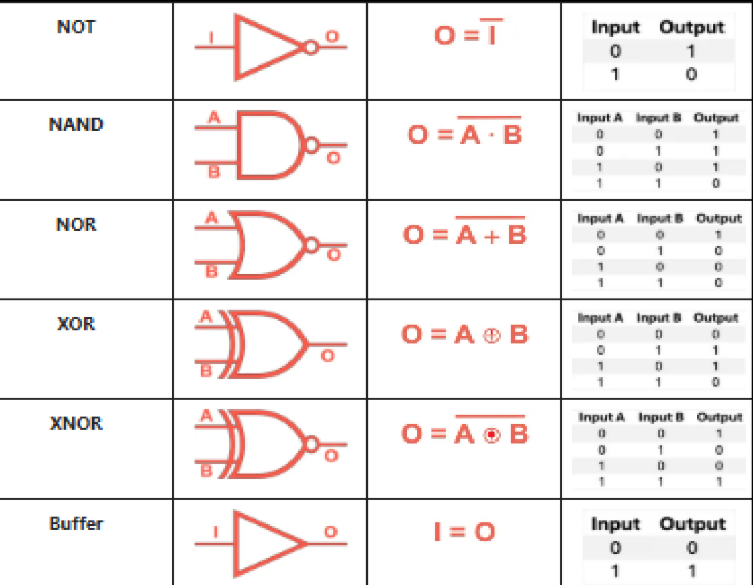
Logic Gates Symbols of NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR and BUFFET: