Chem 1LD Safety
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
The most probable laboratory emergencies are chemical spills, minor burns and cuts, and fires. Which of the following statements are TRUE about responding to emergencies?
If possible turn off lab equipment before leaving lab for a fire alarm
Stay calm
Know where the stairwells are
All laboratories must have two exits
If possible turn off lab equipment before leaving lab for afire alarm
Stay calm
Know where the stairwells are
All laboratories must have two exits
Which of the following common household products contain flammable chemicals? (Select all that apply)
gasoline
rubbing alcohol
bleach
nail polish remover
antifreeze
liquid hand soap
gasoline
rubbing alcohol
nail polish remover
antifreeze
Which of the following are ways to stop a fire? (Select all that apply)
remove ignition sources
place a beaker over a small flame to remove oxygen
ground metal container to prevent static electricity
limit quantities of flammable substances in work area
remove ignition sources
place a beaker over a small flame to remove oxygen
ground metal container to prevent static electricity
limit quantites of flammable substances in work area
Which of the following statements are true about flammability? (Select all that apply)
Inflammable is another word for flammable
Flammable chemicals can be liquids or solids, gases don’t burn.
The boiling point of a flammable liquid is usually high.
A fire cannot start above or below a vapor’s flammability limits.
Combustible is the same as flammable
All volatile chemicals are flammable
Inflammable is another word for flammable
A fire cannot start above or below a vapor’s flammability limits
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) diamond has a [A] section for flammability.
red
blue
yellow
white
red
If the number [B] appears in this section, the chemical is extremely flammable.
4
3
2
1
0
4
If the number [C] appears in this section, the chemical is a combustible, it will catch fire when heated.
4
3
2
1
0
2
The Global Harmonized System (GHS) symbol is a picture of a [D].
fire
fire with an O in the middle
an explosion
an exclamation point
a skull and crossbones
fire
If the hazard category is [E], the chemical is extremely flammable.
HC1
HC2
HC3
HC4
HC1
If the hazard category is [F], the chemical is combustible.
HC1
HC2
HC3
HC4
HC4
Which of the following are true statements about fume hoods? (Select all that apply)
The window on the front of the fume hood is called a sash.
Exhaust air from fume hoods is recycled back through the lab.
A tissue paper held from the bottom of a sash should blow into the hood.
All work should be done at least 6 inches inside the hood.
A fume hood has it’s own power, it’s okay to continue work if the power fails.
Room air should be drawn into the fume hood.
The window on the front of the fume hood is called a sash.
A tissue paper held from the bottom of a sash should blow into the hood.
All work should be done at least 6 inches inside the hood.
Room air should be drawn into the fume hood.
PEL
permissible exposure limit
odor threshold
gas concentration that 50% of the population can detect
odor fatigue
decreased sensitivity to odor over time
IDLH
immediately dangerous to life and health
OEL
occupational exposure limits
Which of these chemicals will you smell after it becomes hazardous? (Select all that apply)
hexane: 50 ppm (PEL), 130 ppm (Odor Threshold)
dichloromethane: 25 ppm (PEL), 130 ppm (Odor Threshold)
ethyl acetate: 400 ppm (PEL), 50 ppm (Odor Threshold)
methanol: 200 ppm (PEL), 5900 ppm (Odor Threshold)
Anything with PEL < Odor Threshold
hexane: 50 ppm (PEL), 130 ppm (Odor Threshold)
dichloromethane: 25 ppm (PEL), 130 ppm (Odor Threshold)
methanol: 200 ppm (PEL), 5900 ppm (Odor Threshold)
Which statement about gloves is true? (Select all that apply)
most gloves protect against most chemicals
only non-disposable gloves protect against most chemicals
no glove material protects against all chemicals
latex gloves are the best choice for most people working in labs
gloves should be removed when they come in contact with any hazardous chemical
no glove material protects against all chemicals
gloves should be removed when they come in contact with any hazardous chemical
Permeation
ability of a chemical to penetrate the glove material through small pores
Degradation
destructive change in the glove material
Breakthrough time
time for the first appearance of a chemical on the other side of the glove
Rate of transfer
speed at which a chemical appears on the other side of the glove
Which of the following are TRUE statements about lab coats? (Select all that apply)
Coats should be worn open, snapping or buttoning the coats prevents quick removal.
Sleeves should never be rolled up.
Lab coats should never be worn outside of lab.
Lab coats do not need to be removed if chemicals are spilled on them.
Sleeves should never be rolled up.
Lab coats should never be worn outside of lab.
Which of the following statements are TRUE about nitrile gloves? (select all that apply)
Nitrile gloves protect against aliphatic hydrocarbons like heptane and limonene.
Nitrile gloves are made of a natural rubber.
Nitrile gloves protect well against aldehydes.
Nitrile gloves could be degraded by acetone (a ketone).
Nitrile gloves protect against aliphatic hydrocarbons like heptane and limonene.
Nitrile gloves could be degraded by acetone (a ketone).
Which of the following guidelines should be followed to protect your skin in the chemistry laboratory? (Select all that apply)
Use gloves when appropriate to do so.
Wear clothing that covers most of your body.
Wear a lab coat.
Wear sturdy close toed and heel shoes.
Use gloves when appropriate to do so.
Wear clothing that covers most of your body.
Wear a lab coat.
Wear close toed and heel shoes.
Acute Toxicity
ability of a chemical to do damage with a single dose
Chronic Toxicity
ability of a chemical to do damage with multiple doses.
LC50
Lethal concentration that kills 50% of a population
LD50
Lethal does that kills 50% of a population
Toxicant
Chemical producing toxic effects
Toxicity
Ability of a chemical to damage
Toxicology
Study of adverse effects of chemicals
Toxin
Toxic substance made by plant, animal, fungi, or bacterium.
Which of the following statements are TRUE about the factors influencing toxicity?
Animal models may not be a good representation of a human response.
The dose makes the poison.
Man-made substances are always more toxic than naturally occurring ones.
The route of exposure has no effect.
The very young and very old are more susceptible to toxic effects.
Animal models may not be a good representation of a human response.
The dose makes the poison.
The very young and very old are more susceptible to toxic effects.
Acetaminophen (tylenol)
Metabolized and removed by the liver.
DDT
Bioaccumulation - stored in fat
Ethylene glycol
Metabolized into calcium oxalate - forms crystals in kidneys
Sensitizer
Formaldehyde
Asphyxiant
Carbon monoxide
Teratogen
Acrylonitrile
Carcinogen
Benzene
Organ toxicant
Ethanol
Neurotoxin
Acetone
Poison
Cyanide
Hazard
potential source of danger
risk
probability of suffering harm
risk level
hazard severity x exposure probability
risk assessment
identification of sources of danger and probability of harm
risk management
wearing personal protective equipment, avoiding spark sources, and using smaller amounts
What are the factors that affect the probability of a lab accident?
How chemicals are used
How other people behave
How risk is managed
How the physical environment is controlled
What type of laws are enforced
How chemicals are used
How other people behave
How the physical environment is controlled
Which of the following must be assessed to reduce the probability of exposure to a hazard?
Amount of chemical used
Containment of chemicals (capping reagents, using chemicals in the fume hood)
Personal knowledge of the hazards
Routes of exposure (skin, eyes, inhalation, ingestion)
Type of personal protective equipment (goggles, lab coat, gloves etc.) needed
Amount of chemicals used
Containment of chemicals (capping reagents, using chemicals in the fume hood)
Personal knowledge of the hazards
Routes of exposure (skin, eyes, inhalation, ingestion)
Type of personal protective equipment (lab coat, gloves, goggles, etc.) needed
While pouring 1M of an aq KMNO4 solution from a 1L reagent bottle, a student’s hand slipped and the bottle fell and broke open. A small amount of solution splashed into the student’s eyes. The solution also spilled across the bench top and dripped down to create a pool on the floor.
If no safety precautions are followed the severity of the hazard is:
catastrophic
minor
moderate
serious
moderate
While pouring 1M of an aq KMNO4 solution from a 1L reagent bottle, a student’s hand slipped and the bottle fell and broke open. A small amount of solution splashed into the student’s eyes. The solution also spilled across the bench top and dripped down to create a pool on the floor.
The probability of the event happening is:
very unlikely
unlikely
possible
likely
very likely
possible
While pouring 1M of an aq KMNO4 solution from a 1L reagent bottle, a student’s hand slipped and the bottle fell and broke open. A small amount of solution splashed into the student’s eyes. The solution also spilled across the bench top and dripped down to create a pool on the floor.
This leads to a risk level that is:
low
medium
high
extreme
medium
Which measure should be taken to manage the risk?
Know what to do if a chemical gets in the eyes
Know what to do if a spill occurs
Wear goggles
All of the above
All of the above
Which of the following would help you determine the severity of a hazard? (Select all that apply)
NFPA fire ratings
GHS symbols
PELs (Permissible Exposure Limits)
lethal dose 50 values
chemical amount used
NFPA fire ratings
GHS symbols
PELs (Permissible Exposure Limits)
lethal does 50 values
chemical amount used
zero risk
no hazards present
balancing
risk allowed increases with benefit of chemical use
technology-based
exposure level is set to level it can be reduce to
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
eye hazards
cause irreversible damage to cornea or iris
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
sensitizers
hypersensitivity to lungs and skin
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
mutagens
produce genetic defects
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
carcinogens
cause cancer or presumed to cause caner in humans
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
reproductive toxicants
cause birth defects
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
target organ toxicants
cause damage to certain organs, affecting their ability to carry out normal functions
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
aspiration hazards
can be fatal if swallowed or inhaled
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
acute toxicants
are fatal if exposed to the smallest amount
Hazard class at its most dangerous hazard category
corrosives
causes severe skin burns and eye damage
Heptane Hazard Classes and Severity
Flammable Liquid
GHS?
Hazard Category?
SDS Useful Info?: flash point, autoignition, extinguishing media, handling precautions, three of these, all of these
fire, 2, all of these
Heptane Hazard Classes and Severity
Skin irritation
GHS?
Hazard Category?
SDS Useful Info?: first aid information, hygiene measures, skin protection, body protection, three of these, all of these
danger, 2, first aid information
Heptane Hazard Classes and Severity
Central nervous system toxicity, single exposure
GHS?
Hazard Category?
SDS Useful Info?: viscosity, ecological information, vapor pressure, melting point, three of these, all of these
specific health toxicity, 3, vapor pressure
Heptane Hazard Classes and Severity
Aspiration hazard
GHS?
Hazard Category?
SDS Useful Info?: suitable extinguishing media, storage conditions, skin protection, first aid measures, three of these, all of these
specific health toxicity, 1, first aid measures
Heptane Hazard Classes and Severity
Aquatic hazard
GHS?
Hazard Category?
SDS Useful info?: suitable extinguishing media, storage conditions, skin protection, first aid measures, three of these, all of these
environmental hazard, 1, three of these
Heptane Exposure and Probability
Inhalation
Useful Info in SDS?: first aid measures, storage conditions, respiratory protection, vapor pressure, three of these, all of these
Probability of happening?
low, heptane was always used in the fume hood
medium, heptane transported out of fume hood, but usually capped in TLC chamber
high, heptane heated, increasing its concentration in the lab air
all of these
medium, heptane transported out of of fume hood, but usually capped in TLC chamber
Heptane Exposure and Probability
Dermal (eyes or skin)
Useful Info in SDS?: LD50 dermal values, persistence and degradability, target organ toxicity results, incompatible materials, three of these, all of these
Probability of happening?
low, heptane was neer poured from one vessel to another
moderate, a small amount of heptane was poured with gloved hands
high, a large quantity of heptane was transferred, no gloves were worn
LD50 dermal values
moderate, a small amount of heptane was poured with gloved hands
Heptane Exposure and Probability
Ingestion
Useful Info in SDS?: advice for firefighters, advice for safe handling, respiratory protection, LD50 Oral values for rate, three of these, all of these
Probability of happening?
low, eating in lab prohibited, use of plastic wrap on computer
moderate, biting fingernails may cause ingestion
high, laboratory procedures may result in exposure by this route
LD50 Oral values for rate
low, eating in lab prohibited, use of plastic wrap on computer
Heptane Exposure and Probability
Injection
Useful Info in SDS?: skin protection, viscosity, hazardous decomposition products, all of these, none of these
Probability of happening?
low, no glass apparatus used in this process
moderate, glass capillaries are small and brittle
high, glassware breakage highly possible with TLC
none of these
moderate glass capillaries are small and brittle
Why is heptane used for the TLC process instead of hexane?
Hexane has more GHS pictograms
Hexane is a reproductive toxicant, heptane is not.
Hexane has a high vapor pressure below room temperature.
Hexane’s flash point is at a lower temperature than heptane’s
Three of these
All of these
Three of these
Which of the following statements apply to green chemistry? (select all that apply)
methods used to eliminate hazards in during chemical use and manufacturing
high yield reactions are desirable
recycle reagents & solvents
choose reactions that can be done at room temperature & pressure
use less hazardous reagents
avoid using catalyst
methods used to eliminate hazards in during chemical use and manufacturing
high yield reactions are desirable
recycle reagents & solvents
choose reactions that can be done at room temperature & pressure
use less hazardous reagents
Which of the following statements about the chemicals or processes in Chem 1LD follow the principles of green chemistry? (Select all that apply.)
Use of starting reagents (eugenol, vanillin, cinnamaldehyde, etc) from renewable feedstocks
Heptane, acetone, and ethyl acetate were recycled as part of experimental procedure
Sunscreen synthesis did not require heat
All syntheses performed had over a 90% yield
Use of starting reagents (eugenol, vanillin, cinnamaldehyde, etc) from renewable feedstocks
Sunscreen synthesis did not require heat
Atom Economy Formula
Molar Mass of Products / Molar Mass of Reactants
What color goes with what caution? What is the pattern for increasing numbers for the NFPA diamond? Label each number!
White? Define OX, COR, Zigzag, ALK, and ACID
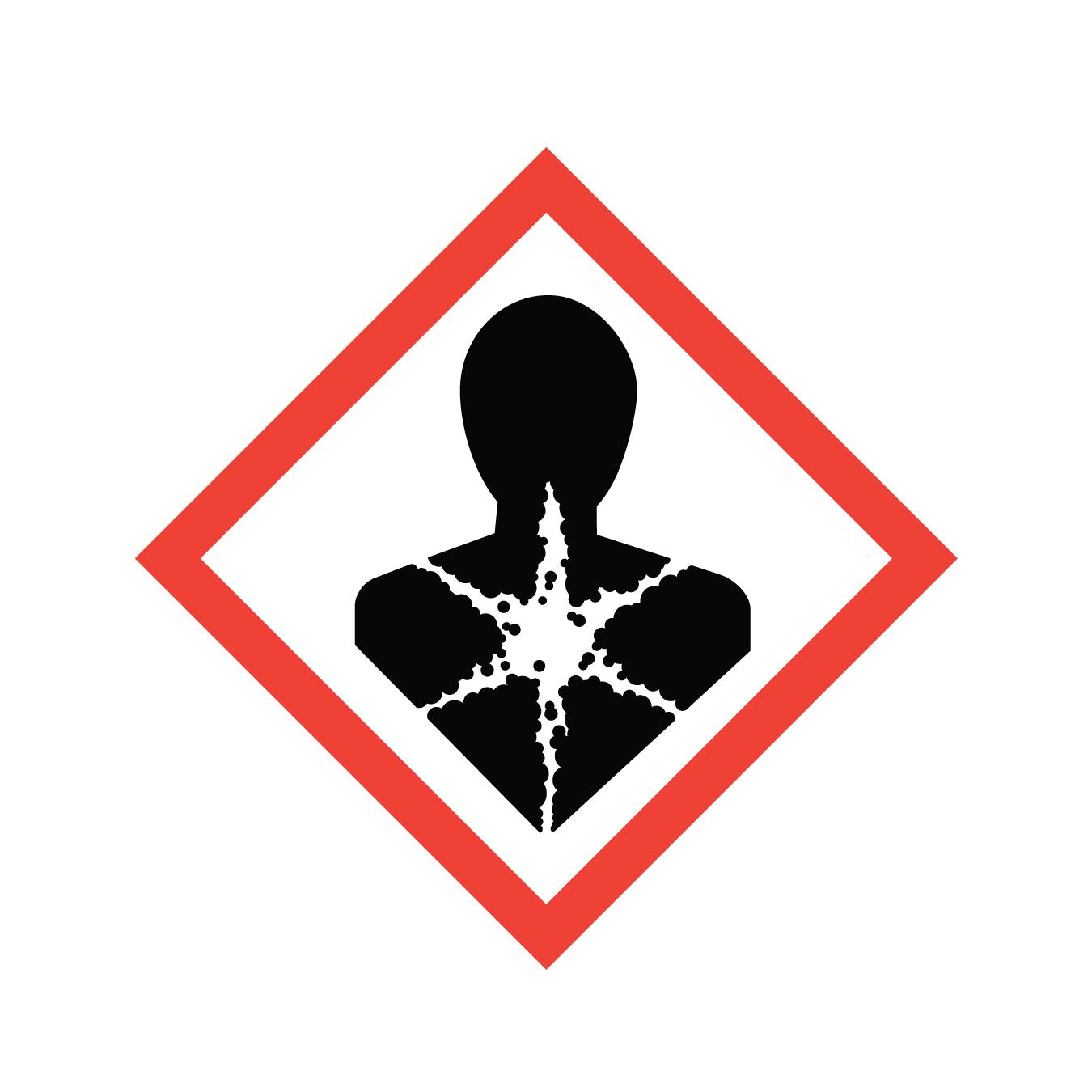


What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Health Hazard: Carcinogen, respiratory, organ, or reproductive toxicity causing damage over time (chronic)
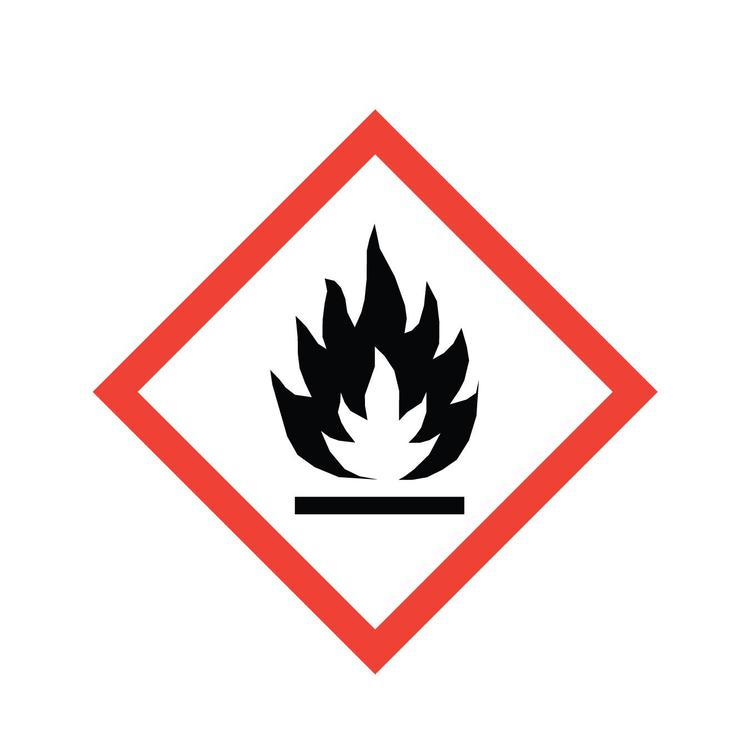

What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Flammable: Self-igniting chemical when exposed to water or air, emit flammable gas. Self-reactive, self-warming
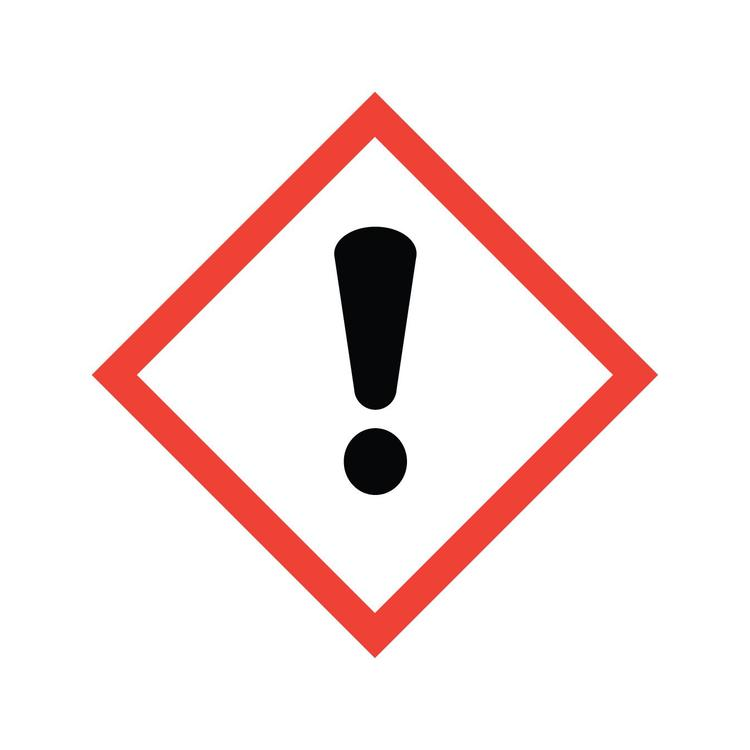

What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Danger: Skin, respiratory tract irritant or narcotic. Skin sensitizer.

What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Gas Cylinder: Gas, liquified gases, dissolved gases stored under pressure
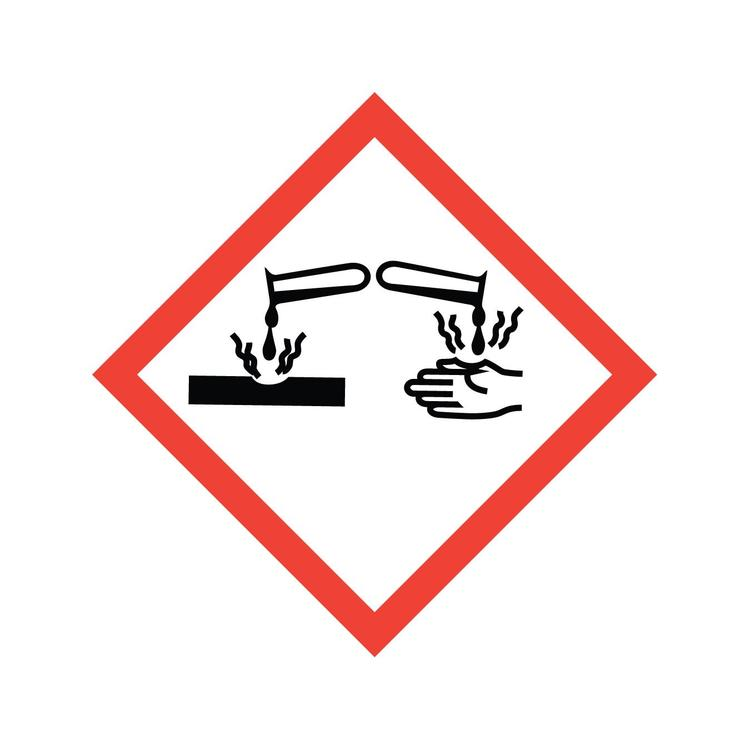
What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Corrosion: Skin corrosion or burn, eye damage, corrodes metals
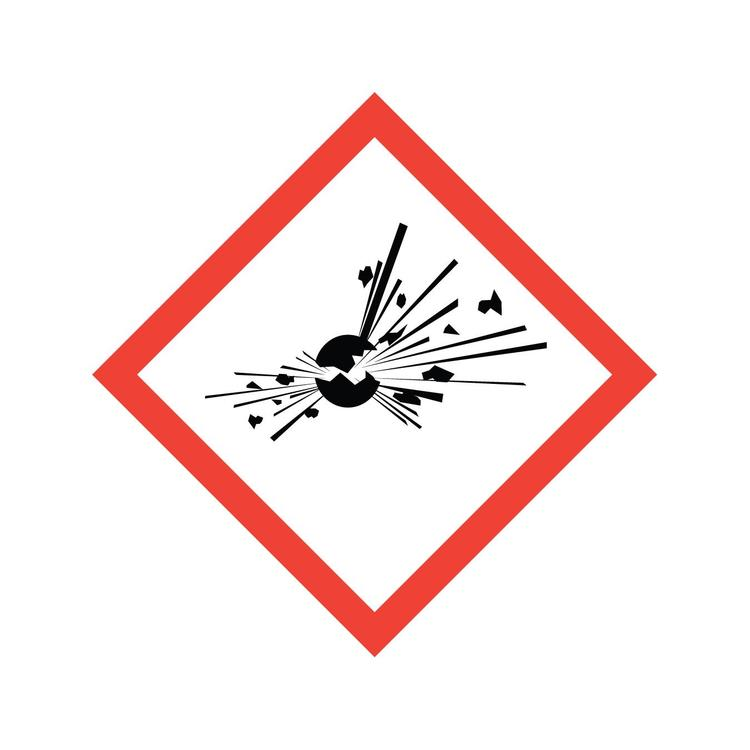

What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Exploding Bomb: Self-reacting even without contact with air, explosives
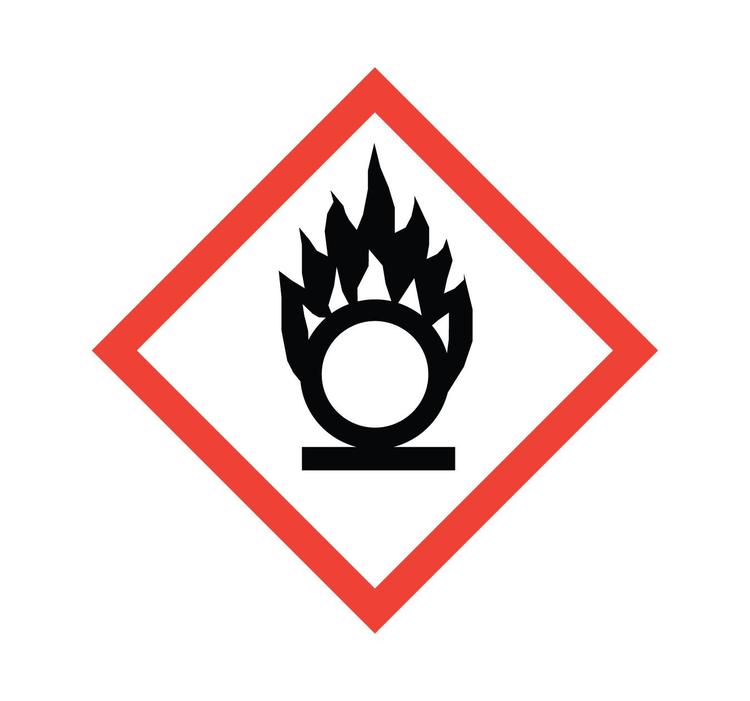

What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Flame Over Circle: Oxidizer, makes fires hotter and longer
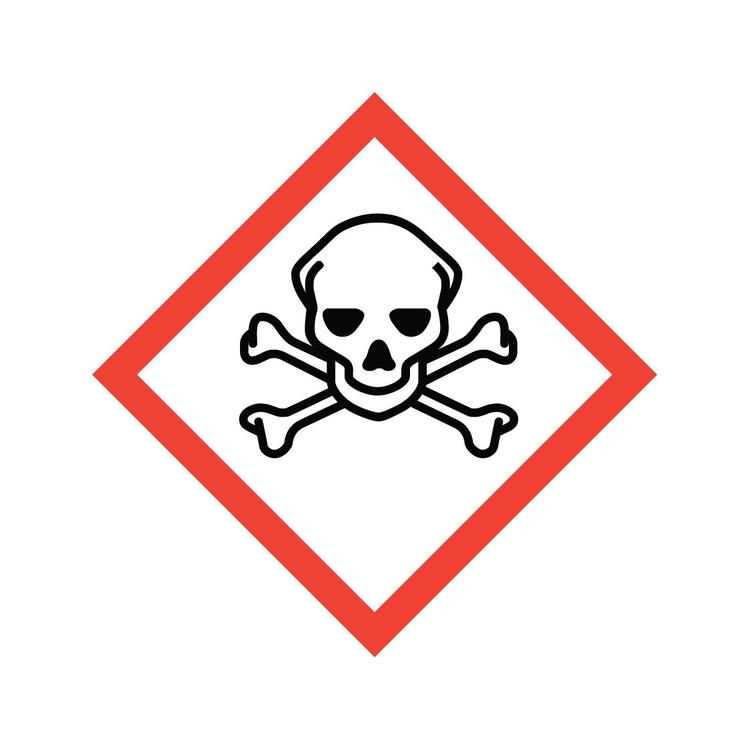

What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Skull and Crossbones: Acute toxicants, poisons, high concentration acids
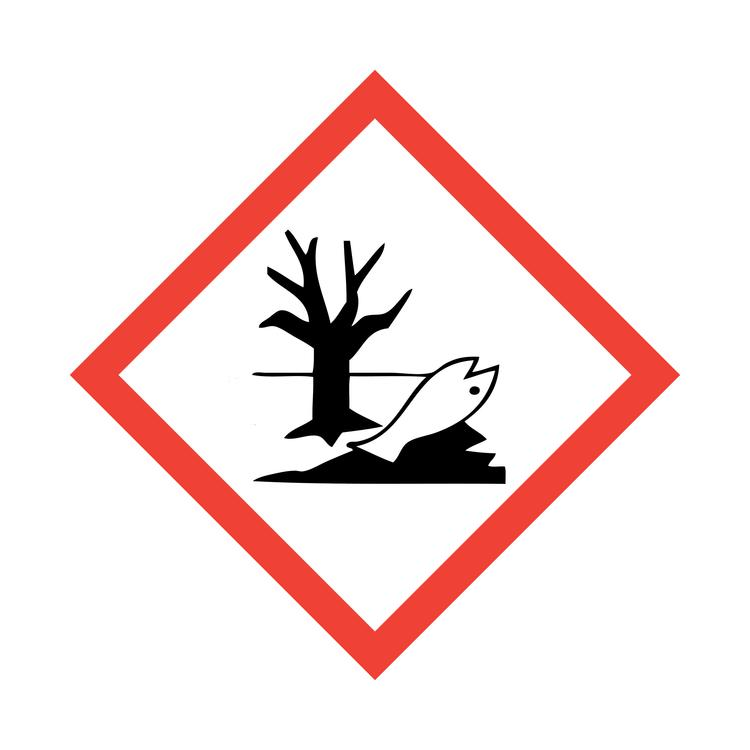

What symbol is this? What does it caution?
Environmental Hazards: Dispose properly, if it hurts the fish it’ll probably hurt you.