U2 Test - Unwin Gov
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the first 3 articles and the main aspects of each? (3-1)
The Legislative Branch: enumerates the powers of Congress and the specific areas in which it may legislate
The Executive Branch: vests the power of the executive branch in the office of the President of the United States, lays out the procedures for electing and removing the President, and establishes the President's powers and responsibilities
The Judicial Branch: establishes and empowers the judicial branch of the national government
Popular Sovereignty/Republicanism (3-1)
The principle that the leaders of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people
Limited Government (3-1)
a system in which the power of the government is limited, not absolute
Seperation of Powers (3-1)
The division of government responsibilities into distinct branches
Individual Rights (3-1)
Also known as natural rights, rights held by individuals by virtue of being human
Checks and Balances (3-1)
Actions from the separated powers to avoid one entity or body wielding too much power
Elastic Clause (3-2)
Clause in Article 1, Section 8, of the Constitution that grants Congress the power to pass all laws necessary and proper for carrying out its enumerated powers
Judicial Review (3-2)
The power of the Supreme Court to declare laws and actions of local, state, or national governments unconstitutional
Enumerated Powers (3-2)
The specific powers granted to Congress by the Constitution, outlined in Article I, Section 8, which include the ability to tax, regulate commerce, and declare war, etc
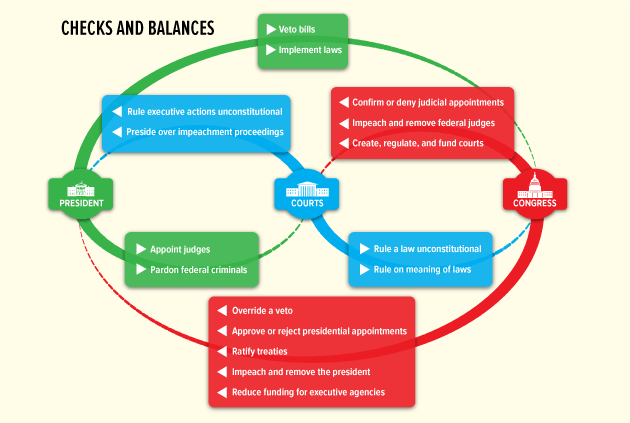
Checks and Balances (chart) (3-2)
1st Amendment (3-3)
Protects the freedom of speech, religion, the press, and making complaints and requests to the government
2nd Amendment (3-3)
Protects the right for Americans to possess weapons for the protection of themselves, their rights, and their property
4th Amendment (3-3)
Protects people from unreasonable searches and seizures by the government
5th Amendment (3-3)
Protects against self-incrimination, meaning an individual cannot be forced to provide evidence or a testimony that could be used against them in a criminal case
10th Amendment (3-3)
States that any powers that are not specifically given to the federal government, nor withheld from the states, are reserved to the states or to the people
Concurrent Powers (4-1)
Powers that both the national government and the states have
Implied Powers (4-1)
Powers the government requires to carry out to carry out its expressed constitutional powers
Expressed Powers (4-1)
Powers directly stated in the Constitution
Reserved Powers (4-1)
Powers that belong strictly to the states
Denied Powers (4-1)
Powers denied to nation and state government branches to maintain balance and fairness
Federal Grants (4-2)
A sum of money given to a state or local government for a specific purpose
Mandates (4-2)
A formal order given by a higher authority
State Obligations (4-2)
Conducting and paying for the elections of all national government officials
Amending the Constitution (when needed)
State Powers (4-3)
Making laws about anything that is not prohibited by the Constitution of national law
Regulate and promote corporations in their borders
Preserve national resources
Make and enforce criminal laws
Protect individual rights
Provide for public health, education, and welfare
Interstate Compacts (4-3)
A written agreement between two or more states
Extradition (4-3)
To return a fugitive who flees across state lines back to the original state