23: soil formation
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what are the six main soil functions?
plant growth medium, water regulation, nutrient recycling, atmosphere modification, habitat for organisms, engineering medium.
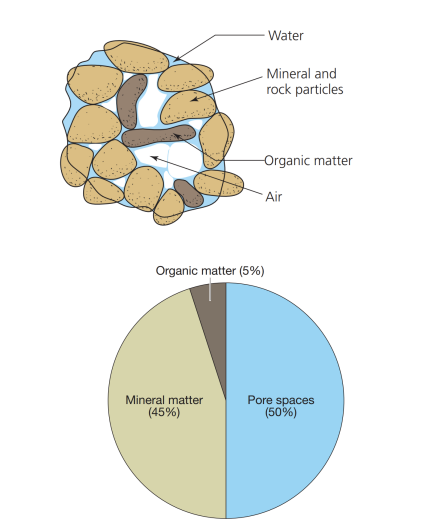
what is soil made of?
minerals, organic matter, water, air, and ~50% pore space.
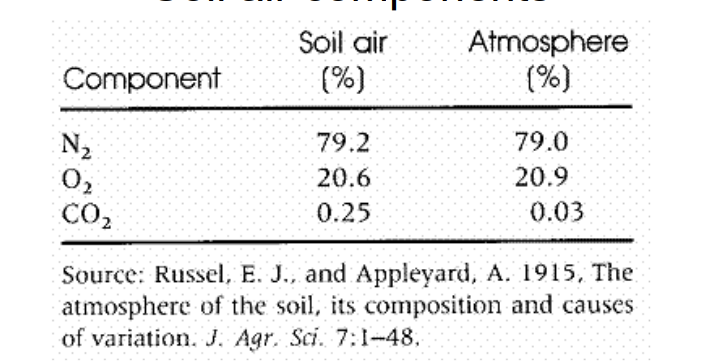
why does soil air have higher CO₂ than atmospheric air?
plant and microbial respiration consumes O₂ and releases CO₂.
what happens to oxygen levels in water-logged soils?
oxygen becomes limited → anaerobic conditions.

how does organic matter affect soil physical properties?
increases water-holding capacity and improves conditions for plants and microbes.

how is soil formed?
through weathering of minerals and rocks by chemical, aeolian, fluvial, or biological processes.
what does the acronym CLORPT stand for?
climate, organisms, relief, parent material, time.
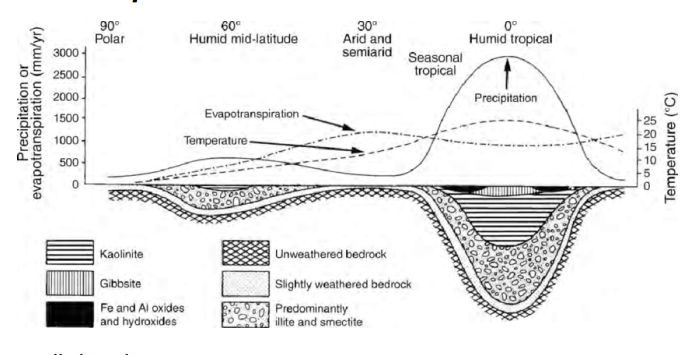
how does climate affect soil formation?
hot/wet climate→ fast development
cold/dry climate → slow development.
higher temperature and water speed up reactions.

how do organisms affect soil formation?
burrowing organisms mix soils and form humus
acidity of organic matter influences decomposition

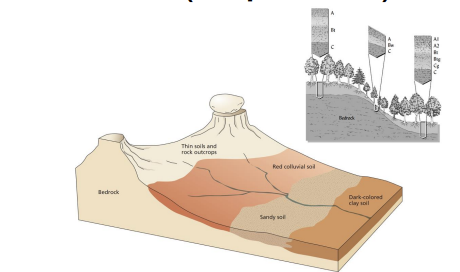
how does relief / topography affect soil?
can slow or speed climate factors
slopes = more erosion → thin soil
valleys = more sediment → thick soil.
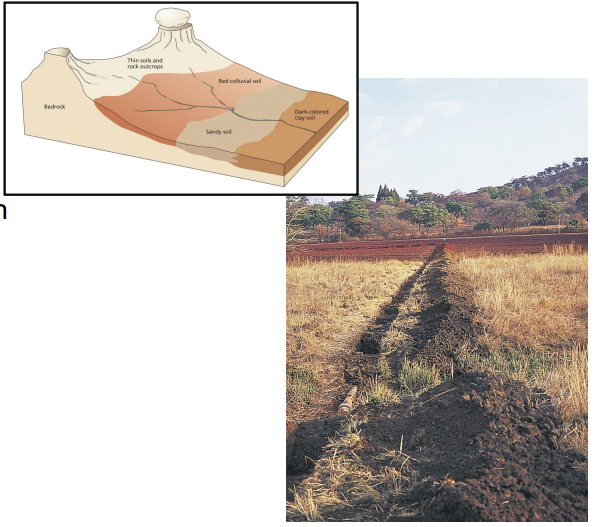
what is a soil catena?
a sequence of soils on a hill where only topography varies.
clay v.s. bedrock

what is parent material in soil formation?
the original geologic or organic material from which soil develops.
black sand beaches with salt
white sand beaches with quartz
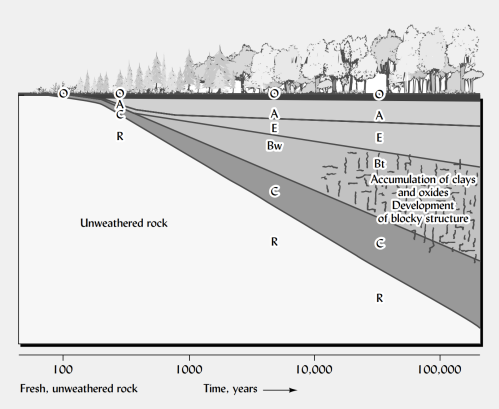
how does time affect soil formation?
more time → thicker, more developed soils. interacts with climate.
what are the four soil-forming processes?
additions, losses (depletion), transformations, and translocation.
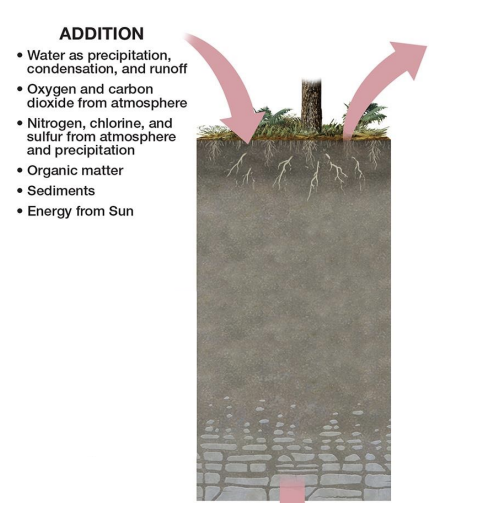
examples of additions to soil.
leaf litter, dead organisms, windblown dust, water, pesticides.
what are losses (depletion) in soil?
removal of nutrients (e.g., nitrate leaching) and erosion of fine particles.

what is transformation in soil?
chemical/physical changes: oxidation of Fe, reduction of Fe/Cu.

what is translocation / soil leaching?
water moves nutrients downward; nitrate washes out easily, ammonium stays.
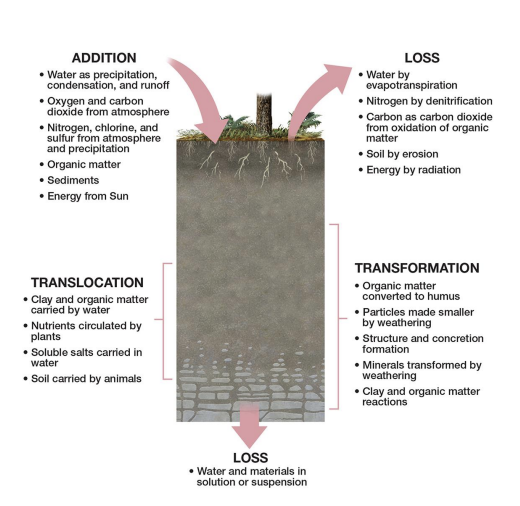
what is translocation?
movement of materials vertically or horizontally in soil by water or organisms.
what is eluviation?
washing out of materials from a horizon (usually E horizon).
what is illuviation?
accumulation of material in a horizon (usually B horizon).
what are the six main soil horizons?
O, A, E, B, C, and R.
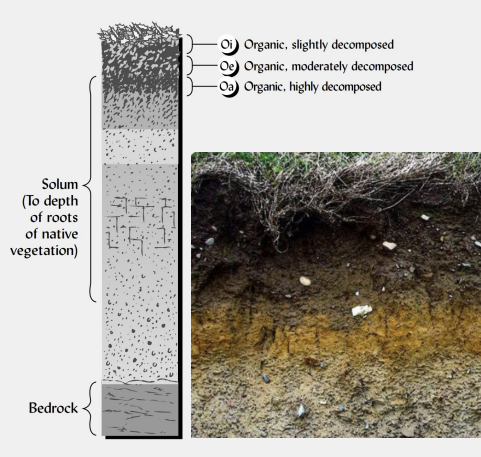
describe the O horizon.
organic, surface layer; dead plant/animal material; “forest floor.”
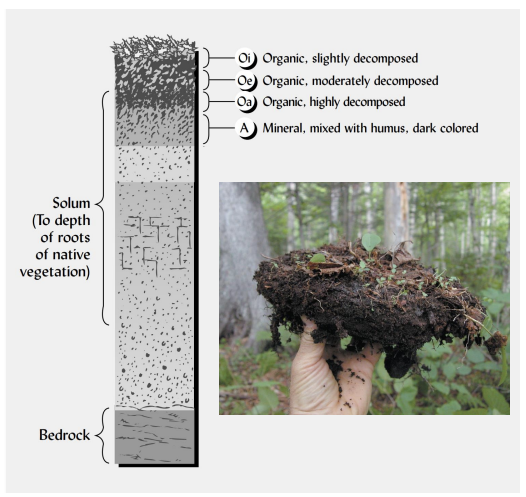
describe the A horizon.
first mineral horizon; contains humus; product of weathering and mixing, course feeling.
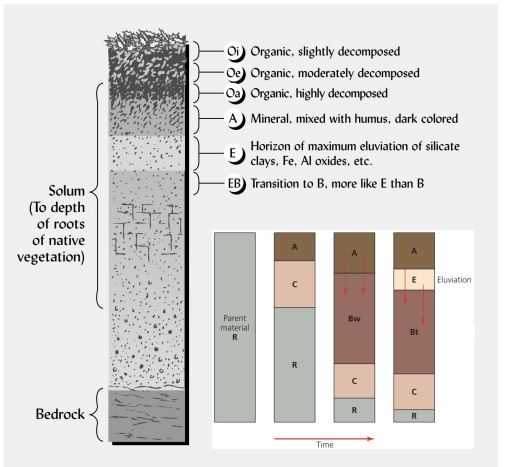
describe the E horizon.
zone of eluviation; light-colored; materials washed downward; forms over time, common in forests
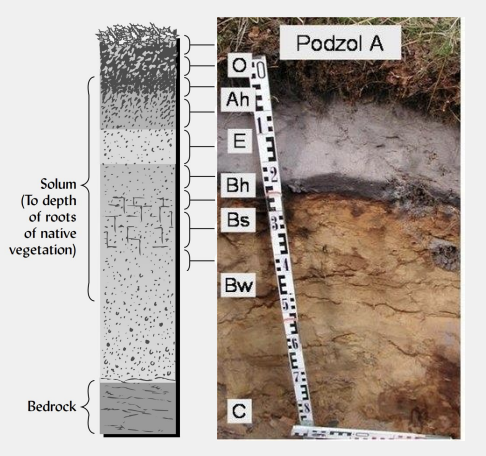
describe the B horizon.
zone of illuviation; accumulates materials; thick in tropics.
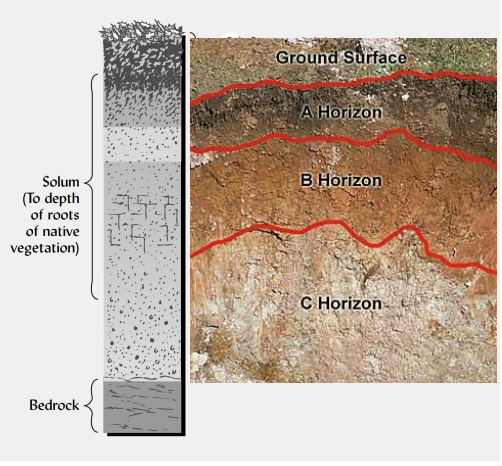
describe the C horizon.
unconsolidated material; loose sediment; resembles parent material.
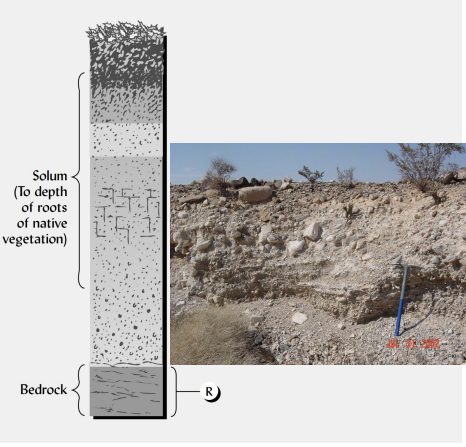
describe the R horizon.
consolidated rock; not soil; may be parent material.
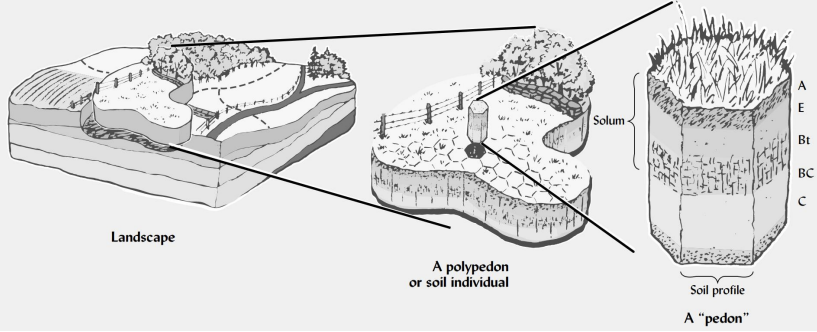
define a pedon and explain why it is necessary.
a pedon is an imaginary 3d soil unit used because soil is heterogeneous; it is the smallest sampling unit that shows all soil characteristics.
a pedon is about 1 to 10 m².
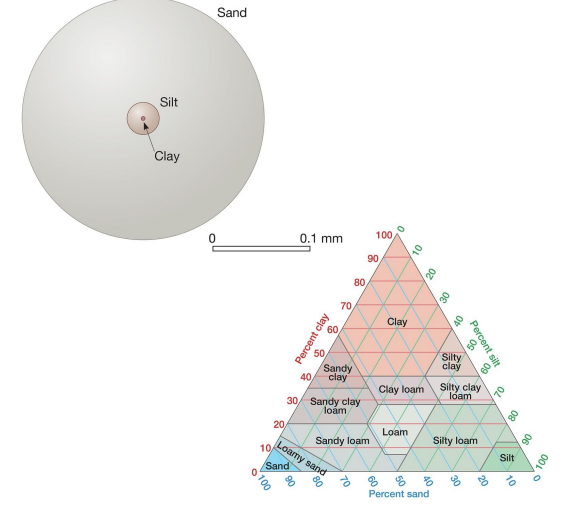
explain the difference between soil texture and soil structure.
soil texture is the proportion of sand, silt, and clay
soil structure is the shape of naturally occurring soil aggregates.
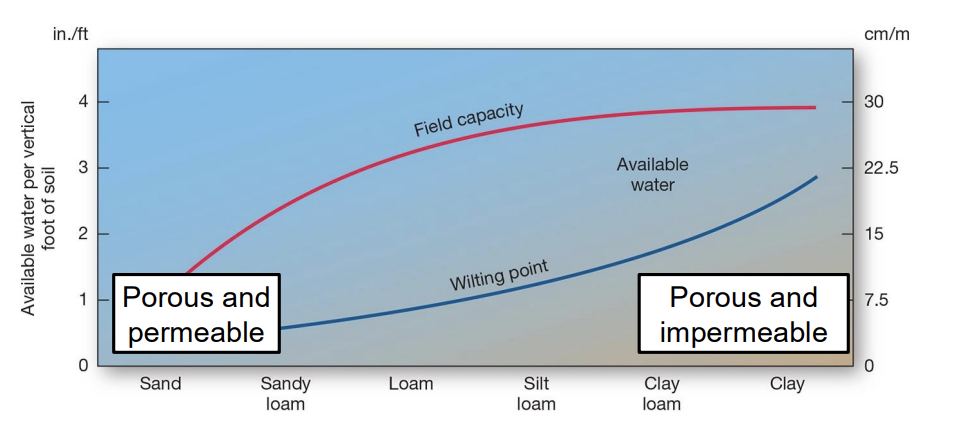
explain why clay-rich soils are often unsuitable for building.
they have very high porosity and low permeability and can expand or shrink, causing instability.
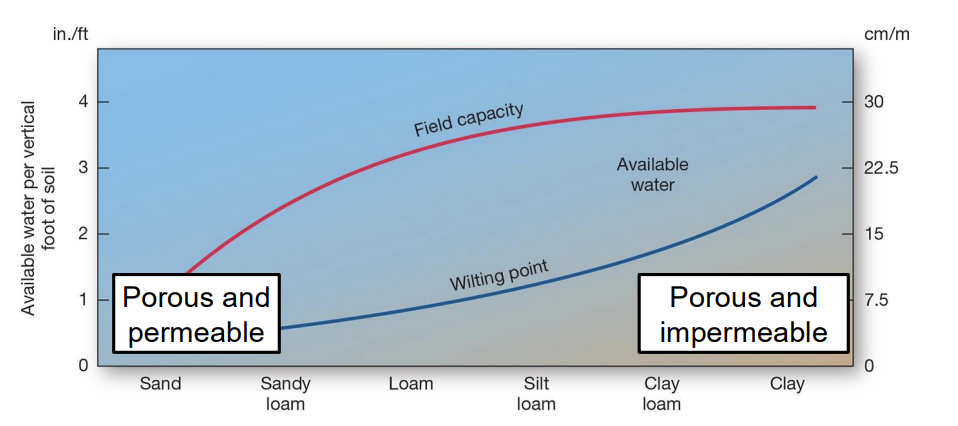
explain why sandy soils are often unsuitable for farming.
they have low porosity and high permeability, so they drain too quickly and retain little water or nutrients.
compare porosity and permeability in clay soils versus sandy soils.
clay soils: high porosity, very low permeability
sandy soils: low porosity, very high permeability.
list the four main soil structure types.
platy, prismatic, blocky, spheroidal.

describe platy soil structure and where it commonly occurs.
thin, stacked aggregates; common in e horizons.
identify processes that cause platy structure.
compaction, freeze–thaw cycles, wetting and drying, or inherited from parent material.

describe prismatic soil structure and where it is usually found.
vertical column-like aggregates; usually in b horizons;
common in arid and semi-arid soils.
shrink swell processes and illuviation

describe blocky soil structure
irregular aggregates that fit together
shrink-swell processes and biological activity

describe spheroidal soil structure and the two subtypes.
small, nearly round aggregates; granular (porous) and crumb (very porous).
produces by biological activity which is common in a horizons
list factors that influence soil color.
soil chemical and physical properties.
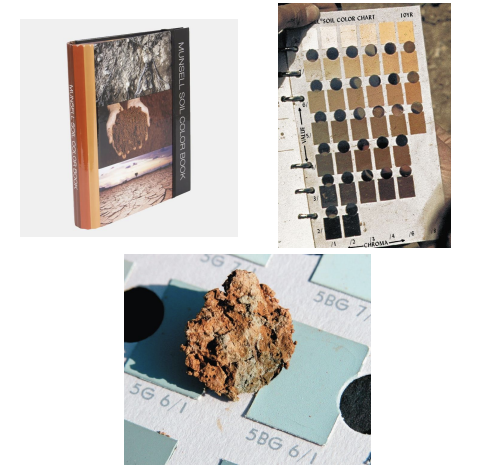

describe how the munsell color chart is used to determine soil color.
select the page with the correct hue, find the closest matching chip, and record the number (e.g., 5yr 6/6).

red soils indicate
oxidized conditions and abundant clays
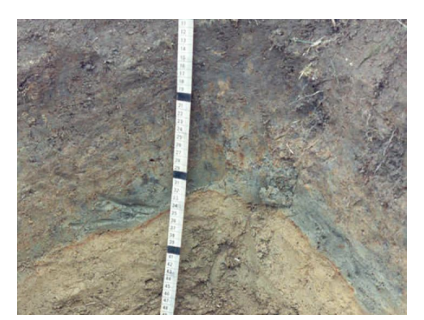
gray/blue soils indicate
reduced conditions

dark brown soils are
rich in organic matter

light gray or white soils contain
calcium and magnesium carbonates

yellow-brown or organic soils
indicate the presence or iron compounds