BU111 Final
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Canadian Population
37.74 million
Life Expectancy
83years
Median Age
40.8
People per hosuehold
2.5
Median household income
$61,400
Smartphones in population
86% of population
Online Shoppers
28.1 million people
Urban Population & Major Cities
81%
Toronto, Montreal, Calgary, Ottawa, Edmonton, Vancouver
Market Segmentation
15-20% are low end
60-65% average
15-20% high end
When to use Population
- Units driven by serving population in geographic area (ie stores)
- Market size/share
- Revenue
- Profitability
- Supply
- Saturation
- Competition
When to use Household
- Calculate consumables (ie hoses vs sock)
- Market size/share
- Revenue
- Profitability
When to use Proxy: Stores
- # of stores in an area; Population/Store
- Company Revenue/Profitability
- Market Size
- Profitability
- Supply
- Saturation of Market
Market Sizing (Estimation)
- Total Addressable Market; every possible consumer that might buy your product that you can reach
- Serviceable Available Market; consumers that are most likely to buy your category of product (target market, size of your segment)
-Serviceable Obtainable Market portion of the SAM you think you can win (market share)
Four Pillars of Canadian Financial System
- Banks
- Alternate Banks
- Specialized Lending/Saving Intermediaries
- Investment Dealer
Chartered Banks (4 Pillars)
Purpose
- Make deposits
- Borrow
- Banks biggest source of revenue is lending
Who Uses it
- Small and medium enterprises' primary lending source
- Lend only, will not buy equity
Alternate Banks (4 Pillars)
- Trust companies & credit unions
Purpose
- Make deposits
- Borrow
Who Uses it
- Small and medium enterprises' lending source
- Go here when they are unable to attain a loan from the chartered banks
Specialized Savings and Lending Intermediaries (4 Pillars)
- Insurance Co, Venture Capital Firms, Pension Funds
Purpose
- Private equity financing/borrowing
- Don't want to be public so saves cost
- Might have shares sold privately
Who Uses it
- Medium to large firms/ enterprises
- Must be relatively large, good track record (millions) before they lend to you
Investment Dealer (4 Pillars)
- Primary/Secondary Market
Purpose
- Going public (stocks and bonds)
- IPO when shares are sold public
- Access to larger amount of money
Who Uses it
- Large and Established enterprises that want to raise lots of many
Bond
- Debt financing (borrowing money but retaining control)
- Represents debt for issuing corporation or government
- A company/govt borrows money from you (investor) and they pay interest each year and pay off the debt on an agreed date
Bond Characteristics
- Legal, binding agreement
- Price at which the bond is bought
- Fixed annual return that is often paid semi annually (Coupon rate/interest)
- Fixed term; principal repaid at maturity (Maturity date, when face value is paid)
- Issuer (company borrowing the money)
- Has priority over stockholders
- Ex: Starbucks 4.6 of 2022 at 97.24
- Assume face value is $1000
Relationship between Interest Rates and Bond Prices
- If economy interest rates go up the yield will increase so you expect to pay more so that yield=econ interest
- Reverse when yield is less than economy interest rate
- The price paid is the only thing that you can change
- Higher yield = economy interest rate + risk premium
- Yield should be same for all bonds of equal risk
Factors Affecting Price
- Inflation/ deflation
- Interest rates
- Employment rates
- Exchange rates
- Affect consumer spending, export opportunities, human resource availability, input costs
Inflation/Deflation
- Rate at which prices are increasing or decreasing
- Inflation is expected
- Consumers don't have as much buying or purchasing power so demand for good might go down
- If input costs suddenly go up, there was no time to think about it, less planning is involved and it's more of a reaction
Interest Rates
- The cost of borrowing
- Consumers and businesses borrow
- If rates go up it becomes harder and more expensive to borrow
- If rates go up the demand for products go down because people can't afford loans or stuff to sit on credit cards
Employment Rates
- Number of people unemployed in a region, people who are actively looking for work
- Consumer's don't have as much money to spend
- High unemployment rates make people nervous so everyone is cautious of spending since their afraid of losing their jobs
- With low unemployment rates companies have hiring issues which will drive up the cost of labour
Exchange Rates
- Value of the CAN dollar
- When CAN$ goes up in value compared to other currency you're dealing with it is then cheaper to buy that stuff and importers are happy
- When CAN$ goes down anyone who exports is unhappy because it makes it cheaper for other to buy CAN goods
Yield
- Yield = What you made/ what you paid
- What you made; interest, capital gain, dividends, profits
- What you paid; investment
- Yield = risk free return (interest rate) + risk premium
Approx Yield to Maturity (Bonds)
= (annual bond interest + annual capital gain)/ price paid for bond
= [(coupon rate x face value) + {(face value-price paid)/years to maturity}]/price paid
Bond Quotes
SunLife 5.3 of 2021 at 91.75
- SunLife is company borrowing the money
- 5.3 is coupon rate, % of face value paid semi annually
- 2021 is maturity date when borrower pays back face value
Stocks
- Represents equity/capital for issuing company
- Give up part of profits and control
Stock Characteristics
- Voting rights
- No fixed term
- Variable return (capital gain when selling)
- Discretionary payment (dividends)
- Higher risk than corporation's bond
Stocks vs Bonds (Company)
Repayment
- Not required (stock/ equity)
- Principal paid on maturity date = increased risk (bonds/ debt)
Claims on Income
- On residual claim ie dividends (stocks)
- Yes, regular, required, fixed is coupon= increased risk (bonds)
Affect on Management Control/ Ownership
- Dilutes ownership and control (stocks)
- None (bonds)
Tax Effects
- Dividends are not tax deductible (stocks)
- Interest paid to bondholders is tax deductible (bonds)
Stocks vs Bonds (Investor)
Repayment
- No (stocks)
- Principal paid on maturity (bonds)
Income
- Dividends but discretionary (stocks)
- Coupon/ interest is required (bonds)
Claims on Assets in Liquidation
- After all other creditors are paid, after bondholders, preferred stocks are ahead of common (stock)
- Along with other creditors and before stockholders (bonds)
Ownership/voting rights
- Yes common votes, preferred does not (stocks)
- None (bond)
Risk and Price Volatility between instruments of same company
- Higher (stock)
- Lower (bond)
Margin Buying
- When you borrow some money to invest from your broker
- Max profit is infinite (less interest and commissions)
- Max loss is price paid for stock plus interest and commissions
- Risks and costs; interest expense, margin calls
- Money paid on a margin call is used by broker to reduce your loan
Rules
- Must qualify for margin account
- Must sign 'hypothecation' agreement (Margin Account Agreement Form) where you pledge securities as collateral for the loan
- Must pay interest on loan
- Investors % equity (margin) in the margined stock must always be >= min margin requirement
Minimum Margin Requirement
(Current Market Value - Loan)/ Current Market Value >= % margin requirement
Going Long
1. Money made from sale of shares
2. Less money paid from purchase of sales
= money from sale
3. Less 2% purchase commission
4. Less 2% sales commission
= Capital gain
Buying on Margin
1. Money made from sale of shares
2. Less total amount paid for shares
= money from sale
3. Less 2% (pc)
4. Less 2% (sc)
5. Less interest (amt broker lent x interest x time)
= Capital gain
Margin Call
- Find Current Market Value (amt of shares x value)
- Find current margin using min margin formula
- Replace loan in formula with (x) and current margin with margin requirement and then solve for (x)
- The difference between loan and (x) is the amount you must pay back to the broker
Stakeholder & Importance
- Also the 5 areas of CSR
- Employees
- Customers
- Investors
- Environment
- Society
- To satisfy one stakeholder it may take away from other stakeholders
- Challenge is the conflicting or varying expectations and Balance depends on CSR approach
Employees (stakeholder)
- Expect; fair pay, safety, respect, development
- Provide; Operations
- Employees want to know that they can progress their careers
- Actions a business can take; employment benefits, responsible hiring and promotion
Investors (stakeholder)
- Expect; honesty (accurate financial statements, how money is used), fair return (ROI), representation (their interest are taken into consideration)
- Provide; funds
- Allows company to grow as an organization
- Actions a business can take; focus on long term return on investment
Customers (stakeholders)
- Expect; respect, safety, value
- Provide; revenue
- Actions a business can take; avoid adverse actions, safe products, fair pricing, ethical advertising and brands
Environment (Stakeholder)
- Expect; responsible production & products
- Provide; natural resources
- Think about how you produce and what you produce
- Govt has started to protect environment because society cares about it
- Protect the environment and it will give back
- Actions a business can take; protect it through environmentally friendly practices
- Importance; provide resources to the business, shift in societal attitudes
Society (stakeholders)
- Expect; education, health and employment
- Provide; employees and customers
- Company must care about society because if people are healthier and more educated they are more likely to be productive as employees and customers are more likely to spend
- Actions a business can take; give back to society (bell let's talk), social entrepreneurship
- Importance; affect human capabilities, societal attitude shift, diffuse the issues of social decay
CSR
- Corporate social responsibility
- How you treat stakeholders + how you balance stake holders demand
- Management decides CSR based on their own values & attitudes
- We can see it as part of the Diamond-E in strategy
Focusing on CSR
Make Environment Manageable
- Unpredictable or hostile
- Focusing on CSR makes environment less hostile and more friendly
- Provide capacity to operate; when you treat stakeholders right they make it possible for you to succeed
- Aligns with Environment; demographics, world is changing and it's expected
Avoids Adverse Actions; increases support by stakeholders, ie wedding venues that kept deposits despite Covid are more likely to face lawsuits or union strikes
- Promotes Favourable Legislation; when you are proactive and increase CSR at some point you may set a stand that the govt will make others do the same, ie A&W with paper straws
Meet KPIs
- Improves profitability; differentiation and brand differentiation
- Improves trust & loyalty of customers, employees & investors
- Promotes operating efficiency
- Encourages continuous improvement & innovation
4 Levels of CSR
- Proactive
- Accommodative
- Defensive
- Obstructionist
Proactive (4 levels)
- Seek opportunities
- Don't wait to be invited or asked
- Goes above & beyond what the law requires and not in response to anything
- Chose to do this without being asked
- Ex; bell let's talk campaign
- Ex: Starbucks workers make more than min wage
Accommodative (4 levels)
- When requested
- Will go above and beyond law but only when requested
- Key between accommodative is that you are fist asked and it's not your own idea
- Ex; someone to bell and asks them to donate to homeless shelters
Defensive (4 levels)
- Legally required
- Respect the law and its purpose
- Ex: law says do not pollute so you don't
Obstructionist (4 levels)
- Bare minimum
- Operate in the grey area possibly illegal
- Ex: Covid mask, people who do not have a legit reason for not wearing one are saying they have a health condition that prevents them, even if they don't
- Ex: law says you can't dump garbage in lake so they dump in the river but the river feeds into the lake
Demographics
- Study of human populations
- Cohorts; homogeneous groups within the larger population
Demographics Importance to Businesses
- Powerful predictor of behaviour/ trends
- Certainty and simplicity of data
- Predicts supply and demand and informs environmental analysis
and human resource decisions
Canadian Population Distribution (Demographics)
- Should be pyramid but there is a bulge at boomers
- Labour force; fever incoming than outgoing
- Economy; fewer supporting pensions
- Market for children of boomers is relatively large
- Move back; more disposable income because parents provide essentials
- Implications; increased elder care needs, increased number of vulnerable seniors, Echo has greater market impact, increasing strain on pension & healthcare, potential labour shortages
Ethnic Composition (demographics)
- Immigration increasing over past decades
- Immigrants younger and more likely to live in city than average Canadian
- Implications; many consumers having difficulty interacting with marketplace
Canadian Households (demographics)
- One person households greater than one-family households
- Driven by the fact that people don't get married as much and the ideals were not the same as they were in the past
- Implications; lost economies of scale in living (shopping), families face time constraints, people share things which reduces costs for the buyer but reduces profits for the company
Geographic Distribution (demographic)
- Shrinking rural communities (Atlantic Canada, Saskatchewan, Territories)
- Increasing urban concentration
- Donut effect (people live around the centre of the city)
- Implication; affects median age in rural areas and access to goods and services
Cohort Characteristics
Economics
- Characteristic; values & priorities
- Implications; how to attract, retain and motivate
Technology
- Characteristics; lifestyle
- Implications; what makes product appealing
World Events/ News
- Characteristics; habits (digital & other)
- Implications; how to attract consumers
Parenting
- Characteristics; mindset
- Implications; how much they spend and what they spend on
Government influence over Business
Service Provider
- Impacts competition and social goals
- Ex: Canada Post competes with Purolator
Business Supporter
- Offers subsidies
- Trade agreements
- Impacts opportunity and protection
- Ex: Govt subsidies green tech to promote environmental friendliness
Laws and Regulations
- Approach; competition, consumer, pollution law, IP rights (motivates innovation)
- Impacts competition, consumer protection, innovation, social goals, barriers
Taxation
- Govt income
- Income, sales, property, restrictive
- Restrictive taxes get added to certain tings to discourage their use, aka sin takes (ex cigarettes)
- Taxes affect consumer spending bc increasing income tax leaves less disposable income
Connection to 5 Forces (govt roles)
- Govt can increase or decrease barrier to entry which could increase or decrease intensity of rivalry and threat of new entrants
- Length of contract for cell services (bell/ roger) would increase or decrease buyer power depending on change
- Tariffs on steal means less suppliers to negotiate with, better agreements means more suppliers
Business Influences Government
- Lobbying
- Collaboration/ Input
- Advertising
Lobbying (Business Influences Government)
- Hired to rep company's/group's interest
- Usually or used to be tied to govt in some way which is why they are able to lobby
- Must disclose the fact you are a lobbyist and that you are lobbying on behalf of a comp so that who you approach knows who you represent
- Lobby Act means you must register and follow the rules
- Trade Associations; small business/individuals join and lobby as an industry lobby group
- Means that you don't need to hire someone else
- You have more people and funding you would be able to lobby the govt through trade associations
Collaboration/ Input (Business Influences govt)
- CRTC consults with industry members
- Canadian Radio and Telecommunication Commission consult with companies in an industry about policies and regulations
Advertising (business influence govt)
- Corporation influence voters
- Ex: contract locked for 3 years so govt (CRTC) considering changing contract to 2 years, Bell/Rogers made ads saying contracts of 2years would be bad so that consumers reach out the govt officials saying they don't want the new govt policy
Forms of Ownership
- Sole proprietorship
- Partnership
- Corporation
Sole Proprietorship
- Owners and business on entity
- No distinction between personal and business assets & liabilities
Owners
- One
Ease of Formation
- Simple
- Inexpensive
Regulations
- Few
Control over Profits and Decisions
- Complete
Resources & Capabilities
- Whatever owner brings
Taxation
- Taxes as personal income (advantage if business has losses)
Liability
- Unlimited
Parntership
- Owners and business on entity
- No distinction between personal and business assets & liabilities
Owners
- 2 to 50 or 2+
Ease of Formation
- Simple
- Inexpensive
- Optional partner agreement
Regulations
- Few
Control over Profits and Decisions
- Shared
Resources & Capabilities
- Slightly more
- More partners= more resources
Taxation
- Taxed as personal income but shared amounts
Liability
- Unlimited except if limited partner
Types of Partnerships
General Partnership
- Active in running business
- All partners have joint and several liability
- Joint liability; together share liability
- Several liability; 1 may be liable for all
Limited Partnership
- Limited partners liability is equal to their investment
- Cannot be active in management
- Must be at least on general partner
Corporation
- Separate entity from owners (shareholders)
- Types; public (starts with IPO), private, crown
Private Corporation
- Corporation separate entity from owner(s)
Owners
- 1 to 49
Ease of Formation
- Slightly harder
- Still straightforward
- Relatively inexpensive
Regulations
- Slightly more but still simple
Control
- Profits and decisions shared with other shareholders
Resources & Capabilities
- Whatever owners bring
Taxation
- Taxed separately from shareholders
- Lower than personal income tax rates
- Potential for double taxation (dividends are first taxed with business and then on personal income if collected)
Liability
- Limited to investment except personal assets brought into the business
Public Corporation
- Corporation separate entity from owner(s)
Owners
- Unlimited
Ease of Formation
- Expensive
- Complicated
Regulations
- Many
Control over Profits and Decisions
- Board of directors makes decisions
- Less control
Resources & Capabilities
- Can afford to buy them
Taxation
- Taxed separately from shareholders
- Slightly higher than private
Liability
- Limited to investment
Social Enterprise
- Generate social value while operating with the financial discipline, determination & innovation of private sector businesses
- Point of social enterprise is focuses on addressing aps in market, market failure, no profits to be made in solving that problem so no for-profit business with bother
- Ex: education, healthcare, environment, poverty
- Social value is primary objective but financial sustainability is imperative
- Implications; economic value not required priority, dual stakeholders (those served & supporting, one or both pay)
Similarities & Differences (Social Enterprise)
Value Definition and Financial Priority
- Financial ROI, finances primary (TE)
- Social ROI, Financial Sustainability only (SE)
Social Benefit Focus
- Secondary (TE)
- Primary (SE)
Who they Serve/ Stakeholders
- Paying customer & investors (TE)
- Underserved populations, can't afford/ access service, supporters/ investors (SE)
Organizational Form
- For profit (TE)
- Various forms (SE)
Globalization
World becoming single interdependent system
Globalization Forces
- Cost and market benefits
- Tech makes it easier, faster, cheaper
- Competitive pressure
Globalization Decision Components
Can We?
- Do we have the basics to consider it
- Can we make needed changes?
- Do we have min resources & capabilities needed?
- Can our HR take on the extra work
- Do we know anything about selling abroad?
- Do we have money to pay for expertise, advice and services?
- Use Diamond E internal
Should We?
- Is there demand for our product?
- Is it worth going?
- How much do foreign consumers spend on this type of product?
- Is there room for us?
- What's the ROI?
- How much do consumers spend on this globally?
- Are we better off trying to grow at home?
- What lifestyles, income, habits does this align with?
- How much we change?
- What's the ROI on the strategy
- Use Diamond E external
Where?
- Where is the best opportunity?
- Compare countries; demand, competition, trade barriers, familiarity, distance
- Use PEST or Porter's
How?
- How to do it, tactical strategies
- Sales, marketing, production, distribution
- It's strategy of Diamond E
Country Comparison (Where to expand)
Population
- Large means large market segment
- More = better
Average Spending
- Average income or high spending on this type of product
- Have money & spend it on our product
Customer Reachability
- No lock in, dominant habit or brand
- Physical reachability
- Can be persuaded
- Able to switch
- Can easily get the product
Competition
- Little
- No one addressing your niche fragmented
- No dominant player
- Opportunity to differentiation
- Uncontested market is easy to win
- Competitors won't or can't shut you out
Liability of Foreignness
- Cultural distance of customers and doing business
- Existing networks & capabilities
- Bigger differences = greater risk
- Must learn to design product, reach & win customer, build distribution network
Distance
- How far do I have to ship or move?
- Further = more costs
Administrative Barriers
- Importing bureaucracy
- Trade barriers
- Lots of regulations
- More time, more hassle, more change, more barriers
Foreign Entry Strategies
- Indirect export
- Sales agent or distributor
- Licensing/ franchising
- Alliance/ joint venture
- Local sales office
- Foreign subsidiary
Indirect Export
- Sell to a 3rd party export merchant in own country
- Export company identifies where to sell and takes care of shipping and obtaining payment
Why Use It?
- No additional cost
- No market knowledge, export experience or new infrastructure needed
- No risk from foreign market political volatility
Risks/Costs
- No customer contact
- No control over destination
- No control over pricing
- Promotion or foreign distribution strategy
Capabilities and Resources Needed
- None
Sales Agent or Distributor
- Hire an agent or distributor to sell you product using their local network and you manufacture domestically and ship abroad
Why Use It?
- You aren't familiar or have the network resources to easily tap into the foreign market
- Limited understanding of foreign market
Risks/Costs
- Share attention with other organizations
- Limited marketing control
- Subject to trade barriers
Capabilities and Resources Needed
- Manufacture in sufficient quantity to satisfy agent/distributor
- Adjust product
- Some understanding of foreign market and exporting
Licensing and Franchising
- Giving local organization the right to use your intellectual property (brand, patent, copyright) in exchange for royalties
- Another company produces goods or services using your intellectual property in exchange for royalties
Why Use It?
- Faster and larger expansion with fewer financial resources
- No need to understand market, export, produce, distribute, etc.
- No need to overcome trade barriers or acquire additional resources
Risks/ Costs
- Damage to intellectual property
Capabilities and Resources Needed
- Intellectual property of value that other company can't easily acquire
Joint Venture
- Partner with local firm for mutual benefit
- Partnership can take many forms (mutual distribution, sharing of knowledge, investment)
Why Use It?
- Political or trade barriers
- Overcome market barriers with lower investment or risk
- Overcome production constraints
Risks/ Costs
- Time, personnel, money
- Partnership doesn't work, partner doesn't deliver, doesn't deliver as expected or promised or is difficult to work with (incompatibilities)
- Not easy to break up
Capabilities and Resources Needed
- Something of value for partner
- Capability to negotiate
- Supervise and work in partnership
- Resources as determined by partnership
Sales Office
- Establish your own sales office but manufacture in your domestic market and ship abroad or contract with local manufacturer
Why Use It?
- Retain marketing control
- Insufficient volume to justify facility
- Have excess capacity in domestic facility
- Don't have resources to build foreign facility
- Don't want to take risk (yet)
Risks/ Costs
- Trade barriers
- Market knowledge
- Investment to establish foreign sales capabilities
Capabilities and Resources Needed
- Understanding of foreign market
- Ability to pay for an supervise foreign office
- Investment in foreign office
- Ability to modify product
Foreign Subsidiary
- Manufacture and sell in foreign market
Why Use It?
- Overcome trade barriers
- Control of IP and marketing
Risks/ Costs
- Cost of facility and establishment of operations
- Sometimes need permission of foreign government
Capabilities and Resources Needed
- Sales volume justifies investment
- Understanding of foreign market and access
- Distribution capabilities
Choose by Applying Diamond E (Expansion strategies)
Management Preferences
- Risk tolerance; do you prefer to enter carefully, test, learn and expand or do you want to enter assertively to capture market quickly and significantly
Organization
- Foreign trade experience; know, can and have time to navigate the bureaucracy?
- Market knowledge & network; how well do you understand the foreign market? do you have existing or easily accessible distribution and/or supplier relationships?
- Management capability & organizational structure; do you have the capacity and knowledge to manage a foreign operation? Are you organized to execute well?
Resources
- Sales volume; large sales expected abroad? Excess capacity at home?
- Intellectual Property; do we have a brand or operational knowledge that is valuable abroad? an we protect it if we license?
- Financial, HR, resources; what capacity and knowledge does your HR have? do you have the money to commit to a more expensive strategy?
Ansoff Matrix
- Growth powered and motivated by revenues
- Summarizes growth options
- Want to know if they can grow
- Devise and distinguish
- Each move into a new quadrant increases risk
- Related Tools; diamond e, porter's, international expansion content
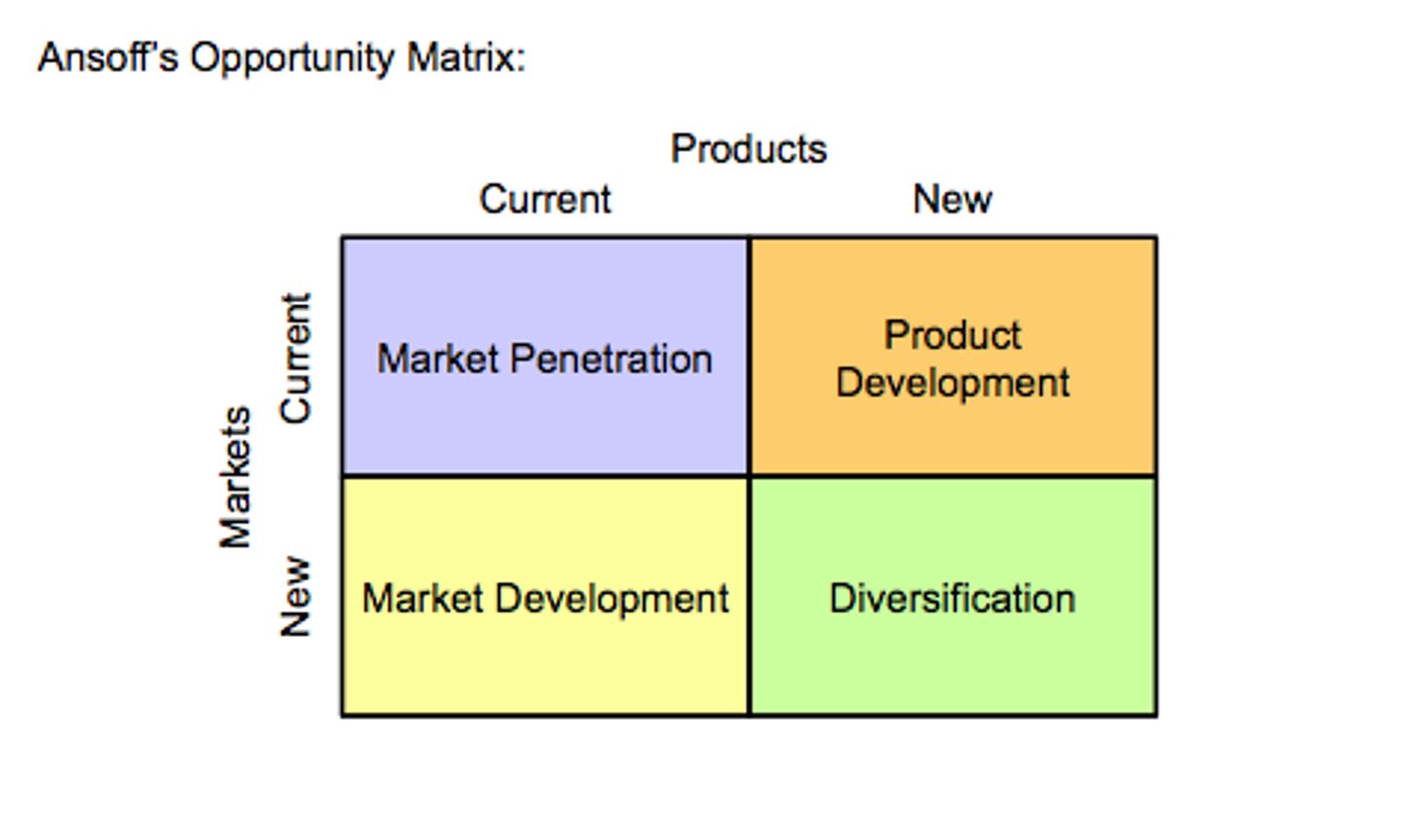
Market Penetration
- Existing product, existing market
- More of the same thing
- Sell more of existing product to existing target market = greater market share and/or greater purchase frequency
- KPI; increase market share
- Lowest risk
- Ex: Instead of customers buying 1 coffee per week get them to buy 5 per week
Why Do It?
- Build on what you have an know, no change
- Economies of scale in production and selling
Challenges
- Competitor reaction
- Winning customers
Tactics
- Cut prices
- Increase advertising, loyalty schemes
- Increase distribution channels
- Volume incentives
- Buy a competitor
Market Penetration Questions
- If I decrease price will volume compensate for lower price?
- Will lower price affect brand image?
Diamond-E
- Can I persuade customers to consume more of my product?
- Do I have to use new distribution channels? Should I? Can I?
- Do I have the production capacity to meet the increased demand?
Porter's
- Buyers; Propensity to switch? Lock in/switching costs? Brand loyalty?
- Rivalry; Fragmented vs concentrated, growing vs declining, aggressive vs passive competitor
- How much share do I already have? Can it grow?
Market Development
- Existing product, new market
- Same product, new customer
- Selling what you already produce to new target markets (market segments) or new geographic markets
- Addition of another market, not instead
- Low risk (not as low as market penetration)
- Need to adjust advertising/packing to appeal to new market
- Not changing the product in any meaningful way
- Identify market that no one else is paying attention to (Porter's Generic Strategies)
Why Do It?
- Capitalize on production capabilities, economies of scale, pursue less contested or larger market
- Diversification of customer base
Challenges
- Customer access and awareness
Tactics
- Create awareness in new market, pitch benefits to new customers
- Expand geographically (use international expansion knowledge)
Market Development Questions
Diamond-E
- Will this affect brand image? Should I use a different brand name?
- Will the product need any adjustments? Can I make them?
- Do I have the resources and knowledge to go international?
- Are there underserved segments that value my product?
- How mush do I know about this new customer?
Porter's
- Can I access the distribution channels to reach this new market?
- Are the customers accessible? Will they switch?
- Rivalry; fragmentation, aggression, growth?
- Differentiation; are there market segments that are under served?
- Barriers to entry?
Product Development
- Existing market, new product
- New product, same customers
- Develop related or unrelated products your customers value (product line extension)
- Medium risk
- Makes sense when you see a big opportunity and can benefit from brand equity (customers already know and trust/like your brand)
- Ex: apple watch product, same customers who have iphones and macs will buy
Benefit
- Build on customer knowledge & brand equity
- Possible distribution synergies & product complementarity/ bundling
Challenge
- Cannibalization ( instead of customers buying new stuff in addition, they buy the new instead of the old stuff)
- Give up production efficiencies
- Must know what and how to develop new product
Tactics
- Extend product
- Repackage existing products
- Create bundles of complementary products that add value to each other
Product Development Questions
Diamond-E
- Can I leverage existing brand and/or distribution?
- Can my facilities manage or do I have to build new ones?
- Can I produce & sell at a profitable scale?
- How much new product expertise will I need?
Porter's
- Will customers be willing to switch to my new product?
- Rivalry; aggression?
- Barriers to entry
Diversification
- New product, new market
- Chasing new customer with new products
- Creating new businesses (concentric/horizontal, vertical, conglomerate)
- Horizontal; products or services that are new and unrelated but still serves some of your customer base (ex: paper company starts to make and sell printers)
- Vertical; along the supply chain (Ex; ford starts making it's own tires and still sell cars but now they can use the tires they make and sell them), both activities will supply itself but also to other consumers/ manufacturers
- Conglomerate; when you go into something totally unrelated (ex: amazon buying whole foods, Samsung started in food product now does fridges and stereos)
- Backward integration is when customers become their own suppliers
Benefit
- Diversify business portfolio by building new business
- Capitalize on existing capabilities in higher growth areas
Challenge
- Many activities and capabilities in higher growth areas
Tactics
- Acquire other business
- Use joint ventures and alliances
Diversification Questions
- Will this affect brand image
Diamond-E
- What new capabilities and resources will I need?
- Can I build or buy them?
- How much will I have to change operations? HR? Structure?
Porter's
- Can I access the distribution channels to reach this new market?
- Are the customer accessible? Will they switch?
- Rivalry; fragmentation, aggression, industry growth?
- Barriers to entry?
Opportunities of Technology
- Products; become more innovative, unique, greater value
- Improved information use, access & sharing
- Competitive advantage; barriers to entry
- Customization
Threats of Technology
- Imitation; information costly to develop but cheap to share
- New technologies and new entrants in unfamiliar areas; need new capabilities, resources & learning
- Information overload & security
- Disconnected employees & customers
Technology Impact on KSF
Achieving Financial Performance
- Opportunity; saves money with its simplicity
- Threat; upgrades/ fixes if you outsource
Meeting Customer Needs
- Opportunity; better more innovative products
- Threat; potential for niche markets to be ignored
Building Quality Products and Services
- Opportunity; better production methods, design better products
- Threat; dependant on technology for manufacturing
Encouraging Innovation and Creativity
- Opportunity; allows for more opportunities to expand
- Threat; riskier if tech is new
Gaining Employee Commitment
- Opportunity; work from home, provides freedom/ autonomy
- Threat; feel less connected to the organization
Distinctive Competitive Advantage
- Opportunity; offer unique products from tech upgrades
- Threat; competitors come up with same upgrades bc tech is easy to imitate
Installed Base
- Number of users
- Higher number of users means it attractive
- Ex: Instagram has 1 billion users
Lock In
- Extent to which a customer is committed to a product or service
- Larger equals greater resistance to switch
- Causes; habit (cereal in the morning) or system (gaming system bc all the games are only compatible with one system), learning (knows all Microsoft software), investment (google home full set), switching costs
- Solution; lower switching costs, offer leap in performance
- Ex: Purchase Xbox, games, controllers, learn to play, make progress in the games
Switching Costs
- Costs of moving to a different technology
- High switching costs makes it hard to get new customers and technology can help reduce switching costs or build them
- Related to lock in
- Ex: cost of PS4, time it will take to learn new system