Electricity
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Current
Rate of flow of charge
Measured in Amps
Charge flow, current and time are linked by the equation:
Charge = current x time
Q = It
A current has the same value at any point in a single closed loop
potential difference
force driving the flow of electrons
Provided by cell/battery
Voltage, measured in volts
What does the current flowing through a component depend on?
both the resistance of the component and the potential difference across the component. The greater the resistance of the component the smaller the current for a given potential difference (pd) across the component.
Resistance
something that resists the flow of electrons
Measured in Ohms
Resistance increases with temperature
Current, potential difference or resistance can be calculated using the equation:
Potential difference = current x resistance
V = IR
Convential current
showing current as flowing from positive to negative
Because electrons are negative, they flow from negative to positive but no one knew about this when electricity was discovered
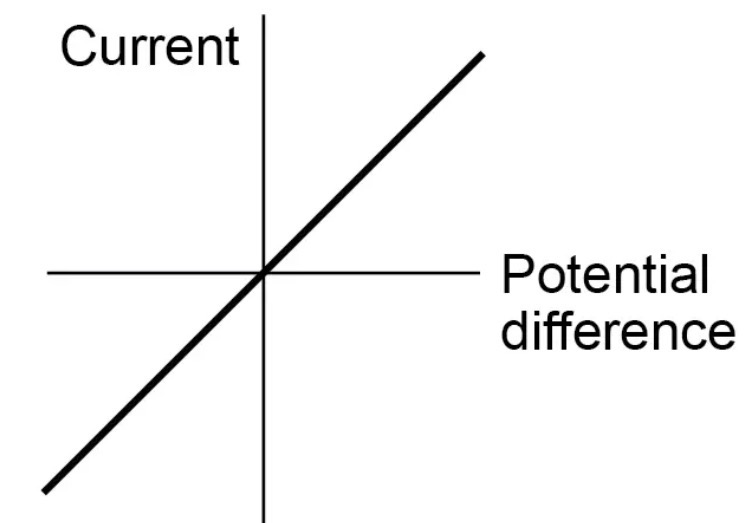
How are the current through an ohmic conductor and potential difference across it related?
directly proportional
Resistance remains constant as current changes
The resistance of components such as filament lamps, diodes, thermistors and LDRs is not constant; it changes with the current through the component.
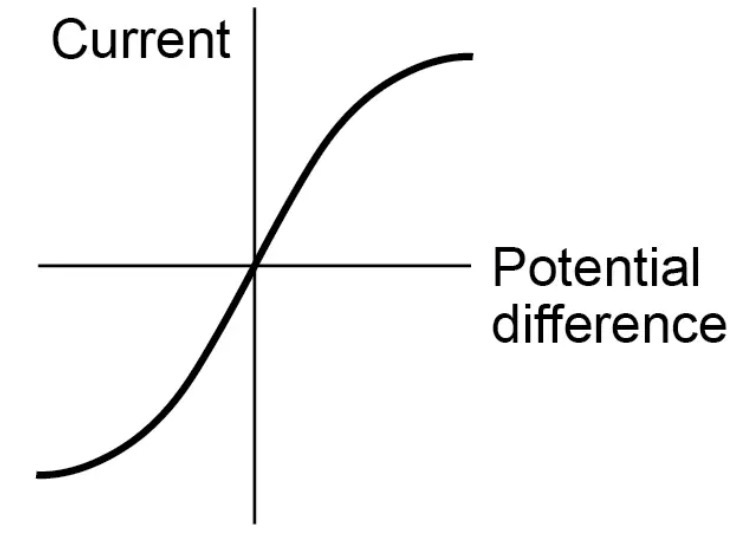
Resistance of a filament lamp
The resistance of a filament lamp increases as the temperature of the filament increases
This is because as current passes through the filament, the wire heats up, which increases resistance
Less current can flow per unit of p.d at higher voltages as temperature and resistance are higher
Curve gets less steep as current increases
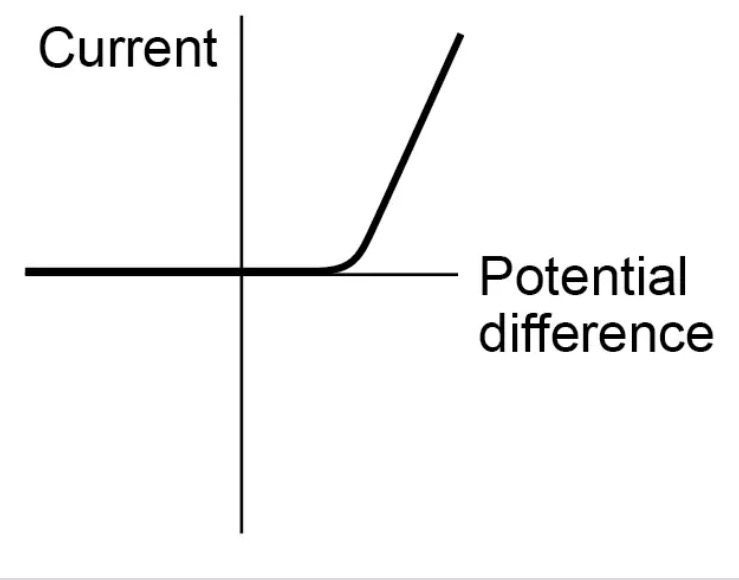
Resistance of a diode
The current through a diode flows in one direction only.
This is because the diode has a very high resistance in the reverse direction, so no current can flow in that direction.

Resistance of an LDR (Light Dependent Resistor)
resistance decreases as light intensity increases
Used in circuits that switch lights on when it gets dark, burglar alarms, etc.
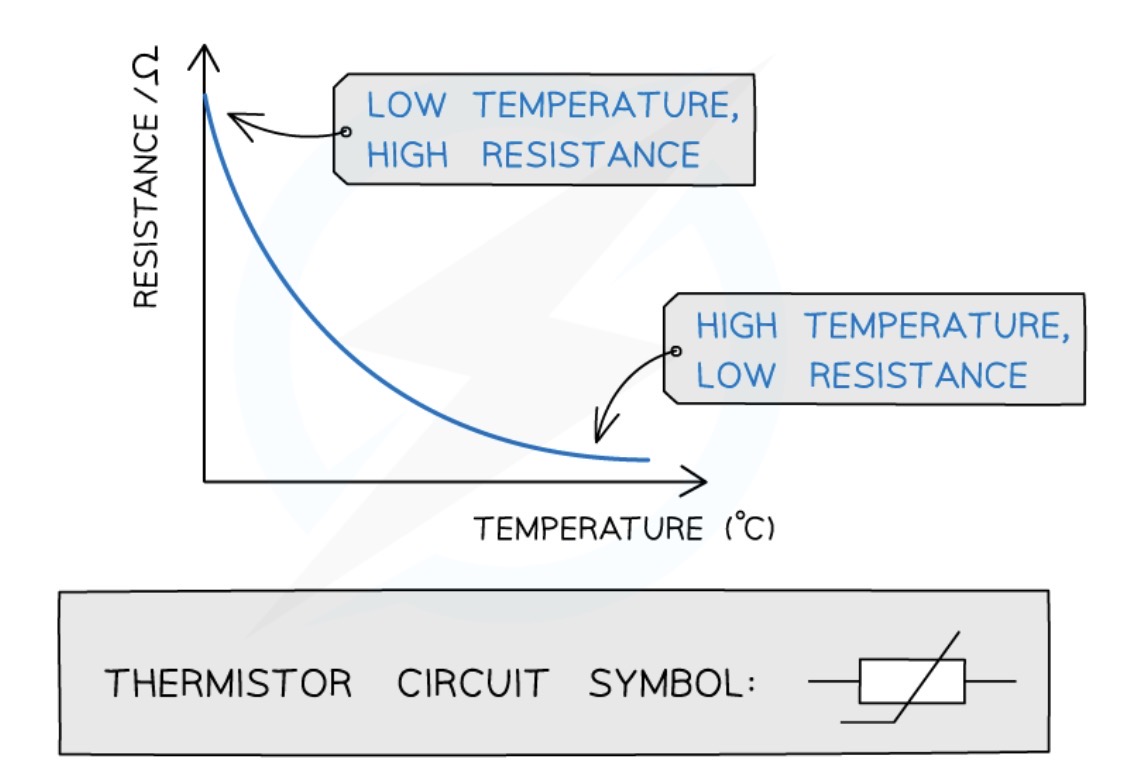
Resistance of a thermistor
resistance of a thermistor decreases as the temperature increases
Used in thermostats, car engines, etc.
What are the two different ways of joining electrical components
in series
In parallel
Series
single loop, components connected one after the other
there is the same current through each component
the total potential difference of the power supply is shared between the components. Sum of p.ds of individual components
the total resistance of two components is the sum of the resistance of each component
Parallel
more than 1 loop
Each loop usually contains a single component
the potential difference across each component is the same
the total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the currents through the separate components
the total resistance of two resistors is less than the resistance of the smallest individual resistor
why adding resistors in series increases the total resistance whilst adding resistors in parallel decreases the total resistance
in series, current has to pass through each resistor in turn, so resistances add up. Total resistance is therefore increased.
In parallel, the total resistance is less than the resistance of the smallest individual resistor. This is because with multiple resistors in parallel there are more pathways for the current to take. More total current will flow through the circuit. If current has increased but p.d has not changed, then total resistance decreases
explain the design and use of dc series circuits for measurement and testing purposes
DC series circuits connect components end-to-end in a single path, making them ideal for testing because current is constant throughout, resistance adds up, and voltage divides, allowing simple measurement of total/individual resistance (using ammeter in series, voltmeter in parallel) and voltage drops (V=IR) to verify laws like Ohm's Law and study component behaviour in basic setups like voltage dividers.
National grid
a system of cables and transformers linking power stations to consumers
Electrical power is transferred from power stations to consumers using the National Grid
How do power stations generate electricity
generate loads of heat
Convert thermal energy into electrical energy
What does the amount of electricity generated depend on
demand
Electricity demand peaks in the afternoon and evening
To cope with surges in demand, power stations need spare capacity, so run well below their maximum power output
what does the national grid need to transmit huge amounts of power
high voltage
High current
What happens to voltage before it is sent across the country
increased with step up transformers
They increase the voltage to around 400,000 volts
This decreases the current
why is the voltage increased?
whenever a high current flows through a wire, lots of heat is generated due to resistance. Lots of thermal energy transferred to surroundings
Very high p.d means very low currents
Which means less thermal energy transferred to surroundings
Which increases the efficiency of power transmission
what happens to voltage before power reaches homes
decreased with step down transformers
they decrease the voltage to around 230V
This increases the current
why is p.d decreased before reaching homes
High voltages are dangerous and could damage household appliances