Cerebral cortex
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
cerebral cortex
highest level of all sensory and somatic motor control
memory, association, cognitive processes
control neural activity
4 lobes
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
angular gyrus
language processing
can be found at the end of the lateral sulcus
premotor cortex
it’s an area
motor planning
locate to the left of pre central gyrus (primary motor cortex) and under the suppl. motor area
supplementary motor area
move based on memory (“muscle memory”)
ex: piano player
located superiorly and left to the pre central gyrus
main long tracts (pathways)
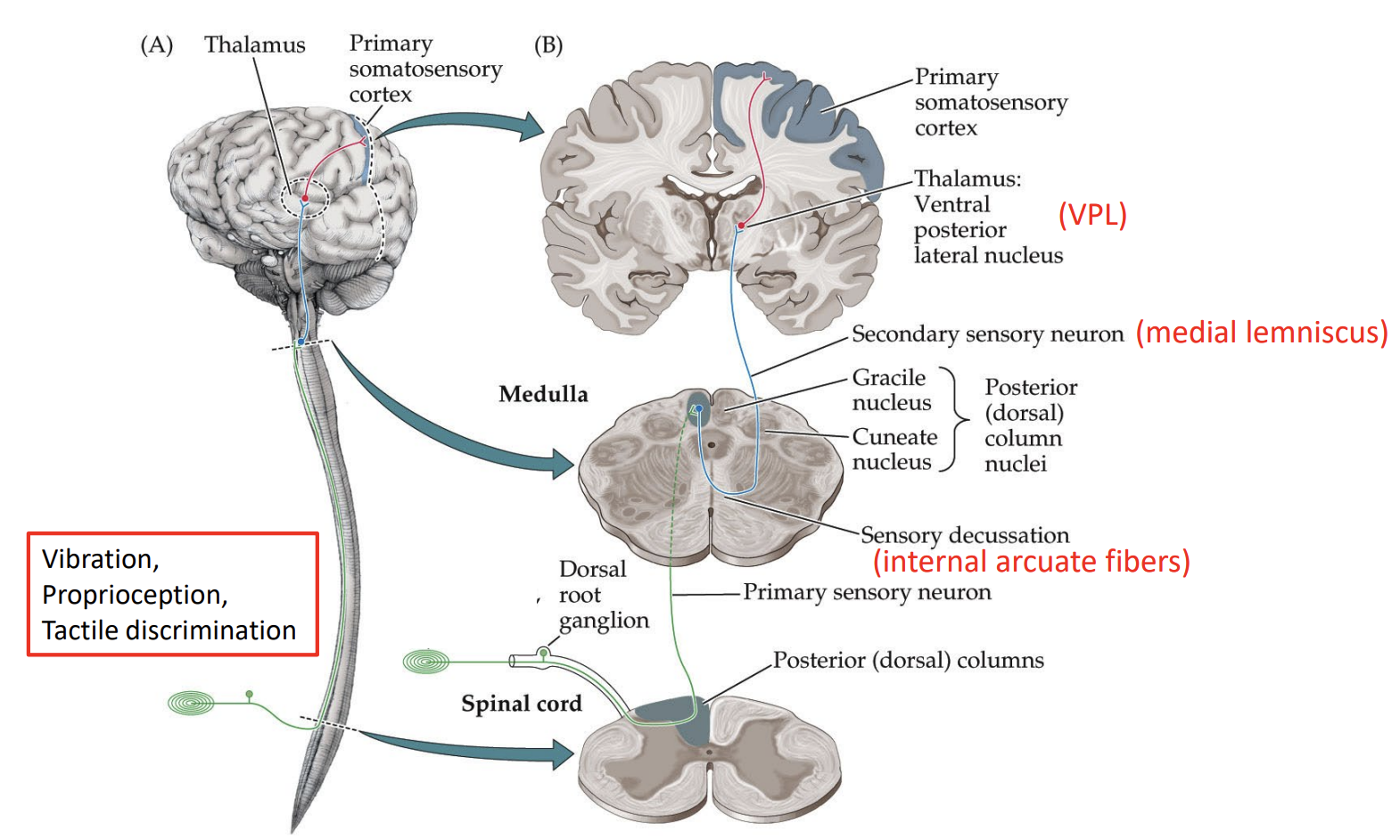
posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway
anterolateral pathway
lateral corticospinal tract
posterior column - medial lemniscus pathway
main somatosensory pathway
vibration, proprioception, tactile discrimnation
contralateral
crosses at the medulla
(primary sensory neuron): signal sent to the dorsal root ganglion → spinal cord → posterior dorsal columns → brain → medulla
(secondary sensory neuron): medulla → crosses over to the other side of the medulla → medial lemniscus → thalamus (ventral posterior lateral nucleus (VPL))
(third sensory neuron): thalamus → post-central gyrus (primary somatosensory cortex)
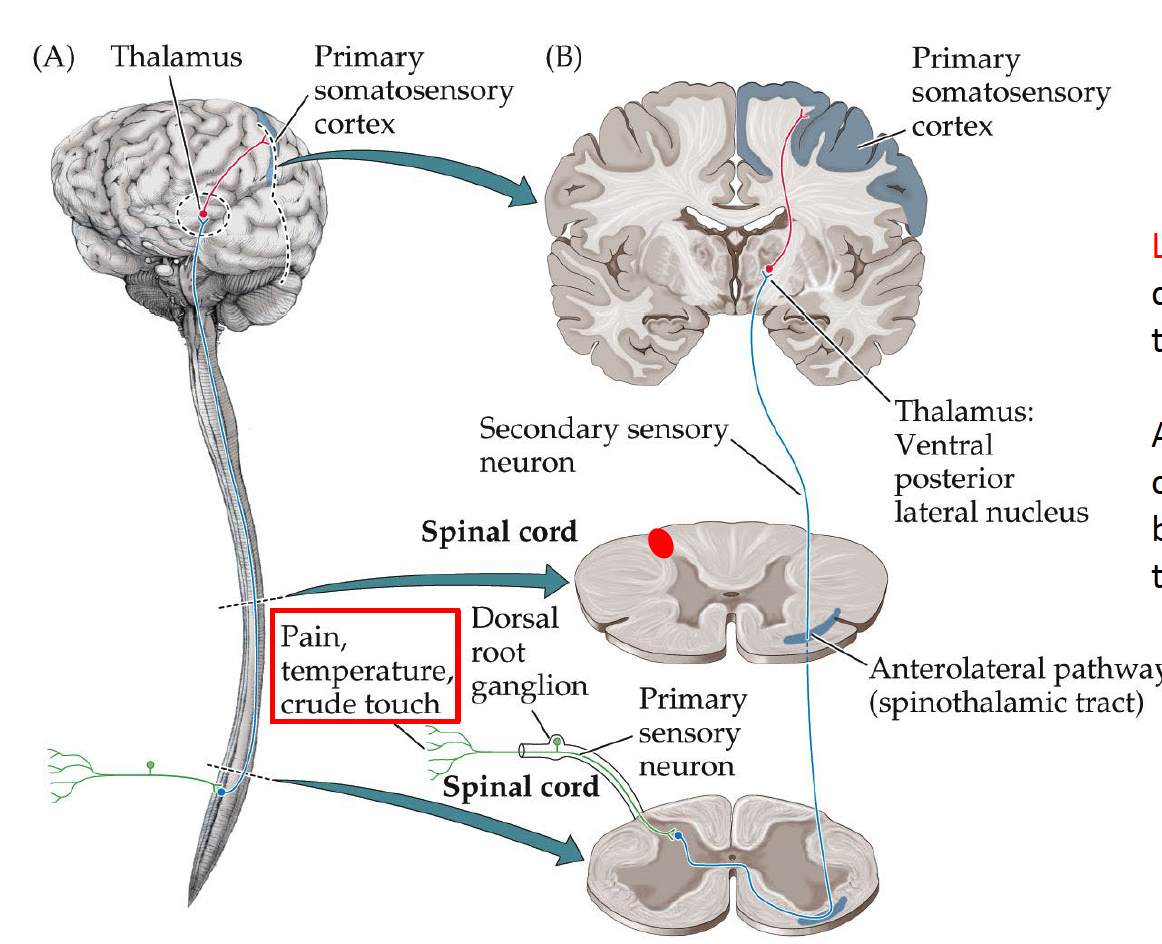
anterolateral (spinothalamic) pathway
main somatosensory pathway
contralateral
crosses at the spinal cord
pain, temperature, crude touch
( primary sensory neuron ) : sensory sent to dorsal root ganglion spinal cord
( secondary sensory neuron):spinal cord → crosses at anterior horn of spinal cord → anterolateral pathway (spinothalamic tract - in the spinal cord) → thalamus (VPL)
(third sensory neuron): thelamus → primary somatosensory cortex
Brodmann’s area
in the occipital lobe:
area 17: primary visual cortex / striate cortex - V1. most caudal of the lobe
area 18 and 19: extra striate cortex - V2. more rostral of the lobe
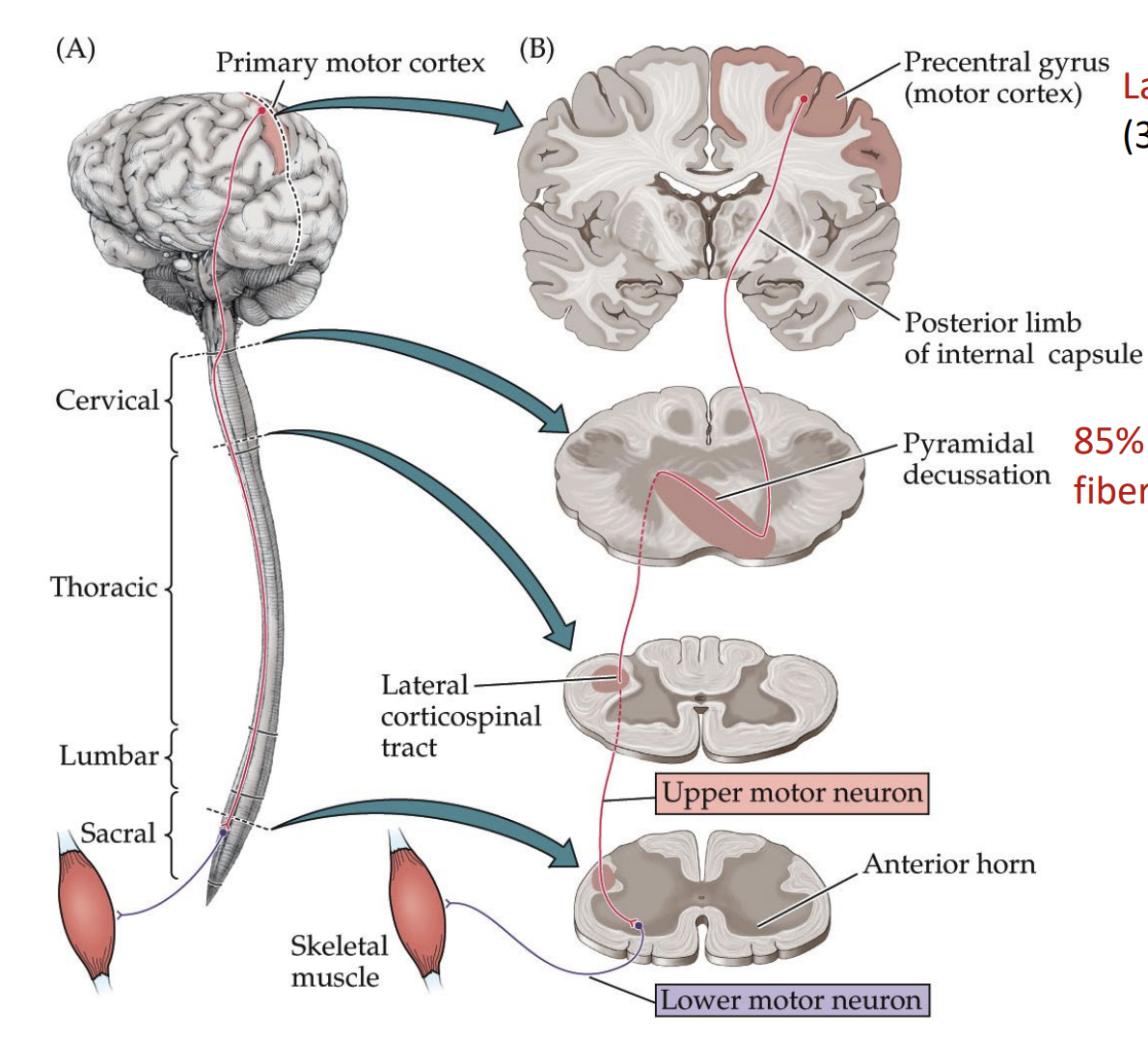
corticalspinal tract (pyramidal tract)
aka pyramidal tract
contralateral
DORSAL ROOT GANGLION DOES NOT INVOLVE
(primary sensory neuron): signal from pre central gyrus → medulla → crosses at medulla
(secondary sensory neuron): medulla → spinal cord → lateral corticospinal tract (by the cervical) → upper motor neuron → anterior horn of spinal cord → muscle
hemi-cord lesion
aka Brown-Sequard syndrome
ipsilateral effect: motor loss, proprio (sense of position) loss, vibration
contralateral effect: pain and temp
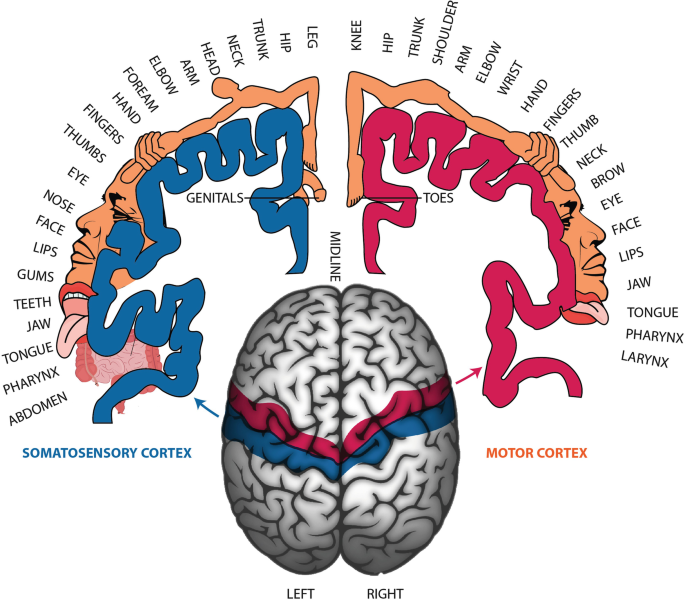
pre central gyrus
primary motor cortex
contralateral
post central gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex
somatosensory and motor homunculus
frontal lobe
body movement, speech (Broca’s), saccadic eye movement, personality/judgement/planning/reasoning
parietal lobe
somatosensory, pursuit eye movement, spatial attention
occipital lobe
vision
temporal lobe
memory, hearing, language comprehension (Wernicke’s), facial/object recognition
primary visual cortex
occipital lobe
visual field analysis
contralateral
calcarine fissure
separate the lingual and cunneas gyrus
lingual gyrus
process superior quadrant of VF
contralateral
ex: L lingual allows for R superior VF
R lingual allows for L superior VF
cunneas gyrus
process inferior quadrant of VF
contralateral
ex: L cunneas allows R inf quad VF
R cunneas allows L inf quad VF
frontal eye field
FEF
contralateral
saccadic eye movement = rapid eye movement
when damage, cannot make saccade to the other eye
located left of the pre motor cortex
Parietal-occiptal-temporal cortex
ipsilateral
aka POT
smooth pursuit eye movement (allow eyes to follow an object)
locate at where all 3 lobes meet
Broca’s
speech formation
locate in the frontal lobe, above the lateral sulcus
Wernicke’s
language comprehension
located in the temporal lobe
right under the lateral fissure, sometimes look like a W
Heschl’s gyrus
primary auditory cortex = hearing
bilateral = when only L side is affected, the person can still hear from the R ear.
located temporally across from the insular cortex (in temporal lobe) where the ears are
insular cortex
taste
located behind the lateral fissure
which hemisphere is dominant for language?
Left
olfactory pathway
does not go thru the thalamus
olfactory receptors in nasal mucosa (nose- → olfactory bulb → olfactory tract → lateral olfactory stria → primary olfactory cortex (at/near uncus) →orbitofrontal olfactory area
olfactory receptors in nasal mucosa (nose) → olfactory bulb → olfactory tract → medial olfactory stria → contralateral olfactory bulb
anosmia
loss of smelll
uncus
in the temporal lobe
in charge of memory
Foster-Kennedy syndrome
Symptoms:
ipsilateral: optic atrophy (pale) in 1 eye → reduced VA
contralateral papilledema: swollen optic nerve on the other eye → due to increased IOP unaffected VA
Causes: anterior cranial fossa meningioma
dead optic nerve can’t swell !!! *
healthy optic nerve: pick, reddish
pale optic nerve: white, white-ish
optic atrophy: dead optic axons → pale looking
spatial neglect
pt tend to neglect the entirety of a side (L or R) due to a damage of the contralateral side of the parietal lobe.
they see it, they just neglect it
palinopsia syndrome
defect in the occipitotemporal cortex
an object that you had seen persist in your vision.
trailing is an example.
ex: you are looking at an apple in front of you, then you look away and you still see that apple.
Alice in wonderland
defect in the occipitotemporal cortex
objects appear unusually smaller or bigger than it actually is
corpus collossum
front to back: rostum, genu, body, splenium
the splenium is the part that connects the occipital lobe
split-brain patients
pt have gone under sx to cut the corpus callosum
left hemisphere: dominant for verbal processing
a pt is shown the word “face” to his right VF → can say “face”
he is now shown to is right VF → can only draw a face but unable to say it
→ the right hemisphere sees the word, but cannot communicate w the left side to form speech.
neocortex
6 layers of the cerebral cortex
IV receives thalamic info
VI sends feedback to thalamus
V sens output to spinal cord, brainstem, and basal ganglion
which part of corpus callosum connect to the occipital lobe?
splenium