2(g) Gas exchange
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Breathing
The movement of gas in and out of the lungs involving intercostal muscles. Also known as ventilation.
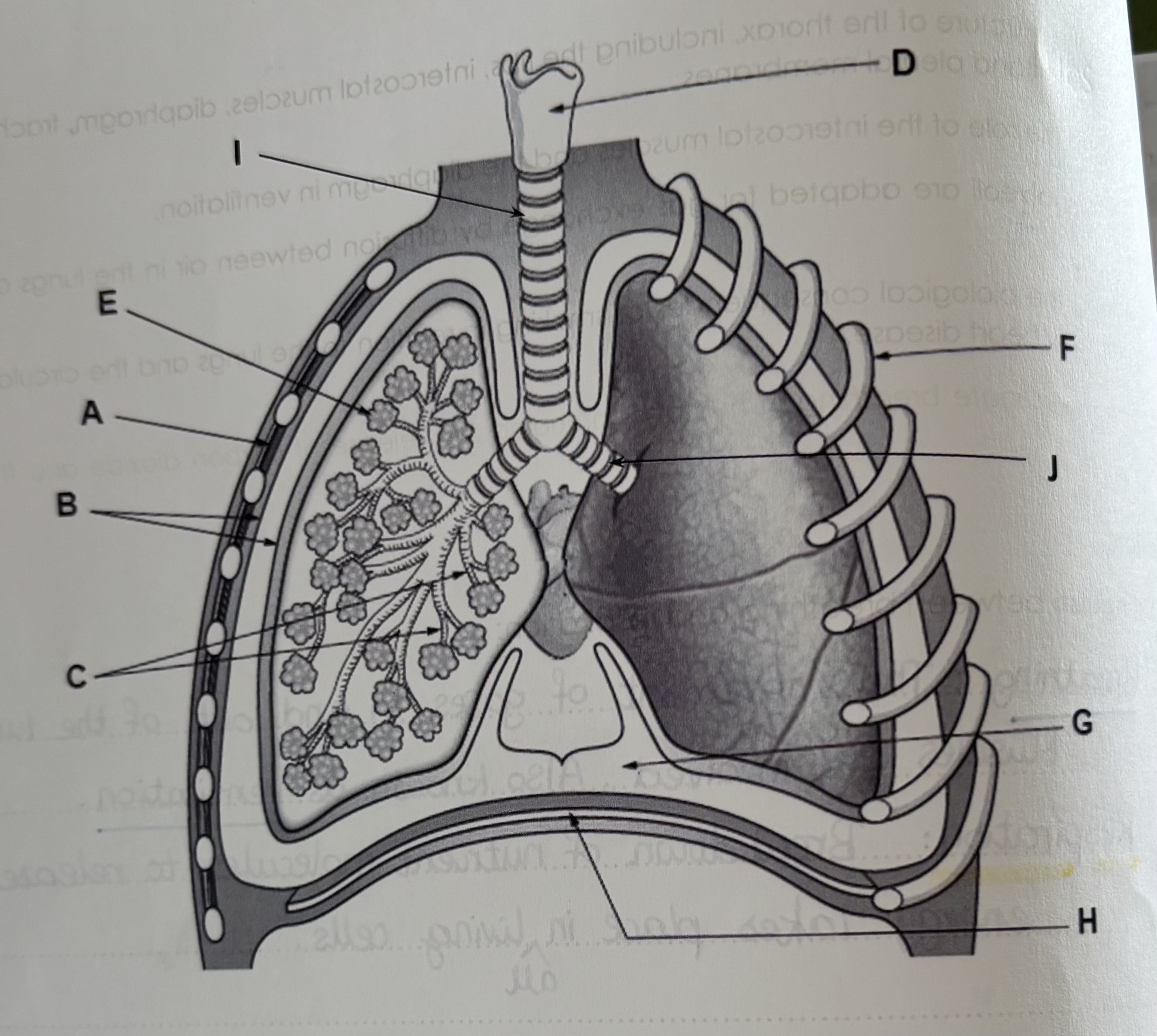
Structure of the thorax
A - intercostal muscles
B - pleural membranes
C - bronchioles
D - voice-box
E - alveoli
F - rib-cage
G - pleural fluid
H - Diaphragm
I - trachea
J - bronchus
Trachea
Tube with incomplete rings of cartilage, carries air to the lungs. Lined with cells making mucus and cells with cilia to move the mucus away.
Bronchi
Two tubes which carry air from the trachea to the lungs
Bronchioles
Smaller tubes that carry air from the bronchi to the alveoli
Alveoli
Tiny air sacks adapted for gas exchange
Diaphragm
Sheet of muscle which is domed.
It helps making breathing movements and separates the thorax from the abdomen.
Rib-cage
Bones that protect and ventilate the lungs.
Intercostal muscles
The muscles in between the ribs which move them for ventilation.
Pleural membranes
Thin, moist membranes forming an airtight seal around the lungs and separating inside of thorax from lungs to stop them from ‘sticking‘.
Inhalation
The intercostal muscles contract, which moves the rib-cage up and out. The diaphragm contracts and flattens(moves down), so the volume of the thorax increases which reduces the pressure(lower than atm. pressure), causing the air to move into the lungs.
Exhalation
The intercostal muscles relax, which causes the rib-cage to move in and down. The diaphragm relaxes and moves up, so the volume of thorax decreases which increases the pressure. Therefore air moves out of the lungs.
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange
There are a lot of alveoli in the lungs which creates a large surface area for diffusion.
It has a rich blood supply to maintain a steep diffusion gradient between the alveoli and the blood for diffusion of Co2 out of the blood into the alveoli and diffusion of oxygen out of the alveoli into the blood.
Short diffusion distance between the air and the blood because the alveoli and the capillary surrounding them only have walls that are one cell thick.
The walls are permeable and are moist to help dissolve gases and increases diffusion rate. Moist surfaces allow gases to dissolve and diffuse across the wall more effectively.
Healthy lungs
In healthy lungs the cells lining the bronchi and bronchioles(called epithelial cells ) have tiny little hairs on them called cilia. There are also goblet cells which secrets mucus, trapping bacteria and dust to stop it entering the lungs. The cilia waft the mucus up the throat where it can be swallowed and destroyed in the stomach acid.
Tar
Tar paralyses the cilia so they cannot move mucus the bronchioles and out of the lungs.
Smokers cough more to move the mucus.
This also leads to bacteria having time to multiply in the mucus which could cause a chest infection.
The immune response causes inflammation which causes bronchitis.
Nicotine
Nicotine causes the blood pressure to increase.
This can damage the lining of the arteries.
The damaged arteries can start to have fatty deposits build up in the damaged areas.
These can block the arteries leading to the heart causing less oxygen to reach the heart cells so they cannot respire and die.
This contributes to heart disease.
Carcinogens
Carcinogens are chemicals that cause cancer.
Tar has many chemicals in it known to cause cancer. These can change the sequence of bases in DNA and cause mutations.
Some of these mutations can cause uncontrolled cell division which is what cancer is.
Carbon monoxide
CO is a poisonous gas. It binds to haemoglobin in the red blood cells which reduces the the amount of oxygen carried around the body.
If less oxygen reaches the developing foetus,Ithen it cannot grow as fast would be born smaller.
Emphysema
A disease that affects breathing.
The smoke damages the alveoli walls. They burst and fuse together. The alveoli are enlarged which reduces the surface area for gaseous exchange. The lungs cannot contract so there is less ventilation.
There is no cure.
Coronary heart disease(CHD)
Smoke damages the circulatory system and increases the risk of developing coronary heart disease.
Fatty deposits will get in the wall of the coronary arteries which normally supply the heart with oxygen.
Eventually these can get blocked entirely by a clot and oxygen will not get to some of the heart, causing a heart attack.
Practical: Effect of exercise on breathing(CORMMSS style)
X
Explain why the breathing rate would remain high for a few minutes after the exercise has finished.
The human still needs oxygen from the air to break down the lactic acid as a waste product due to anaerobic respiration. Lactic acid lowers the pH which could denature the enzymes.