Physics Kinematics Definitions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Law of conservation of momentum (2)
Total momentum does not change (1)
as long as there are not external forces acting on the system (1)
Newton’s third law
If Object A exerts a force on Object B, then Object B will exert a force on Object A which is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction
Linear momentum
Product of mass and velocity of an object
How does conservation of momentum apply to a system with two objects? (5 points)
Forces on the system are equal and opposite
No external force on the system
So net force is zero
Net force = rate of change of momentum
Momentum is conserved
Explain whether an object in circular motion is accelerating (3)
direction constantly changing
velocity is vector
accelerating because velocity is changing
Why is the work of an object in circular motion always zero?
Force is always perpendicular to velocity (no force in same direction as velocity)
Tension force in vertical circular motion at the bottom of rotation is equal to:
Centripetal force plus weight (tension force must provide both centripetal force and counter weight)
viscous drag
the frictional force between an object and a fluid which opposes the motion between the object and the fluid

how can something be considered a single system
if their mass is combined OR they are treated as single body/object
Compare and contrast static vs dynamic friction
Both:
oppose motion
are proportional to the size of the normal force
Difference:
Static friction is variable whereas dyanmic friction is constant
Potential energy
The energy possessed by the system due to the relative positions of its components or parts OR energy possessed by an object due to its position in a field
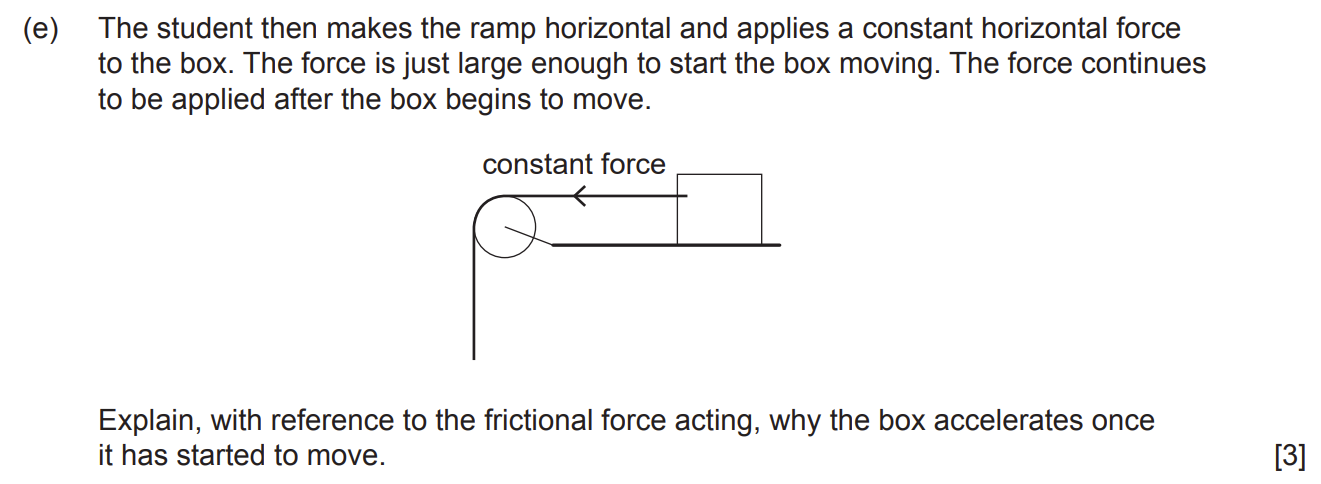
Explain, with reference to the frictional force acting, why the box accelerates once it has started to move.
Coefficient of dynamic friction lesser than coefficient of static friction
Force of dynamic friction less than force of static friction
Resultant force to the left when in motion (which results in acceleration, as F=ma)