Satellites and their purpose for Remote Sensing of the Environment
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
CALIPSO (Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations)
Provides high-resolution vertical profiles of thin clouds and aerosols using lidar.
CloudSAT
Uses cloud radar to measure cloud reflectivity and structure
EarthCARE (Earth Clouds, Aerosols, and Radiation Explorer)
Combines lidar and radar for enhanced cloud and aerosol characterization
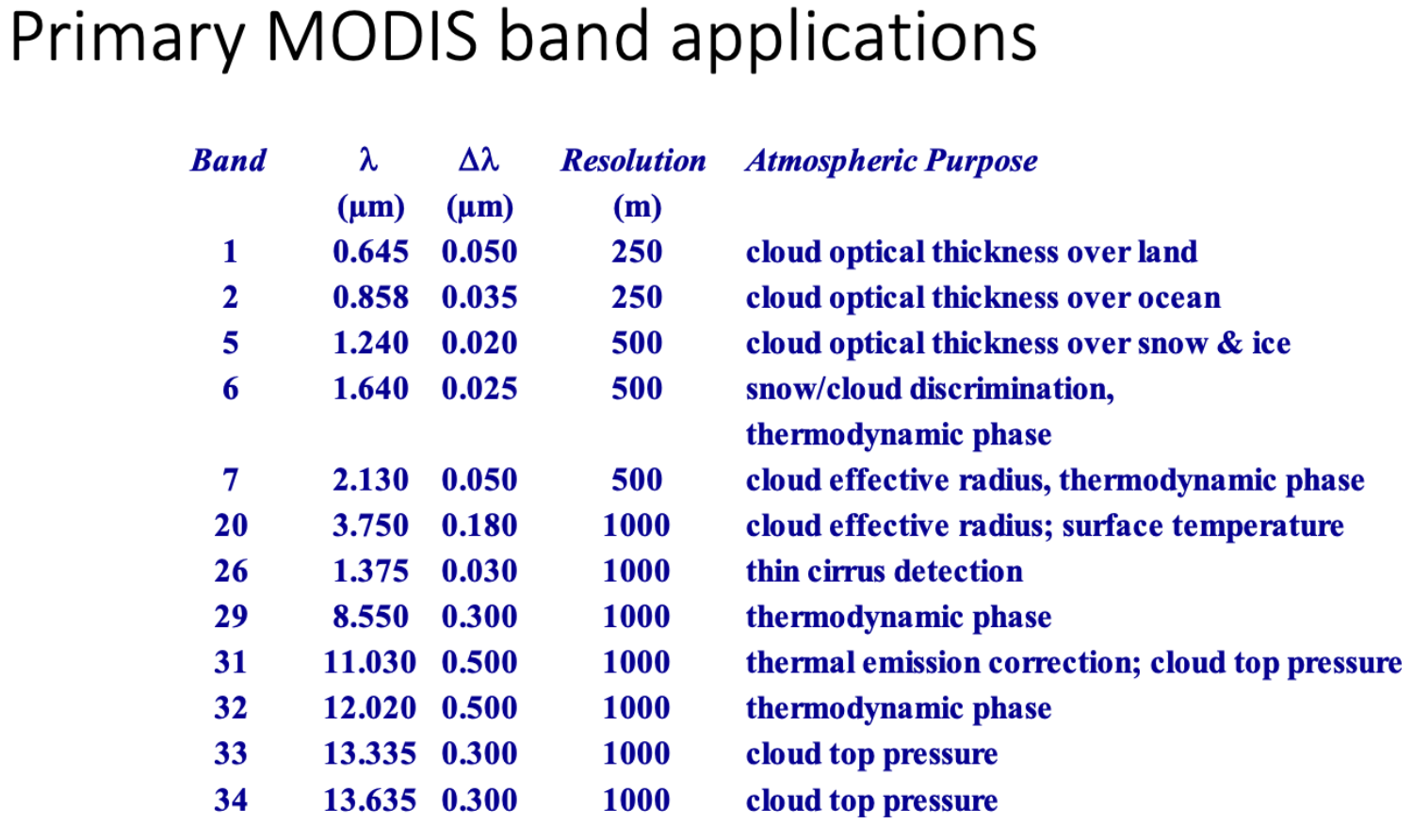
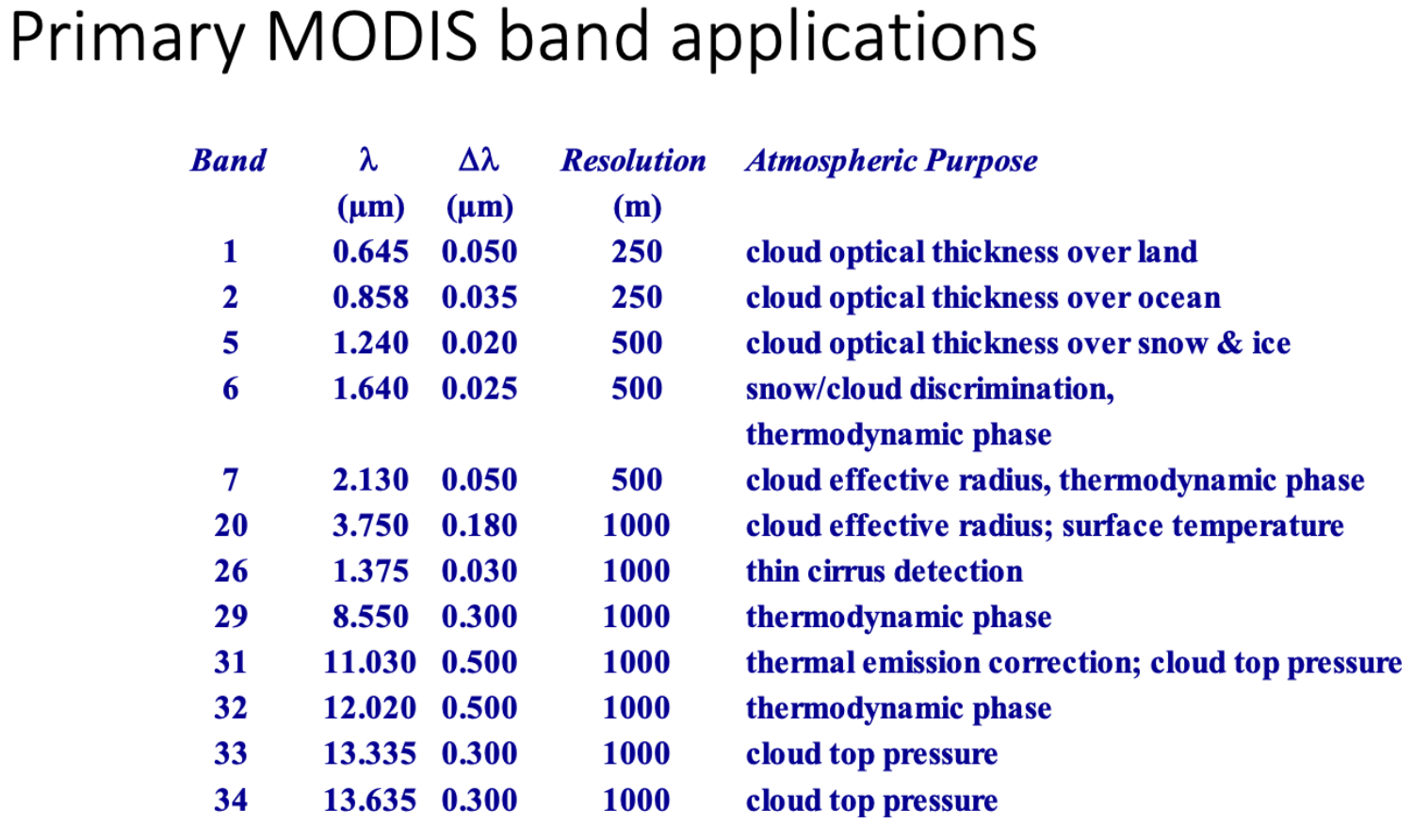
MODIS (Moderate resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer
A satellite-based sensor that measures the Earth’s physical properties concerning the atmosphere, land, and ocean processes, especially Vegetation, land surface cover, ocean chlorophyll fluorescence, cloud and aerosol properties, Fire occurrence, snow cover, and sea ice cover. MODIS is a 36-band spectroradiometer that measures visible and infrared radiation. It views the entire Earth’s surface every one to two days. MODIS instrument on Terra satellite (EOS AM-1) and Aqua satellite (EOS AM-2). Has a spatial resolution of 250-1000 m and an image frequency 1 day.
TOMS (Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer)
On NASA, Nimbus-7, Meteor-3m, ADEOS, Earth Probe and launched on 1978, 1991, 1996 (2 times). Sensor Characteristics: Scanning monochrometer with 6 spectral bands between 0.312 to 0.380 microns, cross-track scan mirror with 2500 km swath width (±51 degrees), spatial resolution of 49 - 26 km depending on altitude of spacecraft), and onboard solar diffuser.
COSMIC (Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere and Climate)
A satellite constellation providing global GPS occultation data
GRACE-FO (Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-ON)
Includes GPS occultation capabilities for atmospheric profiling
MetOp Satellites
European weather satellites equipped with GPS radio occultation instruments
CYGNSS (Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System)
CYGNSS is a NASA Earth Venture mission led by the Department of Climate and Space Sciences and Engineering in the University of Michigan's College of Engineering. It consists of eight satellites that measure surface wind speed in tropical cyclones to improve storm forecasting. Measure wind speeds over Earth’s oceans.
AVHRR
SeaWifs
TES (Tropospheric emission Spectrometer)
MLS (Microwave Limb Sounder)
On NASA’s Aura satellite, measuring temperature, water vapor, and ozone through limb sounding.
OMPS (Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite)
On NOAA’s satellites, provides ozone profiles using limb scattering
MIPAS (Michelson Interferometer for Passive Atmospheric Sounding)
Aboard ESA’s Envisat, used for high-resolution measurements of trace gases
SCIAMACHY (Scanning Imaging Absorption Spectrometer for Atmospheric Chartography)
Combines nadir and limb observations for Atomspheric profiling
Landsat
Multispectral Sensor (57 m) sine 1972. TM, ETM+ and OLI (30 m VNIR) since 1984. Return period 16 days, 10 am overpass, Passive sensor collecting visible, NIR, and Thermal Infrared, has a spatial resolution of 30 - 90 meters.
GOES (Geostationary Operation Environmental Satellite)
The Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES), operated by the United States' National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service division, supports weather forecasting, severe storm tracking, and meteorology research. Spacecraft and ground-based elements of the system work together to provide a continuous stream of environmental data. The National Weather Service (NWS) and the Meteorological Service of Canada use the GOES system for their North American weather monitoring and forecasting operations, and scientific researchers use the data to better understand land, atmosphere, ocean, and climate dynamics.