Human Geography, Culture, Anthropology & Sociology
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Human Geography
The study of how humans interact with the environment, create cultures, and organize space.
Cultural Diffusion
The spread of cultural traits, ideas, or products from one society to another.
Cultural Hearth
A region where a culture originated and from which it spread.
Migration
The movement of people from one place to another.
Push-Pull Factors
Reasons people leave (push) or are drawn to (pull) an area, such as war or jobs.
push
factors or conditions that drive people away from a place (e.g., war, poverty)
pull
factors that attract people to a new place (e.g., jobs, safety).
Political oppression
Which of the following is the best example of a sociological push factor for migration?
Urbanization
The increase in the population of people living in cities.
Job opportunities in another country
Which of the following is an example of a pull factor in migration
Population Density
The number of people per unit of land area (e.g., people per square mile).
Demographics
Statistical data about populations (e.g., age, race, income).
Birth Rate
The number of live births per 1,000 people per year.
Death Rate
The number of deaths per 1,000 people per year.
Immigration
Entering and settling in a country that is not one's native country.
Emigration
Leaving one's country to live in another.
Refugee
A person who flees their country due to conflict, persecution, or disaster.
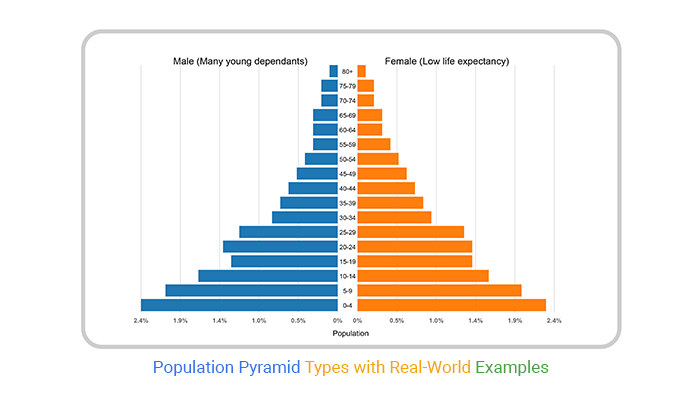
Population Pyramid
A graph that shows the age and sex distribution of a population, often used to understand growth trends and social needs.
A high birth rate and a growing population, often seen in developing countries.
What does a wide base on a population pyramid indicate?,
A low birth rate and aging population, common in developed countries facing population decline.
What does a narrow or shrinking base on a population pyramid suggest?,
It shows a high birth rate and low life expectancy, meaning many young people but few elderly—typical of developing countries.
What does a wide base but narrow top on a population pyramid suggest?
Latitude and Longitude
A grid system used to determine exact locations on Earth.
Absolute Location
Exact location using latitude and longitude.
Relative Location
Location of a place in relation to other places.
Place
The physical and human characteristics that define a location.
Region
An area defined by common features (e.g., political, physical, cultural).
Formal Region
A region defined by official boundaries or data (e.g., states, countries).
Functional Region
A region centered around a node or focal point (e.g., a metro area).
Perceptual Region
A region defined by people's perceptions or feelings (e.g., "the South").
Infrastructure
Basic systems of a society (e.g., roads, water supply, power).
Urban Sprawl
The uncontrolled expansion of urban areas into surrounding rural land.
Site
The physical setting of a settlement.
Situation
How a settlement relates to surrounding features like water, resources, and roads.
Sustainability
Meeting current needs without compromising future generations.
Globalization
The increasing interconnectedness of economies, societies, and cultures.
Resource Scarcity
Limited availability of natural resources like water, oil, or land.
Renewable Resources
Resources that replenish naturally, like water, air, and sunlight.
Non-Renewable Resources
Resources that deplete faster than they replenish (e.g., oil).
Carrying Capacity
The number of people an environment can sustainably support.
Green Revolution
The increase in agricultural production using new technology in the 20th century.
Agricultural Revolution
The shift from hunting and gathering to farming.
Subsistence Farming
Farming to feed one's family with little surplus.
Commercial Farming
Farming for profit, often large-scale.
Desertification
The spread of desert conditions due to overuse and climate.
Deforestation
Clearing forests for development or agriculture.
More Developed Country (MDC)
A country with industrialized, advanced economy.
Less Developed Country (LDC)
A country with little industrialization and low income.
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
A model showing population change based on birth/death rates.
Cultural Landscape
The visible imprint of human activity on the landscape.
Distribution
The spatial location of where people live on Earth.
Biome
A group of ecosystems with similar climate, animals, and plants.
Human Development Index (HDI)
A measurement of health, education, and standard of living.
Culture
Shared beliefs, values, and practices passed from one generation to the next.
Cultural Traits
Individual aspects of human activity that shape social life.
Cultural Diffusion
The spread of cultural traits or ideas from one group to another.
Acculturation
Adopting traits of another culture while maintaining your own.
Assimilation
A minority group adopts the dominant group's culture, often losing its own.
Ethnocentrism
Judging another culture by the standards of your own.
Cultural Relativism
Understanding a culture on its own terms without judgment.
Socialization
The process of learning norms, values, and behaviors accepted by society.
Norms
Social rules that define acceptable behavior.
Values
Core beliefs and standards shared by society.
Role
Expected behavior for someone in a certain social position.
Status
A person's position in society (ascribed or achieved).
Primary Groups
Close, personal relationships (e.g., family).
Secondary Groups
Larger, more impersonal groups (e.g., coworkers).
Social Institutions
Structures like family, education, religion, and government that meet societal needs.
Social Stratification
The division of society into levels based on wealth, power, or status.
Socioeconomic Class
A group defined by similar income, education, or status.
Social Class
A category of people with similar social and economic standing.
Social Mobility
The ability to move up or down in social status.
Gender Roles
Culturally expected behaviors for males and females.
Discrimination
Unfair treatment based on group membership.
Prejudice
A preconceived opinion not based on reason or experience.
Stereotype
An oversimplified belief about a group.
Group Dynamics
How individuals behave and interact in groups.
Social Change
Shifts in society's norms, values, and structures.
Social Movement
Collective effort to promote or resist change (e.g., Civil Rights Movement).
Mass Media
Communication channels that influence large audiences.
Functionalism
Views society as a system where each part serves a purpose.
Conflict Theory
Views social life as a struggle for power and resources.
Symbolic Interactionism
Focuses on how people use symbols to communicate and interact.
Social Control
Ways society encourages conformity (laws, norms).
Positive Sanctions
Rewards for acceptable behavior (e.g., praise, awards).
Negative Sanctions
Penalties for negative behavior (e.g., fines, disapproval).
Cultural Region
An area defined by shared cultural traits (e.g., the Midwest).
Cultural Adaptation?
Adjusting to fit into a new culture.
Nationality?
The state or nation to which someone belongs.
Bias
Prejudiced leanings or unfair assumptions.
Social Conflict
Disagreements or tension between social groups.
Sociological Structures
Social organization that shapes behavior.
Social Solidarity
Unity in a society based on shared values and norms.
Dominant Culture
The culture of the most powerful group in society.