AP Psychology Brain: Neurotransmitters, Nervous Systems & Neurotransmission
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication system, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
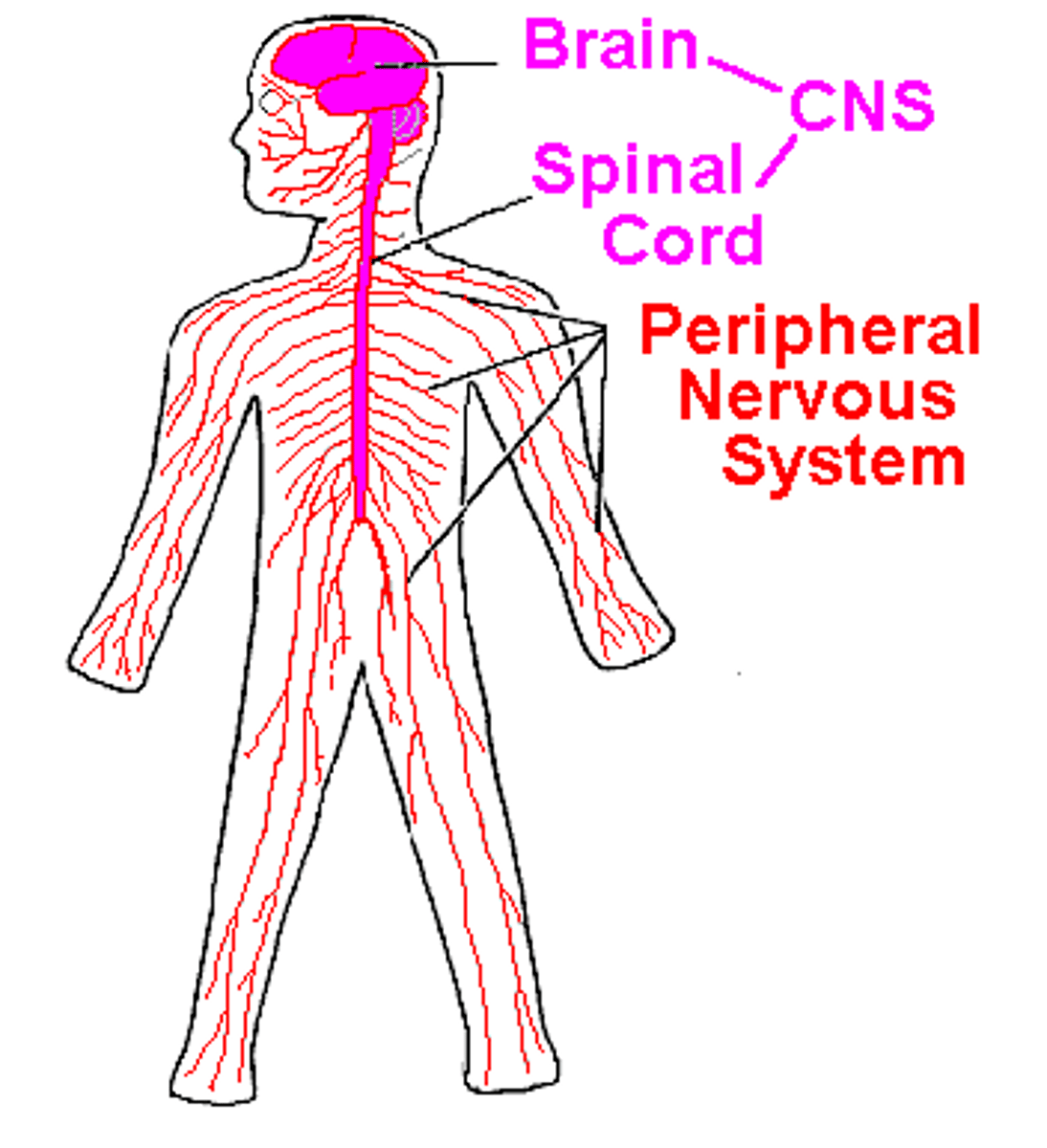
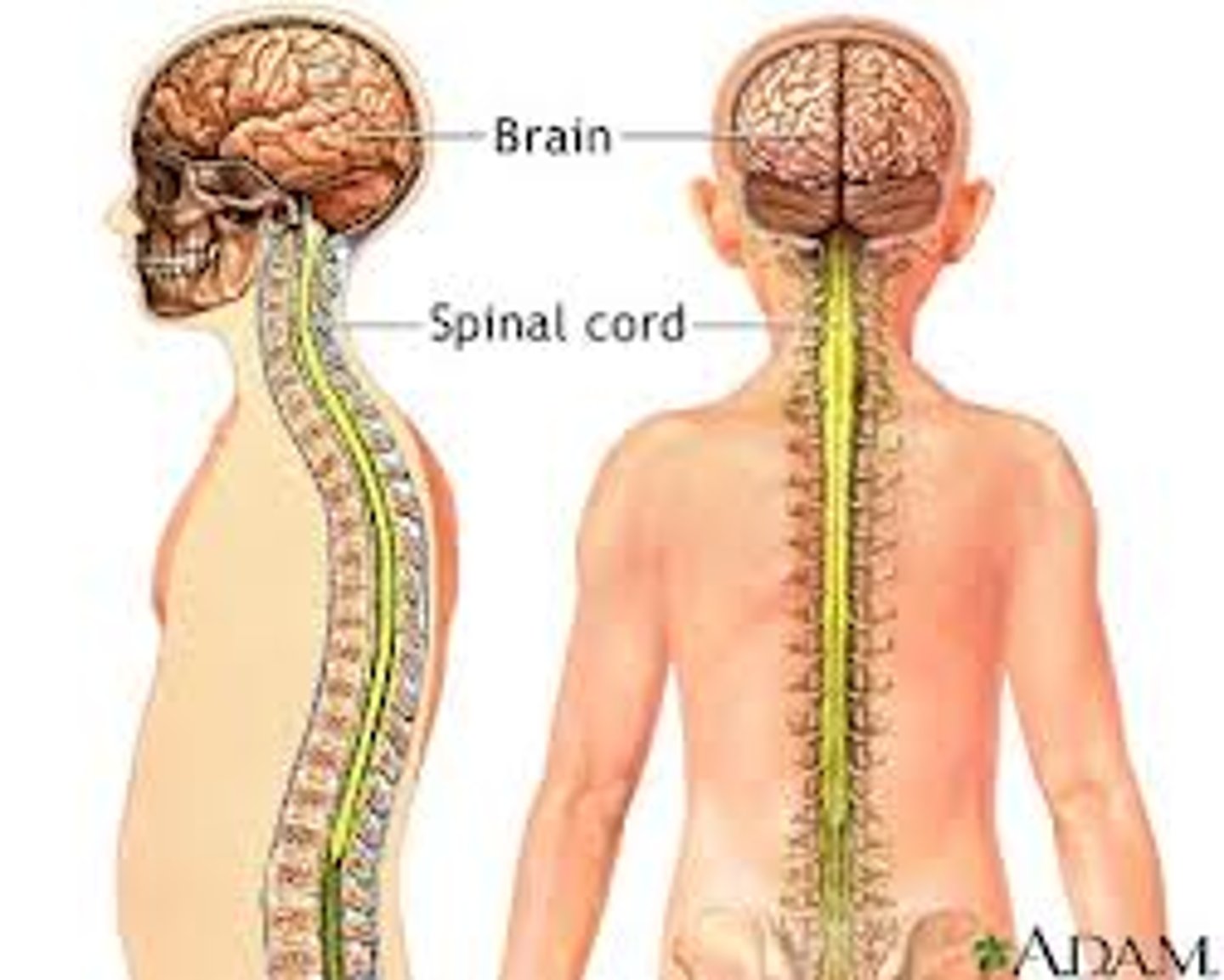
central nervous system
A subdivision of the human nervous system comprising the brain and spinal cord. Transmits & receives messages to & from the PNS
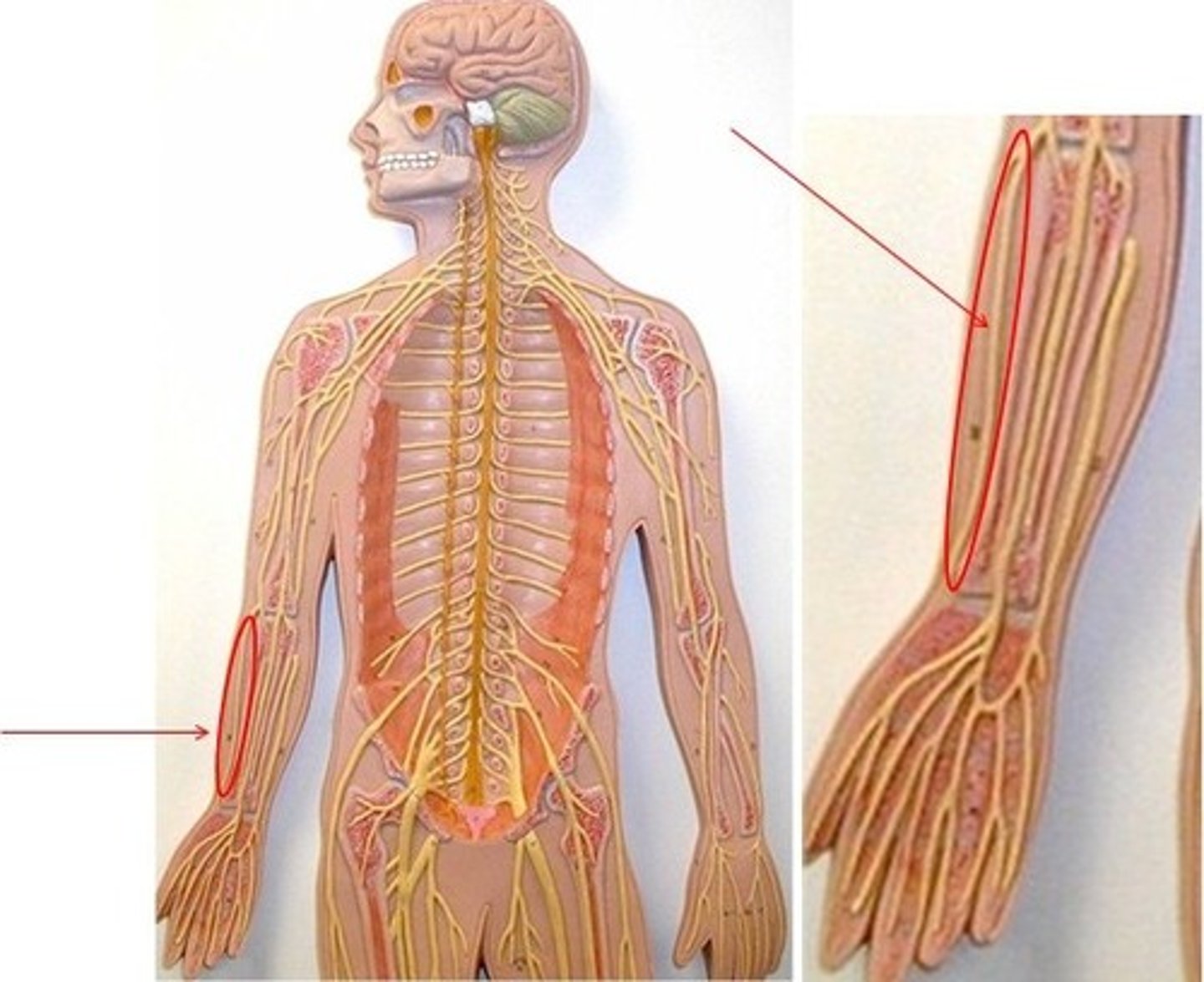
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
nerves
neural cables containing many axons (connect the central nervous system with muscles, glands, and sense organs
sensory neurons
Afferent Neurons; neurons that carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the central nervous system
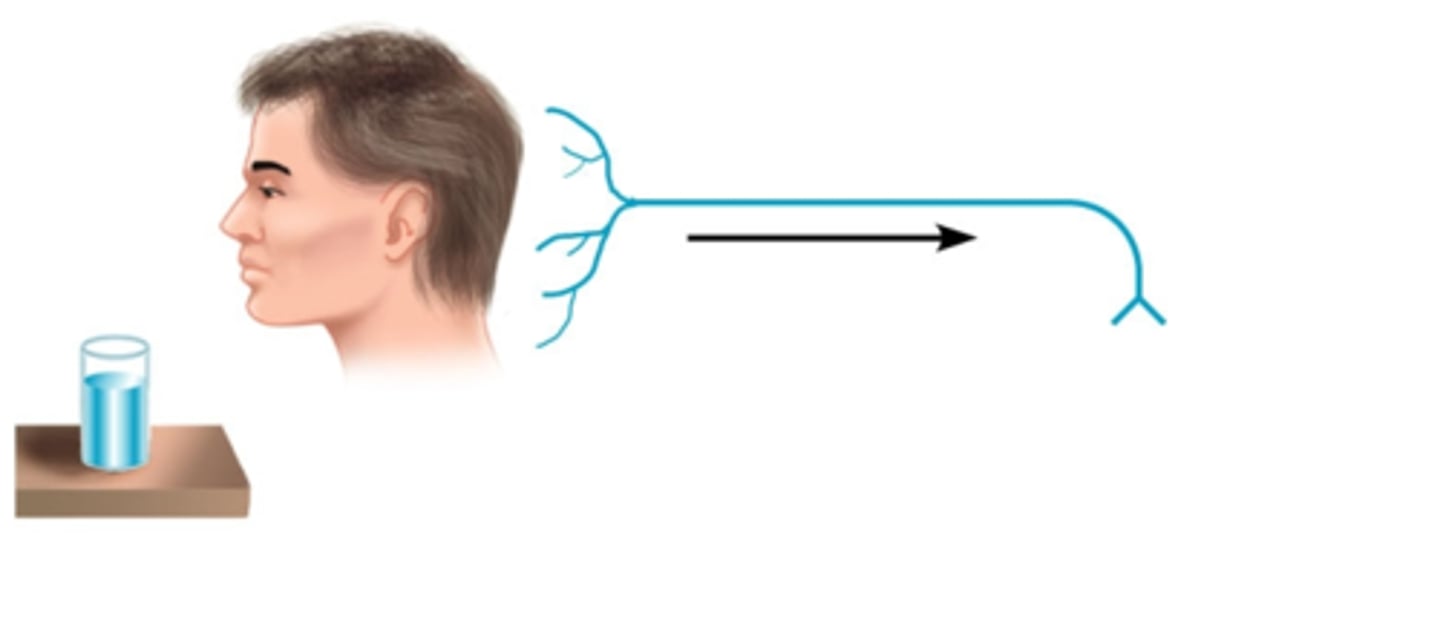
interneurons
central nervous system neurons that internally communicate between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
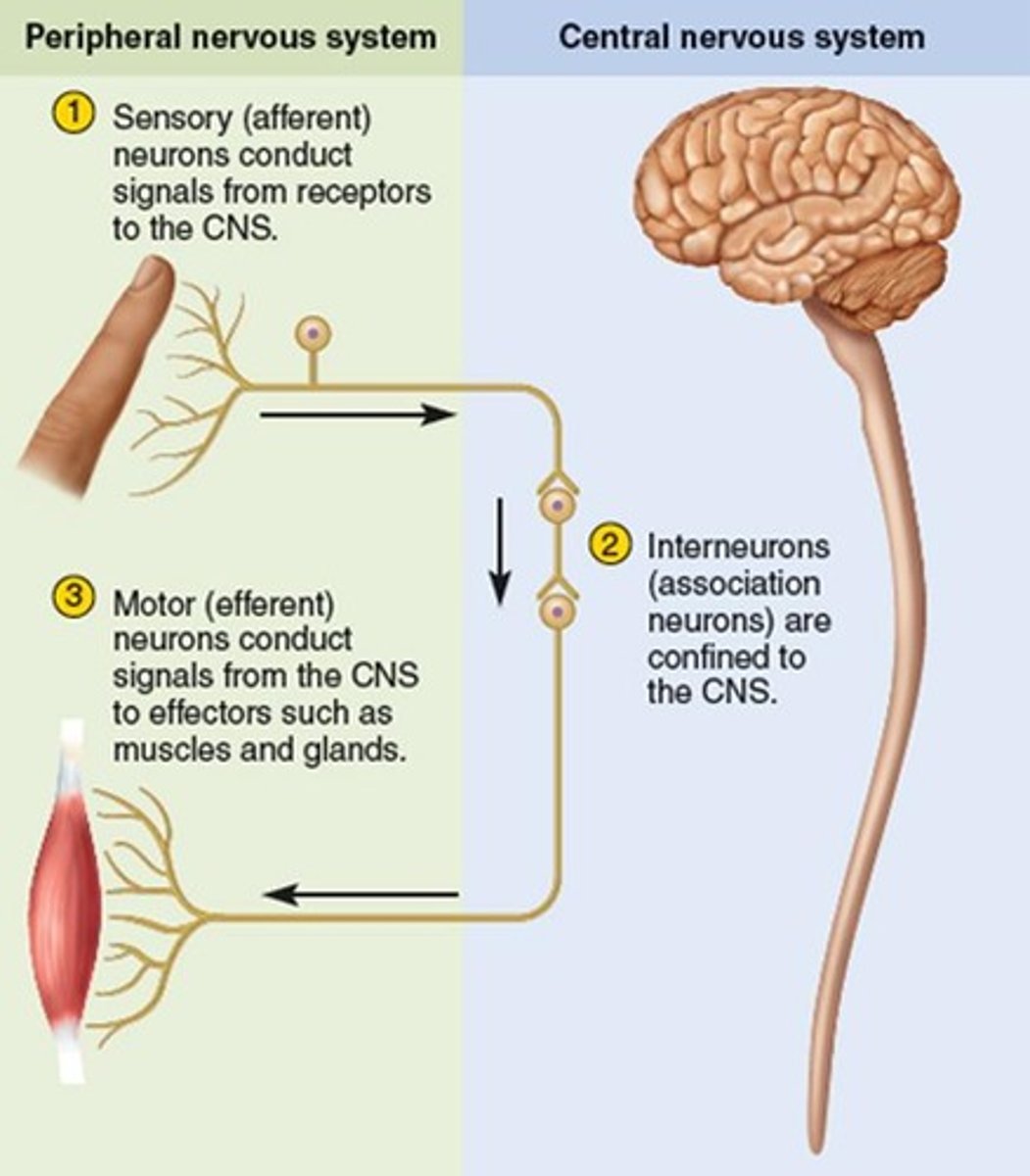
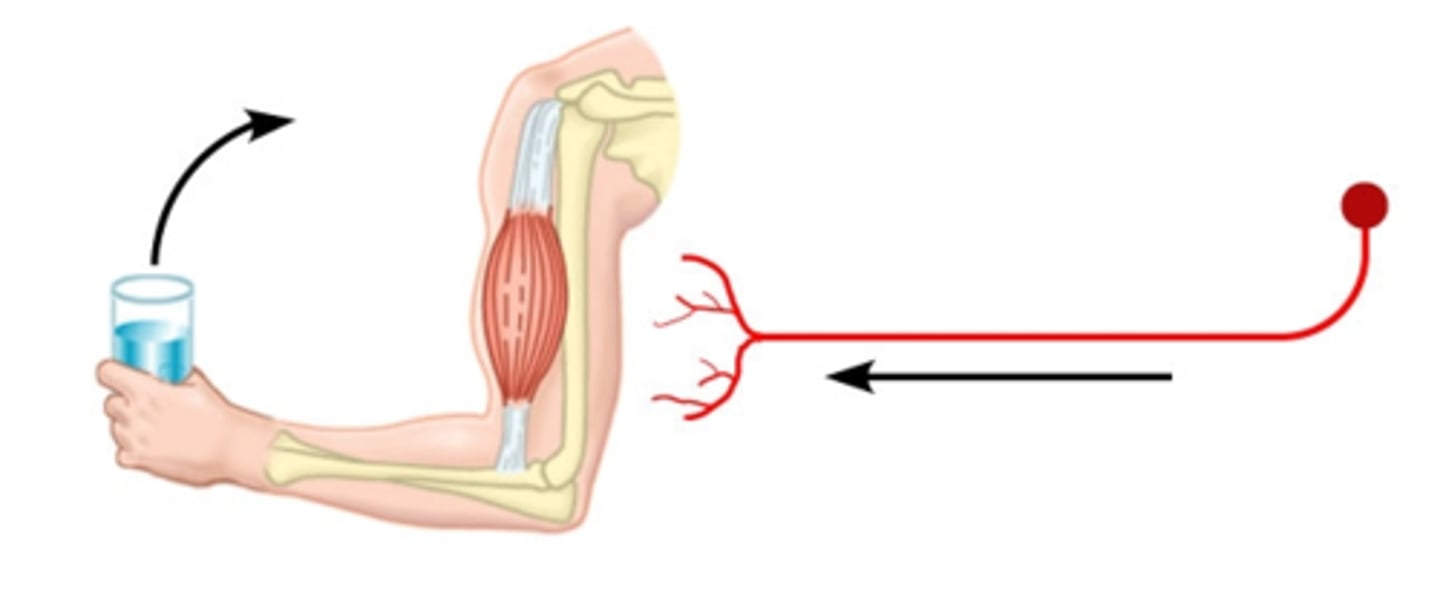
motor neurons
Efferent Neurons; neurons that carry outgoing information from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands
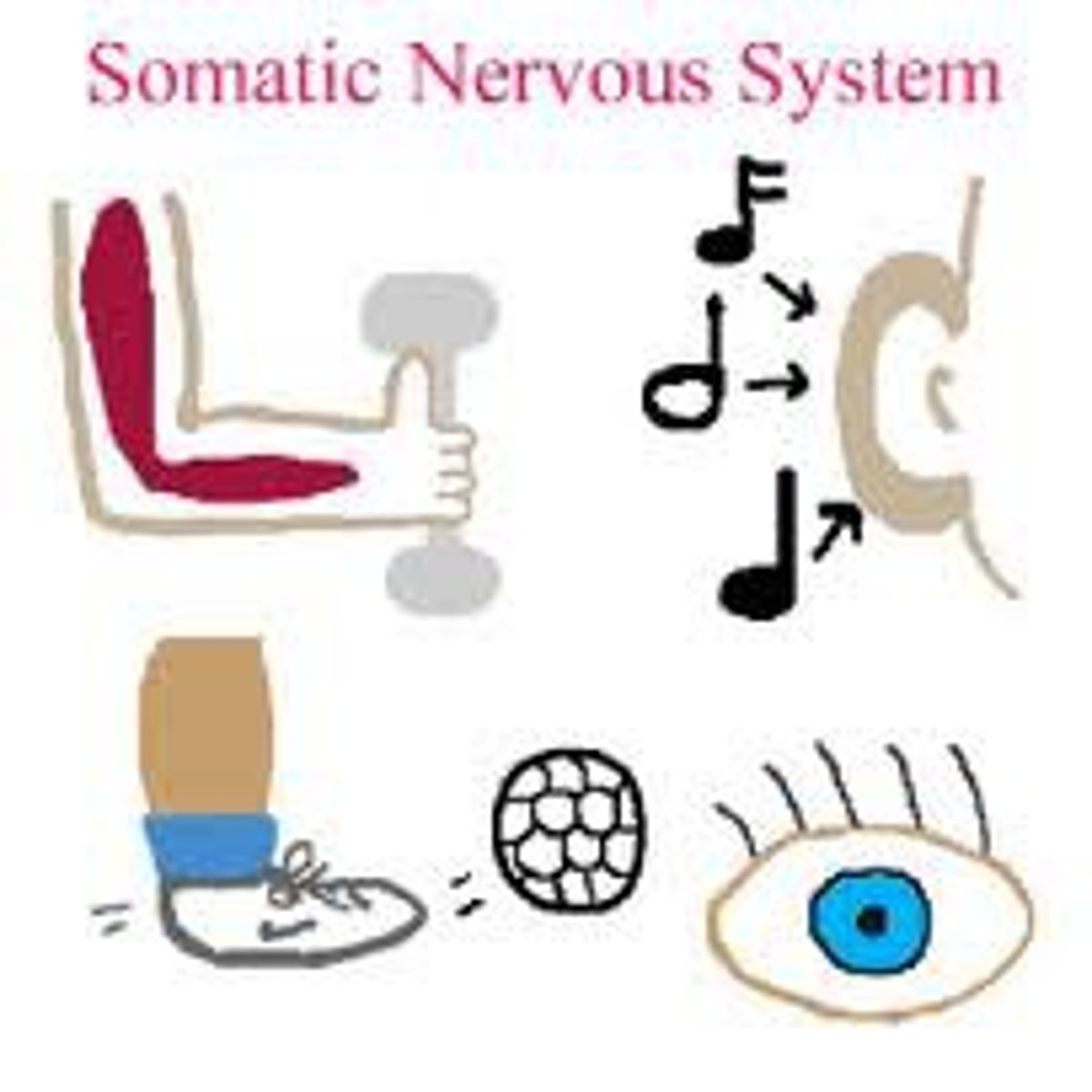
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the bodys skeletal muscles (skeletal nervous system)
autonomic nervous system
the part of the the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs
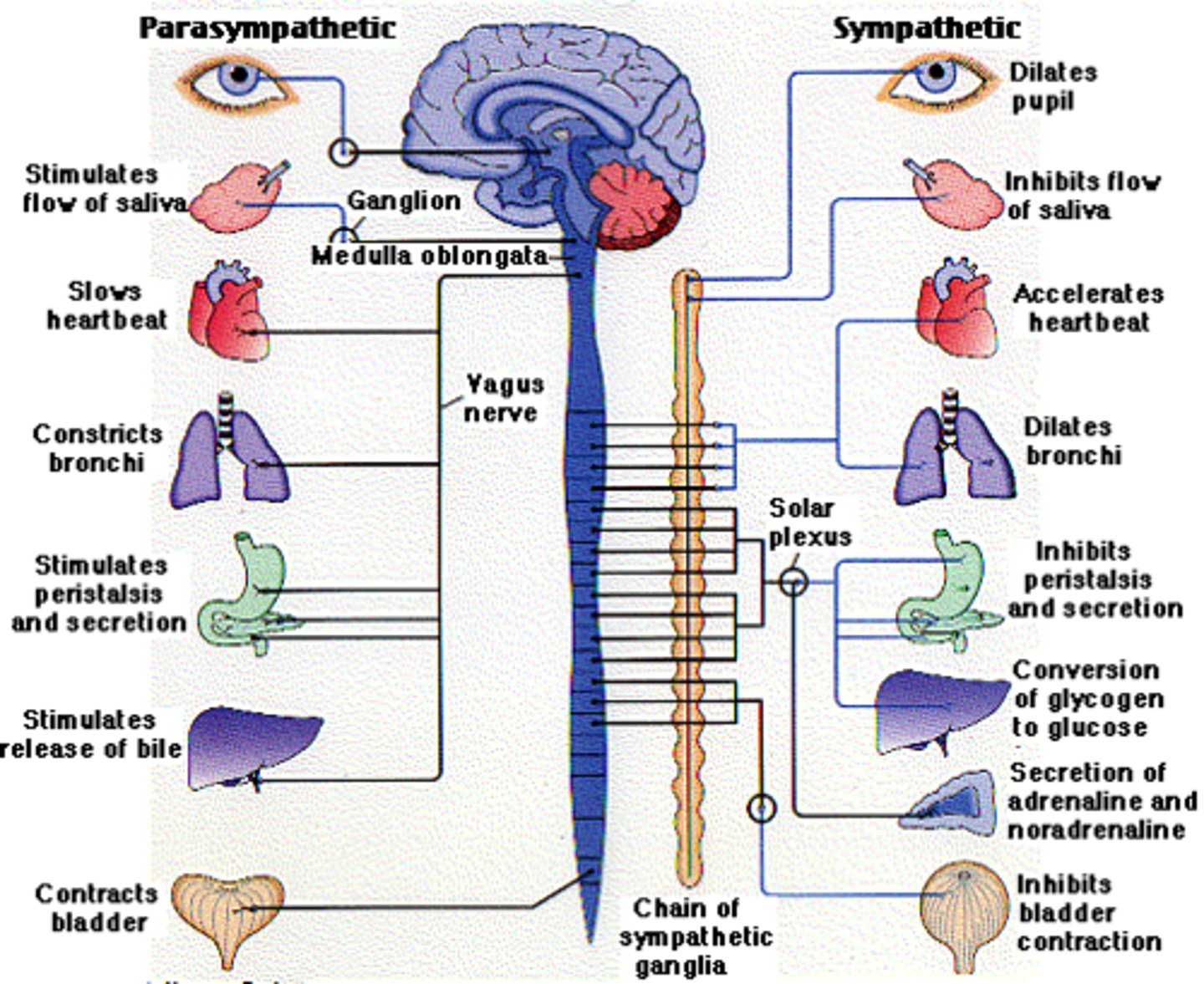
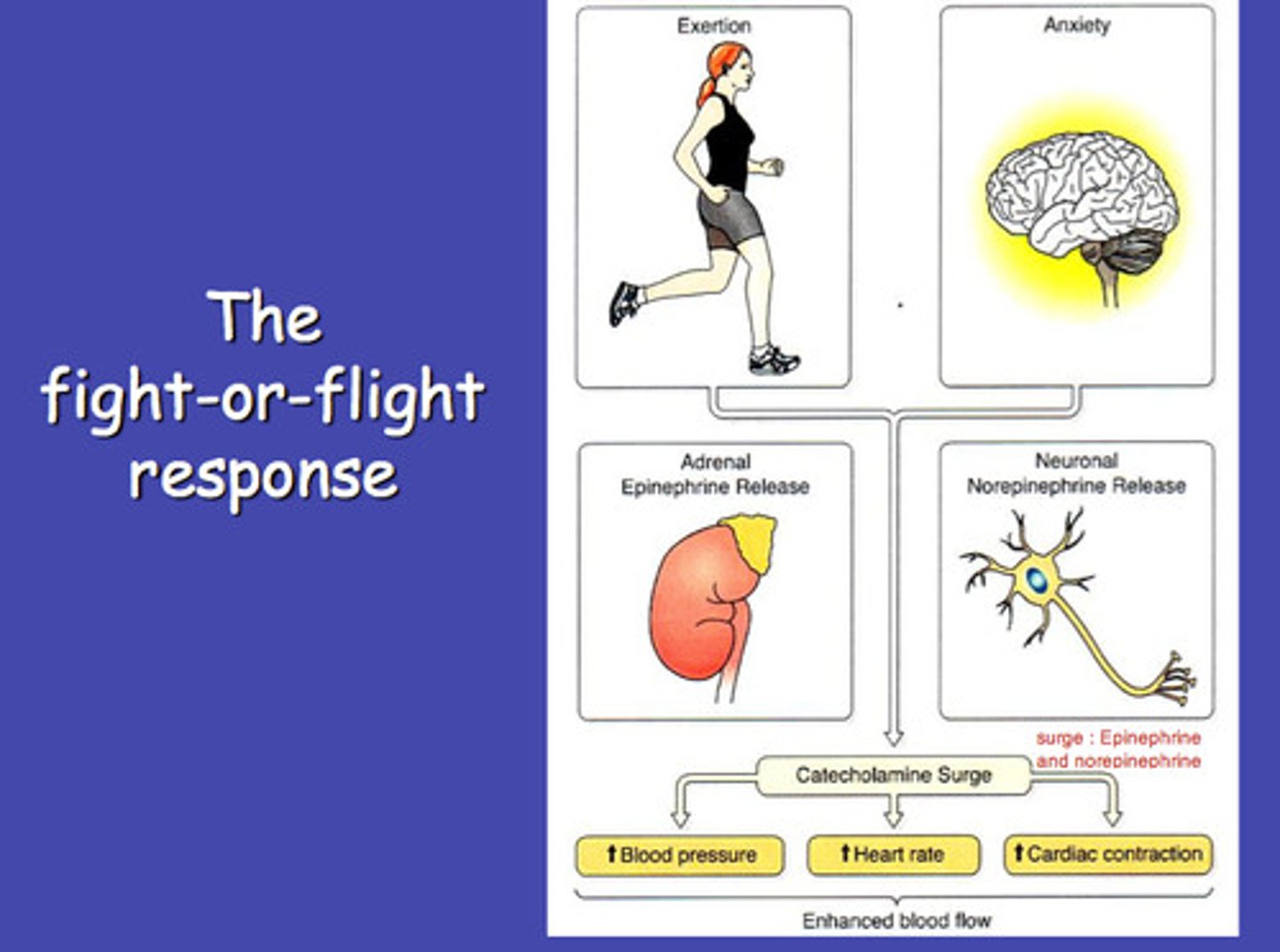
sympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body (mobilizes its energy in stressful situations)
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body (conserves its energy)

reflex
a simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus (knee-jerk response)
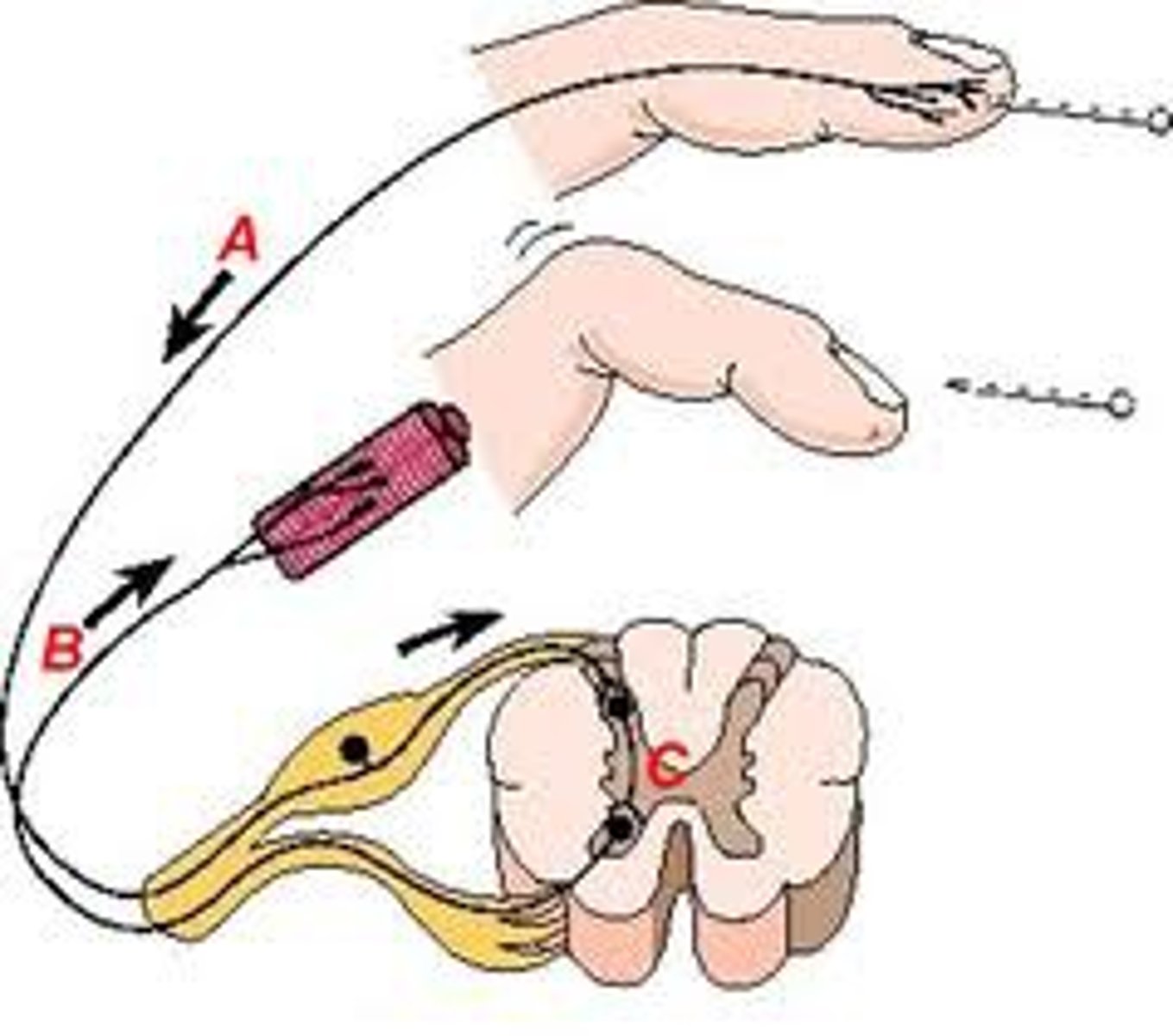
afferent neurons
Nerve cells that carry impulses towards the central nervous system, ie. sensory neurons
efferent neurons
take information from the brain to the rest of the body, ie. motor neurons
Dopamine
a neurotransmitter that regulates motor behavior, motivation, pleasure, and emotional arousal
dopamine hypothesis
the idea that schizophrenia involves an excess of dopamine activity
Acytelcholine (ACh)
activates and inhibits skeletal muscles; memory function; regulates the parasympathetic nervous system; Association with Alzheimers disease
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger, sleep, arousal, and mood.
GABA
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
Glutamate
The most common neurotransmitter in the brain. Excitatory.
Endorphins
natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure
Agonist
A chemical/molecule that mimics the action of a neurotransmitter.
Antagonist
a chemical substance that blocks or reduces the effects of a neurotransmitter
epinephrine and norepinephrine
aid body during stress by raising heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
Neuron Polarization
Electrically neutral
Inside ions positive; outside ions negative
neuron depolarization
A stimulus first causes sodium channels to open, and the neuron "fires". Negative ions from outside rush into Neuron.
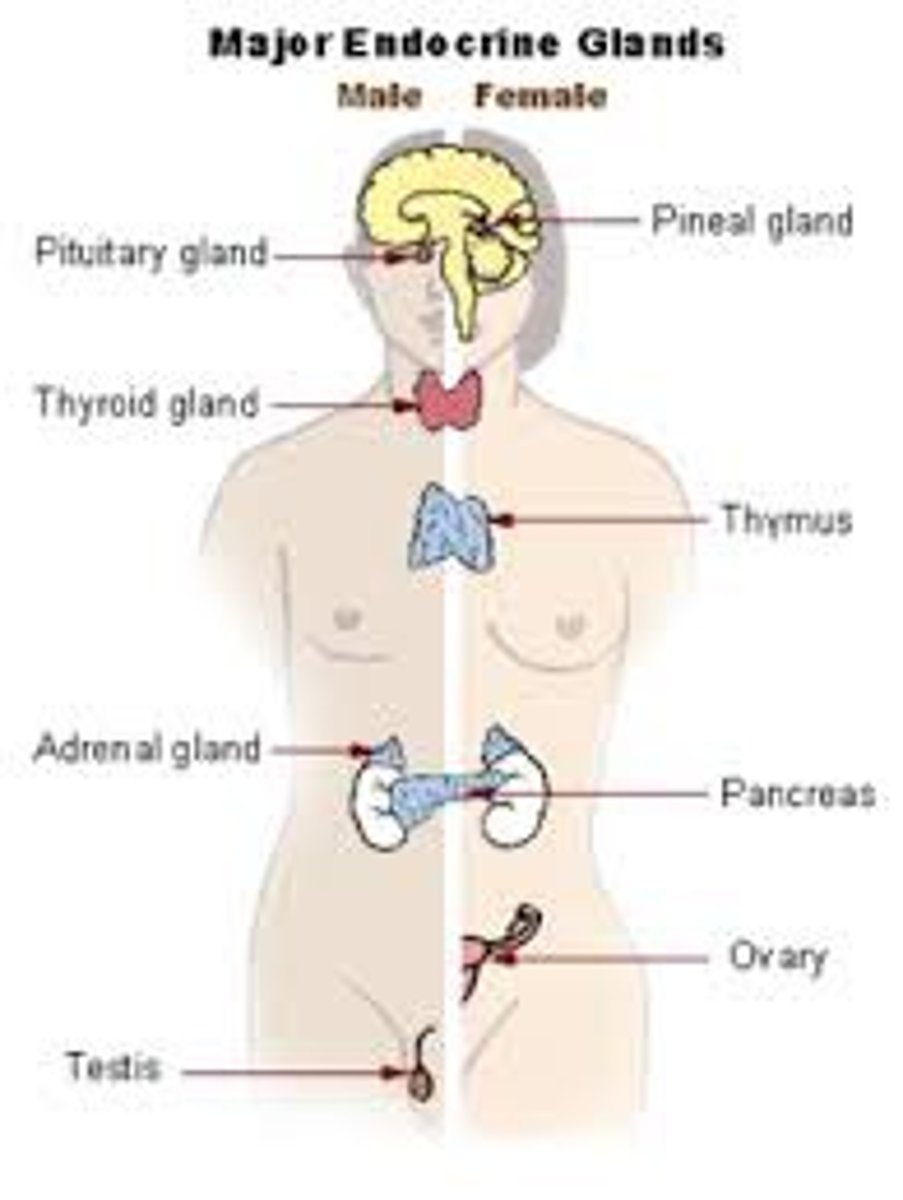
endocrine system
the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
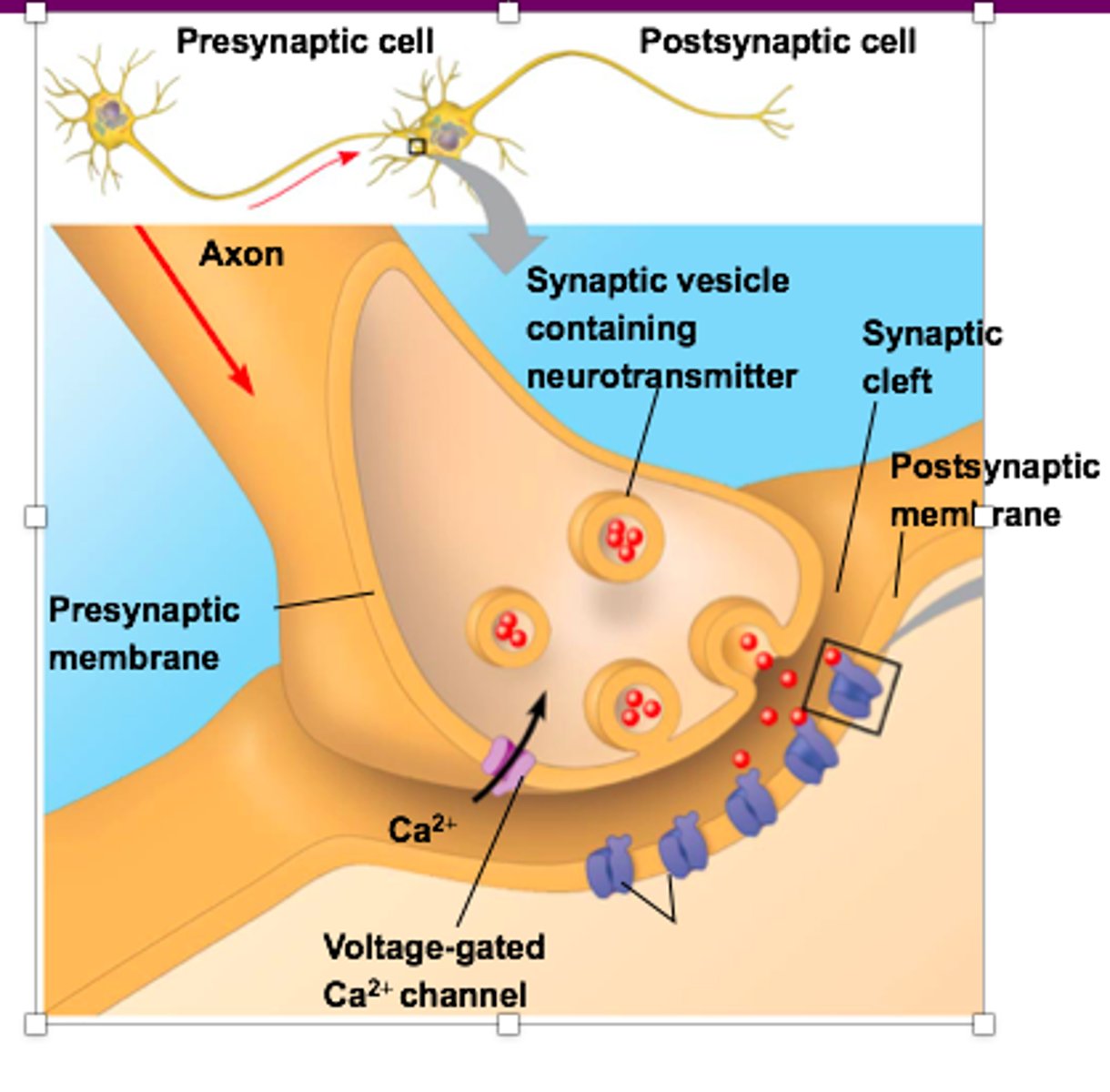
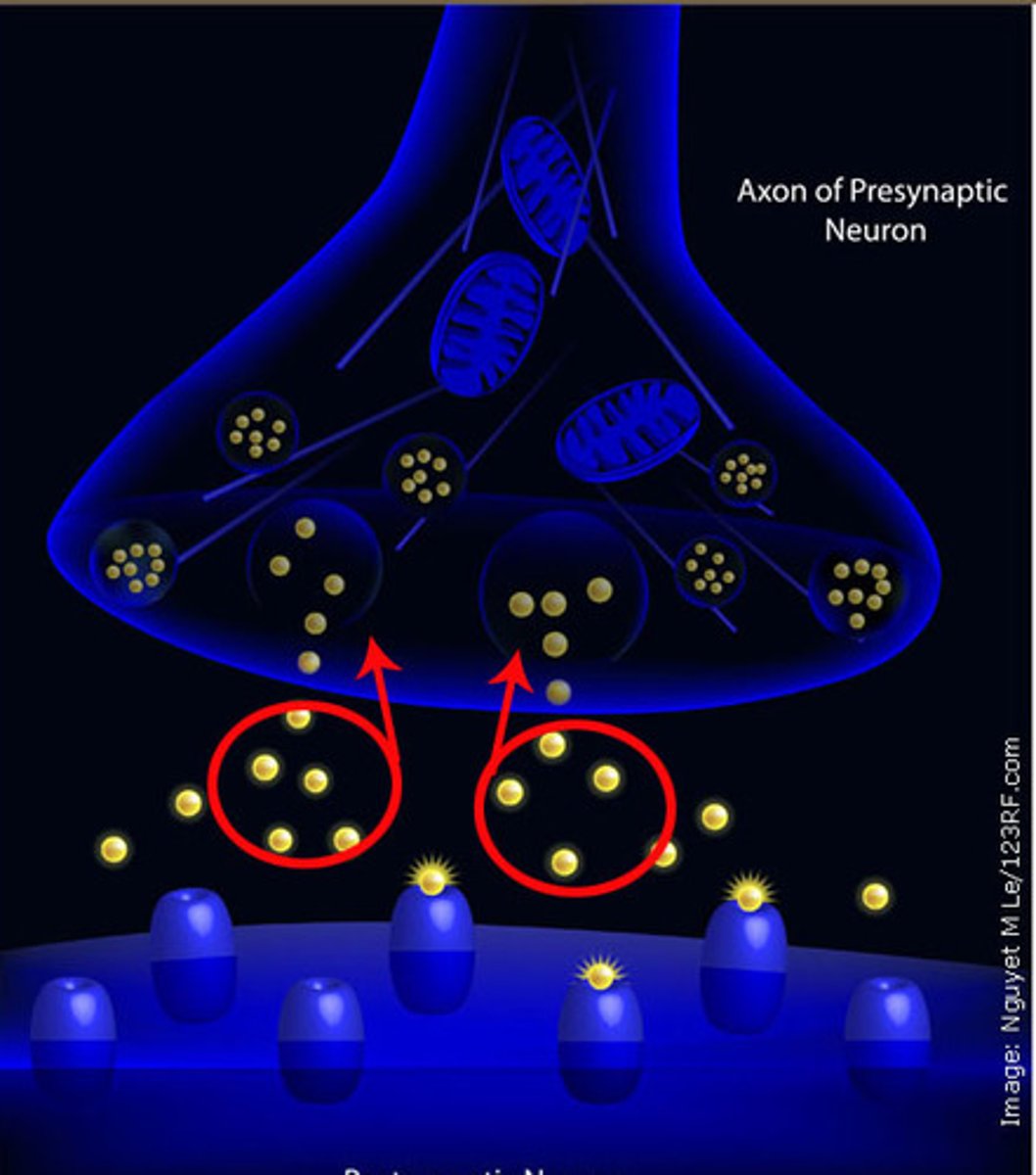
synpases
gaps or junctions between neurons, neurotransmitters are responsible for transmitting the impulse across the synapse
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
myelin sheath
covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
receptor sites
Locations on a receptor neuron into which a specific neurotransmitter fits like a key into a lock.
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Reuptake
a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
Substance P
Perception of pain; assists in promoting inflammation in response to injury
myasthenia gravis
Muscle weakness due to destruction of ACh receptors in muscles
SSRI
class of drugs used to relieve depression/anxiety by limiting reuptake of a neurotransmitter
Multiple Scelorsis (MS)
unpredictable disease of the CNS that disrupt flow of info within the brain and bt the brain and body; Deterioration of the Myelin Sheath
long-term potentiation (LTP)
a process whereby communication across the synapse between neurons strengthens the connection, making further communication easier; basis of learning and memory