eukaryotic organelles
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
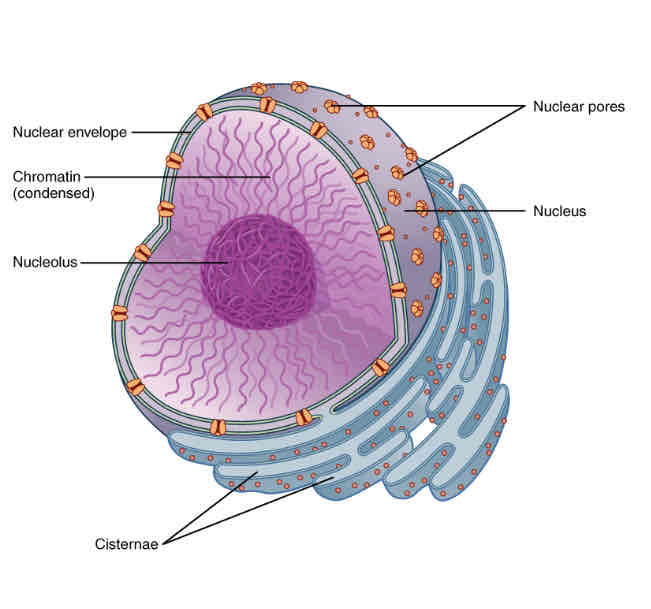
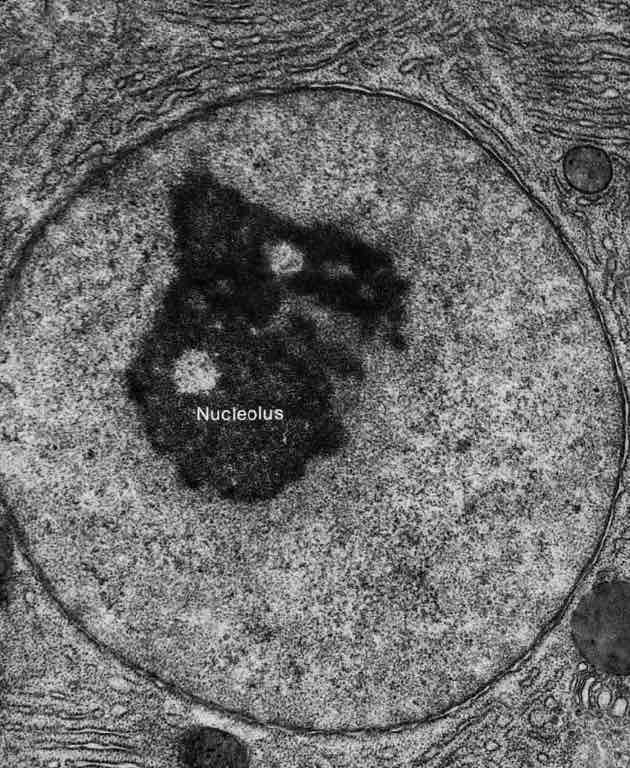
nucleus
STRUCTURE
Double membrane
Nuclear envelope with nuclear pores
Nucleolus
Chromosomes (which are made
from protein-bound linear DNA
FUNCTION
Controls activities of cell by controlling transcription of DNA
site of DNA replication and transcription to produce mRNA
Instructions to make proteins
Contains the genetic material for each cell
Pores allow transfer of substances (RNA)
Nucleolus makes rRNA and is where ribosome subunits assemble
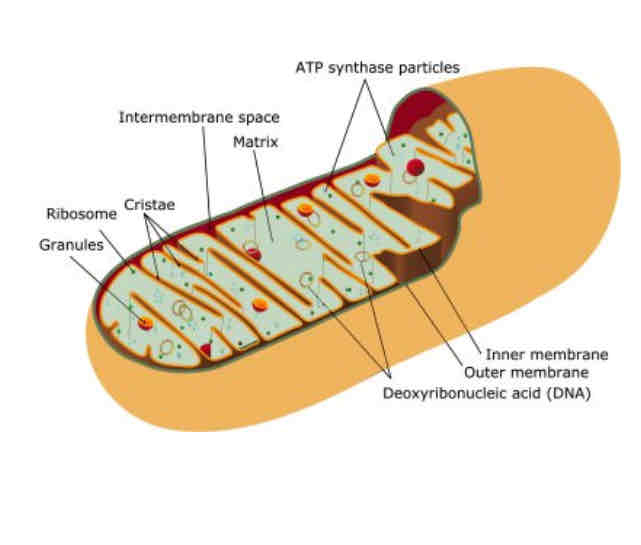
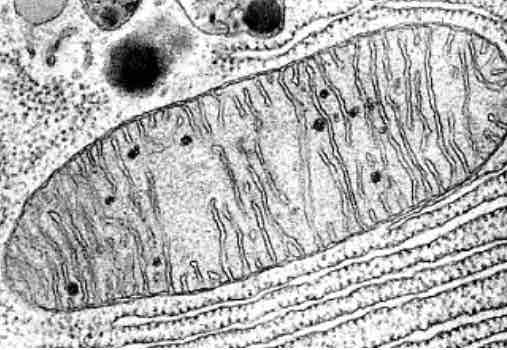
mitochondria
STRUCTURE
Double membrane with intermembrane space
Inner membrane folded to form crista
Matrix inside the inner membrane with enzymes
FUNCTION
Site of aerobic respiration
produce ATP as a product of respiration
Cristae provide larger surface area for oxidative phosphorylation
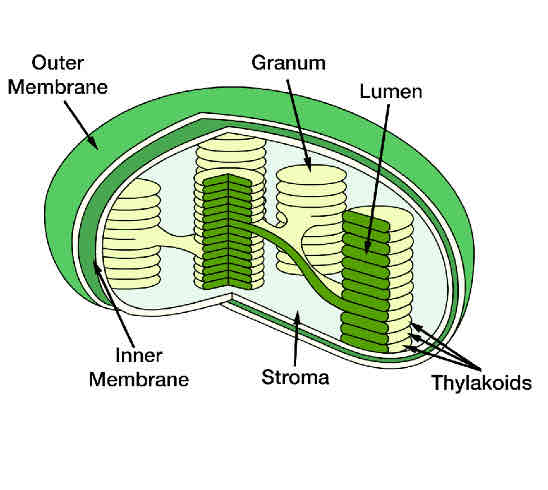
chloroplasts
STRUCTURE
Small, flat organelle in photosynthesising cells
Double membrane
Thylakoids are flat discs with pigment/chlorophyll in and enzymes
Grana - stacked thylakoids
Lamellae are flattened membranes which connect grana to transport chemicals
Stroma is the fluid with starch granules in
FUNCTION
Site of photosynthesis , contains dna and ribosomes for protein synthesis for photosynthesis
contains chlorphyll for the absorption of light for photsynthesis
Light dependent on thylakoids and lamellae
Light independent in stroma which contains enzymes for it
Grana absorb light efficiently
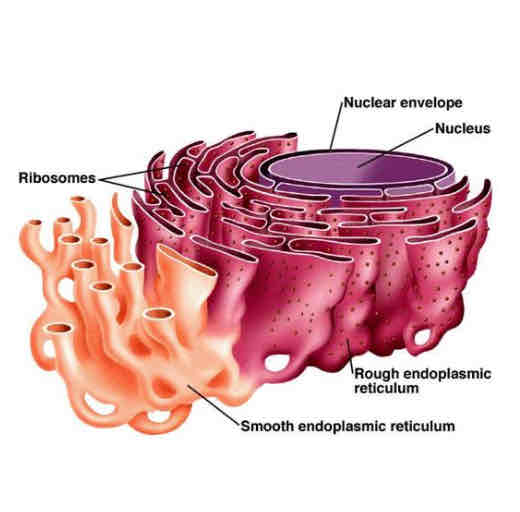
RER AND SER
STRUCTURE
System/sheets of membranes enclosing a fluid filled space
Forms flattened sacs called cisternae.
RER covered in ribosomes on surface
FUNCTION ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Protein synthesis on the ribosomes
Proteins into the lumen of RER and folds into tertiary structure,
polypeptide packed into vesicles to travel to golgi apparatus
FUNCTION SMOOTH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Synthesis and stores lipids and carbohydrates
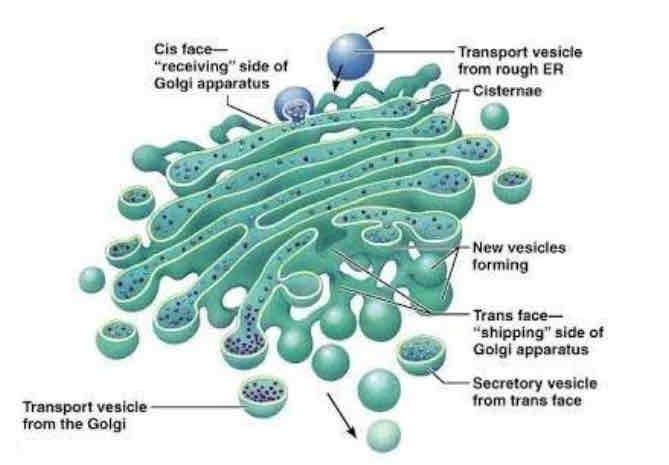
Golgi apparatus
STRUCTURE
System of membranes enclosing a fluid filled space
Folded to form cisternae
FUNCTION
collects and modifies and transports proteins
Packs and transports proteins by packing it into vesicles
Makes vesicles and lysosomes
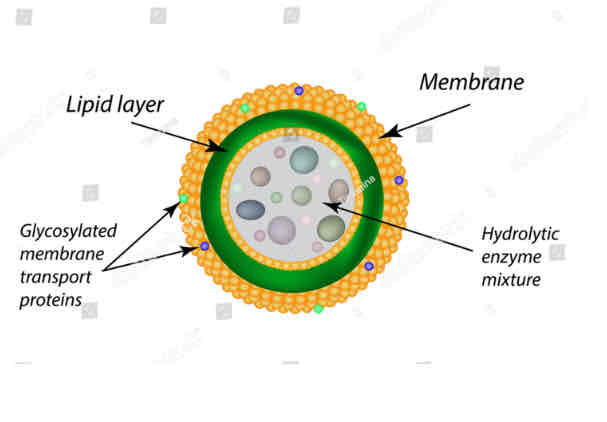
Lysosomes
STRUCTURE
Bags of powerful digestive lysosomal enzymes (hydrolytic enzymes)
Membrane bound sac with no clear internal structure which is acid filled
FUNCTION -
Digest large molecules into smaller/soluble molecules
Key role in phagocytosis
Digest old/worn out organelles in the cell
Digest invading cells
Transfer enzymes out of the cell by exocytosis
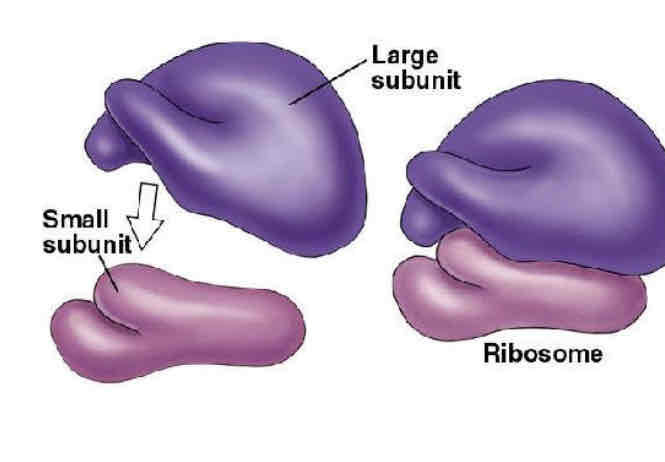
ribosomes
STRUCTURE
Made up of 2 subunits
Made of proteins and RNA
Either floats free in cytoplasm or attached to the surface of the rough ER
FUNCTION
Site of protein synthesis - translation
Proteins made by ribosomes in cytoplasm remain in cytoplasm
Ones made on RER are secreted from the cell by exocytosis
vacuole
STRUCTURE
Permanent in plant cells
Membrane sac, larger than vesicles
Fluid filled - tonoplast
Contains cell sap - weak solution of salts and sugars
FUNCTION
Maintains pressure inside cell
Keeps cell rigid
Stops plants wilting
Isolation of unwanted chemicals
Water in - hydrostatic pressure outwards, vacuole becomes turgid
cell wall
STRUCTURE
Plants and algae - cellulose
Fungi - chitin
Bacteria - peptidoglycan, murein, glycoprotein
FUNCTION
Keeps shape of cell and prevents change of shape
Supports and strengthens
Osmosis - cell wall mechanically strong enough to resist hydrostatic pressure
Permeable to water molecules